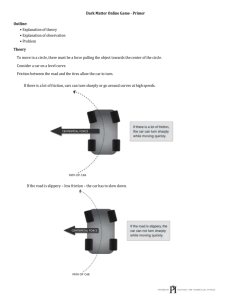
RULES OF THE GAME
advertisement

2 CHAPTER ONE! 3 STARGAZING NIGHT! Lesley, Lauren, Caitlin, and Allie lay on the ground in the middle of the field on a thick, huge, carpet like towel and looked out into the night sky…...It was dark and quiet. There was not a sound around except for the occasional insect chorus that seemed to creep out of no where! Suddenly they saw it, a streak of light, as though somebody had moved a cursor over the sky and made a white line that was powdery and bright across the sky! 4 STARDUST STARGAZING! Did you see that? Did you see that? That is a falling star..No it isn’t…it’s a piece of rock falling through the sky…And their voices gradually died…as the number of white lines crossing the sky grew in number and there was no time to speak at all. “You know we are trying to find out if we are made of star dust this year in school”, said Lesley. “Yeah right” said Lauren. “I wonder how we are going to do that?” asked Caitlin. 5 Lots of pieces of ‘stories’ fall through the sky. Some are big enough to change our way of life! Scientists say that all it takes is about 200 kilograms of asteroid material to ‘kick up’ enough earth material to block out the sun. All planets and their satellites get ‘hit’ by star stuff, all the time! 6 Look at our moon through a good telescope and you can see that it is pock marked with so many asteroid collisions that you wonder how spaceship earth could have escaped such a pummeling!? 7 Some pieces have hit the earth. One of them did actually throw up enough dust to block the sun and make things real uncomfortable for the dinosaurs! Luckily for us those big monster lizards died out and allowed a species like ours to develop. 8 How do we know to ‘read’ the story that each meteor, asteroid, or rock has to say? How do we know that this rock is ‘star stuff’? How would we know if we are ‘stardust’? Read on and you will take a journey of discovery….. 9 RULES OF THE GAME Just a few rules to the game. These rules are there for you to make the best of the game of learning. Remember, in this game winner takes all. Knowledge is power. Play the game well. The most important rule, is for us to respect one another. 10 Being ready for class with all materials, Raising your hand and listening to what is going on in class, shows respect for one another. 11 THINGS TO REMEMBER Bring your Journal and Agenda books with you daily. Write a date and a title for each daily journal entry. Use both sides of the paper. There should be at least 2 sections in your Journal. The rough and the final sections, and they both are equally important. When you listen in class, take down rough notes. Your daily homework is to write final notes, and place it in the final notes section of your journal. 12 13 Rewards, rewards……!!! “when you want to contribute to the discussion in class, think how you will be rewarded for speaking up in class and contributing to the discussion.” – Jonny. Sometimes the teacher is not going to be able to get to your raised hand. You must be patient and await your turn. However, it is very important that you try and contribute in class), 14 How to write notes and succeed! Eye contact with teacher helps in learning to listen attentively. Raise your hand when you want to add to or question any material that is discussed. You are rewarded for intelligent input at all times. Go ahead and raise your hand if you’re sure! 15 What is discussed in class must be noted down in your rough notes section. You can do this in several ways, we will discuss all of them. For now, write a date and title, and start writing these ideas…….what should you write in the rough notes? 16 Writing rough notes….. Use quick sentences, words, concept maps, telegraph , in such a way that you can remember what you discussed in class later at home. You can use the notes the teacher puts on the board or on screen. Add to it with scribbles and notations. Read what the textbook says about the topic, and note down questions. 17 How to write final notes… When you go home there is homework for you to do everyday! It may not take much time, but what you do in the homework is extremely important. Both in terms of what you are intending to learn and in what we want you to develop in science skills. You are also graded for it. That’s how you show others how much you have learnt. It’s a measure of your success! 18 Final notes….. In order to write final notes, you must be able to read and understand what was discussed in class, and then rewrite what you understood in the final notes section. You must now write clear narrative sentences describing what it was that you learnt. Make each sentence count. To this description add information, about the topic, from another source, such as the internet, or a book, or a scientist! 