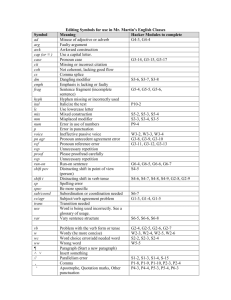
Active Voice - Reeds Spring High School
advertisement

Grammar Unit Mr. Lynch ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE Active and Passive Voice The term voice, when used in English grammar, refers to the structure of a sentence. There are two “voices” in English grammar active voice passive voice. Active Voice In an active voice sentence, the agent (the one who does the action in the sentence) is stated explicitly as the grammatical subject. The thing that the agent does something to (the direct object) comes after the verb. Active Voice Example Active Voice Sentence: Julio cooked fried rice. “Julio” is the agent. He’s the one who does the action. In this case, he’s the one who cooked the rice. In this active voice sentence, Julio is the grammatical subject. What did Julio cook? He cooked fried rice. The words fried rice make up the direct object. The fried rice is the thing that the agent (Julio) does something to. In this case he cooked it. Passive Voice In a passive voice sentence, the thing that the agent does something to, is placed as the grammatical subject of the sentence. The agent (the one who does the action) is placed after the subject, usually in a prepositional phrase. In fact, sometimes the agent is hidden, not even mentioned. Passive Voice Example Passive Voice Sentence: The fried rice was cooked by Julio. (The agent is mentioned.) Passive Voice Sentence: The fried rice was cooked. (The agent is not mentioned.) When to Use the Active Voice Use the active voice in most of the writing you do in school and at work. Studies in readability indicate that active voice sentences, where the agent is stated first, are easier to understand than passive voice sentences. 3 Reasons to Use Passive Voice 1. When the receiver of the action is more important than the agent. Active Voice: The Nobel Foundation awarded President Obama the Nobel Peace Prize. Passive Voice: President Obama was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. The passive voice construction places the emphasis on the receiver of the Nobel Peace Prize, not on the organization that awarded the prize. 3 Reasons to Use Passive Voice 2. When you consciously try to minimize the role of the agent or the agent is not known. Active Voice: Marie Jenkins could not complete the status report because James McDonald misplaced the manufacturing data. Passive Voice: The status report was not completed because manufacturing data were misplaced. 3 Reasons to Use Passive Voice 3. When you write about scientific, technical, or natural processes. Active Voice: The conveyor belt delivers the shrink-wrapped product to the packing station. Passive Voice: The shrink-wrapped product is delivered to the packing station. Active and Passive Conclusion Using active voice or passive voice is a stylistic and rhetorical choice about sentence structure. It’s important to understand the structure so that you control the structure instead of letting the structure control you. Remember; use the active voice in most of your academic and work-related writing. Active and Passive Practice When the Phillie’s Shane Victorino overran him, third base was stolen by Johnny Damon. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive Johnny Damon stole third base when the Phillie’s Shane Victorino overran him. Tip The judicious use of the active voice or the passive voice requires thought. It is up to the writer to determine when the active voice makes sense and when the passive voice makes sense. In this sentence, the focus, the IMPORTANCE, is carried by Johnny Damon. Active and Passive Practice A happy Thanksgiving is wished by me for everyone. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive I wish everyone a happy Thanksgiving. Tip This sentence is fairly simple. “I” is the agent, and should be the grammatical subject of the active voice construction. Active and Passive Practice The attorney general indicted the notorious gangster, Al Capone, for federal income tax evasion. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive The notorious gangster, Al Capone, was indicted for federal income tax evasion. Tip This sentence forces students to determine what the focus of the sentence should be. Should it be the attorney general? Should it be Al Capone? Most readers would find that the focus should be Al Capone. In fact, the agent seems insignificant compared to the receiver of the action. The trailing prepositional phrase (“by the attorney general”) is best left out. Active and Passive Practice The student services committee forwarded revised disciplinary procedures to the campus president. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive The revised disciplinary procedures were forwarded to the campus president. Tip The “revised disciplinary procedures” carry more weight than the student services committee. It’s a judgment call. Active and Passive Practice Six Thousand shares of Disney stock were bought by Jenny Allen when she was only nineteen. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive Jenny Allen bought six thousand shares of Disney stock when she was only nineteen. Tip The focus really should be on the agent, a young woman who had enough foresight (and money!) to buy 6000 shares of Disney at age 19. Active and Passive Practice People can view the dazzling meteor shower from the observation tower at the planetarium. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive The dazzling meteor shower can be viewed from the observation tower at the planetarium. Tip The focus should be the “dazzling meteor shower.” Who (or what) else could “view” it, if not people? Again, although the word “people” is the agent, the focus should be on the recipient of the action, the meteor shower. Active and Passive Practice The acceptance letter from Harvard was received by Jenny Arteaga last Tuesday. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive Jenny Atreaga received the acceptance letter from Harvard last Tuesday. Active and Passive Practice An invitation to Francis Suarez’s victory party was received by Mr. Packer, the state party chairman. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive Mr. Packer, the state party chairman, received an invitation to Francis Suarez’s victory party. Tip Although the idea is not related to active/passive voice, some students will want to omit the appositive “the state party chairman” from the revised sentence. Remember that using an appositive is a good way of defining a term within the flow of the sentence. Active and Passive Practice The Baseball Writers Association of America named Joe Mauer, the Minnesota Twins’ catcher who led the American League with a .365 batting average, MVP for 2009. Possible Answers: A) Active B) Passive Joe Mauer, the Minnesota Twins’ catcher who led the American League with a .365 batting average, was named MVP for 2009. Tip The focus of this sentence should clearly not be “The Baseball Writers Association of America”; it should be Joe Mauer. Apostrophe Errors Apostrophe Errors it's vs. its: A common error in our writing is using the apostrophe (or NOT using it) incorrectly when trying to show that something belongs to someone. Here is a common mistake: Error: The dog lost it's collar. It is correct to refer to a dog using "it." A dog is not a person, and despite our sometimes inordinate love for our pets, pets are not human. Only humans deserve "his" or "her." Forms of its and it’s (it is) The word its is the possessive form, the one that shows ownership. The word, it's is actually a contraction of two words, it is. Correct Form: The dog lost its collar. Formal Writing In formal writing, it is best (not “it’s best”) not to use contractions. Use the expanded form it is, instead of the contraction it’s. The form its’ does not exist. Do not use it, ever. Who’s vs. Whose Another common error is confusing whose with who's. Error: The post office manager, who's mother is in the hospital, retired. Correct: The post office manager, whose mother is in the hospital, retired. You’re vs. Your Some students often confuse the homonyms you’re (you are) and your (possessive). Error: The dog ran away with you’re coat. Correct: The dog ran away with your coat. They’re vs. There vs. Their The most commonly confused apostrophe error comes from the correct usage of they’re (they are), there (location), and their (ownership). Error: There not going their tonight. Correct: They’re not going there tonight. Apostrophe Practice If you think your going to the movies tonight, your mistaken. Correct: If you think you’re going to the movies tonight, you’re mistaken. TIP: This sentence would be grammatically correct if spoken, but conventional English requires the use of the apostrophe “re”. Tip As a “rule of thumb”: Do not use contractions in formal academic writing unless writing dialogue or consciously using an informal tone. Apostrophe Practice The boy who's dog was sent to the pound cried uncontrollably. Correct: The boy whose dog was sent to the pound cried uncontrollably. Apostrophe Practice A good dog always cleans its’ food bowl. Correct: A good dog always cleans its food bowl. TIP: Remember its’ is not a word. Apostrophe Practice The Sisters of Saint Joseph support they're convent with outside employment. Correct: The Sisters of Saint Joseph support their convent with outside employment. Apostrophe Practice Its never as good a deal as the salesperson makes it out to be. Correct: It’s never as good a deal as the salesperson makes it out to be. Apostrophe Practice The rugby players promise that their not going to stop playing after August. Correct: The rugby players promise that they’re not going to stop playing after August. Apostrophe Practice Their not going to the carnival, and your not either. Correct: They’re not going to the carnival, and you’re not either. Apostrophe Practice Its never too late to apply, even when the registrar's office closes it's doors. Correct: It’s never too late to apply, even when the registrar's office closes its doors. Apostrophe Practice Its’ important to realize whose