File - Official Mathematics Revision Website
advertisement

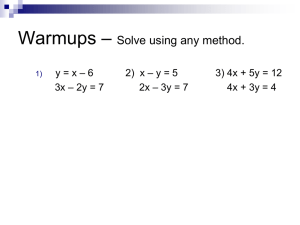
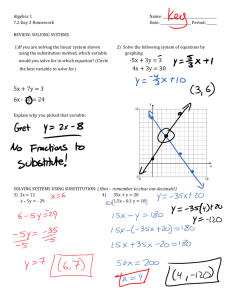
Solving Simultaneous When you solve simultaneous equations you are finding where two lines intersect Q. a) Find the equation of each line. b) Write down the coordinates of the point of intersection. 4 y=x+2 3 (1,3) y = 2x + 1 2 1 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Q. a) Find the equation of each line. b) Write down the coordinates where they meet. y=x 2 1.5 y=-x-1 1 0.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0.5 (-0.5,-0.5) 1 1.5 2 0.5 1 1.5 2 Q. a) Plot the lines: y=x y = 2x - 1 b) Write down the coordinates where they meet. 2 1.5 1 (1,1) 0.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 0.5 1 1.5 2 Draw each pair of lines on the same diagram and solve the equations by finding the point of intersection 1 3 5 7 9 x + y = 10 x-y=4 y=x x+y=9 y = 2x - 5 y=x–2 y=8-x y=x+2 y = 2x + 3 y=x–2 2 4 6 8 10 y = 2x y=x+4 y=x-3 y=5-x x+y=2 x - y = -10 y = 3x y=x+6 2x + y = 7 y=x+1 We can use straight line theory to work out real-life problems especially useful when trying to work out hire charges. Q. I need to hire a car for a number of days. Below are the hire charges for two companies. Complete tables and plot values on the same graph. Anrnold Palmer Car Hire Per Day 0 1 2 3 4 5 Total Cost £ £100 120 140 160 180 200 4 5 240 300 Swinton Direct Car Hire Per day 0 1 2 Total Cost £ 0 60 120 3 180 Total Cost £ Summarise data ! Who should I hire the car from? Up to 2 days Swinton Over 2 days Arnold Days Key steps 1. Fill in tables 2. Plot points on the same graph ( pick scale carefully) 3. Identify intersection point ( where 2 lines meet) 4. Interpret graph information. 13-Mar-16 Created by Mr. Lafferty Maths Department Algebraic Method : Solving by substitution “Solve simultaneously” y = 2x + 1 (1) y = - x + 7 (2) The graphs of these lines cross where y = y They are both equal to y, so: 2x + 1 = - x + 7 +x +x 3x + 1 = 7 -1 -1 Put x = 2 into equation (1) y = 2x + 1 y=22+1 y=5 3x = 6 x=2 These lines would cross at (2 , 5) Algebraic Method : Solving by substitution extended y = 2x + 1 3x + 2y = 9 Put y = 2x + 1 into 3x + 2y = 9 “Solve simultaneously by substitution method” Put x = 1 into y = 2x + 1 y=2x1+1 3x + 2(2x + 1) = 9 y=2+1 3x + 4x + 2 = 9 7x + 2 = 9 7x = 7 x=1 y=3 Simultaneous Equations - Substitution Solve each of the sets of equations below using the method of substitution. 1 2x + 3y = 9 y = 2x – 5 2 5x + y = 22 y=x+4 3 4x – 3y = 7 y=x+1 4 3x + 2y = 8 y = 2x – 3 5 8x + 5y = 16 y = 2x - 4 6 y=x+8 x + y = 12 2x + 3y = 9 y = 2x – 5 Put y = 2x – 5 into 2x + 3y = 9 2x + 3(2x – 5) = 9 2x + 6x - 15 = 9 8x = 24 x=3 Put x = 3 into y = 2x – 5 y=6-5 y=1 5x + y = 22 y=x+4 Put y = x + 4 into 5x + y = 22 5x + x + 4 = 22 6x + 4 = 22 6x = 18 x=3 Put x = 3 into y=x+4 y=3+4 y=7 7 10x + 2y = 6 y = 3x – 5 8 5x + y = 15 y=3–x 9 y=x+8 x + 3y = 44 10 4x + 3y = 10 y=2–x 11 5x – 2y = 16 y = 2x – 7 12 y = 10 + x 3x + 2y = 25 13 4x + 7y = 37 y=x-1 14 y = 2x 3x + 2y = 42 7 y = 2x - 5 y = 4x – 3 8 y=x+4 y = 3x - 7 9 y=x+2 4x + 3y = 27 10 5x - 2y = 10 y=2–x 11 y=x+9 2x + 3y = 37 12 y = 4x x + y = 12 13 y = 6x 2x + y = 4 14 y = 1.5x 3x + 2y = 24 Set 2 Solve each of the sets of equations below using the method of substitution 1 2x + y = 13 y=x+1 2 x + y = 13 y=x-2 3 2x + y = 15 y = 3x 4 y = 2x +7 y=x+4 5 y=7-x y = 3x - 5 6 y=1-x 3x + 2y = 8 Simultaneous Equations Elimination Solving Simultaneous Equations: Elimination 3x + 4y = 26 (1) (2) 7x - y = 9 (3) = (2) x 4 (1) (1)+(3) “Solve simultaneously” Make either coefficient of x or y ‘same size’ 28x - 4y = 36 3x + 4y = 26 31x = 62 x= 2 Put x = 2 into equation (1) 3x + 4y = 26 32 + 4y = 26 6 + 4y = 26 4y = 20 y=5 Simultaneous Equations - Elimination 1 Solve each of the sets of equations below using the method of elimination. 