19 Final take….. The final notes should take you 20 minutes each day. If you have not finished what you wanted to write for that day in 20 minutes leave it for the next day. Don’t leave it for too many days undone. It will be hard for you to catch up!!! Have a date and a title for each day and topic. Add further information on the topic by researching, from the internet, at the library, or your textbook. Add the proper bibliography when you do this. 20 BEING SUCCESSFUL….HOW TO… Weekly schedules tell you what is going to be studied for a period of time and helps you plan for those weeks. Attach it safely in your journal. This year we will be trying to find out if we are all made up of “stardust”! 21 GRADING IS DONE WITH: 30% GIVEN TO YOUR JOURNAL, 30% TO LAB REPORTS AND LAB WORK, 30% TO TESTS, AND 10% TO QUIZZES AND CLASS PARTICIPATION. Always be prepared with all the materials you need for class. ( i.e. Pens (black, blue and red pens – for correcting; pencils, graph paper, scissors, protractor, ruler etc.) 22 WHAT MAKES SCIENCE CLICK..! What makes science click is that we always start with an idea. This idea does not have to be correct. But we always do something about finding out whether it is true or not! Suppose you were given a loop of paper and you were asked to guess how many pieces of it you would have, if you cut it lengthwise? What would your idea be? 23 Checking out an idea!? Take the strip of adding machine paper and make a loop out of it and stick the ends together, after you have made one twist with one of the ends, just before attaching the ends together with masking tape. You will then be asked to cut along one surface (lengthwise!) until you have reached the place where you began. If this is difficult, please ask. THIS IS THE HARD PART! 24 WHAT’S WITH THE MOBIUS STRIP? How many pieces of paper would you have when you do this? Was it the same idea you had before you started the activity? What if…..you had made two twists to the end before you stuck it together? How many pieces would you have? 25 MOBIUS STRIP The Mobius strip is a curious paper model. It has mathematical significance, but we are not really interested in all of that. The Mobius strip is the simplest geometric shape with one surface and edge. You could be traveling for ever on a mobius strip. Try running your finger on any one surface. For your final notes research on the internet about this… 26 A hypothesis about shapes! When you did this activity you made a Hypothesis. A Hypothesis is another name for the idea with which you start any work in science. It does not have to be correct and you may find that it is not correct after you finish the experiment.. This happens a lot in Science! 27 What is your hypothesis? In the previous activity your hypotheses was to guess how many pieces you would have when you cut it along one surface. It was an educated guess based on past observations and experiences. Was it correct? Does it matter? 28 Chapter 2 29 THE COOKIE CONNECTION When you try writing rough notes today why don’t you try a concept map. It helps you write notes and put in a lot of details quickly. While you chew on the cookie I gave you, savor the ingredients that it is made up of. Then tell me what they are. Your answer would probably be: Flour, sugar, salt, milk, butter etc. But what are those materials made up of? 30 Elements that make up cookies! These elements that the cookie is made up of are themselves made up of smaller little pieces. The first people to get this idea were the ancient Greek Philosophers like Democritus. They concluded that all matter must be made up of small ‘atomos”! 31 A person called John Dalton eventually said that ‘elements’ are substances that have only one kind of atom in them. 32 THE COMPOUND Elements come together to form Compounds. There is always two or more elements in a compound. Compounds can be made up of similar elements but be totally different! 33 The watery compound! Water is made up of 2 atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen, however, if your increased the number of oxygen atoms, from one to two you would have a totally different compound! 2 atoms of hydrogen and 2 atoms of oxygen combine to form Hydrogen Peroxide. 34 DANGEROUS SALT ON YOUR EGG! Salt is made up of two elements: Sodium and Chlorine. Sodium is a very explosive metal, and Chlorine is a very poisonous gas. It was used in WWII. You can guess why it was used! 35 Mixing elements…. Mix these two dangerous elements together and you get a totally new compound which has its own, wonderful, safe, characteristics or properties. Sugar is made up of three elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. 36 JUST WHAT IS PAPER? If you tried to analyze what paper was made up of, you would find that it is made up of the same elements that sugar is made up of. However, the amount of each element in paper and sugar are different. C12H22O11 – SUGAR; C10H11012 - PAPER 37 So what about us humans? By changing the amount of elements that are together it is possible to make a totally different compound! Sugar has three elements in it; Carbon, Hydrogen, and oxygen. We human beings are quite a bunch of elements combined together! 38 Where did it all begin? If we could tell where these elements actually got made, we could begin to understand where it all began. One of the first concepts or ideas we are going to investigate is: Where do these elements come from and how are they made? 39 NATURE’S KITCHEN If these elements, that everything is made up of, come from stars then we would be made up of star dust! This is our quest for this year. We are trying to investigate whether this may be true. Where’s Nature’s Kitchen, Where the elements are cooked, Where does life begin…? Where should our search begin!!! 40 Chapter 3 ! 41 Measurements In order to investigate where elements come from and how they are made, it is necessary to establish standards of measurements. 42 Why have measurements? Without these standards it would be difficult to tell someone what we found out. Everything that is stated must be backed up with standards. These standards are there to help us in our quest and to communicate with others in the scientific community. 43 Measurements. In the world of Science, measurements are done in the Metric System. This system is not new in our country, although we do not use it frequently. Measuring in the Metric system means, measuring in tens! 44 The metric system is easy…! Its so easy! For example 1000 meters is a kilometer. This is easy as we can count in 10’s. A thousand is a hundred of the 10’s. Similarly a 100 is 10 of the ten’s! The English system is the confusing one, we do not use it in science at all! (Pounds, Ounces!) 45 Prefixes in the metric system. Kilo stands for thousand in the metric system. While 100 meters would be a Hectometer, 10 meters would be a decameter. Similarly 1/10th of a meter would be a decimeter, 1/100th of a meter would be centimeter, and 1000th of a meter would be a millimeter. In this way there are prefixes that tell us exactly what we are talking about. 46 WHAT EXACTLY IS A KILOGRAM ? THE PICTURE SHOWS THE PLATINUM-IRIDIUM INTERNATIONAL PROTOTYPE, AS KEPT AT THE INTERNATIONAL BUREAU OF WEIGHTS AND MEASURES UNDER CONDITIONS SPECIFIED BY THE 1ST CGPM IN 1889. THE KILOGRAM IS THE UNIT OF MASS; IT IS EQUAL TO THE MASS OF THE INTERNATIONAL PROTOTYPE OF THE KILOGRAM. IT IS ESTABLISHED TO END ANY CONFUSION REGARDING THE MEANING/DEFINITION OF THE WORD “WEIGHT”. 47 MEASUREMENT cont’d There are different units used to measure different kinds of quantities. Mass is measured in grams, volume in liters and length in meters. Prefixes in the metric system helps us understand what portion we are talking about. ‘Kilo’ means you have have a thousand units of a measurement, and ‘milli’ means you have a thousandth of a measurement. 48 How much do you have? If you take a bottle of water and weigh it, you say that it weighs 2 kilograms, or that you are holding 2 kilograms of mass. However, if you took a bottle and measure how much water you have in it you say you have 2 liters of water in the bottle. You can also weigh the bottle of water and express how many grams of water you have in the bottle. Measurements work to communicate how much material you have! 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Chapter 4 56 So what is Mass??? Mass is something that cannot be destroyed or created. It is what anything is made up of. It is a fundamental property of any matter. In other words mass is something that all things that have matter have! If you burn paper then all you are left with is ash. 57 Where did the paper go? However, the rest of what the paper is made up of did not disappear. Parts of paper changed from the solid form to the gas form! Paper is made of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. Ash that is left over is the carbon. 58 Where did the paper go? The Hydrogen and the oxygen does not disappear but moved from being a part of the solid paper to gases. The connections between carbon, oxygen and the hydrogen elements is destroyed. This enables the oxygen and hydrogen to be released as gas into the air! 59 The difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas object is the space between the atoms or molecules that makeup that object. 60 Liquid atoms….. In the first picture you have the atoms/molecules are very close together. In the second picture you have material in which the atoms/molecules are together and yet are far enough to enable them to slip and slide past each other. 61 Putting you finger through a table!