Chapter 3 Test Review
advertisement

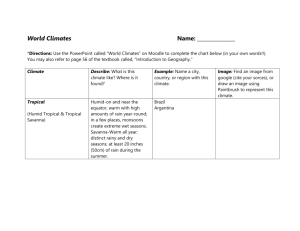
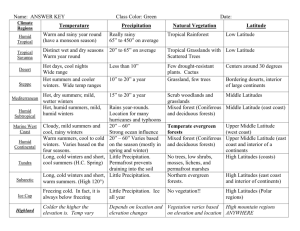
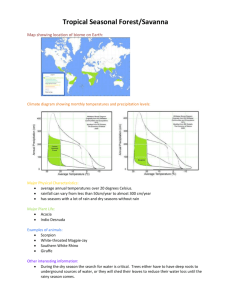
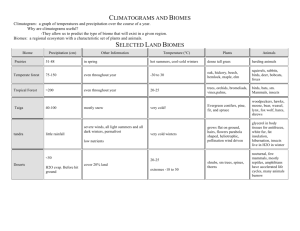
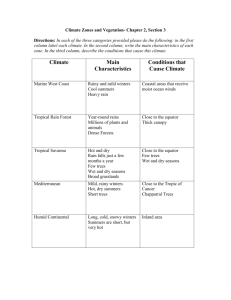
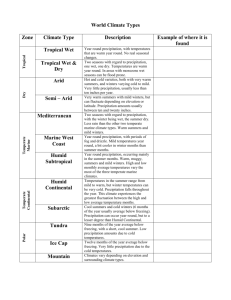
Chapter 3: Section 1 As the earth revolves around the sun it is tilted at a 23.5 degree angle in relation to the sun. The earth’s seasons are related to the earth’s tilt and revolution This tilt causes the changing Seasons on the earth. The tilt causes different parts of the earth to receive Sunlight for more hours of the day at certain times of the year. The longest day of the year is called the Summer Solstice. This occurs on what day in the northern hemisphere? June 22nd or June 23rd. What marks the farthest point north the sun’s rays shine directly overhead at noon? Tropic of Cancer What marks the farthest point south the sun’s rays shine directly overhead at noon? Tropic of Capricorn The shortest day occurs on December 22nd or 23rd (Winter Solstice) in the northern hemisphere. The day in which the days and nights all over the world are equal in length is called the Equinox. What two seasons does this mark the beginning of? Autumn (Fall) and Vernal (Spring) Define Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a particular location and time. Define Climate: weather conditions at particular location over a long period of time. What are the major factors that cause weather? Water vapor, cloud cover, landforms and bodies of water, elevation, air movement. Define Precipitation: Falling water droplets in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or hail. What are the 3 classifications of precipitation? convectional, orographic, frontal Where does convectional precipitation occur? Hot climates Where does orographic precipitation occur? Windward side of a mountain. The leeward side of a mountain range is often called a Rain shadow because it gets little rain. A front is the boundary between 2 air masses of different temperatures. Circular storms that form over warm tropical waters are called Hurricanes or Typhoons. Define Tornado: A powerful funnel-shaped column of spiraling air.. Define Blizzard: A heavy snowstorm with winds of more than 35 mph and reduced visability. Define Drought: A long period of time without rain. What weather extremes listed in the book are likely to occur in Texas? Hurricanes, toronados, droughts, and floods. Chapter 3: Section 2 What are the 4 major factors that influence climate of a region? Wind and ocean currents, latitude, elevation, and topography. What is the number one factor in determining climate of a region? Latitude. Define convection: Transfer of heat in the atmosphere by upward motion of air. Ocean currents are like Rivers flowing in the ocean. Warm water currents generally flow away from the equator while cold water currents flow to it. What are the 3 zones of latitude? Low, Mid, and High. The warming of the waters off the coast of South America is known as El Nino Define Greenhouse Effect: Layer of gases in the atmosphere that causes higher temperatures. Chapter 3: Section 3 Judging by the map on page 60, Corpus Christi borders which 2 types of climate? Semiarid and humid subtropical. What are the two most significant factors in defining different climates? Temperature and Precipitation What are the 5 general climate regions? 1. Tropical (Low latitudes) 2. Mid latitudes 3. High Latitudes 4. Dry 5. Highland Chapter 3: Section 4 The world’s food supply depends greatly on an area’s Topsoil. Define ecosystem: An interdependent community of plants and animals. Maple, oak birch and cottonwood are examples of broadleaf (deciduous) trees. Pine, fir, and cedar are examples of Needle leaf or coniferous trees. What two types of plant life are you likely to find in the desert? Cactus and Sagebrush. A savanna is similar to a Steppe. Based on the description below which climate area would you be in? In mountains where temperature varies according to how high you are. Highland Summers are hot and dry and winters are cool and rainy; good agricultural area. Mediterranean Moderated temperatures due to locations next to oceans; frequently experience foggy, damp, cloudy conditions. Marine West Coast Hot, humid summers and mild winters; most often found on eastern coasts of continents including the U.S. and China; often experience hurricanes; good climate for agriculture . Humid Subtropical Have four distinct seasons with great temperature & precipitation variety based on latitudes; mostly found in mid-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere Humid Continental Long, cold winters and short, cool summers; evergreen forests called taiga exist here. Subartic Based on the description below which climate area would you be in? Frigid temperatures, little precipitation and permafrost. Tundra Lots of ice and permanently freezing temperatures; AKA polar deserts. Ice Cap Receive less than 10 inches of rainfall a year; can be hot or cool/cold. Desert Located on the interior of continents and around desert zones; receive about 16 inches of rain a year; hot summers and mild/cold winters. Semiarid Warm, wet summers and dry, cool winters. Tropical Wet and Dry Hot, rainy conditions year around; located in areas around the equator like Southeast Asia and Northern South America. Tropical Wet