chapter_4-3_population_ecology_pps
advertisement

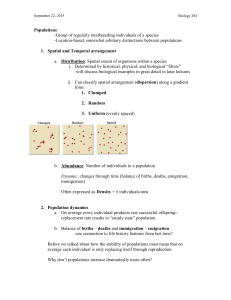
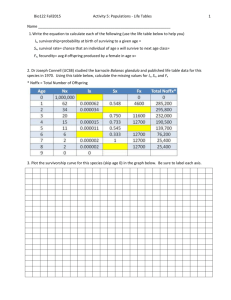
CHAPTER 4 Population EcologyContinued Lesson 4.2 Describing Populations Age Structure • Age structure describe the relative number of organisms of each age group within population • Can be used to predict future population growth of a population • Individuals capable of having offspring make up the reproductive group • Young individuals who have not yet reached the age where they can reproduce are called pre-reproductive • Older individuals past the age of having offspring are called post-reproductive Age Structure • Population with even age distribution will likely remain stable (births = deaths). • Population made up of mostly post-reproductive individuals will likely decline over time. • Population made up of mostly pre-reproductive individuals will likely increase over time. Age Age Structure Diagram How will each population change over time? Lesson 4.2 Describing Populations Sex Ratios • Proportion of males to females • Age structure diagrams give information about sex ratios. • For a monogamous species, the ideal sex ratio is 50:50. Lesson 4.3 Population Growth Birth and Death Rates • A population’s relative birth and death rates (natality and mortality) affect how it grows. • When birthrate is greater than death rate, population size increases. • When death rate is greater than birth rate, population size decreases. • Survivorship curves show how the likelihood of death varies with age. Birth and Death Rates •Survivorship curves: •Graphs that show how the likelihood of death varies with age •Type I curve has higher mortality at older ages •Type II curve has equal mortality rates at all ages •Type III curve has higher mortality rate at younger ages Survivorship Curves Birth and Death Rates • Age Structure and Population Growth: • For a population following a type I survivorship curve (higher mortality at older ages): • If population is made up of more young people, there is likely to be more births than deaths • If population is made up of more old people, there is likely to be more deaths than births. Lesson 4.3 Population Growth Immigration and Emigration • In addition to births and deaths, population growth is affected by immigration and emigration—individuals moving into and out of a population. • Migration, seasonal movement into and out of an area, can temporarily affect population size. Lesson 4.3 Population Growth Calculating Population Growth • Determined by the following equation: (birthrate + immigration rate) – (death rate + emigration rate) • Growing populations have a positive growth rate; shrinking populations have a negative growth rate. • Usually expressed in terms of individuals per 1000 Lesson 4.3 Population Growth Exponential Growth • Population increases by a fixed percentage every year. • Normally occurs only when small populations are introduced to an area with ideal environmental conditions • Rarely lasts long • Ex: Mold growing on bread Lesson 4.3 Population Growth Logistic Growth and Limiting Factors • Growth almost always slows and stops due to limiting factors. • Limiting factors: Environmental characteristics slow population growth and determine carrying capacity (largest population size a given environment can support). • Density-dependent: Influence changes with population density; examples are competition for resources, predation, disease • Density-independent: Influence does not change with population density; Examples are floods, fires, landslides Logistic Growth and Carrying Capacity Population Growth In Nature Fluctuating: •Cycle indefinitely above and below carrying capacity Rise and Crash •Rise very quickly, overshoot the carrying capacity, and then crash Lesson 4.3 Population Growth Biotic Potential • An organism’s maximum ability to produce offspring in ideal conditions • Many factors influence biotic potential, including gestation time (time to “be born”) and generation time (span from time of organism’s birth until time it has its own offspring). • Organisms with high biotic potential can recover more quickly from population declines than organisms with low biotic potential.