Light
advertisement

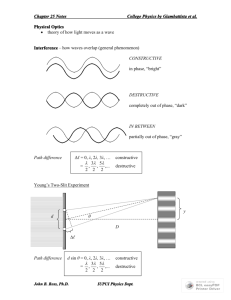
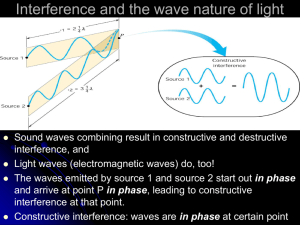
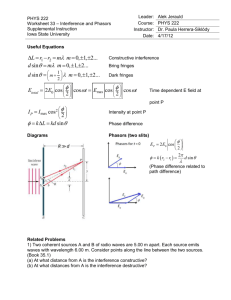
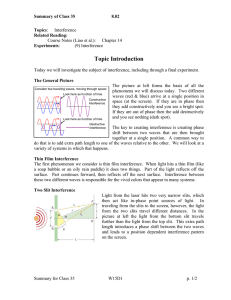
Light WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT Is light what we see? Is there light where there is no one to see it? Dualism of light Isaac Newton believe light to be a ray of corpuscles (particles) Robert Hooke believed light to have the wave-like nature Newton won… until over a century after his death… LIGHT INTERFERES! 1801 – Thomas Young produces interference of light Light is a chameleon of science Particles which interfere like waves? A wave that travels in straight lines Three views on light Waves Light rays Photons Most common Visible light – part of EM spectrum Interference and diffraction of light Light travels in straight lines Optics: mirrors, lenses, etc. Photoelectric effect Photons as particles (quanta of energy) Quantum mechanics: Not so much Covered in HS physics Waves or not? Waves diffract (like sound). Light doesn’t seem to Waves or not? When the opening is comparable to the wavelength, shadows are cast Light does diffract when it goes through a tiny slit Young’s Experiment Constructive and destructive interference Constructive and destructive interference The waves coming from the slits interfere constructively or destructively, depending on the difference in distances between the slits and the screen. d sin sin m m 0,1,2,3, d sin m 1 2 d m 0,1,2,3, Example Red light (664 nm) is used in Young’s experiment with slits separated by 0.000120 m. The screen is located a distance 2.75 m from the slits. Find the distance on the screen between the central bright fringe and the third-order bright fringe. q = 0.951 x3 = 0.0456 m Formula for ‘bright spots’ sin m d d sinq = ml m 0,1,2,3, m = 0,1,2,3,… xm = L tanq Providing the screen is very-very distant, sin q = m tanq » q » sinq l d ml xm » L d Guess: what would the formula look like for dark spots? Measuring wavelength of light A double-slit interference pattern is observed on a screen 1.0 m behind two slits spaced 0.30 mm apart. The distance from the center of one particular fringe to the center on the ninth bright fringe from this one is 1.6 cm. What is the wavelength of the light? l = 540nm Double-slit interference pictures Single-slit diffraction a L Huygens’ Principle Diffraction The wavelets going straight forward all travel the same distance to the screen. Thus they arrive in phase and interfere constructively to produce the central maximum Note the brightness (intensity)! Dark spots Ray 2 is a/2 away from ray 1. If the two rays arrive counter-phase (trough / crest), destructive interference occurs. Ray 2 travels a longer distance by a Dr12 = sin q 2 Destructive interference will occur if: Dr12 = l 2 Dark spots Position of destructive interferences (dark spots) L a sin q » q » tanq pl xm » L a p = 1,2,3, 4... Note that p is not 0! That would be the central bright stripe How wide would the stripe be? How does the picture change?? 2l w=L a http://bcs.wiley.com/hebcs/Books?action=mininav&bcsId=4678&i temId=0470223553&assetId=160341&reso urceId=15300 Grating Diffraction ml xm » L d Sometimes More IS More