… In the third picture the atoms/molecules are far from each other. That is why you can put your finger through air (a gas) but you cannot put your finger through a solid table. Unless you tried very hard!!! 62 ROGER BACON Roger Bacon (1214-1294) Studied geometry, arithmetic, music, and astronomy as a young man. He received a degree from the university of Paris around 1241 and lectured on Aristotle’s ideas. 63 Roger Bacon’s interests His interests in mathematics and sciences were nurtured at oxford where he came back to in 1247. Introduced the idea of using mathematics to illustrate ideas in science with data generated from experimentation. 64 The scientific method… This method of using data from experiments in science is the important part of the scientific method. The Scientific method is one of the standards or basic procedures that we are going to use in order to see whether we are made up of stardust! 65 Chapter 5 66 Lab 1 at last!!! In Lab 1 you are going to investigate measurement and the scientific method, while blowing bubbles! First take a cup of soap solution, which you will make from the containers of soap you have in front of you. Wet an area about 45 cm diameter on your lab table. Use a wet napkin to do this. 67 Bubble, Bubble….. Take the straw that is provided and then dip one end of it into the soap solution that you made. Bring this dipped end onto the wet surface you had prepared and blow gently through the other end to make a bubble. You will find that you may have to make several tries before you become an expert in this task. 68 Which one is the best bubble maker? You may add any number of breaths you want to make it big or small. But you must use the same amount of breaths for all the different kinds of soaps. You need to make five different bubbles for each soap. Measure the diameter of each bubble when it breaks. An impression of circle will appear on the lab table when the bubble breaks. 69 Which one is the best? Repeat this with every brand of soap and measure the bubble’s diameter. Decide which brand gives the biggest bubble. Calculate the average bubble diameter for each brand of soap. 70 LAB 1 REPORT. The purpose of lab I is to take you, the student, through the scientific method, as outlined by Roger Bacon, and every scientist after him. 71 The scientific method. The scientific method is a process by which any idea in science could be tested. In order for any idea to be accepted as scientific theory or fact, it has to be tested and the experiment must show numerical values (numbers and units) that show that the idea is correct or not. 72 What you are doing in the lab.. What you are going to do is simple. The hypothesis, or the educated guess that you are going to make, about the outcome of the experiment, will be tested and shown to be either correct or incorrect. Remember there is no wrong or right answer until it is tested and the correct answer is found. 73 What is a lab report? You will be testing several soap solutions and you have to decide which one produces the biggest bubble. You must start with a reasonable estimate or hypothesis as to which soap solution will eventually produce the biggest bubble. Your hypothesis does not have to be correct in the end. You will present your results in a lab report. 74 The lab report The lab report will consist of, 1)The purpose (to investigate the scientific method). 2) An introduction (an essay describing the idea that you are investigating, in this lab it is the Scientific method and soap) . 3) A procedure (which describes what you did in the lab), 4) Observations (which could be presented in the form of a paragraph and/or data tables/graphs). 5) Finally, the conclusions that you reach. 75 How to write an introduction… In order to do the introduction you will have to first research on three topics. A) the scientific method, b) Roger Bacon, and c) soap. Go to the internet, or a book, or a scientist and collect 10 ideas about these three topics. List them in your own words in your final notes section with bibliography. 76 How to write an introduction… The 10 ideas you had listed in your final notes section must be expanded to write your introduction to Lab 1. Plan your time well. You can break up your work into several days. Do work everyday in science (at least 25 minutes). Combine two or three ideas and form a paragraph. In this way by using the 10 ideas you will have a short essay with all the ideas presented well. 77 WHAT'S IN A DATA TABLE? The purpose of a table is to record the data you collected while doing an experiment. The data can be used to make a graph. 