Multimedia Security And Forensics

Multimedia Security And Forensics
Authentication of Digital Images
CS525 Semester Project
Spring 2006
Sarah Summers
Sarah Wahl
Motivation
Seeing is believing … or is it?
Easy to be deceived
Goals
Identify image tampering methods.
Assess methods available for protecting images.
Assess image authentication techniques.
Identify directions for future work.
Categories of Image Tampering
There are three main categories of image tampering:
Enhancing
Compositing
Copy/Move
Enhancing
Changing the color of objects
Changing the weather conditions
Blurring out objects
Compositing
Combining two or more images to create a new image
Copy-Move
Copying regions of the original image and pasting into other areas .
The yellow area has been copied and moved to conceal the truck.
What can be done to protect digital images?
Watermarking
Fragile watermarks
Semi-fragile watermarks
Self-embedding watermarks
Digital cameras with watermarking capabilities
Digital Fingerprinting/Signatures
Digital cameras with fingerprinting capabilities
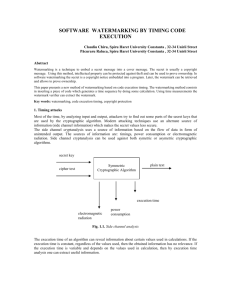
Digital Watermarking
The basic concept of digital watermarking an image is that a low level signal is placed directly into the image data.
Any manipulation of the image will impact the watermark and subsequent retrieval of the watermark and examination of its condition will indicate if tampering has occurred.
Fragile Watermarks
Fragile watermarks are designed to detect every possible change in pixel values .
Variety of Techniques but in most cases, the watermark is embedded in the least significant bit (LSB) of the image.
Advantages: Pick up all image manipulations – malicious and nonmalicious
Disadvantages: Too sensitive
Semi-Fragile Watermarks
They are robust, to a certain extent, and are less sensitive to pixel modifications.
Techniques:
Divide image into blocks and utilize bits from each block to calculate a spread spectrum noise like signal which is combined with DCT coefficients and inserted as a watermark.
Divide image into blocks, construct watermark in DCT domain from pseudo-random zero-mean unit variance
Gaussian numbers, take the inverse DCT and insert into the image.
Advantage: less sensitive than fragile watermarks
Self-Embedding
Tampered images result in lost information. The previous techniques will only detect and localize areas of interest when authentication is carried out.
Self-embedding allows tamper detection and recovery of missing information.
General concept is that the image is embedded in itself in an encrypted form.
Advantage: Potential for original data to be retrieved.
Disadvantage: Tampering with the image can remove blocks of the original image making retrieval of content impossible
Digital Cameras with
Watermarking Capabilities
Watermarking based on secret key, block ID and content. The image is divided into blocks and each block watermarked using a frequency based spread spectrum technique incorporating the secret key, block ID and block content.
Image of photographers iris is combined with the camera ID, the hash of the original image and other details specific to the camera.
Digital Fingerprints/Signatures
Based on the concept of public key encryption.
Hashed version of image is encrypted using a private key.
Encrypted file provides a unique signature/fingerprint of the image which can be used to authenticate by decryption with public key.
Mainly used in transmission of images.
Digital Cameras with
Fingerprinting Capabilities
Epson Image Authentication System (IAS)
The IAS software in the camera instantly seals the captured images with an invisible digital fingerprint.
Verification of image is achieved by any
PC with Image Authentication System software installed
Authentication Techniques
Active Authentication
Rely on the presence of a watermark or fingerprint.
Require knowledge original image
Algorithm/key used to embed the watermark or fingerprint.
Passive Authentication
No requirement of knowledge of original image.
Does not rely of presence of watermark or fingerprint.
Passive Authentication
Techniques
Detecting Copy-Move
Detecting Traces of Re-sampling
Detecting Light Inconsistencies
Copy-Move Detection
Original Image Tampered Image
Exact Match Robust Match
Copy-Move Detection
Original Image Tampered Image PCA Detection
Re-sampling Detection
Original Image Tampered Image
Fourier Transform of unaltered region
Periodic pattern in Fourier
Transform of altered region
Inconsistencies in Lighting
Genuine Image
Tampered Image
Future Research
Development of a better self embedding technique.
Development of an all inclusive passive authentication technique.
Conclusions
Digital image forgeries can be used to deceive the public and the authorities.
They are here to stay.
Until non destructible/ non removal digital watermarks are perfected, passive authentication will remain necessary.
Currently no single passive authentication technique can detect all types of digital forgeries.
References
Hany Farid, Creating and Detecting Doctored and Virtual Images: Implications to The
Child Pornography Prevention Act, Technical Report, TR2004-518, Dartmouth
College, Computer Science.
Detection of Copy-Move Forgery in Digital Images, Jessica Fridrich, David Soukal and Jan Lukas, Proceedings of Digital Forensic Research Workshop, August 2003, www.ws.binghamton.edu/fridrich/Research/copymove.pdf
Detection of image alterations using semi-fragile watermarks, E.T. Lin, C. I.