actually using the computers in the lab. Correct: It’s important to realize who’s actually using the computers in the lab. ATTRIBUTIONS Attribution When students (or any writers, for that matter) use material from secondary sources, they must attribute or “give credit” to the writer of the material. Teachers expect students to use this standard academic practice when they write anything (research papers, reviews, or critical essays) that uses another writer’s material as the basis for an essay. Verbs of Attribution Certain verbs make “giving credit to” or attributing information to others easy. These verbs are called verbs of attribution. Several verbs of attribution exist, but we will list only a few of the most common ones. Verbs of Attribution • Affirms • Argues • Asserts • Believes • Claims • Concludes • Contends • Explains • Maintains • Observes • Remarks • States • Suggests • Writes Although all of these verbs “give credit to” someone for saying something, the verbs mean slightly different things. For example, it is different to “argue” something than it is to “suggest” it. Pay attention to the subtleties of meaning. Attribution in Direct Quotation To quote directly means to use the exact words as the original. Example: Willa Cather writes that “on either side of this road straggled two uneven rows of wooden buildings.” Appositives If necessary, tell the reader who the author is by using an appositive, a short definition set off by commas. Example: Willa Cather, an American novelist who described frontier life, writes that “on either side of this road straggled two uneven rows of wooden buildings.” Using “that” in Attributions Sometimes, when you quote an author directly, you may use a verb of attribution without the relative pronoun that, as in the following sentence. In this case, the first word of the quoted sentence is capitalized. Example: Willa Cather, an American novelist who described frontier life, writes, “On either side of this road straggled two uneven rows of wooden buildings.” Attributions in Paraphrasing To paraphrase means to say, in your own words, something as close to the original as possible, ideally to say the same thing as the original – but in your own words. Example: Brené Brown, a research professor of social work at the University of Houston, concludes that whole-hearted people typically embrace vulnerability. Tips on Attributions If an idea is within quotation marks, it is the original author’s exact words and must be placed within quotation marks. Brackets [ ] indicate the addition of a word, a minor change that is not in the original author’s text. If the idea lacks quotation marks, it is a paraphrase of the original. Attribution Practice (Machiavelli) “it is much safer to be feared than loved, when, of the two, either must be dispensed with.” Answer 1: Machiavelli claims that “it is much safer to be feared than loved, when, of the two, either must be dispensed with.” Answer 2: Machiavelli claims, “It is much safer to be feared than loved, when, of the two, either must be dispensed with.” Attribution Practice (William Sumner, an early proponent of Social Darwinism) “every effort to realize equality necessitates a sacrifice of liberty.” Answer 1: William Sumner, an early proponent of Social Darwinism, concludes that “every effort to realize equality necessitates a sacrifice of liberty.” Answer 2: William Sumner, an early proponent of Social Darwinism, concludes, “Every effort to realize equality necessitates a sacrifice of liberty.” Attribution Practice (Benjamin Franklin) if people want to convince someone else of their opinion, they should adopt the guise of “the humble inquirer and doubter.” Answer 1: Benjamin Franklin maintains that if people want to convince someone else of their opinion, they should adopt the guise of “the humble inquirer and doubter.” Attribution Practice (Adam Smith, a classical economist) “The real price of everything … is the toil and trouble of acquiring it.” Answer 1: Adam Smith, a classical economist, states that “the real price of everything … is the toil and trouble of acquiring it.” Answer 2: Adam Smith, a classical economist, states, “The real price of everything … is the toil and trouble of acquiring it.” Attribution Practice (Mrs. Goddard Orpen) “A grain of sand, or some such minute foreign substance, gets within the jealous valves of the [oyster] and causes great irritation to the soft body of the pulpy inhabitant.” Answer 1: Mrs. Goddard Orpen explains that “a grain of sand, or some such minute foreign substance, gets within the jealous valves of the [oyster] and causes great irritation to the soft body of the pulpy inhabitant.” Answer 2: Mrs. Goddard Orpen explains, “A grain of sand, or some such minute foreign substance, gets within the jealous valves of the [oyster] and causes great irritation to the soft body of the pulpy inhabitant.” Attribution Practice (Frederick Douglass) he does “not remember to have ever met a slave who could tell of his birthday.” Answer 1: Frederick Douglass asserts that he does “not remember to have ever met a slave who could tell of his birthday.” Answer 2: Frederick Douglass asserts, “I do not remember to have ever met a slave who could tell of his birthday.” Attribution Practice (W. E. B. Du Bois) “education among all kinds of men always has had, and always will have, an element of danger and revolution, of dissatisfaction and discontent.” Answer 1: W. E. B. Du Bois contends that “education among all kinds of men always has had, and always will have, an element of danger and revolution, of dissatisfaction and discontent.” Answer 2: W. E. B. Du Bois contends, “Education among all kinds of men always has had, and always will have, an element of danger and revolution, of dissatisfaction and discontent.” Attribution Practice (Susan B. Anthony) when people come together to form a nation, they do not relinquish their rights. Answer 1: Susan B. Anthony suggests that when people come together to form a nation, they do not relinquish their rights. COMMA SPLICES Comma Splices To understand comma splices you must understand grammatical terms like "clause" and "independent clause.” Comma Splice vs. Fused Sentence Some people use the term “run-on sentence” to refer both to fused sentences and comma splices. These two terms refer to two different errors. Comma Splice vs. Fused Sentence A comma splice is a comma that joins (splices) two independent clauses. A clause is a group of words that has a subject and a verb. Comma Splice vs. Fused Sentence A fused sentence, on the other hand, occurs when two independent clauses (complete ideas) are joined without any punctuation. Comma Splice vs. Fused Sentence It is better to avoid the term run-on sentence altogether and use only the terms comma splice and fused sentence. They are more specific and more descriptive. Comma Splices In standard written American English, comma splices are not allowed. In other English-speaking communities, they are more accepted. If you are writing for a North American audience, it is important to avoid comma slices. Independent Clauses Example of an Independent Clause: Robert ate worms. This is a clause. Robert is the subject, and ate is the verb. This clause is "independent" because it can stand alone as a sentence. Now let's take another independent clause: Mary dislikes Robert. Comma Splices If you take two independent clauses and join them with a comma, you have a comma splice: Robert To ate worms, Mary dislikes Robert. splice means to join, and in standard American English, you're not supposed to use comma splices in writing. It is a formal rule. Comma splices are easy errors for teachers and editors to notice. How to Fix a Comma Splice Make two sentences instead of one: Use a semicolon (;). Because Robert ate worms, Mary dislikes Robert. Use a semicolon plus a conjunctive adverb (therefore, then, however,...). Robert ate worms; Mary dislikes Robert. Use a subordinating conjunction (because, when, since, although,...). Robert ate worms. Mary dislikes Robert. Robert ate worms; therefore, Mary dislikes Robert. Use a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) after the comma. Robert ate worms, so Mary dislikes Robert. Conjunctions Remember, you can’t use words like however and so just because they make grammatical sense. These words mean something. The words although, however, but, and yet indicate a contrast: I was on a diet; however, I still gained weight. Conjunctions The words because, therefore, and so indicate a cause and effect relationship. The words and and then indicate that you are simply adding information. Use words cautiously. Comma Splice Practice This sentence is wrong, it has a comma splice. Two sentences: This sentence is wrong. It has a comma splice. Semicolon: This sentence is wrong; it has a comma splice. Subordinating Conjunction: This sentence is wrong because it has a comma splice. Conjunctive Adverb: This sentence has a comma splice; therefore, it is wrong. Coordinating Conjunction: This sentence has a comma splice, so it is wrong. Comma Splice Practice Eliza ran to the store, then she bought some candy. Two sentences: Eliza ran to the store. Then she bought some candy. Semicolon: Eliza ran to the store; then she bought some candy. Subordinating Conjunction: When Eliza ran to the store, she bought some candy. Conjunctive Adverb: Eliza ran to the store; then she bought some candy. Coordinating Conjunction: Eliza ran to the store, and then she bought some candy. Comma Splice Practice The stock market has moved in one direction lately, it has gone down. Two sentences: The stock market has moved in one direction lately. It has gone down. Semicolon: The stock market has moved in one direction lately; it has gone down. Comma Splice Practice Elvis Presley was a great singer, he was never really accepted by the country music's mainstream. Two sentences: Elvis Presley was a great singer. He was never really accepted by the country music's mainstream. Semicolon: Elvis Presley was a great singer; he was never really accepted by the country music's mainstream. Subordinating