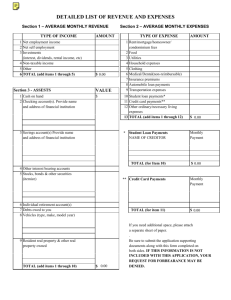
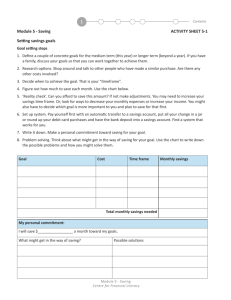
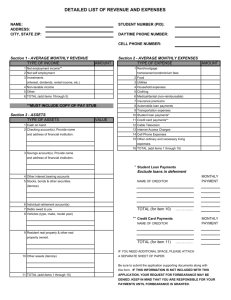
Your Money, Your Goals Content modules
advertisement

Your Money, Your Goals A FINANCIAL EMPOWERMENT TOOLKIT FOR SOCIAL SERVICES PROGRAMS Denise DeVaan, Senior Consultant, ICF International Patty Avery, Office of Financial Empowerment, CFPB NACHC Training. Baltimore, MD June 2014 YMYG Toolkit Training Agenda—Today! Introduce the YMYG Toolkit for Social Services and the CFPB Coordinator Training Responsibilities Coordinator and Member Self Assessment to Increase Confidence Emotional and Cultural Influences on Money Community Health Corp Briefing on Health Topics Starting the Conversation with Patients (health, finances) Debt, Emergency Savings, Income & Resources, Spending, Paying Bills All connected to Cash Flow Budget Setting Goals Coordinator Training Responsibilities with Members Take this four hour training and replicate it. The key training objective is to: Provide information and tools to patients on key topics they raise. Support patients in taking small actions to strengthen their financial lives. Examples: reduce out of pocket medical costs, use the Earned Income Tax Credit to reduce debt & establish small $500-$1000 emergency savings; tracking income/resources/spending; prioritizing bill paying to make ends meet. Provide referrals Use the slides, exercises, and Your Money Your Goals Toolkit for Social Services. Administer pre-surveys and post surveys to Members at beginning and end of training. Complete trainer survey after training. Send these to NACHC Office 3 Tool 2: Resource and referral guide template 4 Instrument 3A: Member Training pre-survey 5 Instrument 3B: Member Training post-survey 6 Your Money, Your Goals Module 2: Assessing the situation 7 Tool 1: Financial empowerment self-assessment, P11 8 Organization of Your Money, Your Goals Introductory modules Module 1: Introduction to the toolkit Module 2: Assessing the situation Module 3: Starting the conversation Module 4: Emotional & cultural influences on financial decisions Module 5: Using the toolkit 9 Organization of Your Money, Your Goals Content modules Module 6: Setting goals Module 7: Saving for the unexpected, emergencies, & goals Module 8: Managing income & benefits Module 9: Paying bills & other expenses Module 10: Managing cash flow Module 11: Dealing with debt Module 12: Improving credit reports & scores Module 13 Evaluating financial service providers, products, & services Module 14: Protecting consumers rights 10 Scavenger Hunt Use the Overview of Your Money, Your Goals, which lists Introductory and Content Modules and Tools. Where would you go to find information and tools if a client: 1. Felt overwhelmed by debt? 2. Felt like she couldn’t make ends meet? 3. Wants to buy a car and get the best rate she can for the money she must borrow? 4. Wants to understand direct deposit and payroll cards? 11 Scavenger Hunt… (continued) 5. May qualify for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)? 6. Has used high-cost credit products in the past and wants to avoid these in the future? 7. Wants to make changes but does not have clear goals? 8. Has many financial issues, and you don’t know where to start? 9. Has no savings but wants to start? 10. Wants to open an account but doesn’t know what kind of account or where? 12 Introduction to the CFPB Consumer Financial Protection Bureau The CFPB’s mission is to make markets for consumer financial products and services work for Americans. 13 Introduction to the CFPB Education: Your Money Your Goals Toolkit • for Social Services – Field test, 2013. – Now, ready for national rollout. – Ten national organization partners. NACHC is the first! Thanks! – Each trains a minimum of 500 case workers, front line staff. • for Workers (current pilot) • for Community Volunteers (current pilot) • for Legal Aid Attorneys and Offices (current pilot) Enforcement Study 14 Financial empowerment What is financial empowerment? How is it different than financial education, financial literacy, financial capacity, or other commonly used terms? Financial literacy Ability Financial empowerment 15 Financial empowerment, and case managers Access Trust Opportunities for providing financial empowerment 16 Module 14: Protecting Consumer Rights Submitting a complaint to the CFPB Question: What kind of topics might come up that hurt patients, financially, and should be reported to the CFPB? Complaint submitted Complaint reviewed and routed Company response Consumer review CFPB review and investigation Analysis and report 17 Tool 3: Submitting a complaint 18 19 Your Money, Your Goals Module 4: Emotional and cultural influences on financial decisions 20 Module 4: Emotional and cultural influences on financial decisions 21 Table Exercise: Emotional, Cultural Influences on Financial Decisions Brainstorm common differences in how money is handled or financial decisions are made. How can this understanding help in my work with patients? • Gender • Culture • Religion • Ethnicity • Race • Other Your Money, Your Goals Module 3: Starting the conversation 23 Module 3: Starting the conversation 24 Role Play Exercise: Talking to a Patient Begin with: health insurance topics to reduce out of pocket medical costs Examples: managing chronic conditions, getting generic drugs, taking advantage of clinic or community resources THEN Listen for an opening or initiate a question on the topic of money, personal finances. “What do you feel good about in the way you are handling the large topic of money?” “Is there a money topic that you want to handle better?” Module 8: Managing Income and Benefits Tool 4: Increasing your income through tax credits 26 Earned Income Tax Credit Maximum tax credit (for 2013) $6,044 with three or more qualifying children $5,372 with two qualifying children $3,250 with one qualifying child $487 with no qualifying children All information regarding tax credits from the Internal Revenue Service at www.irs.gov. 27 Your Money, Your Goals Module 11: Dealing with debt 28 Tool 1: Debt management worksheet 29 Tool 3: Debt-reduction worksheet 30 Tool 5: When debt collectors call 31 Your Money, Your Goals Module 7: Saving for the unexpected, emergencies, and goals 32 Tool 1: Savings plan 33 Your Money, Your Goals Module 10: Managing cash flow 34 Module 10: Managing cash flow What is a cash flow budget? How is it different from a regular budget? What do you think may be the benefit of this approach for your clients? 35 Module 10: Managing Cash Flow Tool 1: Cash flow budget Week 1 Week 2 $37.00 $142.37 Income from job $305.34 $290.80 SNAP $280.00 Public housing voucher $650.00 Beginning balance for the week Sources of cash and other financial resources Total sources of cash and other financial resources $1,272.34 $433.17 Uses of cash and other financial resources Housing $650.00 Utilities $59.97 $95.50 $180.00 $80.00 Transportation $240.00 $60.00 Total uses of cash and other financial resources $1,129.97 $235.50 $142.37 $197.67 Groceries Eating out (meals and beverages) Ending balance for the week Ending balance from previous week. To get a starting balance, total your cash, debit card , and account balances 36 Your Money, Your Goals Module 8: Managing income and benefits 37 Tool 1: Income and financial resource tracker 38 One-time Seasonal Irregular Regular Total Week 4 Week 3 Week 2 Week 1 Module 8:Managing Income and Benefits Tool 1: Income and financial resource tracker Job Second job Self- employment income SNAP TANF SSI Child support Gift Tax refund Weekly total 39 Module 9: Paying Bills and Other Expenses Tool 1: Spending tracker 40 Module 9: Paying Bills and Other Expenses Tool 1: Spending tracker, continued Savings Saving for goals, saving for emergencies, saving for children’s education, saving for retirement, saving for holiday purchases, saving for back to school shopping Debt payment Credit card payments, payday loan payments, pawn loan payments, car title loan payments, and other loan payments Housing Rent, mortgage, insurance, property taxes Utilities Electricity, gas, water, sewage, phone, television, Internet service, cell phone Household supplies and expenses Things for your home like cleaning supplies, kitchen appliances, furniture, other equipment Groceries Food and beverages to be brought into the home, including baby formula and food Eating out (meals and beverages) Any meals or beverages purchased outside of the home Savings Saving for goals, saving for emergencies, saving for children’s education, saving for retirement, saving for holiday purchases, saving for back to school shopping Debt payment Credit card payments, payday loan payments, pawn loan payments, car title loan payments, and other loan payments 41 Module 9: Paying Bills and Other Expenses Tool 1: Spending tracker (continued) Transportation Health care Gas, car payment, insurance payment, repairs Co-payments, medication, eye care, dental care Personal care Haircuts, hygiene items, dry cleaning, pet costs Childcare and school expenses Child care costs, diapers, school supplies, school materials fees, field trip and other activity fees Entertainment Going to the movies, going to concerts, sports equipment/fees, sporting events, lottery tickets, memberships, alcohol, books/CDs, subscriptions Court-ordered obligations Child Support, restitution, etc. Gifts, donations, and other Donations to religious organizations or other charities, gifts, other expenses Transportation Gas, car payment, insurance payment, repairs Health care Co-payments, medication, eye care, dental care 42 Tool 2: Bill calendar 43 Tool 3: Strategies for cutting expenses 44 Tool 4: When cash is short – prioritizing bills and spending 45 Tool 5: Prioritizing bills 46 Your Money, Your Goals Module 6: Setting Goals 47 Module 6: Setting Goals Tool 1: Goal setting tool 48 Setting Goals, Tool 1. PP. 57,58,59 In pairs at your table: • Identify up to three short term goals that patients can address to meet their health care needs, manage chronic diseases, reduce medical expenses. • What might be one or two long term goals to strengthen the financial condition of your patient’s finances? Table Exercise: 10-15 Minutes with a Patient I will…… What are the common money topics that will come up in your interaction with patients? Which collection of topics and tools will you have ready to share? Directions Each table answers these two questions. Put answers on newsprint. Report to the larger group. Coordinator Training Responsibilities with Members Review… Take this four hour training and replicate it. The key training objective is to: Provide information and tools to patients on key topics they raise. Support patients in taking small actions to strengthen their financial lives. Examples: reduce out of pocket medical costs, use the Earned Income Tax Credit to reduce debt & establish small $500-$1000 emergency savings; tracking income/resources/spending; prioritizing bill paying to make ends meet. Provide referrals Use the slides, exercises, and Your Money Your Goals Toolkit for Social Services. Administer pre-surveys and post surveys to Members at beginning and end of training. Complete trainer survey after training. Send these to NACHC Office 51 Your Money, Your Goals Closing 52