5 nm
advertisement

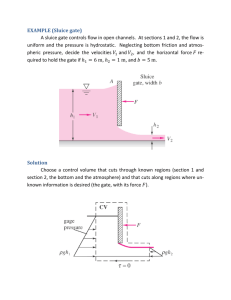
In0.53Ga0.47As MOSFETs with 5 nm channel and self-aligned source/drain by MBE regrowth Uttam Singisetti PhD Defense Aug 21, 2009 *uttam@ece.ucsb.edu 1 Outline • Motivation: why III-V MOSFETs, target device structure • Approach: self-aligned source/drain by MBE regrowth • FET and contacts results • Conclusion and future work 2 Why III-V MOSFETs Silicon MOSFETs: Gate oxide may limit <16 nm scaling Id / Wg ~ cox(Vg-Vth)vinj IBM 45nm NMOS Narayan et al, VLSI 2006 Alternative: In0.53Ga0.47As channel MOSFETs low m* (0.041 mo) → high injection velocity, vinj (~ 2-3×107 cm/s)* → increase drive current, decreased CV/I * Enoki et al , EDL 1990 3 Key challenge : high-k on III-V 1 B. Shin et al, ECSSL, 12, G40, 2009 Dielectric goals : 0.6 nm EOT , Dit 1×1012 cm-2 eV-1 , low leakage Dielectrics & approaches: Atomic layer deposition (ALD) Al2O31 2 R. E. Herbert et al, APL, 95, 0629081, 2009 Chemical beam deposition ZrO22 Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) GGO3 3 R.Hill et al, Device research conference, 2009 4 MOSFET scaling*: lateral and vertical Goal : double package density → lateral scaling Lg, Wg, Ls/d double the MOSFET speed keep constant gate control vertical scaling tox, tqw, xj *Rodwell, IPRM 2008 5 Drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) (DIBL) qb sub-threshold slope (S) Vg Gate modulates qb Drain modulates qb qb goal V g q b Vd (DIBL) q b >> Vd 6 DIBL : 2-D electrostatics* Cg-ch ~ oxWg Lg / tox Cd-ch ~ qwWg tqw / Lg 2 d 2 x d y 2 2 dx dy qw aspect ratio Cg-ch / Cd-ch =g 2 = ox Lg2 / tqw tox qw* g = 5-10 for long channel like sub-threshold behavior* *Yan et al, TED, 39, 1704, 1992 7 MOSFET aspect ratio Lg / qw → DIBL aspect ratio active region rectangle → tox / ox tqw / qw constant aspect ratio: Lg↓ → tox↓, tqw↓ and xj↓ 8 Target device structure 3 Al O Energy (eV) 2 2 3 1 0 -1 InGaAs InAlAs -2 -3 -4 0 50 100 150 Y (Ang.) 200 250 Target 22 nm gate length Control of short-channel effects vertical scaling 1 nm EOT: thin gate dielectric, surface-channel device 5 nm quantum well thickness < 5 nm deep source / drain regions 9 InGaAs MOSFET: target drive current CtotalVdd td Id C gs,iVdd Lg t int Id v increase Id to reduce circuit delay (td ) ~3 mA/mm target drive current low access resistance self-aligned, low resisitivity source / drain contacts self-aligned N+ source / drain regions with high doping 10 22 nm InGaAs MOSFET: source resistance LS/D I di Id 1 g mi Rs Rs c Wg LS / D Lg sheet LS / D 2Wg IBM High-k Metal gate transistor Image Source:EE Times • Source access resistance degrades Id and gm • IC Package density : LS/D ~ Lg =22 nm c must be low • Need low sheet resistance in thin ~5 nm N+ layer • Design targets: c ~1 W-mm2, sheet ~ 400 W 11 22nm ion implanted InGaAs MOSFET Key Technological Challenges • Shallow junctions ( ~ 5 nm), high (~5×1019 cm-3) doping • Doping abruptness ( ~ 1 nm/decade) • Lateral Straggle ( ~ 5 nm) • Deep junctions would lead to degraded short channel effects 12 InGaAs MOSFET with raised source/drain by regrowth HAADF-STEM1 InGaAs regrowth Interface InGaAs 2 nm Self-aligned source/drain defined by MBE regrowth1 Self-aligned in-situ Mo contacts2 Process flow & dimensions selected for 22 nm Lg design; present devices @ 200 nm gate length 1Wistey, EMC 2008 JVST 2009 2Baraskar, 13 Regrown S/D process: key features Self-aligned & low resistivity ...source / drain N+ regions ...source / drain metal contacts Vertical S/D doping profile set by MBE no n+ junction extension below channel abrupt on ~ 1 nm scale Gate-first gate dielectric formed after MBE growth uncontaminated / undamaged surface 14 Process flow* * Singisetti et al; Physica Status Solidi C, vol. 6, pp. 1394,2009 15 Key challenge in S/D process: gate stack etch Requirement: avoid damaging semiconductor surface: Approach: Gate stack with multiple selective etches* FIB Cross-section SiO2 Damage free channel Cr W Process scalable to sub-100 nm gate lengths * Singisetti et al; Physica Status Solidi C, vol. 6, pp. 1394,2009 16 Key challenge in S/D process: dielectric sidewall -3 electron concentration (cm ) sidewall 19 2.8 10 source gate 19 2.4 10 2 10 19 19 1.6 10 19 1.2 10 8 10 18 4 10 18 10nm SiN 20 nm SiN 30 nm SiN 0 10 20 30 40 50 distance (nm) n under sidewall → electrostatic spillover from source and gate tsw 10 nm 20 nm 30 nm n (cm-3) > 1×1019 > 5×1018 ~ 4×1018 60 70 80 spillover Rs (W-mm) 6 20 60 Simulation in Atlas, Silvaco 17 Key challenge in S/D process: dielectric sidewall Sidewall must be kept thin: avoid carrier depletion, low leakage • Target < 15 nm sidewall in 22 nm Lg device • 20-25 nm SiNx thick sidewalls in present devices • Pulse doping in the barrier: compensate for carrier depletion from Dit 18 Surface cleaning before regrowth • 30 min UV Ozone • Ex-situ HCl:H2O clean HAADF-STEM* InGaAs regrowth Interface • In-situ 30 min H clean InGaAs 2 nm TEM by Dr. J. Cagnon, Stemmer Group, UCSB c(4×2) reconstruction before regrowth → minimum process contamination * Wistey, EMC 2008 MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 19 Self-aligned contacts: height selective etching* Mo PR PR PR InGaAs Dummy gate No regrowth * Burek et al, J.Cryst.Growth 2009 20 1st generation MOSFETs 100 Drain current ( mA) Drain Current, uA Lg=10mm, W g=50mm Vg 0 V to 2 V in 0.25 V steps 80 60 100 Lg 10 microns, Wg 50 microns Ron ~ 0.7 MW-mm! 40 Vds=2V 80 60 40 20 20 0 0 0 0 0.5 1 Vds, Volts 1.5 0.5 2 1 V (Volts) 1.5 2 gs • Extremely low drive current: 2 mA/mm • Extremely high Ron= 0.7 MW-mm • Why is Rs so high? 21 Source resistance : gap in Regrowth SEM Ti/Au Pad SiO2 cap Mo+InGaAs W / Cr / SiO2 gate W/Cr gate Gap in regrowth SEM / Cr / SiO • Shadowing by gate: No regrowth nextWto gate 2 gate • Gap region is depleted of electrons High source resistance because of electron depletion in the gap MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 22 Migration enhanced epitaxial (MEE) regrowth* High T migration enhanced Epitaxial (MEE) regrowth* 45o tilt SEM No Gap gate Top of SiO2 gate Side of gate regrowth interface No Gap High temperature migration enhanced epitaxial regrowth *Wistey, EMC 2008 Wistey, ICMBE 2008 MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 23 MEE source/drain regrowth MOSFET SEMs SiO2 SiNx Cr W InGaAs regrowth W/Cr gate Pad Original interface Cross-section after regrowth, but before Mo deposition Mo +InGaAs Ti/Au Pad Top view of completed device MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 24 Regrown S/D FETs: Images gate Mo Mo gate post 25 MOSFET characteristics 4.7 nm Al203 , 1×1013 cm-2 pulse doping 1 L =0.8mm, W g g =0.5 V 0.6 ds 0.4 0.2 =12mm g,eff V = -1 V to 3.5, V 0.8 gs_step I (mA/mm) ds I (mA/mm) gs L =1.0mm, W g,eff V = -1 V to 3.5, V 0.8 1 =9mm gs =0.5 V gs_step 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 0 0.5 V (V) ds 1 1.5 2 V (V) ds • Maximum Drive current (Id): 0.95 mA/mm • Peak transconductance (gm): 0.37 mS/mm Id and gm below expected values 26 FET source resistance 7000 SEM V =3.0 V gs 6000 4000 3000 R on (W-mm) 5000 2000 R +R 1000 S D = 1.0 kW-mm 0 0 2 4 6 Gate Length (mm) 8 10 • Series resistance estimated by extrapolating Ron to zero gate length • Source access resistance ~ 500 W-mm 27 Source resistance : regrowth TLMs 40 SEM Resistance (W) 35 SEM W~ 20 mm FET 30 25 W / Cr / SiO2 gate Regrowth TLMs No regrowth 20 15 10 R sh 5 ~ 29 W Rc ~ 5.5 W-mm (12.6 W-mm) 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 Contact Separation ( mm) 25 30 • TLMs fabricated on the regrowth far away from the gate • Regrowth sheet resistance ~ 29 W • Mo/InGaAs contact resistance ~ 5.5 W-mm2 (12.6 W-mm) TLM data does not explain 500 W-mm observed FET source resistance 28 Source resistance: electron depletion near gate SiO2 SiNx R1 InGaAs regrowth Cr W R2 Original interface • Electron depletion in regrowth shadow region (R1 ) • Electron depletion in the channel under SiNx sidewalls (R2 ) MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 29 Regrowth profile dependance on As flux* SiO2 InAlAs InGaAs InGaAs increasing As flux Cr InGaAs W InGaAs regrowth surface uniform filling multiple InGaAs regrowths with InAlAs marker layers Uniform filling with lower As flux * Wistey et al, EMC 2009 Wistey et al NAMBE 2009 MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 30 InAs source/drain regrowth Gate InAs regrowth InGaAs 100 nm Improved InAs regrowth with low As flux for uniform filling1 InAs less susceptible to electron depletion: Fermi pinning above Ec2 1 Wistey et al, EMC 2009 Wistey et al NAMBE 2009. 2Bhargava et al , APL 1997 MBE growth by Ashish Baraskar, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 31 Regrown InAs S/D FETs top of gate side of gate Mo S/D metal with N+ InAs underneath gate Mo S/D metal with N+ InAs underneath 4.7 nm Al203, 5×1012 cm-2 pulse doping MBE growth by Dr. Mark Wistey, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 32 InAs S/D E-FET DC Characteristics 0.8 L = 350nm W = 8 mm 0.7 g g V : 0 to 4 V in 0.5 V steps 0.6 gs 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 g g V : 0 to 4 V in 0.5 V steps 0.6 D 0.5 L = 0.45 mm W = 8 mm 0.7 drain current, I (mA/mm) D drain current, I (mA/mm) 0.8 gs 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 0 0.2 0.4 V DS (V) 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.4 V DS D drain current, I (mA/mm) 0.8 4.7 nm Al203, InAs S/D E-FET 0.2 (V) 0.6 0.8 1 L = 1 mm W = 8 mm 0.7 g g V : 0 to 4 V in 0.5 V steps 0.6 gs 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 0.5 1 V DS 1.5 2 (V) 33 L = 200 nm W = 8 mm 0.8 g g V : 0 to 4 V in 0.5 V steps gs 0.6 Ron = 600 W-mm D drain current, I (mA/mm) InAs S/D E-FET DC characteristics 0.4 0.2 0 0 0.5 1 V DS 1.5 (V) 0.85 mA/mm peak Id , ~0.36 mS/mm peak gm 4.7 nm Al203, InAs S/D E-FET * Singisetti et al, IEEE EDL, submitted 34 Sub-threshold characteristics 10 -2 L =1.0 mm L =0.35 mm 10 -3 10 -4 10 -5 10 -6 10 -7 g 325 mV/decade d I (A) g 10 290 mV/decade V =0.1V V =0.1V V =1.0V V =1.0 V ds ds -8 ds ds 10 -9 -1 0 1 2 3 V (V) 4 5 -1 gs 0 1 2 3 V (V) 4 5 gs • Ion / Ioff~ 104:1 • High sub-threshold swing • Hysteresis 35 Source-drain access resistance* 3 2 1.5 on R (kW-mm) 2.5 600 W-mm 1 0.5 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 gate length (mm) • Ron = 600 W-mm for Lg=0.2 mm so Rs< 300 W-mm • Rs is too small to explain observed gm or Id *Wistey et al, NAMBE 2009 36 Source access resistance Gate InAs regrowth InGaAs 100 nm Mo/InAs contact resistance : 3.5 W-mm2 (8.5 W-mm) InAs sheet resistance: 20 W Electron depletion at Al2O3/InGaAs interface under sidewall MBE growth by Ashish Baraskar, device fabrication and characterization by U.Singisetti 37 Key challenge in S/D process: dielectric sidewall -3 electron concentration (cm ) sidewall 19 2.8 10 source gate 19 2.4 10 2 10 19 19 1.6 10 19 1.2 10 8 10 18 4 10 18 10nm SiN 20 nm SiN 30 nm SiN 0 10 20 30 40 50 distance (nm) n under sidewall → electrostatic spillover from source and gate tsw 10 nm 20 nm 30 nm n (cm-3) > 1×1019 > 5×1018 ~ 4×1018 60 70 80 spillover Rs (W-mm) 6 20 60 Simulation in Atlas, Silvaco 38 Gate dielectric Dit 10 -2 10 -3 10 -4 10 -5 10 -6 10 -7 cd L =1.0 mm G S cox d I (A) g 300 mV/decade cox cd qDit S 60 mV / decade cox V =0.1V 10 ds -8 cd V =1.0V ds 10 -9 -1 0 1 2 3 V (V) 4 cit qw tqw cit qDit 5 gs Dit from sub-threshold swing = 2 ×1013 cm-2 eV-1 39 3 Al 0.48 0.52 As E -1 f 18 0 10 Energy (eV) 1 -2 -3 -4 -3 Vg= 0 V InGaAs electron concentration (cm ) In 2 Al2O3 10 19 Threshold voltaget (Vt ) 10 17 -5 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Y (Ang.) Expected Vt = -0.75 V, actual Vt = 0.6 V Dit = ∆ Vt / qCox = 1.5 ×1013 cm-2 eV-1 40 Higher S in 200 nm device: DIBL ? 0 10 -1 10 -2 10 -3 10 -4 10 -5 10 -6 10 -7 D drain current, I (mA/mm) 10 500 mV/decade V =0.1 V ds L =200 nm g -1 0 1 2 3 4 V (V) gs higher sub-threshold swing for 200 nm device → is it DIBL Lg / tqw = 200/5 = 40 → clearly not DIBL 41 Electron confinement under source/drain InAs InAlAs Ef InGaAs Insufficient electron confinement under source/drain Need a AlAsSb barrier or higher p+ doping in buffer 42 Conclusion • Self-aligned source/drain for thin channels ( ~ 5nm ) → scalable • InAs Source/Drain E-FETs: Rs < 300 W-mm, peak Id= 0.85 mA/mm, peak gm= 0.36 mS/mm • Device gm, Id not limited by Rs • Next: scale to ~50 nm Lg scale sidewalls gate dielectric quality 43 Acknowledgements Prof. Mark Rodwell, Prof. Umesh Mishra, Prof. Art Gossard, Prof. Chris Palmstrøm Dr. Mark Wistey, Dr. Seth Bank, Dr Yong-ju Lee Stemmer group: Dr Joël Cagnon McIntyre group (Stanford) : Eunji, Byungha Yuan Taur group (UCSD) : Yu Yuan Rodwell group members: Navin, Colin, Zach, Erik, Munkyo, Greg, Vibhor, Evan, Ashish Mishra group, photonics group clean-room buddies Nanofab staff: Jack, Brian, Don, Bill, Mike, Bob, Adam, Tony, Aidan, Luis MRL staff: Dr Tom Mates Friends and family 44