Conjunction: Although Elvis Presley was a great singer, he was never really accepted by the country music's mainstream. Conjunctive Adverb: Elvis Presley was a great singer; however, he was never really accepted by the country music's mainstream. Coordinating Conjunction: Elvis Presley was a great singer, but he was never really accepted by the country music's mainstream. Comma Splice Practice Computer programs help us live saner lives, obviously the people who write them should make lots of money. Two sentences: Computer programs help us live saner lives. Obviously the people who write them should make lots of money. Semicolon: Computer programs help us live saner lives; obviously the people who write them should make lots of money. Subordinating Conjunction: Since computer programs help us live saner lives, the people who write them should make lots of money. Conjunctive Adverb: Computer programs help us live saner lives; therefore, the people who write them should make lots of money. Coordinating Conjunction: Computer programs help us live saner lives, so obviously the people who write them should make lots of money. Comma Splice Practice Dubai has built magnificent office towers with luxuries and conveniences, it is considered a great location in which to conduct international business. Two sentences: Dubai has built magnificent office towers with luxuries and conveniences. It is considered a great location in which to conduct international business. Semicolon: Dubai has built magnificent office towers with luxuries and conveniences; it is considered a great location in which to conduct international business. Subordinating Conjunction: Because Dubai has built magnificent office towers with luxuries and conveniences, it is considered a great location in which to conduct international business. Conjunctive Adverb: Dubai has built magnificent office towers with luxuries and conveniences; therefore, it is considered a great location in which to conduct international business. Coordinating Conjunction: Dubai has built magnificent office towers with luxuries and conveniences, so it is considered a great location in which to conduct international business. Comma Splice Practice Brazil has won several world cups championships in soccer, they are always considered a good team. Two sentences: Brazil has won several world cups championships in soccer. They are always considered a good team. Semicolon: Brazil has won several world cups championships in soccer; they are always considered a good team. Subordinating Conjunction: Because Brazil has won several world cups championships in soccer, they are always considered a good team. Conjunctive Adverb: Brazil has won several world cups championships in soccer; therefore, they are always considered a good team. Coordinating Conjunction: Brazil has won several world cups championships in soccer, so they are always considered a good team. CONFUSING SENTENCES Confusing Sentences What is a confusing sentence? The entire sentence lacks a certain logic. It’s as if the writer transferred his or her thoughts quickly to the paper and then forgot to revise. A Confusing Sentence Consider the following sentence: The purpose of the program allows a student to solve a quadratic equation interactively. We understand what the writer is trying to say, but the sentence is confusing. Revising a Confusing Sentence “The purpose” of anything never simply “allows.” Revision 1: The purpose of the program is to allow a student to solve a quadratic equation interactively. This revision is correct, but it is wordy. Revising a Confusing Sentence Who (or what) does the action in the sentence? In other words, who (or what) is the agent? Revision 2: The program allows a student to solve a quadratic equation interactively. If we make “The program” the doer of the action, then a program certainly “allows” a student to solve a quadratic equation. Better yet: Revision 3: The program solves a quadratic equation interactively. In Revision 3, the agent is the grammatical subject, and what the agent does (solves) follows as the main verb of the sentence. Revising a Confusing Sentence If we make “a student” the agent, then we have a sentence like Revision 4. Revision 4: A student solves a quadratic equation interactively by using the program. 3 Guidelines to Clarity Determine who the “main character” in the sentence is. The “main character” is usually the person who does the action. Sometimes we call this “person (or thing) who does the action” the agent. Start the sentence with the person who does the action. In other words, start the sentence with the agent. 3 Guidelines to Clarity Determine what the agent is doing. What the agent is doing is usually stated as the main verb. Look for verbs that actually say something, strong verbs, rather than the verb “to be.” 3 Guidelines to Clarity If there are embedded clauses within the sentences, do the same with those clauses. Example Confusing: The reason for Smith’s firing is because he lied in his employment application. Revision: Smith was fired because he lied in his employment application. Confusing Sentence Practice After finally applying the prescribed medication for a few days, is when Michael started feeling better. Michael started feeling better after he applied the prescribed medication for a few days. Confusing Sentence Practice Sometimes because of our jobs it prevents us from spending more time with the whole family and is the reason that normally we all get together on holidays. We don’t spend as much time as we would like with our families because of our jobs, so we normally all get together on holidays. Confusing Sentence Practice Now that the little boy lied to his aunt makes him believe that there is no Santa Claus. The little boy no longer believes in Santa Claus because he lied to his aunt. Confusing Sentence Practice In my opinion of the Aesop fable is that I don't think the old gardener was playing a trick on his sons, however, it was a lesson that the old gardener wanted to teach his sons about the orchard. The old gardener was not playing a trick on his sons; he was teaching his sons a lesson about the importance of cultivating the orchard. Confusing Sentence Practice By telling them of a treasure will be found in the garden was a perfect way to have his sons involve in the garden, for his the old gardener didn't have much time to live. The old gardener told his sons about a treasure in the garden because the gardener didn't have much time to live and he wanted his sons involved in cultivating the garden. Confusing Sentence Practice First reason why I treasure my watch is because my sister bought it for me before she left for the army. I treasure my watch because my sister bought it for me before she left for the army. Confusing Sentence Practice When I was about 6, I watched my mom stare at her miniature spoon collection before she walked out the door forever. I thought why would she do that. When I was about 6, I watched my mom stare at her miniature spoon collection before she walked out the door forever. I always wondered why she would do that. Confusing Sentence Practice By running for student council was the reason why Roderick improved his popularity. Running for student council improved Roderick’s popularity. DANGLING PARTICIPLES Participles Participle: A verb form used as an adjective. It usually ends in ing, en, or ed. Example: chair. Laughing, Julio fell out of his Gerunds Gerund: A verb form used as a noun. It ends in ing – always. Example: Laughing makes me cry sometimes. Dangling Participles Gerunds take care of themselves. Rarely do students write confusing sentences using gerunds. Participles, however, can “dangle” or be misplaced. Dangling Participle Example Dangling Participle: Slipping on the wet sidewalk, the keys fell from Amaury’s pocket. This sentence reads as if the keys slipped on the wet sidewalk. Dangling Participles Dangling and misplaced participles often give rise to absurdly humorous scenarios. A “dangling participle” has no noun in the sentence to which the participle would logically attach. A “misplaced participle” does have a noun, but that noun does not come directly after the participle, thus creating a confusing sentence. For our purposes, “dangling” and “misplaced” are equivalent. Fixing a Dangling Participle Turn the Misplaced or Dangling Participle Into a Dependent Clause. This means that you take the ing word (the participle), give it a subject, turn it into a verb, and attach it to the main clause. Let’s take the example above, with Amaury’s unfortunate slip on the wet sidewalk. Correct: When Amaury slipped on the wet sidewalk, the keys fell from his pocket. Here we have taken the original participial phrase (Slipping on the wet sidewalk), and we have turned it into a dependent clause. We understand that “Amaury slipped,” not the keys. Fixing a Dangling Participle Make the Thing Being Modified by the Participle, the Subject of the Main Clause. This means we take what is being modified by the ing phrase and place it first in the sentence, right after the comma. Again, let’s use the example of Amaury’s unfortunate slip. Correct: Slipping on the wet sidewalk, Amaury lost his keys when they fell from his pocket. Note that “Amaury,” the person, NOT “Amaury’s keys” is placed after the comma. You may be tempted to write “Amaury’s keys,” but then you would have the same problem. Keys, even “Amaury’s keys,” do not slip on wet sidewalks; people, like Amaury, do. Fixing a Dangling Participle Place the Participle as Close as Logically Possible to the Noun it Modifies. Misplaced: Crying and screaming, Mrs. Williams led three-year old Mindy away from the toy store. Correct: Mrs. Williams led three-year old Mindy, crying and screaming, away from the toy store. Dangling Participle Practice Shaken, martinis. James stirred. not stirred, James Bond likes his Bond likes his martinis shaken, not Dangling Participle Practice Shaken, martinis. James stirred. not stirred, James Bond likes his Bond likes his martinis shaken, not Dangling Participle Practice While driving to the