Unpacked 1.NBT.C.6
advertisement

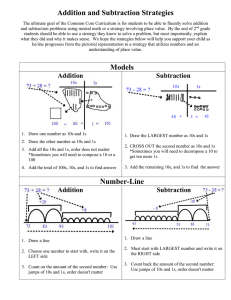
1.NBT.C.6 Subtract multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 from multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 (positive or zero differences), using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. Unpacked This standard is foundational for future work in subtraction with more complex numbers. Students should have multiple experiences representing numbers that are multiples of 10 (e.g. 90) with models or drawings. Then they subtract multiples of 10 (e.g. 20) using these representations or strategies based on place value. These opportunities develop fluency of addition and subtraction facts and reinforce counting up and back by 10s. Examples: 70 - 30: Seven 10s take away three 10s is four 10s 80 - 50: 80, 70 (one 10), 60 (two 10s), 50 (three 10s), 40 (four 10s), 30 (five 10s) 60-40: I know that 4+2 is 6 so four 10s + two10s is six 10s so 60-40 is 20 Students may use interactive versions of models (base ten blocks, 100s charts, number lines, etc.) to demonstrate and justify their thinking. First Grade students use concrete models, drawings and place value strategies to subtract multiples of 10 from decade numbers (e.g., 30, 40, 50). Example: There are 60 students in the gym. 30 students leave. How many students are still in the gym? See the five different strategies below: Student 3 I used a number line. I started at 60 and moved back 3 jumps of 10 and landed on 30. There are 30 students left. Student 4 I used ten frames. I had 6 ten frames- that’s 60. I removed three ten frames because 30 students left the gym. There are 30 students left in the gym. Student 5 I thought, “30 and what makes 60?. I know 3 and 3 is 6. So, I thought that 30 and 30 makes 60. There are 30 students still in the gym. 30 + 30 = 60 Note: This standard in no way addresses using an algorithm to solve. It specifically states: using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. The strategies above demonstrate what this should look like at this point in time. Speaking Level 2 Emerging Describe how to subtract multiples of 10 in the range of 1090 by explaining strategies using their native language to fill in gaps while working with a partner. Level 3 Developing Describe how to subtract multiples of 10 in the range of 1090 by discussing the strategies in a small group. Level 4 Expanding Describe how to subtract multiples of 10 in the range of 1090 by discussing the strategies and reasoning in a small group and by using complete sentences. Level 5 Bridging Describe how to subtract multiples of 10 in the range of 1090 by discussing the strategies and reasoning independentl y and by using complete sentences. ELD Standard #3: English Language Learners communicate information, ideas, and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Mathematics. Level 6 Reaching Level 1 Entering Describe how to subtract multiples of 10 in the range of 1090 by explaining strategies in their native language while working with teacher support.