Similarities & Differences Math PowerPoint
advertisement

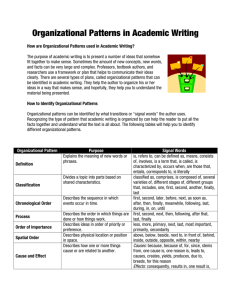
Identifying Similarities & Differences Research-Based Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement From Classroom Instruction that Works by R. Marzano, D. Pickering, J. Pollock Created by The School District of Lee County, CSDC in conjunction with Cindy Harrison, Adams 12 Five Star Schools Participant Outcomes Participants will: • Understand the purpose and importance of identifying similarities and differences • Determine ways to implement identifying similarities and differences in the classroom • Review examples of identifying similarities and differences activities Categories in Instructional Strategies That Affect Student Achievement Average Effect Percentile Size (ES) Gain Identifying similarities and differences 1.61 45 31 Summarizing and note taking 1.00 34 179 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition 0.80 29 21 Homework and practice 0.77 28 134 Nonlinguistic representations 0.75 27 246 Cooperative learning 0.73 27 122 Setting objectives and providing feedback 0.61 23 408 Generating and testing hypotheses 0.61 23 63 Questions, cues and advance organizers 0.59 22 1,251 Category No. of ESs Identifying Similarities & Differences Fractions Decimals Research and Theory about Identifying Similarities & Differences Generalizations based on research: 1. 2. 3. 4. Presenting explicit guidance in identifying similarities & differences enhances ability to understand and use knowledge. Asking students to independently identify similarities & differences enhances ability to understand and use knowledge. Representing similarities & differences in graphic or symbolic form enhances ability to understand and use knowledge. Identification of similarities & differences can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Research and Theory about Identifying Similarities & Differences Generalization #1: Presenting explicit guidance in identifying similarities & differences enhances ability to understand and use knowledge. • • Teacher-directed Directly present with steps and give the information to compare Generalization #2: Asking students to independently identify similarities & differences enhances ability to understand and use knowledge. • • • Student-directed Students identify topics for comparison Stimulates divergent thinking Research and Theory about Identifying Similarities & Differences Generalization #3: Representing similarities & differences in graphic or symbolic form enhances ability to understand and use knowledge. • • Graphic/symbolic forms require students to deeply process information Increases number of distinctions students find Generalization #4: Identification of similarities & differences can be accomplished in a variety of ways. • • 4 ways to identify similarities and differences Comparing, classifying, creating metaphors, and creating analogies Recommendations for Classroom Practice on Identifying Similarities & Differences a. Use comparing, classifying, creating metaphors, and creating analogies b. Give students a model c. Use a familiar context to teach steps d. Use graphic organizers e. Guide students Recommendations for Classroom Practice on Identifying Similarities & Differences a. 4 basic processes should be taught Comparing The process of identifying and articulating similarities & differences among items. Classifying The process of grouping things into definable categories on the basis of their attributes. Creating Metaphors The process of identifying and articulating the underlying theme or general pattern in information. Creating Analogies The process of identifying relationships between pairs of concepts (e.g., relationships between relationships. Recommendations for Classroom Practice on Identifying Similarities & Differences b. Give students models of the 4 processes 1. Select items want to compare 2. Select characteristics of the items on which you want to base your comparison 3. Explain how the items are similar and different with respect to the characteristics you selected. Example of Comparison Square Rectangle 1. Identify items 2. Describe key attributes of an important item and identify other items with same attributes 3. Create a category by specifying attribute 4. Select another item, describe key attributes, identify other items with same attributes 5. Create 2nd category by specifying attribute 6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 until all classified 7. If necessary, combine or split categories Example of Classification Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Square Rhombus 1. Identify important or basic elements. 2. Write basic information as a general pattern by • Replacing works for specific things with words for more general things • Summarizing info when possible. 3. Find new information/situation to which the general pattern applies. Example of Metaphor Proportions are the Swiss Army Knife of mathematics. 1. Identify how the 2 elements in the first pair are related. 2. State the relationship in a general way. 3. Identify another pair of elements that share a similar relationship. Example of Analogy • 80 is to 8 as a dime is to a penny • Circumference is to circle as perimeter is to polygon • Mean is to average as mode is to most often Recommendations for Classroom Practice on Identifying Similarities & Differences c. Use a familiar context to teach steps Example:Using the prefix tri, associate it with a tricycle, triangle, and trinomial. Example: When discussing slope, stairs have rises and runs. Recommendations for Classroom Practice on Identifying Similarities & Differences d. Use graphic organizers Examples: Venn Diagrams Comparison Matrix Classification Graphic Organizers Recommendations for Classroom Practice on Identifying Similarities & Differences e. Guide students as they engage in this process. Gradually give less structure and less guidance. Think, Pair, and Share What have you learned about identifying similarities and differences? What thoughts, questions, challenges, or ideas do you have?