Homestead Campus, a pillow fell from James’s car. A pillow fell from James’s car as he drove to the Homestead Campus. Dangling Participle Practice Shocked by the foul language on television, the remote control dropped from Aunt Sherry’s hand. Aunt Sherry dropped the remote control because she was shocked by the foul language on television. Dangling Participle Practice Running across Tropical Park, the paddle boats on the lake appeared to be floating on air. As I ran across Tropical Park, the paddle boats on the lake appeared to be floating on air. Dangling Participle Practice Attacked by the school bully, the backpack fell from Abner’s shoulder. Attacked by the school bully, Abner dropped his backpack. Dangling Participle Practice Walking barefoot through the tall grass, dew drops felt good between my toes. As I walked barefoot through the tall grass, dew drops felt good between my toes. Dangling Participle Practice Driven by insatiable ambition and greed, the computer ran Henry’s stock trading program all day. Henry, driven by insatiable ambition and greed, ran his stock trading program on the computer all day. Dangling Participle Practice Confused by the new layout of the house, the soiled diaper fell off the baby as he cried and ran from room to room. The baby, confused by the new layout of the house, dropped the soiled diaper as he cried and ran from room to room. Dangling Participle Practice Staring up at the tall buildings, the wallet fell from Jasmine’s purse. As Jasmine stared up at the tall buildings, the wallet fell from her purse. DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUNS Demonstratives The demonstratives this, that, these, and those can make your writing easy to read or difficult. They can also provide the emphasis that you as a writer want to make. The word this, especially, can be confusing if it is used carelessly at the beginning of a sentence. Potentially Unclear The little league baseball team refused to shake hands with the opposing team after a lopsided loss. This set a bad example for the players on both the losing team and the winning team. In this sentence, the demonstrative word this is used as a pronoun. Grammatically Correct? Some writers may look at the first sentence and think, “There’s nothing wrong with the sentence,” and they would be correct. There is nothing grammatically wrong. The word this is a demonstrative pronoun and serves as the subject of the sentence. Why the Sentence is Unclear But in using only the pronoun this, the writer forces the reader to “fill in” the concept that is being referred to. Make things easy for your reader and communicate your intention or emphasis as a writer clearly. Notice that there are many terms that a reader can use to “fill in” the concept after this: bad behavior, refusal, petulance, immaturity… Which one do you, as a writer, want to emphasize? A Clear Sentence The little league baseball team refused to shake hands with the opposing team after a lopsided loss. This poor sportsmanship set a bad example for the players on both the losing team and the winning team. In this revision, the demonstrative word this is used as an adjective, modifying poor sportsmanship. A General Rule When you start a sentence with a demonstrative pronoun (this, that, these, and those, especially this), make sure that the next word (or words) is a noun that defines the idea in the previous sentence. In other words, turn the demonstrative pronoun into an adjective. Another Example Potentially Unclear: The football coach did not collect signed permission forms from the parents, forgot to request the playing field, and failed to schedule the school bus for use as transportation. This prompted the principal to reprimand the coach. Importance of Explanation The reader knows that the pronoun this in the second sentence refers to “all those things that the coach did not do.” The concept is fairly obvious. However, a careful writer identifies the concept and creates an emphasis or connotation that the reader may not “fill in.” Does the writer mean these lapses, this neglect, this irresponsibility, these minor oversights (note the emphasis), these intolerable mistakes? Revised as a Clear Sentence Clearer: The football coach did not collect signed permission forms from the parents, forgot to request the playing, and failed to schedule the school bus for use as transportation. These minor oversights prompted the principal to reprimand the coach. Demonstratives Practice The chef forgot to include basil in making the spaghetti sauce. This caused the meal to be bland and led to a bad review in Food magazine. This mistake caused the meal to be bland and led to a bad review in Food magazine. Demonstratives Practice Mary Ellen made the honor roll, won an essay contest, and was admitted to Mu Alpha Theta. This improved her chances of being admitted to a top university. These accomplishments improved her chances of being admitted to a top university. Demonstratives Practice Maria waits until the last minute to do everything. This causes her to lose out on financial aid and lose the classes she needs to take. This procrastination causes her to lose out on financial aid and lose the classes she needs to take. Demonstratives Practice Xavier always completed his assignments on time, never complained about coworkers, and seldom took any sick time. This led to his promotion. This positive attitude led to his promotion. Demonstratives Practice Marble Slab Creamery offers waffle cones, wafer cones, several ice cream flavors, and many different toppings. This is what makes their ice cream so delicious. This variety makes their ice cream so delicious. Demonstratives Practice Alicia forgot she had to take care of her little sister and went out with her friends instead. This got her in trouble with her mom. This negligence got her in trouble with her mom. Demonstratives Practice Our server did not bring drink refills, communicated our order wrongly to the chef, and sat down to speak with other guests while we waited for our check. This kept her from getting a generous tip. This poor service kept her from getting a generous tip. FEWER vs. LESS Fewer vs. Less Confusing the words fewer and less is a common error in student writing. The most common error occurs when students use less when they should use fewer. Usage of Fewer and Less Wrong: The Korea initiative creates less jobs for Asian workers than the Beijing Project. Problem: The word jobs is countable. We can count the jobs that are created. In the language of linguistics, the word fewer is used with “count nouns” (nouns we can count), while the word less is used with “non-count nouns” (nouns we cannot count). Correct: The Korea initiative creates fewer jobs for Asian workers than the Beijing Project. Rule of Thumb Use the word less only with “non-count nouns.” Use the word fewer with “count nouns.” Non-count nouns may be physical nouns that cannot be counted or abstract nouns. Physical Nouns (Non-count) advice air aluminum applause Arabic baseball beer biology boating cake cheese cloth Creole cricket dancing dust economics electricity English equipment experience flour French furniture geography glass glue hair harm heat history hockey homework ice leather luggage math meat metal milk oxygen Papiamento photography plastic poetry porcelain publicity reading rice rugby sand smoking soccer Spanish steel sugar sunshine traffic Urdu water weather wheat wine wood wool Abstract Nouns (Non-count) Ambiguity emotion graciousness irreverence loyalty peace success belligerence ego hope jealousy maturity pride tenacity courage fecundity honesty joy negativity romance truth dexterity friendship infatuation liberty omen sadness will The Word “Less” Use the Word less With Non-count Nouns Correct: Animals consume less water in the desert than they do in a rain forest. Units of Measure Physical nouns that cannot be counted can be made “countable” by including some unit of measure. Wrong: Animals consume less liters of water in the desert than they do in a rain forest. Correct: Animals consume fewer liters of water in the desert than they do in a rain forest. We cannot count “water”; however, we can count “liters of water.” Thus the correct forms are “less water” and “fewer liters of water.” Abstract Nouns Abstract nouns cannot ever be made “countable” except in a figurative sense, as in “The coward does not have an ounce of courage.” Fewer vs. Less Practice There are less markers in the cabinet today than yesterday. There are fewer markers in the cabinet today than there were yesterday. Fewer vs. Less Practice Chefs use less kilograms of flour making pastries than making bread. Chefs use fewer kilograms of flour making pastries than making bread. Fewer vs. Less Practice Less automobiles cross the bridge at night than in the afternoon. Fewer automobiles cross the bridge at night than in the afternoon. Fewer vs. Less Practice Energy-efficient appliances consume less electricity than older appliances. Correct. We cannot count the word electricity, so we “consume less electricity” but “fewer kilowatts.” Fewer vs. Less Practice Energy-efficient appliances consume less kilowatts of electricity than older appliances. Energy-efficient appliances consume fewer kilowatts of electricity than older appliances. Fewer vs. Less Practice Janice exhibits less emotional outbursts than Alicia. Janice exhibits fewer emotional outbursts than Alicia. Fewer vs. Less Practice Modern buildings use much less steel beams than older buildings. Modern buildings use much fewer steel beams than older buildings. Fewer vs. Less Practice This spring, I plan to spend less Euros travelling than I did last year. This spring, I plan to spend fewer Euros travelling than I did last year. Fewer vs. Less Practice People spend less days vacationing than they did in the past. People spend fewer days vacationing than they did in the past. Fewer vs. Less Practice Peter has lost less weight than John because he does not eat less candy bars at snack time. Peter has lost less weight than John because he does not eat fewer candy bars at snack