Podilchuk, and E.J. Delp, http://shay.ecn.purdue.edu/~linet/papers/SPIE-2000.pdf
Semi-fragile watermarking for Telltale Tamper Proofing and Authenticating, H. H. Ko and S. J. Park, http://www.hongik.edu/~sjpark/udt/Semi-
Fragile%20Watermarking%20for%20Telltale%20Tamper%20Proofing%20and%20A.d
oc
Methods for Tamper Detection in Digital Images, Jiri Fridrich, Proc. ACM Workshop on Multimedia and Security, Orlando, FL, October 30-31, 1999, pp. 19-23, http://www.ws.binghamton.edu/fridrich/Research/acm99.doc
Information Authentication for a Slippery New Age, S. Walton, Dr. Dobbs Journal, Vol.
20, No. 4, pp 18-26, Apr 1995
Blind Detection of Photomontage using Higher Order Statistics, T. Ng, S. Chang and
Q. Sun, http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~qibin/papers/qibin2004_iscas_1.pdf
References (continued)
A Digital Watermark, R. van Schyndel, A. Tirkel and C. Osborne , Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 2, pp. 86-90, Austin,
Texas, November 1994 http://goanna.cs.rmit.edu.au/~ronvs/papers/ICIP94.PDF
A Watermark for Image Integrity and Ownership Verification, P. Wong, IS&T’s 1998
Image Processing, Image Quality, Image Capture, Systems Conference, Portland,
Oregon, May 1998, pp. 374
– 379
An Invisible Watermarking Technique for Image Verification, M. Yeung and F. Mintzer,
Proc. ICIP’97, Santa Barbara, California 1997
Image watermarking for tamper detection, Jiri Fridrich, Proc. ICIP '98, Chicago, Oct
1998, http://www.rl.af.mil/programs/shid/downloads/icip98_434.pdf
Methods for Detecting Changes in Digital Images, J. Fridrich, Proc. of The 6th IEEE
International Workshop on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems
(ISPACS'98), Melbourne, Australia, 4-6 November 1998, pp. 173
–177, http://www.ws.binghamton.edu/fridrich/Research/ispacs.doc
A Robust Content Based Digital Signature for Image Authentication, M. Schneider and S. Chang, Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing,
1996, Volume 3, Issue , 16-19 Sep 1996 Page(s):227 - 230
References (continued)
A New Fingerprinting Method for Digital Images, V. Fotopoulos and A. N. Skodras, http://www.upatras.gr/ieee/skodras/pubs/ans-c35.pdf
Mehdi Kharrazi, Husrev T. Sencar and Nasir Memon, Blind Source Camera
Identification, International Conference on Image Processing, 2004, ICIP’04, Volume
1, 24-27 Oct. 2004, pp. 709 -712
Rotation, Scale and Translation Invariant Digital Image Watermarking, J.J.K.
O’Ruanaidh and T. Pun, Proceedings of the ICIP, VOl. 1, pp 536-539, Santa Barbara,
California, Oct 1997.
Secure Digital Camera, Paul Blythe and Jessica Fridrich, http://www.dfrws.org/2004/bios/day3/D3-lyth_Secure_Digital_Camera.pdf
Alin C. Popescu and Hany Farid, Exposing Digital Forgeries in Color Filter Array
Interpolated Images, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Vol. 53, Issue 10, Part
2, October 2005, pp 3948-3959
Epson's Image Authentication for digicams, http://www.dpreview.com/new/9904/99040501epson.asp
When is Seeing Believing, W. J. Mitchell, Scientific American, pp. 44 -49, February
1994.
References (continued)
Exposing digital forgeries by detecting inconsistencies in lighting by M. K. Johnson and H. Farid, ACM Multimedia and Security Workshop, New York, NY, 2005, http://www.cs.dartmouth.edu/~farid/publications/acm05.pdf
Exposing Digital Forgeries by Detecting Traces of Re-sampling, A. C. Popescu and H.
Farid, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 53(2):758-767, 2005, http://www.cs.dartmouth.edu/~farid/publications/sp05.pdf
Exposing digital forgeries by detecting duplicated image regions, A. C. Popescu and
H. Farid, Technical Report 2004-515, Dartmouth College, http://www.ists.dartmouth.edu/library/tr-2004-515.pdf
A Tutorial on Principal Components Analaysis, Lindsay I. Smith http://csnet.otago.ac.nz/cosc453/student_tutorials/principal_components.pdf
Automatic Estimation of the Projected Light Source Direction, P. Nillius and j.
–O.
Eklundh, Proceddings of the IEEE Computer Science Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2001
Protection of Digital Images Using Self Embedding, J. Fridrich and M. Goljan,
Symposium on Content Security and Data Hiding in Digital Media , New Jersey
Institute of Technology, May 14, 1999, http://www.ws.binghamton.edu/fridrich/Research/nj_may14.doc
A Model for Image Splicing, T. Ng and S. Chang, ICIP '04. International Conference on Image Processing,. Volume 2, 24-27 Oct. 2004 Page(s):1169 - 1172 Vol.2