78 The graph… The graph shows the same material that is in the data table, but as a picture. In fact it might allow you to determine some more ideas about the data. 79 DATA TABLE FOR LAB 1 SOAP Tria Trial Trial Trial Trial Avg l1 2 3 4 5 (Cm ) Publix 18 23 16 16 12 17 Sunli 14 15 17 13 12 14.2 Dawn 11 15 18 17 16 15.4 Palm 18 31 16 29 33 25.4 Joy 10 17 10 14 5 11.2 Dove 18 20 17 22 15 18.4 80 ORDER OF THE DIFFERENT PARTS OF LAB 1 REPORT. Purpose, Introduction, Procedure, Observations/data table, Graph, and conclusion (Inference). According to your data which soap was the most effective “bubble maker”? In what way does the experiment illustrate the Scientific method. 81 Lab instruments…. There are many lab instruments that scientists can use. You are going to use many of them this year. These Lab instruments are all used to measure various materials. The units you will use depend on what exactly you are measuring, and what you want measured. 82 Beakers and graduated cylinders. A Beaker is a glass utensil that is used to measure volume in liters or milliliters. However, if you wanted to measure out 20 milliliters then you would probably use a graduated cylinder which allows you to measure smaller quantities. 83 Volume in meters! You can also measure volume using the length units. We did build a cubic meter. This makes it possible to measure volume in length units. When you built a metric cube you had to notice that there was a length, a width, and a depth involved. You need to multiply these three length measurements together to get the volume in a metric cube. 84 Another instrument Another lab instrument you can use would be a thermometer. This instrument measures temperature. Temperature is actually the measure of the energy of particles around the thermometer. The unit used to measure temperature is centigrade although the universal standard is Kelvin. 85 CHOOSE YOUR CONSTELLATION This assignment will require a trip to the library. In ancient times, there were no television shows or radio shows or even theaters. People invented their own fantasies. They were mostly interested in getting food on the table and maintaining their relationship with god and making sure they reaped good harvests. 86 The harvest moon! Most of the food in those days came from working on a communal farm. The planting seasons and harvesting seasons were marked my important days. It was important for the farmers to look to the sky for guidance. The night sky became the backdrop for stories. These stories eventually became folklore! People passed these stories down through the ages. 87 Constellations. Your task is to choose one constellation. A constellation is a pattern of stars in the sky that seem to resemble mythical gods, people, or animals. Make a drawing of your constellation with the stars that make up the outline. Name at least 3 stars in it, 3 important items about it, and a mythological ‘story’ connected to it. 88 Your star assignment… Write in your own words a story connected to this constellation. If you cannot find a story, then make up your own! Find out the names of the main stars that make up your constellation. 89 Chapter 6 90 In order to know what the stars are, it is necessary for us to examine how our ideas about stars developed over the thousands of years through which stars have been studied. 91 Archimedes Archimedes lived from 287 BC to 212 BC. Whenever we count years before AD (Anno Domini), we usually count down to ‘0’, when 1 AD begins. We are now in 2000AD (that is 2000 years after the birth of Christ)., and 2000 years since the end of 1 BC!(Before the birth of Christ) 92 Story of Archimedes…. There are many fantastic stories about Archimedes and his inventions. One of the most fascinating stories is the one about his solution to a problem given to him by King Hiero II of Syracuse. 93 Crown……of gold? It was a story about a crown that was made by an artist. The king suspected that the crown did not have all the gold that was supposed to be used and he suspected that silver may have been mixed in as a substitute. Since the crown had a religious significance it could not be melted or changed. 94 How he did it! Archimedes had to find out whether the crown had all the gold it was supposed to have without damaging the crown. He thought about this for many days and then stumbled upon the solution while he was in a bath. He was so happy he ran out into the streets shouting ‘eureka’ (which means I got it!) not realizing that he was not dressed! 95 Density…. The answer included the concept of density. This concept refers to the idea that anything that has mass has its own particular density. Density is the amount of mass that is packed into a particular volume. It is expressed in the unit grams per milliliter or centimeter cubed (g/ml or g/cm3). 96 Volume in length measurements….! Remember volume can be measured in milliliters (unit of volume) or cm3 (which is a length unit cubed). 97 ARCHIMEDES THE INVENTOR! Archimedes invented many machines, which were used by his king to save the city. He was, therefore, a very important person in Syracuse. Amongst the machines he designed were the war catapult, the Archimedean screw, and mirrors that reflected light and burnt approaching ships sails!! 98 ARCHIMEDEAN INVENTIONS THE ARCHIMEDEAN SCREW THAT ENABLED PEOPLE TO BRING WATER FROM A LOWER PLACE TO A HIGHER ELEVATION! THE GRAPPLER HOISTED SHIPS RIGHT OUT OF THE WATER! 99 ARCHIMEDEAN INVENTIONS THE MIRRORS THAT HE INVENTED COULD BE FOCUSED IN SUCH A WAY THAT THE SUNS RAYS WERE CONCENTRATED ON THE ENEMY’S SHIPS SAILS AND THE SHIP ITSELF, THUS SETTING IT ON FIRE. 100 ARCHIMEDES AND THE CROWN. This is a statue of Archimedes that has survived. The notorious crown that gave him fame probably looked like the one shown here. The crown was made for a statue of a god in a temple, and therefore had a religious 101 HOW ARCHIMEDES SOLVED THE CROWN PROBLEM! If the crown and an equal mass of gold was taken and immersed in water, the density of the crown and the mass of gold should be the same. If the crown had the same amount of gold! 102 The gold crown… Density is dependent on both the weight and the volume of the crown. In other words how much mass of gold is packed into a particular volume of space. The chunk of gold would have a particular mass of gold atoms packed into its volume. 103 So does it have it all…? The crown too would have its own arrangement but with added material which substituted the gold. If the crown had more density then it would be known that it was more tightly packed than actual gold. 104 Among the famous ideas that he introduced is that, the volume of an irregular object can be found by immersing this object (such as a rock) in water and measuring the volume of an irregular object. Put the rock in a glass of water and measure how much water rises in the glass when the rock is in it, then the volume of the rock would be exactly equal to the volume of water that rises in the glass. 105 Density and Buoyancy Density and Buoyancy are two basic concepts that are used to measure and make a distinction between materials. This way we can have a good understanding of what material we are dealing with! 106 BUOYANCY Buoyancy is a concept that describes how anything can float on liquids. Water is a liquid, oxygen is a gas, and a piece of iron is a solid. When you put something in water or air, it looses a bit of weight. According to Archimedes this is because the water that you put the solid in, exerts a force on the solid. The amount of weight it loses in water will be equal to the force that the water is exerting on the solid. 107 Density of a rock! If you weigh the rock and then divide the weight by its volume, you will be able to determine the density of the rock. This tell us how much mass or matter is stuffed into the space that the rock takes up. Remember volume can be measured in milliliters or cubic meters. (ml OR cm3 ) 108 BUOYANCY BUOYANT FORCE ACTS UPWARD AGAINST THE FORCE OF WEIGHT WHICH IS ACTING DOWNWARD. IF THE TWO ARE EQUAL, YOU WILL FLOAT! IT IS LIKE THE ICEBERGS THAT ARE FLOATING ON THE WATER IN THE PICTURE. 109 If you put a piece of wood into water then the water is pushing up on the piece of wood. If the push/force exerted by water is equal to the weight of the piece of wood in water, then it would float. If you were to put a piece of wood in a beaker, and measure the volume of water that rises, you would find that it equals the volume of the piece of wood. Also amazingly, the weight of water that rises will be exactly the same as the weight the piece of wood loses when it is put in the 110 water! Things about buoyancy you need to know….. Loss of weight of object in water = weight of water that is displaced by the object. Weight of water that is displaced = buoyant force applied by water on the object. Volume of water displaced = volume of object in water. 111 BOAT/PENNY LAB 2 You could make a paper boat and an aluminum boat and compare the amount of pennies each would be able to carry. Make a paper boat and an aluminum boat, using the same area of material. Conduct three trials on each boat by putting pennies in the boats and counting till it sinks. You may have to make three paper boats. Always remember to use the same amount of paper, for each boat. 112 Data and conclusions for lab 2 Represent your data in this manner on a separate sheet of paper titled lab 2: Trail 1 - 45 pennies Trail 2 - 68 pennies Trail 3 - 102 pennies Why did some designs work better than others? Why do some shapes float? Remember you have to use Archimedes’ ideas on buoyancy to answer this question. Do you find that the larger the surface area the more pennies you are able to fit into the aluminum boats? Can you see that pressure depends on force and the area its applied over? 113 MUST HAVE STUFF NOTES FROM LAST 2 WEEKS LAB 1 NOTES PREP LAB 1 DATA TABLE ROUGH ONLY SCIENTIFIC METHOD ROGER BACON ETC RESEARCH ORGANIZATION ARCHIMEDES, CONCLUSION QUEST. RESEARCH LIST TEST REVIEW 2 114 Chapter 7 115 LAB 3 PREP In this lab you will be investigating density. Density is a property of matter. It describes how compactly packed the stuff in the object can be. In terms of how much mass there is in a unit of volume. 