time. Fewer vs. Less Practice When Ali moved to Brisbane, he packed less bags than his sister. When Ali moved to Brisbane, he packed fewer bags than his sister. Fewer vs. Less Practice The winery shipped less barrels of wine this year. The winery shipped fewer barrels of wine this year. Fewer vs. Less Practice Chinese food uses less grams of cheese per serving than Mexican food. Chinese food uses fewer grams of cheese per serving than Mexican food. Fewer vs. Less Practice Florida ships less tons of sugar today than it did last decade. Florida ships fewer tons of sugar today than it did last decade. FUSED SENTENCES Fused Sentences Some writers, in fast and furious drafting, may write sentences that contain two complete ideas, punctuated only with a comma or containing no punctuation at all. Both are wrong in standard American English. Fused Sentence - Definition A fused sentence occurs when two independent clauses are joined (fused) without any punctuation. Example My father designs and installs wind turbines he travels all over the Saudi Arabia as an energy consultant. Notice that we have two ideas in two independent clauses: My father installs and designs wind turbines He travels all over Saudi Arabia as an energy consultant. Another Example Fashion shows in the clothes we wear, it is constantly changing and repeating itself although fashion in the form of haute couture is everywhere, it isn’t for everyone. Separation of Clauses This sentence has four clauses: Fashion shows in the clothes we wear (independent – can stand alone as a sentence) it is constantly changing and repeating itself (independent – can stand alone as a sentence) although fashion in the form of haute couture is everywhere (dependent – cannot stand alone) it isn’t for everyone (independent) Fixing a Fused Sentence To fix a fused sentence, determine where one MAIN IDEA ends and another one begins. In the previous sentence, for example, there seems to be a logical division between the words itself and although. Fixing a Fused Sentence Although there are other ways to correct a fused sentence, the two most obvious are: 1. Placing a period between the two main ideas. Revision: Fashion shows in the clothes we wear, and it is constantly changing and repeating itself. Although fashion in the form of haute couture is everywhere, it isn’t for everyone. Fixing a Fused Sentence 2. Placing a semicolon between the two main ideas. Revision: Fashion shows in the clothes we wear, and it is constantly changing and repeating itself; although fashion in the form of haute couture is everywhere, it isn’t for everyone. Fused Sentence Practice Janine’s uncle never graduated from high school he started his own landscaping company at sixteen. Although Janine’s uncle never graduated from high school, he started his own landscaping company at sixteen. Fused Sentence Practice I have had a Mac computer for a year already I have no regrets about buying it. Although I have had a Mac computer for a year already, I have no regrets about buying it. Fused Sentence Practice People make their way across the desert they arrive in trucks with little ventilation, and they are often beaten by the men who smuggle them. People make their way across the desert. They arrive in trucks with little ventilation, and they are often beaten by the men who smuggle them. Fused Sentence Practice These political victories add up It’s not just money, but dignity at home and on the job. These political victories add up; it’s not just money, but dignity at home and on the job. Fused Sentence Practice Immigrants can be sentenced to prison most are sent back to their native homelands. Immigrants can be sentenced to prison, but most are sent back to their native homelands. LIE vs. LAY Lie vs. Lay Many native and non-native speakers of English alike do not understand the difference between using the word lie and using the word lay. Lie vs. Lay Both lie and lay are verbs, meaning that they indicate an action of some sort. However, the verb lie and the verb lay are two absolutely different words, like rhinoceros and apple. They are not variants of the same word. If we want to use formal grammatical terms (and we must), the verb lie is "intransitive"; the verb lay is "transitive." The Verb Lay A "transitive" verb indicates that something is being done to someone or something. For example, take a look at the following sentence: Transitive Verb (lay): Every morning, I lay the newspaper on the table. The Verb Lay I (the subject) do something to the newspaper (direct object) every morning. I lay the newspaper on the table. The word lay is the verb (in the present tense), and the noun newspaper is the thing that something is done to (the direct object). Think of it this way: You have to lay something. The Verb Lie An "intransitive" verb, on the other hand, does not indicate that anything is being done to anything or anyone. The person or thing does the action of just lying (NOT laying) there. Intransitive Verb (lie): In the afternoon, my dog, Maxi, lies on the living room couch. The Verb Lie Maxi is not doing anything to anyone or anything. Maxi is simply lying on the couch; the verb lie is "intransitive." A common error occurs when parents tell children, incorrectly, to "lay" down. Sadly, the children grow up thinking that this use of lay is correct, thus perpetuating the cycle of misuse. Correct Usage Incorrect: Scott, I want you to lay down this minute or you have a time out. Correct: Scott, I want you to lie down this minute or you have a time out. Why is this Confusing? People do not confuse the words rhinoceros and apple, so why do people confuse the verbs lie and lay? Well, both words start with the letter "L" and are made up of three letters. And they both mean similar things. After all, if you LAY an apple on the table, the apple LIES on the table. And if you LAY a rhinoceros,... Well, let's just not go there. Forms of Lie Lie (to stretch out, recline) Past Tense = Lay Past Participle = Lain Present Participle = Lying Forms of Lay Lay (to place, to put) Past Tense = Laid Past Participle = Laid Present Participle = Laying Correct Examples of Lie Jerry lies on the bed every day after school. The dog just lay on the rug as the burglars ransacked the house. That apple has lain on the table for two days now. Roberta is lying on the recliner in the family room. Correct Examples of Lay Jerry lays his head on the pillow when he lies in bed. Susan laid her books down when she walked through the door. The contractors have laid the tile in the kitchen. The President is laying the foundation for comprehensive health reform. Lay vs. Lie Practice Mrs. Khan (lies, lays) an eraser on her desk as soon as she enters the room. Possible Answers: A) Lies B) Lays Lay vs. Lie Practice When Kieran saw the beach, he thought he had (lain, laid) his eyes on paradise. Possible Answers: A) Lain B) Laid Lay vs. Lie Practice Lester likes to (lie, lay) in his room for about an hour after he wakes up. Possible Answers: A) Lie B) Lay Lay vs. Lie Practice The dog (lies, lays) her paws all over the furniture when we go out. Possible Answers: A) Lies B) Lays Lay vs. Lie Practice This clay pot has (lain, laid) in the underground cave for thousands of years. Possible Answers: A) Lain B) Laid Lay vs. Lie Practice Uday, please (lie, lay) down before you faint from exhaustion! Possible Answers: A) Lie B) Lay Lay vs. Lie Practice The factory will dismiss employees if they (lie, lay) down on the job. Possible Answers: A) Lie B) Lay Lay vs. Lie Practice The factory will dismiss employees if they (lie, lay) down their tools. Possible Answers: A) Lie B) Lay Lay vs. Lie Practice When farmers harvest mangoes, they must (lie, lay) mulch so that the harvest trucks have proper traction. Possible Answers: A) Lie B) Lay Lay vs. Lie Practice EMX has (lain, laid) aside its prejudices and will consider all applicants, regardless of background. Possible Answers: A) Lain B) Laid Lay vs. Lie Practice The goat enjoys (lying, laying) on the haystack in the afternoon. Possible Answers: A) Lying B) Laying NOMINALIZATIONS Nominalization Definition - A sentence may seem unclear to a reader because verbs and adjectives (words that describe nouns) are turned into nouns. Avoid Turning Verbs to Nouns A re-examination of the evidence led prosecutors to a reconsideration of the defendant’s guilt. Prosecutors re-examined the evidence and reconsidered the defendant’s guilt. Most readers would say that the second sentence is clearer than the first. An Examination The words re-examination and reconsideration are nouns. Generally, words that end in tion are nouns. The verb forms, re-examined and reconsidered, seem clearer to most readers. More Nominalizations The following table lists just a very few nominalizations and their corresponding verb forms. Nominalization Verb Form Analysis Analyze Belief Believe Comparison Compare Conclusion Conclude Determination Determine Failure Fail Reaction React Suggestion Suggest Overall In general, choose the verb form over the nominalization. Be careful, though. Some nominalizations are useful and necessary. Use them prudently. Adjectives and Nouns The same principle applies with adjectives. Avoid turning an adjective, such as careless, into its corresponding nominalization, carelessness. Avoid: His carelessness in driving caused a multi-car accident. Prefer: His careless driving caused a multi-car accident. Adjective Nominalizations Nominalization Adjective Form Carelessness Careless Difficulty Difficult Intensity Intense Nominalization Practice The steering committee raised an objection to the proposed parking garage north of the stadium. Explanation How many words are in this sentence? What words end in “tion” or “cion?” Objection Is there a verb equivalent? 