Chapter 17A: Binomial Distributions
advertisement

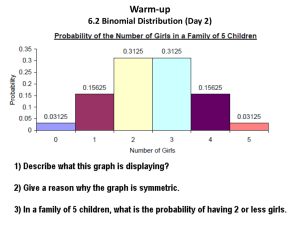
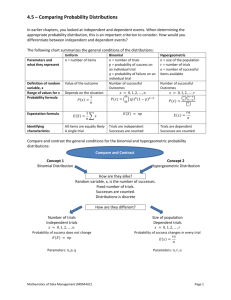
CHS Statistics Objective: To solve multistep probability tasks with the concept of binomial distribution Warm-Up AT&T directory assistance provides customers with correct responses 90% of the time. Using your method of choice, find the following probability: P(exactly 3 correct responses for 5 directory assistance requests) Binomial Distributions Bernoulli Trials A binomial distribution will have the following requirements: 1. The procedure has a fixed number of trials. 2. The trials must be independent (the outcome of any individual trial does not affect the probabilities in the other trials). 3. Each trial must have all outcomes classified into two categories (usually success or failure). 4. The probabilities must remain constant for each trial. Notation for Binomial Distributions n = the total fixed number of trials x = the specific number of successes in n trials p = the probability of success q = the probability of failure (1 – p) Examples You select a card from a standard deck. You look to see if it is a club, then replace the card. You do this experiment 5 times. Find n, p, q, and possible values of x. Examples (cont.) Decide whether the following experiments are binomial experiments. If they are, specify the values of n, p, q, and list possible values of x. If not, explain. A certain surgical procedure has an 85% chance of success. A doctor performs the procedure on 8 patients. The random variable represents the number of successful surgeries. A jar contains five red marbles, nine blue marbles, and six green marbles. You randomly select three marbles from the jar, without replacement. The random variable represents the number of red marbles. Examples (cont.) Decide whether the following experiments are binomial experiments. If they are, specify the values of n, p, q, and list possible values of x. If not, explain. You take a multiple choice quiz that consists of 10 questions. Each question has four possible answers, one of which is correct. To complete the quiz, you randomly guess the answer to each question. The random variable represents the number of correct answers. Binomial Probability Formula The probability of exactly x successes in n trials is: P(X) = nCx ∙ 𝒑𝒙 ∙ 𝒒𝒏−𝒙 or P(X) = 𝒏 𝒙 ∙ 𝒑𝒙 ∙ 𝒒𝒏−𝒙 n = the total fixed number of trials x = the specific number of successes in n trials p = the probability of success q = the probability of failure (1 – p) Example Micro-fracture knee surgery has a 75% chance of success on patients with degenerative knees. The surgery is performed on three patients. Find the probability of the surgery being successful on exactly two patients. Find the probability that fewer than two are successful. Binomial Probability Calculator Techniques 2nd DISTR binompdf( Note the pdf for Probability Density Function Used to find any individual outcome Format: binompdf(n,p,x) 2nd DISTR binomcdf( Note the cdf for Cumulative Density Function Used for getting x or fewer successes among n trials Format: binomcdf(n,p,x) Note: if you wanted to find up to a #, use the complement rule. All possible probabilities in the model will add up to 1. Examples Let’s complete the warm-up using binomial distribution formulas: Find the probability of getting exactly 3 correct responses among 5 different requests from At&T directory assistance. Assume that in general, AT&T is correct 90% of the time. Find the probability of less than 2 Find the probability of more than 1. Examples (cont.) A survey indicates that 41% of women in the US consider reading their favorite leisure time activity. You randomly select four US women and ask them if reading is their favorite leisure-time activity. Find the probability that exactly two of them respond that reading is their favorite leisure time activity. Find the probability that at least 3 respond that reading is their favorite leisure time activity. Find the probability that fewer than 1 respond that reading is their favorite leisure time activity. Examples (cont.) A survey indicates that 21% of men in the US consider fishing their favorite leisure-time activity. You randomly select five US men and ask them whether fishing is their favorite leisure-time activity. Find the probability that exactly three of them respond that fishing is their favorite leisure-time activity. Find the probability that at least 4 respond that fishing is their favorite leisure-time activity. Find the probability that more than 1 respond that fishing is their favorite leisure-time activity. 4.4 Mean and Standard Deviation of a Binomial Distribution Mean: 𝜇 = 𝑛𝑝 Standard Deviation: 𝜎 = 𝑛𝑝𝑞 Example In Pittsburgh, about 56% of the days in a year are cloudy. Find the mean and standard deviation for the number of cloudy days in the month of June. Assignment Pp. 401-404 # 1, 3, 7, 17 (skip a), 19 (skip c), 21 Be sure to check your answers with the solutions manual online.