116 Density of iron….. For example the Density of pure water is 1 gm/ml or in other words there is always one gram of water in one milliliter of space. Similarly, Iron would have a different density as it is a solid, and there would be more stuff packed into one milliliter of iron than one milliliter of water! 117 Why does iron sink in water? This is why Iron is heavier than water and it will sink in water. Density is a property of matter. It describes how compactly packed the stuff in the object can be, in terms of how much mass there is in a unit volume. 118 More on Lab 3….. In Lab 3 you will be comparing the densities of three different substances. By calculating the densities of these three materials you will understand how to find out density, and that different materials have different densities. 119 Procedure for lab 3 Take three cups and label them A, B, and C. Measure the mass of each cup. Fill each with the following materials: cup A with 10 ml of water; cup B with 10 ml of oil; and cup C with 10 ml of molasses. Do not taste the molasses even if you know its going to be sweet!!! 120 Procedure for lab 3 Find the mass of each material in each cup by taking away the weight of the empty cup from the weight of the material and the cup. Find the density of each material by dividing the weight (mass) of each material by the volume of that material. Make a data table listing all the measurements you got… 121 Data table lab 3 Cup A Wt of 25 ml of water + cup= 100 g Wt of cup = 75 g Wt of 25ml of water = 25 g Volume of water = 25 ml Density of water =M/V = 25g/25ml = 1 g/ml Repeat these steps for each cup, placing them in the same order, keeping in mind that the material would be different in each cup! 122 LAB 3 DATA Having a good data table helps in understanding what was done in the experiment, and what your data has achieved. Lab data should be listed in a clear and concise fashion, so that anybody can see that you have got results that can be checked out. 123 TEST 3 REVIEW 10 MULTIPLE/FILL IN BLANKS SCIENTIFIC METHOD, METRIC SYSTEM, MASS, VOLUME, DENSITY, ARCHIMEDES. 3 CALCULATIONS WITH DENSITY REMEMBER MASS/VOLUME = DENSITY L X W X H = VOLUME i.e. 3cmX3cmX3cm = 27cm3 VOL. OF IRREGULAR OBJECT- PLACE IN WATER HOW MUCH WATER RISES IS THE VOLUME OF THE OBJECT. 124 LAB 3 REPORT The results and the general description of ideas that you have investigated in this lab must be written down in a report. The report is a formal presentation of your findings. It is as valuable as a test, so spend some quality time preparing it. Following the format would be advisable. 125 Lab report on density. INTRODUCTION: (Use these topics to write a good essay connecting the ideas given to you. Try to present them in a logical sequence. Which means that you should try to write the essay as though it were a story you were telling me, with a beginning, a middle and a end. Use the topics listed to make up the ‘story’ or description. Mass, Volume, Density, Archimedes 126 . PROCEDURE: state what you did so that someone else could perform the same experiment using your procedures. 127 OBSERVATIONS: (In this lab the data table would be your observations, however, if you want to add anything ineresting that you saw then it adds to your report. MASS OF CUP A + WATER= 32.64g MASS OF CUP A = 10.46g MASS OF WATER = 22.28g VOLUME OF WATER = 25.00ml DENSITY OF WATER = M/V 22.28g/25ml = 0.91g/ml REPEAT FOR ALL THREE STEPS IN THE SAME WAY. SHOW AND LIST ALL MEASUREMENTS AS SHOWN ABOVE, FOR ALL THREE CUPS. 128 CONCLUSION :– In this section please discuss the following in the narrative style: 1. Which liquid was the most dense? Why? 2. If you arranged the liquids in a cup which one would be under which? Why? 3. How does water’s density compare to the other liquids? 129 ELEMENTS The next topic we are going to investigate is the element.. We already know that elements make up all the matter we see around us. Now we will study what is inside these elements. This will enable us to see what happens in stars and how stars cook them up! 130 Chapter 8 131 There are about 109 elements in the known universe. Elements are special materials. Each of them is made up of one basic component. For example if you were to take a piece of gold (which is an element) and cut it into half you would have two equal pieces of gold. 132 Each of these halves would be exactly the same as the original piece. Now if you continued to cut each half that you have, into further halves, after 90 divisions of exact halves, you would eventually reach an atom of gold. The piece of gold that you originally had was made up of billions of these same gold atoms. 