15 Object Rewrite the sentence with the agent as the subject thereby reducing the words to 13. Remember “LESS IS MORE” Without Nominalizations The steering committee objected to the proposed parking garage north of the stadium. Nominalization Practice When the faculty senate has made a determination about the desirability of a lecture series, a proposal will be presented to the chancellor. (Hint. Perhaps we have ONE useful nominalization.) When the faculty senate determines the desirability of a lecture series, it will propose the idea to the chancellor. Nominalization Practice Negligence on the part of hospital workers was the reason for the failure of the kidney machine. Negligent hospital workers broke the kidney machine. Nominalization Practice Mercy Hospital made a decision to expand its geriatric facilities. Mercy Hospital decided to expand its geriatric facilities. Nominalization Practice It was the intention of the screening committee to interview all candidates face to face. The screening committee intended to interview all candidates face to face. Nominalization Practice The investor made an incorrect assumption about the volatility of Brazil’s emerging economy. Some information might be missing in the original sentence. Did the investor think that the volatility of Brazil’s emerging economy was high or low? How can the meaning be made clearer? The investor incorrectly assumed the high volatility of Brazil’s emerging economy. Nominalization Practice The parole board did not give an explanation for the early release of such a dangerous inmate. The parole board did not explain the early release of such a dangerous inmate. Nominalization Practice It I is my hope that you apply this material. hope that you apply this material. PARALLELISM Parallelism A sentence exhibits parallelism if similar ideas are expressed using the same syntactic and grammatical structure. Writers use parallel structures to communicate ideas that have the same importance using the same grammatical structure. Parallelism Parallelism is most common using gerund phrases (verb + ing) or infinitives (to + verb). Faulty parallelism occurs when writers do not use a parallel structure to communicate a series of ideas. Faulty Parallelism Faulty Parallelism: Without good pitching, the Marlins can be expected to lose more than eighty games, to draft early in next year’s draft, and attendance will suffer greatly. Faulty Parallelism What are the ideas that seem to have the same importance? The Marlins will lose more than eighty games The Marlins will draft early in next year’s draft. The Marlins’ attendance will suffer greatly. Correct Parallelism Correct Parallelism: Without good pitching, the Marlins can be expected to lose more than eighty games, to draft early in next year’s draft, and to suffer greatly in attendance. Correlative Conjunctions The term parallelism also applies to using correlative conjunctions and comparisons properly. Correlative Conjunctions: both, and; not, but; not only, but also; either, or; whether, or; neither, nor. These conjunctions connect words, phrases, and clauses that have the same level of meaning in the same sentence. Use the same grammatical structure with both elements of the correlative. Correlative Conjunctions Faulty Parallelism: Andrew was both an industrious student, and he was also an excellent athlete. Correct Parallelism: Andrew was both an industrious student and an excellent athlete. Comparisons Use a parallel structure when you connect two words, phrases, or clauses with a comparison word, including than or as. Faulty Parallelism: Sharon’s grade point average is much higher than her brother. Comparisons Correct Parallelism: Sharon’s grade point average is much higher than her brother’s (grade point average). Correct Parallelism: Sharon has a higher grade point average than her brother (does). Parallelism Practice We debated between two options immigration had given us: going back to Nicaragua or to stay in the US with no hope of ever returning. We debated between two options immigration had given us: going back to Nicaragua or staying in the US with no hope of ever returning. Parallelism Practice My uncle Julius likes bagels, lox, and eating chicken salad. My uncle Julius likes eating bagels, lox, and chicken salad. Parallelism Practice Bill not only runs five miles every day, he consumes eight thousand calories. Bill not only runs five miles every day, but he also consumes eight thousand calories. Parallelism Practice Jose’s daughter will either attend Harvard, or she plans to go to the Stanford. Jose’s daughter will either attend Harvard, or Stanford. Parallelism Practice The principal is excited about both the swim team earning national honors, and that the debate team won its first tournament. The principal is excited about both the swim team earning national honors and the debate team winning its first tournament. Parallelism Practice Fatima’s knowledge of accounting is greater than Farah. Fatima’s knowledge of accounting is greater than Farah’s. Parallelism Practice Miranda’s flowers are neither red, nor are they orange. Miranda’s orange. flowers are neither red nor PERSISTENT POINT OF VIEW Point of View Mixed Point of View: We were slowly getting closer to our destination, but you could see that everyone was getting frustrated. This sentence has a mixed point of view. The pronoun We is 1st person plural; the pronoun you is 2nd person; and if we really want to get fanatical, the pronoun everyone is 3rd person singular. Point of View Definition: Point of view refers to the perspective from which the sentence is told. When we discuss point of view, we use a term called “person,” meaning “who (or what) is the focus of the sentence.” In English grammar we have three persons, 1st person, 2nd person, and 3rd person. Consistent Point of View Consistent 1st Person Point of View: We were slowly getting closer to our destination, but we could see that we were getting frustrated. Consistent 3rd Person Point of View: The Gomezes were slowly getting closer to their destination, but they could see that they were all getting frustrated. Reword the Sentence These sentences may be consistent, but sometimes a rewording of the sentence may improve readability. For example, The Gomezes were slowly getting closer to their destination, but they were getting frustrated. This revision cuts four words and improves the flow of the sentence. Many times, this type of revision improves the readability of a sentence more than merely focusing on point of view. Point of View Practice The author suggests that the truth is sometimes painful, but telling the truth is better than living a life being someone you are not. The author suggests that the truth is sometimes painful, but telling the truth is better than living a lie. Point of View Practice When Margo married a widower her life became complicated because you can’t help but feel jealous about a deceased wife. When Margo married a widower her life became complicated because she can’t help but feel jealous about his deceased wife. Point of View Practice Although it may be painful for a parent not to be your child’s role model, Patrice Grant doesn’t have the right to be angry with her son’s choice. Although it may be painful for parents not to be their children’s role model, Patrice Grant doesn’t have the right to be angry with her son’s choice. Point of View Practice As the soldiers marched away from the battleground, you felt as if the war may finally be over. As the soldiers marched away from the battleground, the nation felt as if the war may finally be over. Point of View Practice A softball player who wants to develop her pitching form knows you will develop more skills at a sleep away camp. A softball player who wants to develop her pitching form knows she will develop more skills at a sleep away camp. Point of View Practice Students underestimate the amount of time required to study nursing because you simply cannot pass your tests without extensive study and practical experience. Students underestimate the amount of time required to study nursing because most students simply cannot pass their tests without extensive study and practical experience. Point of View Practice Regardless of how much teachers try, you cannot make sure that students attend every class. Regardless of how much teachers try, they cannot make sure that students attend every class. Point of View Practice When When I ran, you would get cramps. people run, they sometimes get cramps. PRONOUN / ANTECEDENT AGREEMENT Pronoun / Antecedent Agreement Here we tackle the sticky question of agreement between a pronoun and its antecedent. What do antecedent and agreement mean? An antecedent is a word that comes before something. The root ante, meaning “before,” gives you a clue. Agreement and Number In English grammar we have a term called number, and, unlike number in math, number in grammar means one of two things: singular (only one) plural (more than one). Agreement and Number When your English teacher says, “A pronoun must agree in number with its antecedent,” you know what he’s saying: If you use a singular noun or pronoun, you have to use a singular pronoun to refer to the original. You can’t (you’re not supposed to!) use a plural one. Correct Agreement Correct: The Students lost their privileges. original noun is Students, which is plural; the possessive pronoun, their, refers (or points back) to Students. The word Students is the antecedent, and both Students and their are plural in number. No problem here. Incorrect Agreement Wrong: This Everyone who went on the field trip was supposed to bring their permission form. sentence may look right, but look again. The pronoun their is plural. However, it refers to the pronoun everyone, which is singular. Singular Words Certain words are ALWAYS singular, even though they may seem plural. Anybody Each Everybody Somebody Someone Fixing the Problem How do We Fix the Problem? We could (but don’t!) simply use the pronoun his or her, as in: Poor: Everyone who went on the field trip was supposed to bring his permission form. But unless you’re talking about all boys, you should not use his. Could you use his or her? Yes, but that sounds too clunky, too heavy and awkward. Solution Your best solution is to rewrite the sentence and turn singular nouns into plurals. That way you are grammatically correct and you do not use sexist or clunky language. Better: Students who went on the field trip were supposed to bring their permission form. Omit the Pronoun We can also rewrite the sentence omitting the pronoun. Better: Everyone who went on the field trip was supposed to bring a permission form. Each method works. If you have enough creativity, sentences can be written in many different ways. Some ways work better than others. Pronoun/Antecedent Practice Would everyone please bring their computer to the writing workshop? Would everyone please bring a computer to the writing workshop? Pronoun/Antecedent Practice The principal indicated that every staff member had to submit their self evaluation by Wednesday. The principal indicated that every staff member had to submit a self evaluation by Wednesday. Pronoun/Antecedent Practice The operations officer noted that every soldier should have their own blanket. The operations officer noted that soldiers should have their own blankets. Pronoun/Antecedent Practice School psychologists note the importance for every student to express their emotions. School psychologists note the importance for every student to express emotions. Pronoun/Antecedent Practice Is every candidate for the position going to be given their application materials at the interview? Is every candidate for the position going to be given application materials at the interview? Pronoun/Antecedent Practice If any investor has a question about the quarterly reports, they should contact their broker directly. If investors have questions about the quarterly reports, they should contact their brokers directly. Pronoun/Antecedent Practice If every customer complains that an item is missing in their order, something is wrong with our procedure. If customers complain that an item is missing in their order, something is wrong with our procedure. Pronoun/Antecedent Practice Would everyone who attended the meeting, please bring their tee shirt to the rally? Would everyone who attended the meeting, please bring a tee shirt to the rally? SENTENCE FRAGMENTS Sentence Fragment Definition: A sentence fragment is a piece of a sentence. A piece is not whole or complete. In a formal sense, a sentence fragment is a group of words that is punctuated as a sentence but that cannot stand alone as a sentence. Sentence Fragment Here's an example: Sentence Fragment: The paper on the desk. This is an easy one. The paper on the desk. What about the paper on the desk? This group of words starts with a capital letter and ends in a period. It is punctuated as a sentence, but it is not a sentence. This group of words is missing a verb or a verb phrase. Complete Sentence: The paper on the desk fell to the floor. How do you fix a fragment? Add a verb or verb phrase FRAGMENT: hillside. COMPLETE The cows grazing on the SENTENCE: The cows were grazing on the hillside. How do you fix a fragment? Attach the sentence fragment to the sentence before it or after it. FRAGMENT: Rivers cut deep canyons in the landscape. Weaving their way hundreds of miles through forests and mountains until they reach the ocean. COMPLETE SENTENCE: Rivers cut deep canyons in the landscape, weaving their way hundreds of miles through forests and mountains until they reach the ocean. How do you fix a fragment? Use a conjunctive adverb (however, therefore) instead of a subordinating conjunction (although, because, since). FRAGMENT: Jason never thought he could play baseball. Although, he eventually worked hard and started for his high school team. COMPLETE SENTENCE: Jason never thought he could play baseball. However, he eventually worked hard and started for his high school team. How do you fix a fragment? Attach a clause with a relative pronoun (who, whom, that, which, whose) to the sentence it belongs to. FRAGMENT: Mom always asked me to walk the dog. Who never had to go out anyway. COMPLETE SENTENCE: Mom always asked me to walk the dog, who never had to go out anyway. How do you fix a fragment? Attach a verb phrase that is punctuated as a sentence (the fragment) to the sentence it belongs to. FRAGMENT: The psychologist met with his clients in a relaxing environment. And encouraged them to meditate after the session. COMPLETE SENTENCE: James counseled his clients in a relaxing environment and encouraged them to meditate after the session. Sentence Fragments Practice Salt-water fish can be very colorful. For example, Parrot Fish. Salt-water fish can be very colorful. Take, for example, Parrot Fish. Sentence Fragments Practice Merwin passed the exam. Although, he got the last five questions wrong. Although Merwin got the last five questions wrong, he passed the exam. Sentence Fragments Practice Robert has met his long-lost daughter. Who had been searching for him over twenty years. Robert has met his long-lost daughter who had been searching for him over twenty years. Sentence Fragments Practice Because the cities on the west coast of Florida receive cool breezes and warm water from the Gulf of Mexico. The cities on the west coast of Florida receive cool breezes and warm water from the Gulf of Mexico. Sentence Fragments Practice Jenny never finished high school. Despite the fact that her parents were supportive and allowed her to stay at home after her arrest. Jenny never finished high school despite the fact that her parents were supportive and allowed her to stay at home after her arrest. Sentence Fragments Practice The conductor finished with a flourish. Waving his baton and gesticulating wildly with his free hand. The conductor finished with a flourish, waving his baton and gesticulating wildly with his free hand. Sentence Fragments Practice The house survived the tornado. Which clearly demonstrated that the building and zoning codes were sufficiently strict. The house survived the tornado, which clearly demonstrated that the building and zoning codes were sufficiently strict. STRONG AUTHORIAL VOICE Strong Authorial Voice This lesson discusses techniques for communicating your opinion in what we call a strong authorial voice. This means that when you write, you should establish your position as the author and call on the reader to accept your credibility. Strong Authorial Voice Let’s bring the abstraction down to an example. Weak Authorial Voice: In my opinion, pedestrians should not cross the street when they have a red light. Strong Authorial Voice: Pedestrians should not cross the street when they have a red light. Strong Authorial Voice If you are writing an essay or report about traffic problems, readers know that YOU are the author, no one else. The phrase “In my opinion” takes away from the strength of your writing. It fills space without adding any content and, in fact, diminishes your credibility as a writer. Strong Authorial Voice Certain phrases or expressions appear in our writing frequently, and all they do is clutter up the space and take away from the message. In my opinion It is my belief I believe I feel My belief My thoughts on It seems to me It is my understanding I think When you give your thoughts, beliefs, feelings, or opinions about a subject, you generally do not have to specify that those thoughts, beliefs, feelings, or opinions are yours. Attribution is Sometimes Necessary There are times when you write a letter, essay, report, or some other document where you discuss the beliefs or opinions of different people or organizations. In these cases, make sure you attribute (give credit to) the opinion to that particular source. Where Attribution is Necessary Example: “Derek Bok argues that first amendment rights outweigh any concerns for offending the public’s sensibilities, while Juliet Tabor contends that the risk of offending large segments of the population must be considered in determining what a newspaper should print.” Where Attribution is Necessary If you follow this sentence with an opinion of your own, you do not need to attribute it to yourself. Own the opinion as yours and state it strongly. Weak Authorial Voice: It seems to me that Juliet Tabor fails to take into account the spirit of hard-earned democratic freedoms by promoting censorship based on public perception. Strong Authorial Voice: Juliet Tabor fails to take into account the spirit of hard-earned democratic freedoms by promoting censorship based on public perception. Not only is the strong sentence shorter by five words (always a good thing), it carries the voice of authority and conviction. Advice Write with authority and conviction. Strong Voice Practice I think that what this mother is trying to explain makes perfect sense. What this mother is trying to explain makes perfect sense. Strong Voice Practice It is my understanding that most men feel a bit emasculated when asked or forced to help complete tasks other than those classified acceptable by other men. Most men feel a bit emasculated when asked or forced to help complete tasks other than those classified acceptable by other men. Strong Voice Practice I strongly believe that high schools should do something about the harassment of students who are different from most other students. High schools should do something about the harassment of students who are different from most other students. Strong Voice Practice I think Blomfield is incorrect in implying that people are judgmental if a man is unable to support his family due to unemployment. Blomfield is incorrect in implying that people are judgmental if a man is unable to support his family due to unemployment. Strong Voice Practice In my opinion as I read Paturel’s article, it seemed as if Paturel was the one who really needed to make peace with Brandon’s first marriage. It seemed as if Paturel was the one who really needed to make peace with Brandon’s first marriage. Strong Voice Practice Although people tend to feel they have to measure up to someone else’s level to be accepted, I think people should just be themselves if they really want to be accepted. Although people tend to feel they have to measure up to someone else’s level to be accepted, people should just be themselves if they really want to be accepted. Strong Voice Practice I think that in our day and age that