Medical Terminology
advertisement

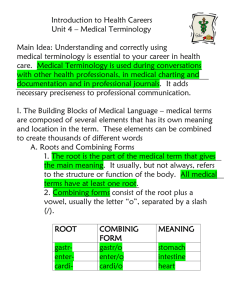
Medical Terminology Introduction to Basic Word Elements Spelling & Pronunciation What is Medical Terminology Language of medical terms or words Derived from Latin or Greek Used to describe diseases, diagnosis, investigations, procedures, signs and symptoms, anatomy and physiology Structure / Elements of medical words Are a combination of smaller words / or word parts Consist of one or more of the following parts 1. Root words 2. Prefixes 3. Suffixes 4. Combining vowels 5. Combining forms 1. Word Root Is the basic word part or foundation of the word Provides the meaning to the word Usually refers to a body part E.g. cardi refers to the heart gastr refers to the stomach Examples of word roots Word Root Gastr Body Part Stomach Gastric juices means acids in the stomach Example Word Root cardi Body Part heart Cardiac Arrest means heart attack Example Word Root trache Body Part Trachea i.e. windpipe Tracheitis means inflammation of the trachea Pg 1 2.Prefixes ( pre means before) Is the element at the beginning of the word Comes before the word root Prefix modifies or changes the meaning of the root word Application of prefixes The prefix pan means whole E.g. pan + arthritis = panarthritis arthritis of the joints Application of prefixes E.g. INTER/COSTAL inter (between) (prefix) + costal (ribs) (word root) INTERCOSTAL pg1. 3.Suffixes Come at the end of the word root Modifies the word root Adds to the meaning to the word root Pg 2 Application of Suffixes Itis - means inflammation E.g. appendicitis means inflammation of the appendix Algia - means pain E.g. pharynalgia means pain of the throat Pg 2 Suffixes that mean relating to ac cardiac Relating to the heart al skeletal Relating to the skeleton ar muscular Relating to the muscle ary urinary Relating to urine ic epigastric Relating to above the stomach ive infective relating to infection ous nervous Relating to nerves 4.Combining vowels used to join various parts of the word a,e,i,o,u Most common vowels used are “o” and “i” Acts like a maths “+” sign E.g. cardi /o/ logist Pg 2,3 5.Combining form Is simply a root word plus a combining vowel E.g. gastr = root word for stomach gastro = combining form of stomach Gastro can now be joined to another root word or suffix Makes words easier to pronounce More combining forms Body Part Word Root stomach gastr Combining Form gastro intestine enter entero heart cardi cardio nose rhin rhino skin * dermat dermato * Interpreting the meaning of medical terms Breaking the words down makes it easier E.g. Gastro /enter / itis then look up meaning of each component Read the word backwards beginning with the suffix Listen to experts Ask your supervisor for clarification if unsure Interpreting medical terms e.g. Gastroenterology 1.break up the word into its components 2.e.g.gastro / entero / logy 3.then read the meaning backwards i.e. 1.logy = study of 2.entero = intestines 3.gastro = stomach Meaning – study of the intestines and stomach Interpreting medical terms e.g. gastroenteric Gastr (stomach) root / o combining vowel / enter (intestines) / ic root Gastroenteric means relating to the stomach & intestines suffix Interpreting medical terms e.g.Rhinoplasty Rhin (nose) / root o combining vowel / plasty (surgical repair of) suffix Rhinoplasty means surgical repair of the nose Dermatologist Dermat (skin) root / o combining vowel / logist (specialist) suffix Dermatologist means specialist who studies the skin Dropping a vowel when joining words If root word ends in a vowel & suffix begins with a vowel, combining vowel is dropped e.g. gastr/o + -itis (stomach) (inflammation of) = gastritis If a prefix ends in a vowel & root word begins with a vowel the combining vowel is dropped e.g. anti + (against) acid (acid) = antacid (not antiacid) (works against acid) When to leave the combining vowel in If the suffix begins with a consonant the combining vowel stays e.g. cardio + pathy = cardiopathy Pronunciation Lightly emphasise the first syllable Break up the words E.g. pericarditis peri card it is gastroenteritis gastro entero it is Myocardium myo cardi um Using dictionaries Stress marks used when word has > one syllable Stress mark ‘ or , placed before syllable to be stressed Symbol “ə” is a neutral or unstressed vowel e.g. “a”in above or “e” in sicken Look up respiration gastrostomy Hints for pronouncing Consonant Example c (before a,o,u) = k Cavity, colon,cure c (before e,i ) = s Cephalic, cirrhosis ch = k cholesterol g (before a, o, u) = g gallstone,gonad g (before e, i ) = j generic, giant Hints for pronouncing Consonant Example ph = f phase, pharnyx pn = n pneumonia ps = s psychiatry, psychology pt = t ptosis, pterygium rh,rrh rhythm, haemorrhoid Spelling medical terms correctly Abduction Adduction move away from move towards Arteritis Arthitis inflammation of an artery inflammation of a joint Ileum Ilium lower part of small intestine hip bone Plurals Most words are made plural by adding used “s”, or replacing “y” with “ies” but Latin words use other letters Application of plurals Singular ending Plural Singular ending example Plural example meaning -a -ae vertebra hernia vertebrae herniae part of spine protrusion of an organ -is -es diagnosis diagnoses testis testes identification of a disease male sex organ -um -a bacterium ovum bacteria ova microorganism female egg cell -us -i bronchus bacillus bronchi bacilli small airway type of bacterium English & American Spelling American spelling drops any silent vowels i.e an “o” or “a” that is silent is left out of the spelling If “c” is pronounced as a hard “k” sound the Americans will spell it with a “k” Both English & American is used American versus English spelling English American Pronunciation Meaning diarrhoea diarrhea di – a - rear watery bowel motion foetal fetal fee - tal child in womb haematologist hematologist hem –a – tol ogist blood specialist leucocyte leukocyte lew – ko - site white blood cell oedema edema e- deema swelling paediatrics pediatrics peedi - atrics area of child health Medical terms Diseases and disorders Aetiology - study of cause of diseases Signs – clinical evidence of cause of diseases or disorders Symptoms – indicators of disease that the patient is experiencing Disease – set of signs and symptoms that disrupts normal function of a body system or organ Diagnosis – is when the doctor finds or decides what is causing the signs and symptoms i.e. the disease or disorder Diseases and disorders Prognosis – forecast of the outcome / recovery from the disease Morbidity – presence of illness or disease Mortality – death Acute – beginning abruptly and usually intense Chronic – refers to something lasting for a long time Terminal - will cause death Pg 6 Disorder prefixes Disorder Prefixes Meaning a, an without brady slow dys difficult or painful hyper above hypo below oligo few poly many tachy fast Disorder Suffixes pg 6 Disorder suffix Meaning -ema -trophy -ia -iasis swelling nourishment condition of abnormal condition of -megaly -oma enlargement tumour (mass which may or may not be cancerous) -osis -ptysis -staxis abnormal condition spitting up dripping blood