Altruism - The Richmond Philosophy Pages
advertisement

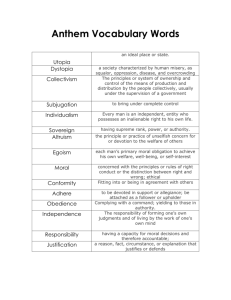
ALTRUISM An attempt to overcome some problems with Hobbes Task Complete the task on the sheet This activity forces us to consider what would happen if everyone behaved in a certain way What becomes clear is that everyone’s behaving self-interestedly means they are all worse off On this basis it has been argued that those of us who develop dispositions to altruism are going to be better off than those who remain short-sightedly self-serving in their behaviour What This Means So with time we will all internalise the need for cooperative behaviour and thus willingly contract into moral behaviour without the need to be coerced by authority On this account we can imagine human beings having genuinely altruistic motives, while at the same time the existence of such motives can be explained in terms of what best serves their individual as well as collective interest Do You Agree? Do you agree with this? What effect, if any does it have on social contract theory? Altruism Is In Our Genes There is an alternative approach that has developed from the perspective of evolutionary biology Altruistic behaviour amongst modern humans may be explained because it leads to greater evolutionary success In other words, if strong altruistic instincts in an animal lead to its having more offspring than lack those instincts, then such interests are evolutionarily beneficial Evolution and Altruism Such animals, of course, never chose to be moral There was never a conventional agreement struck in the understanding that this would be mutually advantageous But the fact that it is mutually advantageous to behave morally means that the genes which tend to produce such behaviour will survive So... So modern humans may well have genuinely altruistic motives which are hard wired precisely because this is an effective survival strategy, and those of our ancestors who were not so moral have died out Discussion Do you think altruism is beneficial for the development of humans? Can you see any problems with this? Criticism Morality involves adopting an impartial perspective: Any account of moral behaviour that explains why it is advantageous can still be accused of failing to understand what morality is really about Morality necessarily involves taking an impartial perspective on matters Even if it turns out that moral behaviour is to my and others advantage, this is not what makes it moral Rather it is moral precisely to the extent that it is unconcerned with serving the advantage of any party, or, because moral behaviour is good in-itself, irrespective any agreements made or advantages sought Continued Criticism Moral principles are applicable universally, to all persons equally This means that in order to discover them we have to adopt a point of view which is impersonal, from which we can consider all interested parties equally, rather than from the narrow perspective of self-interest Recap of Rawls A more recent version of the contract approach to ethics comes from John Rawls The key problem with Hobbes’ approach is that individuals will not enter into negotiation over a contract on equal footing, meaning that in the state of nature those who are stronger are going to gain advantages over the others Can Rawls Overcome This Problem? Unlike Hobbes, for Rawls it is essential to a just social arrangement that each of us should be free from fear or having their rights violated and so, even if I happen to be in a minority, the majority cannot act in a way which benefits them at my expense To ensure that we come up with a system of rules which doesn’t unfairly benefit anyone, Rawls reckons the contract needs to be negotiated from a position of equality How Do We Do This? The position from which we must negotiate the rules by which civil society is going to be organised must be one in which we are unaware of the place in society we are going to hold In Rawls’ words we must negotiate from behind a ‘veil of ignorance’ which ensures our impartiality This approach sees moral reasoning as intrinsically to do with adopting an impartial perspective and emphasises the importance of fairness