unemployment is a very common theme in America. In our day and age, unemployment is a very common theme in America. STRONG VERBS Strong Verbs This lesson confronts a writing problem that may go undetected. Although readers may not notice the problem, it still affects how they perceive your writing. Weak Verbs vs Strong Verbs Weaker: The philanthropist is careful to give only to organizations that have low administrative costs. Stronger: The philanthropist gives only to organizations with low administrative costs. Do the sentences mean exactly the same thing? No. There is a subtle difference. Weak Verbs vs Strong Verbs The first sentence underscores the care with which the philanthropist gives. However, unless you mean to emphasize this care, the second sentence conveys the message more strongly than the first. The second sentence is also shorter by four words. Shorter is usually better. Weak Verbs vs Strong Verbs Weaker: William was late to the meeting. Stronger: William arrived late to the meeting. These two sentences use the same number of words, six. However, note how the verb in the second sentence, arrived, sounds more vigorous, describes the act of attending the meeting more clearly, than the verb in the first, was, which merely describes a state of being. What to Avoid The main culprits include the verbs “to be” and “to have.” These verbs may hide in the forms listed below. Any time you use one of these verbs (Be, Is, Are, Was, Been, Being, Were, Has, Have, Having, Had) ask yourself if the sentence should be rewritten. Rewriting Sentences To rewrite sentences using strong verbs: 1. Underline any use of Be, Is, Are, Was, Been, Being, Were, Has, Have, Having, Had. 2. Look for a noun or adjective that you can convert to a strong verb. 3. Rewrite the sentence using that strong verb. Example 1.John is the manager of the produce department. 2. John is the manager of the produce department. (noun – predicate nominative) 3. John manages the produce department. Strong Verb Practice Janet Smith is the supervisor of the customer service department. Janet Smith supervises the customer service department. Strong Verb Practice Walt Disney was the initiator of a mass movement in family entertainment. Walt Disney initiated a mass movement in family entertainment. Strong Verb Practice Jenny Millhouse is the owner of two gas stations in Florida City. Jenny Millhouse owns two gas stations in Florida City. Strong Verb Practice The sugar cane refinery is the employer that is the driving force for employment in south central Florida. The sugar cane refinery drives employment in south central Florida. Strong Verb Practice The shipped product was different from the one that was advertised in the catalog. The shipped product differed from the one advertised in the catalog. Strong Verb Practice The Foster family has a fruit stand near Krome Avenue. The Foster family owns a fruit stand near Krome Avenue. Strong Verb Practice After a questionable call at home plate, the manager had an argument with the umpire. After a questionable call at home plate, the manager argued with the umpire. SUBJECT/VERB AGREEMENT Subject/Verb Agreement Every sentence has a subject and a verb. They must agree. A singular subject requires a singular verb form, while a plural subject requires a plural verb form. Subject-Verb agreement is simple, in principle, but it is not always easy to carry out in speaking and writing. Three verbs, in particular, often confuse students: to be, to have, and to do. Number, Person, and Tense Number: English is simple, in a sense. When we refer to “number” in English, we mean only one of two things: singular (only one) plural (more than one. That’s it. There are only two “numbers” in English: “one” and “more than one.” Number, Person, and Tense Person: We have three “persons” (not people): First person (1st person) refers to the person or group speaking (“I” or “we”). Second person refers to the person (or people) being spoken to (you). Third person refers to the people or thing that is being written about (when it is not “I” or “me”). Number, Person, and Tense Tense: There are many tenses in English, but we will examine two basic tenses: present (the current moment) past (before the current moment). The Verb “To Be” (was, were) The different forms of the verb “to be” are Singular Plural Present Tense I am We are Past Tense I was We were You are You are You were You were He, She, It is They are He, She, It was They were 1st Person 2nd Person Present Tense Past Tense 3rd Person Present Tense Past Tense The Verb “To Be” Error: Mrs. Adams and Margaret was standing next to the train station when the sheriff arrived. “Mrs. Adams and Margaret” is the subject of the verb “to be.” The subject is more than one (plural), so the correct form should be “Mrs. Adams and Margaret were standing next to the train station when the sheriff arrived.” The Verb “To Be” Error: Because eleven students is always late for class, the principal decided to eliminate spirit week. “Eleven students” is the subject of the verb “to be.” The subject is more than one (plural) so the correct form should be “Because eleven students are always late for class, the principal decided to eliminate spirit week.” The Verb “To Be” As A Helping Verb: The rules of subjectverb agreement also apply when the verb “to be” is used as a helping verb, as in “were running” or “was baking.” The Verb “To Have” (has, had) The different forms of the verb “to have” are Singular Plural I have We have I had We had You have You have You had You had Present Tense He, She, It has They have Past Tense He, She, It had They had 1st Person Present Tense Past Tense 2nd Person Present Tense Past Tense 3rd Person The Verb “To Have” (has, had) Error: The Robertson Company have a legitimate complaint about the zoning regulations that were just passed. “The Robertson Company” is the subject of the verb “to have”; it is singular and 3rd person. Therefore, the correct form should be “The Robertson Company has a legitimate complaint about the zoning regulations that were just passed.” The Verb “To Have” (has, had) Error: When Karina and Marie has the time, they would like to travel to Greece. “Karina and Marie” is the subject of the verb “to have”; it is plural and in the 3rd person. Therefore, the correct form should be “When Karina and Marie have the time, they would like to travel to Greece.” The Verb “To Do” (do, does) The different forms of the verb “to do” are Singular Plural Present Tense I do We do Past Tense I did We did Present Tense You do You do Past Tense You did You did He, She, It does They do He, She, It did They did 1st Person 2nd Person 3rd Person Present Tense Past Tense The Verb “To Do” (do, does) Error: Yesenia and Jorge does the catering for the Elk’s lodge in Peoria. “Yesenia and Jorge” is the subject of the verb “to do”; it is 3rd person and plural. Therefore, the correct form should be “Yesenia and Jorge do the catering for the Elk’s lodge in Peoria.” WHO vs. WHOM Who vs. Whom People are so mystified (confused) about the use of who and whom that some of us are tempted to throw our hands in the air and say, “it just doesn’t matter.” But it does matter. Those who know (and not just English teachers), judge those who misuse it. Not using who and whom correctly can cost you, not just in school, but also in life. Who and Whom are Pronouns That’s right; who and whom are pronouns. And if you recall, a pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. We would not say, “Jesse doesn’t like the principal Ms. Thomas was hired at his school.” The name Ms. Thomas is a noun. For this sentence to flow, we would write, “Jesse doesn’t like the principal who was hired at his school.” It All Depends on Case In English grammar, we have a term called case, which refers to pronouns. The case of a pronoun can be either subject or object, depending on its use in a sentence. Take a look at this table. Subject Object I me he him she her we us they them who whom The pronoun who is used as a subject; whom is used as an object. Correct Usage Who used correctly: Janice is the student who has read the most books. Whom used correctly: Janice is the student whom the teachers picked as outstanding. Correct Usage How do you determine which to use? Break the sentence into two parts: Janice is the student. She (Janice) has read the most books. Janice is the student. The teachers picked her (Janice) as outstanding. Correct Usage If you use I, he, she, we, or they, then the correct form is who. If you use me, him, her, us, or them, then the correct form is whom. Rule of Thumb Generally, if you can omit the who/whom entirely, the correct form is whom. If you need it, then it’s who. Example: Janice is the student the teachers picked as outstanding. Sentence makes sense without the who/whom structure, so the correct form is whom.) What About Questions? For questions, turn the question into a statement and follow the previous suggestion. Example: (Who, Whom) should I invite to the dance? I should invite – her – to the dance. When you turn the question into a statement, you use the pronoun her, so whom is correct. What About Questions? Example: (Who, Whom) is the president of student government? She is the president of student government. Again, when you turn the question into a statement, you use she, so who is correct. Prepositions Always use whom as the object of a preposition. Example: I don’t know to (who, whom) I should send the package. The correct form is whom because whom is the object of the preposition to. In 99% of the cases, the correct form after a preposition is whom. Who vs. Whom Practice (Who, Whom) did Mom invite to Marcela’s birthday party? Whom Who vs. Whom Practice Any man's death diminishes me, because I am involved in mankind, and therefore never send to know for (who, whom) the bells tolls; it tolls for thee. (John Donne) whom Who vs. Whom Practice (Who, Whom) invited Richard to be the representative for the entire class? Who Who vs. Whom Practice Susan is the chef (who, whom) will create an exquisite menu for our ten-year reunion. who THE END