Physiographic Provinces of Virginia
advertisement

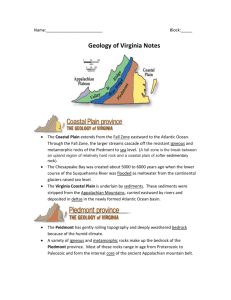
Physiographic Provinces of Virginia Earth Science 5 Virginia is divided into ____ major physiographic provinces (physio-physical features, graphic—map of). W Appalachian Plateau Coastal Plain Valley & Ridge E Blue Ridge Piedmont 1. Coastal Plain The Coastal Plain runs from the fall line on the west, to the Atlantic Ocean on the east It is a terraced landscape Sand, silt and clay produced by erosion of the Appalachian Mts. covers the plain As sea levels rose and fell, fossils were left at various layers Virginia Fossils Fossils include various marine organisms like clams, scallops, sharks teeth, and other hard remains Virginia Fossils Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic fossils are found in Virginia The Coastal Plain A gently seaward sloping surface in Eastern Virginia 300’ -Coastal Plain Pile “_______” of loose sediments that have eroded from the mountains. 0’ sea level Sediments The highest elevation is about 300 ft. above sea level. 1. Kinds of rocks: Sedimentary, loose sediments 2. Ages of rocks: 0-225 MYA 3. Fossils: Sea critters 4. Features: Wetlands This area is rich in _____ sand and gravel resources. ______ These resources are used to build roads. The Chesapeake Bay is found here where this region borders the Atlantic Ocean. Also called the Tidewater Region it is the region closest to sea Coastal Plain Note Card: Flat, layered w/ sediments & fossils Youngest region of VA Formed from the erosion of the Appalachian Mountains and deposition of these sediments onto the Coastal Plain. Contains gravel and crushed stone used for road construction. Fall Line: a. Waterfalls and rapids are located here. b. Major cities are located here. Fall line Note Card: Separates the Coastal Plain from the Piedmont. It is a boundary between an upland region and a coastal plain. Rivers from the upland region drop to the plain as falls or rapids. A fall line is formed in an area where the rivers have eroded away the soft rocks of a coastal plain more quickly than the older harder rocks of an upland region. 2. Piedmont Mining the Piedmont High quality slate is mined from this area The Piedmont host one of the worlds largest kyanite mines ( see picture of kyanite ) The Piedmont A gently rolling area with hills and valleys (pied-foot, mont-mountains). This is located in Central Virginia. Blue Ridge Piedmont W Lynchburg VA Coastal Plain E subduction An episode of ___________ that occurred before the formation of the Appalachian Mountains created these rocks. They are part roots of of the ______ the mountains. 1. Kinds of rocks: Igneous and metamorphic (some sediment) 2. Ages of rocks: 245-570 mya 3. Fossils: None Exception: Culpepper Co. Dinosaur tracks Piedmont Note Card: This is where we live Rolling hills underlain by ancient igneous and metamorphic rock. Igneous rocks here are the roots of volcanoes formed during an ancient subduction occuring before the formation of the Appalachian Mountains. Located west of the fall line. 3. Blue Ridge Mountains Blue Ridge A narrow line of mountains north of Roanoke, a broader, upland surface south of Roanoke. Highest mountains in Virginia. _________ The Appalachian mountains are older eroded ________ and more _________ than the Rocky Mountains. Mount Rogers Elevation: 5719’ W Highest ___________ peak _______ in Virginia. 1.Kinds of rocks: Igneous & metamorphic 2.Ages of rocks: 245 mya-1 bya 3.Fossils: None Metamorphosis ____________ occurred during the Appalachian Mountain formation. oldest rocks in These are the ________ Virginia. Blue Ridge Note Card: A high ridge between the Piedmont and Valley & Ridge Province. Billion year old rocks are the oldest in the state. (Metamorphic & Igneous) Some Metamorphism occurred during the formation of the Appalachians. Valley and Ridge The Valley and Ridge Province is an area of long parallel ridges and valleys underlain by ancient folded and faulted sedimentary rocks Cambrian fossil algal structures are found in the V&R Province Limestone outcrops are common in the Valley and Ridge Province Valley and Ridge An area of long, parallel ridges separated by valleys W Ridges Valleys Great Valley Blue Ridge Plateau Thrust Faults Sections of hard, resistant rocks make up the ridges, while soft, eroded limestone makes up the valleys. ________ Limestone has eroded and leaves caves and caverns (karst topography). Sink holes! Caverns! Folding and faulting occurred during the formation of the Appalachian Mountains (when N. America collided with Africa and Europe). This occurred during the Paleozoic Era (300-265 million years ago). 1.Kinds of rocks: Sediment 2.Ages of rocks: 350-570 mya 3.Fossils: Sea critters Valley and Ridge Note Card: Long parallel ridges and valleys underlain by ancient folded and faulted sedimentary rock. Folding and faulting occurred during a continental collision between Africa and North America in the late Paleozoic Era. This collision created the Appalachian Mountains! Contains limestone caves or “Karst Topography”. Limestone is used to make concrete 5. Appalachian Plateau Appalachian Plateau This is a series of plateaus separated by faults. “The Boot” This area is known for rich coal ____, oil deposits of ____, and natural gas _________. Coal seams COAL! Virginia Coal Most of Virginia's coal is found in the Appalachian Plateau. 1.Kinds of rocks: Sediment 2.Ages of rocks: 286-360 mya 3.Fossils: Scale trees Ferns Some sea critters W E Appalachian Plateau Plateaus Valley & Ridge Faults Appalachian Plateau Note Card: Rugged, Irregular Topography Underlain by ancient flat lying Sedimentary Rocks A series of plateaus separated by faults This area contained an ancient swamp responsible for most of VA’s coal. Let’s Review each region: