Stages of Child Development
advertisement
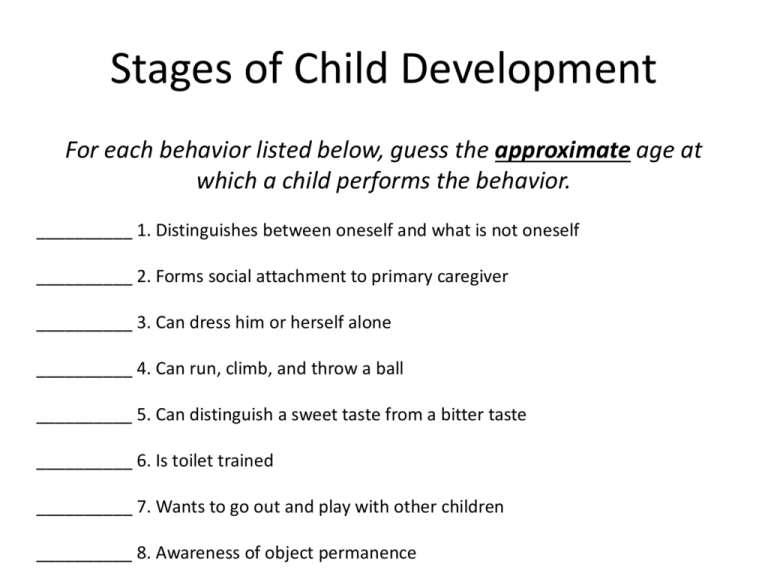
Stages of Child Development For each behavior listed below, guess the approximate age at which a child performs the behavior. __________ 1. Distinguishes between oneself and what is not oneself __________ 2. Forms social attachment to primary caregiver __________ 3. Can dress him or herself alone __________ 4. Can run, climb, and throw a ball __________ 5. Can distinguish a sweet taste from a bitter taste __________ 6. Is toilet trained __________ 7. Wants to go out and play with other children __________ 8. Awareness of object permanence Stages of Child Development For each behavior listed below, guess the approximate age at which a child performs the behavior. __________ 9. Grasps the concept of conservation of number __________ 10. Grasps the concept of conservation of volume __________ 11. Begins to understand simple cause-and-effect relationships __________ 12. Plays pat-a-cake __________ 13. Has a vocabulary of around 1,000 words __________ 14. Can sit up with some support __________ 15. Can walk alone __________ 16. Recognizes household members Stages of Child Development Answers 1. 1 year 9. 6 years 2. 6 months 10. 11 years 3. 6ish years 11. 1-2 years 4. 4 years 12. 9-12 months 5. Newborn 13. 3 years 6.1 1/2 years 14. 4 months 7. 4-5 years 15. 15 months 8. 1 year 16. 3-6 months Study of growth and changes as we progress through the life cycle. (Physical, Social, Moral, Cognitive) Capacities? • Newborns have the ability at birth to see, hear, smell and respond to the environment. Reflexes must be triggered by the right stimulus… • Reflexes: Inherited, automatic, coordinated movement patterns 1. Rooting and Sucking 2. Walking or Stepping 3. Grasping or Palmer 4. Startle or Moro 5. Babinski Rooting: • If the infant is touched anywhere near the mouth, he/she will more their head and mouth toward the source. • Disappears around 4 months and becomes voluntary… Sucking: • Accompanies rooting • Automatically suck anything that touches mouth or roof of mouth http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NksbJQr5_xw&feature=related Present at birth; › Can’t support own weight… Soles of feet touch a flat surface infants will attempt to “walk” placing one foot in front of the other. This reflex disappears at 6 weeks as an automatic response http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bal9fYVGv74&feature=related › Infants response to a touch on the palm of the hand. a. Strength? John B. Watson, a godfather of American behaviorist psychology, tests the grasp reflex in a baby, circa 1916-20. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FV-qWSVNFt8&feature=related › A response to an unexpected noise or when the infant feels as if they are falling. Following the startle, infants will spread out arms and legs and grasp upward › Disappears by 4-5 months. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jsLqoT4fIH8 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jsLqoT4fIH8 Babinski Reflex How would you respond to someone running their thumbnail up the center or side of the bottom of your foot? Your toes would curl and your foot would withdraw. Before an infants first birthday, they have the exact opposite response…. Babinski Reflex Upon stimulation of the side of the foot, infants extend the big toe. In time the Babinski response vanishes and, under normal circumstances, should never return. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AHRTXorQkyQ&feature=related Perceptual Development • Do infants have depth perception? • Gibson and Walk 1960 – Visual Cliff – 6+ Months – Refuse – Newborns – increase in heart rate suggesting some perceptual abilities Language Development Several steps in learning language… • Cry --> Cooing --> Babble (includes all sounds humans can make – Chinese vowels, African clicks etc…) • ONE YEAR -->Imitate sounds of language that surrounds them --> Sounds become words • TWO YEARS --> Words (500 – 1,500) Simple sentences… • THREE YEARS --> Combining words to make complex sentences • 18 MONTHS – 5 YEARS --> Add 5-10 words/day Cognitive Development? • Jean Piaget • Through research, found that intelligence, or the ability to understand, develops gradually. • We use different logic to understand the world around us. How Knowing Changes… • Understanding the world involves mental representations of the world (called SCHEMAS) • Each of us constructs intellectual schemas, applying them and changing them as needed. Dog schema = 4 legs and fluffy Assimilation vs. Accommodation • We try to understand a new or different object or concept by using one of our preexisting schemas. • Assimilation: We try to fit the new object into existing schemas. • Accommodation: We change our schema to fit the characteristics of the new object. Assimilation and Accommodation • A child believes that "All furry four legged animals are dogs". He sees a breed of dog that he's never seen before and says, "That's a dog." That's assimilation. • Then the child sees a horse (or a cat, squirrel whatever) and the child says, "That's a dog." But his parents tell him it isn't a dog, it's a horse. So the child accommodates, "Not all furry four legged animals are dogs, some are raccoons." Assimilation and Accommodation • Young children can go from riding a big wheel to riding a tricycle with no problem--they can assimilate--it is 'sort of the same'; but to go to a bicycle there is much accommodation that must take place. Assimilation and Accommodation • A child learns his father is called Daddy, so he calls other males ( e.g. the mailman) Daddy. This is assimilation. • He is quickly told that the other man is not Daddy, he is Bob. Again, the schema for “Daddy” is modified. This is accommodation. Adults and Assimilation and Accommodation? • When I was growing up my parents believed that tattoos were bad, so I created a schema for people with tattoos. I assimilated such information as "probably rides a motorcycle," "is dirty," and "probably has been in jail" into this schema during my childhood (because that's what my parents said). • When I got to college, I met a lot of people with tattoos who did not fit into my schema, and thus had to do some accommodation to accept those people. Game • You are to create a game that is designed to help children practice assimilation and accommodation. • Be creative!!







