Business Law: Ch 9
advertisement

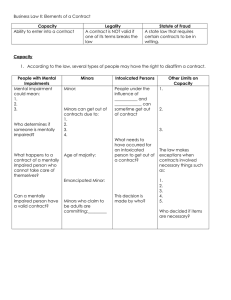
Business Law: Ch 9 Legal Capacity to Contract What is Capacity • Contractual Capacity – Ability to understand the consequences of a contract – Does not require that a person understand the actual terms of the contract Lack Some Capacity • Three groups lacking some capacity 1. Minors 2. Intoxicated 3. Mentally Impaired Minors • Minors – Under the age of majority – In Ohio the age of majority is 18 – Ends the day before the birthday of the age Protecting those lacking capacity • Contracts of those lacking capacity are voidable – Disaffirmance – Protection granted to those lacking capacity • In contract law it means a refusal to be bound by a previous legal commitment • When a protected party disaffirms a contract, by law the protected party is to receive whatever they have put into the contract »The other party may or may not get back their consideration Disaffirm • Example – A protected party bought a fourwheel ATV from a dealership and then wrecked it. You can disaffirm the contract and recover any payments made. – The dealership would only be able to recover the damaged ATV Necessities • Necessities – things needed to maintain life – The protected must at least pay a reasonable value for the necessities even if they disaffirm the actual purchase contract Minors • Contracts are considered voidable (may get out of) • May also disaffirm for a reasonable length of time after achieving the age of majority. • After majority, the power to disaffirm is immediately cut off if you ratify the contract • Minors also may find themselves bound to their contract if they are Emancipated Emancipated • Emancipated – Severing the parent-child relationship – Ends the duty of the parent to support a child and the duty of the child to obey their parent – Upon reaching the age of majority you are emancipated Emancipated • Formal emancipation – Court decrees the minor emancipated • Informal emancipated – Arises from the conduct of the parent and minor Informal Emancipated • The parent and minor agree that the parent will cease support • The minor marries • The minor moves out of the family home • The minor becomes a member of the armed forces • The minor gives birth • The minor undertakes full-time employment Mentally Incapacitated • Mentally Incapacitated - A person lacks the ability to understand the consequences of his or her contract • If permanently Insane – Contract is Void • Temporary Insane – Contract is Voidable Intoxicated • Does the person have the ability to understand the consequences • Courts typically allow disaffirmance only for those who are so temporarily intoxicated that they do not even know they are contracting – Stricter because intoxication is a voluntary act • If a person is in a permanent state of intoxication – Contract is void Who has contractual capacity in organizations • Scope of Authority – has capacity to contract • People acting outside the scope of authority, are personally liable when the organization isn’t 9-1 Assessment • Turn to page 161 and complete the 9-1 Assessment Questions When can disaffirmance occur • Disaffirmance – can happen: 1. Any time still under the incapacity 2. Within a reasonable time after attaining capacity • After attaining capacity, a person can ratify their contract – Ratification – Action by the party indicating intent to be bound by the contract Ratification • For a minor, ratification must occur after achieving majority. • Ratification may consist of: 1. Giving a new promise to perform as agreed 2. Any act (such as making a payment) that clearly indicates the party’s intention to be bound What must be done upon disaffirming • When a minor disaffirms, anything of value the minor received and still has must be returned. • The minor is entitled to get back everything that was given to the other party. Contracts that cannot be disaffirmed • Court approved contracts • Major commitments – armed services, educational loans • Banking contract • Insurance Contracts • Work Related Contracts • Sales of Realty • Apartment rental Misrepresenting Age • Minors who lie about their age may disaffirm contracts • However, they are liable for the tort of false representation 9-2 Assessment • Turn to page 165 and complete the 8 questions