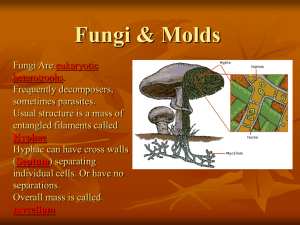
Chapter 3, Section 3 – Fungi What are fungi? Eukaryotes Have cells
advertisement

Chapter 3, Section 3 – Fungi I. II. III. IV. What are fungi? a. Eukaryotes b. Have cells walls c. Heterotrophs (absorb food) d. Reproduce by using spores Cell Structure a. Multicellular (except for unicellular yeast) i. Cells surrounded by cell walls ii. Cells arranged in hyphae (branching, threadlike tubes) iii. Arrangement of hyphae gives fungi its appearance 1. Loosely tangled hyphae (ex. Food molds) 2. Tightly packed hyphae (ex. Mushrooms) iv. Hyphae form threadlike maze underground Obtaining Food a. Fungi are heterotrophs i. Absorb food through hyphae that grow into the food source ii. Digestive materials go through hyphae into food iii. Chemicals breakdown food into smaller substances that can be absorbed iv. Some fungi are decomposers while others are parasites Reproduction in Fungi a. Reproduction using spores i. Spores are produced in fruiting bodies ii. Lightweight spores are surrounded by protective covereing iii. Can be carried easily through water or air to other places b. Asexual reproduction i. Spores are made asexually when cells at the tips of the hyphae divide ii. Unicellular fungi (yeast) reproduce asexually through a process called budding 1. No spores are formed – small yeast cells grow from the body of the parent cell and then break off to live on their own c. Sexual reproduction i. Occurs when growing conditions become unfavorable ii. Hyphae of two fungi grow together and exchange genetic material iii. A new reproductive structure is formed and spores are produced iv. The spores develop into fungi that differ from each parent d. Classification of Fungi i. Three major groups (named for appearance of reproductive structures) 1. Club fungi (ex. Mushrooms, puffballs) 2. Sac fungi (ex. Yeasts, truffles, and morels) 3. Zygote fungi (ex. Fruit and bread molds) V. The Role of Fungi in Nature a. Environmental recycling i. Many fungi are decomposers ii. May live in soil and break down chemicals in dead plant material b. Food and fungi i. Yeast helps to make bread and alcohol ii. Mushrooms are a food source c. Disease-fighting fungi i. Alexander Fleming discovered Penicillium mold that kills bacteria ii. First antibiotic: penicillin d. Disease-causing fungi i. Fungi that are parasites attack plants and animals 1. Plants – ex: corn smut and wheat rust 2. Animals – ex: ring worm and athlete’s foot e. Fungus-plant root associations i. Partnerships between plants and fungi ii. Both benefit (mutualism) iii. Fungi lives on plant roots iv. Hyphae absorb more water and nutrients for the plant v. Plant produces extra food for fungi f. Lichens i. Fungus and algae or bacteria living together ii. Fungus benefits from the food produced by algae iii. Algae/bacteria get shelter, water, and minerals from fungus iv. Lichens are known as “pioneer species”