1 x + y = 11 x–y=7 2 x+y=9 x–y=2 3 x–y=4 x + y = 24 4 2x + y = 7 x–y=2 5 3x + y = 7 x–y=5 6 2x – y = 7 x+y=5 7 5x + 2y = 6 x – 2y = 6 8 4x + y = 14 3x – y = 7 9 x + 3y = 1 x – 3y = 13 10 x + 2y = 6 -x + y = 0 11 4x + 3y = 14 2x – 3y = 16 12 x+y=7 2x – y = 8 13 3x – 2y = 10 x + 2y = 6 14 5x + 2y = 19 x – 2y = -1 Elimination (1b) 1 x + y = 13 x–y=5 2 x - y = 14 x+y=6 3 x–y=1 x+y=9 4 3x + y = 13 x–y=3 5 5x + y = 12 x–y=0 6 2x – y = 11 4x + y = 25 7 3x + 2y = 20 x – 2y = -4 8 7x + 2y = 4 3x – 2y = -4 9 2x + 3y = 15 2x – 3y = -3 10 6x + 2y = 2 -6x + y = -8 11 9x + 2y = 15 x – 2y = -5 12 x + 5y = 8 2x – 5y = -14 13 3x – 7y = 5 x + 7y = 11 14 11x + 2y = 5 x – 2y = 7 Elimination (2) 1 3x + 2y = 8 x–y=1 2 5x + 3y = 11 2x – y = 0 3 7x + 2y = 13 x-y=7 4 4x - 5y = 3 x+y=3 5 3x - 2y = 5 x+y=0 6 6x + 5y = 17 -3x + 2y = -4 7 5x + 9y = -8 x – 3y = 8 8 2x + 3y = 9 -x + y = -2 9 4x - 7y = 7 x + y = 10 10 5x + 4y = 1 x-y=2 11 5x + 3y = 16 3x – 2y = 2 12 2x + 5y = 12 13x – 2y = 9 13 7x – 3y = 20 3x + 4y = -2 14 x + 2y = 1 3x – 7y = 29 Elimination (2b) 1 5x + 3y = 4 2x – y = 6 2 3x + y = 9 7x – 2y = 8 3 4x + 3y = 19 x-y=3 4 6x - 5y = 1 x+y=2 5 2x - 3y = -2 -x + 5y = 8 6 5x - 8y = 10 3x + 4y = 6 7 2x + y = 9 5x – 3y = 39 9 5x + 4y = 14 3x - 2y = 4 11 3x +7y = 14 -x +3y = 6 8 2x + 3y = 11 3x - y = 11 10 -x + 6y = 1 2x - 5y = 5 12 6x - 4y = -2 5x + 2y = 9 Elimination (2c) 1 3 5 7 9 11 3x + 2y = 10 5x – 3y = 4 7x + 2y = 11 2x - 3y = -4 3x - 4y = -6 2x + 5y = 19 8x - 3y = 2 5x +2y = 9 3x - 7y = 7 2x + 3y = -3 10x - 3y = -13 4x +5y = 1 2 4 6 8 10 12 2x - 5y = 7 3x + 4y = -1 6x - 5y = 12 4x + 3y = 8 9x - 5y = 14 2x + 3y = -1 4x - 5y = 18 5x + 6y = -2 5x - 2y = 11 4x + 3y = -5 9x + 5y = -1 4x - 3y = 10 Elimination (2d) 1 5x + 3y = 11 2x + y = 4 3 8x + 5y = -2 3x + 4y = -5 5 9x + 4y = 1 3x + 2y = -1 7 10x + 3y = 1 3x +2y = -3 9 3x + 7y = -1 2x + 3y = 1 11 10x + 7y = 14 3x +5y = 10 2 7x + 2y = 17 3x + y = 8 4 4x + 5y = 18 x+y=4 6 5x + 6y = 12 3x + 5y = 10 8 4x + 7y = 1 x + 3y = -1 10 5x + 2y = 16 4x + 5y = 6 12 6x + 5y = 8 x + 3y = -3 5 pens and 3 rubbers cost £0·99 while 1 pen and 2 rubbers cost £0·31. Make two equations and solve them to find the cost of each. Let p = pen, r = rubber 5p + 3r = 99 p + 2r = 31 p = 15, r = 8 3 plum trees and 2 cherry trees cost £161 while 2 plum trees and 3 cherry trees cost £154. Make two equations and solve them to find the cost of each. Let p = plum tree, c = cherry tree 3p + 2c = 161 2p + 3c = 154 p = 35, c = 28 4 bottles of red wine and 5 bottles of white wine cost £35·50 while one bottle of each cost £8. Find the cost of each type of wine. Let r = red wine, w = white wine 4r + 5w = 35∙5 r+w=8 r = £4.50, w = £3.50 Tickets on sale for a concert are £25 each for the front section and £20 each for the back section of the theatre. If 212 people attended the concert and the total receipts were £4980, how many of each price of ticket were sold ? Let f = front seat, b = back seat f + b = 212 25f + 20b = 4980 f = 148, b = 64 Meals in a restaurant are available at £28 per person for the fish courses menu and £30 per person for the meat courses menu. There are 95 guests attending the function in the restaurant and the total bill came to £2 760. How many guests chose each menu ? Let f = fish course, m = meat course f + m = 95 28f + 30m = 2760 f = 45, m = 50 Calendars cost £9 and £5 each and are on sale in a card shop. If 760 calendars are sold and the total takings for them were £5 240, how many of each price of calendar were sold ? Let x = £9 calendars, y = £5 calendars x + y = 760 9x + 5y = 5240 x = 360, y = 400