133 All elements are made up of atoms that are similar in mass and other ways. In each element you will find only one kind of atom. Silver is made up of silver atoms. Hydrogen is made up of hydrogen atoms. The names and other information about elements are found of the periodic chart. 134 ELEMENTS/ PERIODIC TABLE Many elements on the periodic chart were discovered only in the recent past. But for hundreds of years people around the world have recognized the value of some elements. Gold and silver were used since ancient times and everyone knew of them. Copper was used to make brass and thus elements that were useful were known a long time ago. 135 Iron and copper like other metallic elements were used to make weapons and useful tools. With metal it was easy for farmers to make crude farm instruments that would last many years. 136 The periodic chart was designed in such away that anybody looking at it could know quite a bit about these elements.. Some have symbols are based on Latin names. Pb - (PLUM BUM)lead, Al -Aluminum, C- Carbon, Si-Silicon, Zn-Zinc, Ca -Calcium, Fe - (FERROUS) Iron, Sn - TIN, Cu - (CUPRIC) Copper, NaSodium ETC. 137 the periodic table arranged…. They are all arranged according to the number of protons in their nucleus. In order to know what this means we must look at what an atom looks like. 138 The periodic chart was first designed by a Russian scientist called Dimitri Mendeleev. It has changed since then but it has always been arranged according to the number of protons an atom of an element has. 139 The atom looks so much like a sphere that has a cloud of fast moving electrons on the outside and a center made up of neutrons and protons. The sphere’s outer portion looks fuzzy since these electrons are moving close to the speed of light as it revolves around the nucleus. 140 The protons and electrons have electrical charges. The electron is negatively charged and the proton is positively charged just like a battery. The neutrons have a special job and are neutral in terms of charge. It keeps these opposite charges from getting together. 141 If opposite charges are kept near each other, they tend to attract each other. Like poles of a magnet repel each other. Unlike poles attract each other. Each atom of an element has its own number of protons, neutrons and electrons. 142 The atomic number gives you the number of protons and electrons. If the atomic mass is rounded up it becomes the atomic mass number. When the atomic number is taken away from the atomic mass number you get the number of neutrons. 143 144 145 ATOMS/PERIODIC CHART The electrons are buzzing away and circling outside the nucleus moving at 300,000km/sec. Although the electron is about 1600 times smaller than the proton/neutron it packs an equal punch in terms of charge. 146 The proton has a positive charge, there are always an equal number of protons and electrons in a normal atom. In every atom there is always a balance of charges. We will not get a shock when we touch ordinary items made of these atoms since there is this balance. Charges are exactly equal in number and cancel each other out. 147 AN OXYGEN ATOM IN ALL IT’S GLORY! 148 RECOUPING! We have come across so much so far….Lets review it so we know where we are exactly… 149 We know what elements are and what they are made up of, and that we are made up of elements. Elements are made up of atoms that are all similar. 150 Each of these atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons to cancel out the charges, and the neutron number can be calculated by using the rounded up atomic mass (atomic mass number) and taking it away the atomic number from it. 151 We know how to measure matter and how to communicate in science, and how scientist go about trying to find out about stars, ourselves, and nature. That is a lot of stuff already…but where do we go from here….??? 152 We need to find out where these elements come from…. so that we can know whether we are made up of stardust…. 153 Chapter 9 154 ENERGY/WAVES Our next task is to investigate energy. Energy is the only tool we have to investigate stars. When you throw a stone into a pond you can see that there are circular waves that go out from the spot where the stone fell. These waves are caused by the energy that the stone gave to the water as it collided with the water. 155 Energy causes vibrations that travel in the form of waves. When a slinky is stretched and touched different waves could be created. Longitudinal (compressional waves) and transverse (sine waves) waves. 156 Light is energy. It behaves just like a stone thrown into a pond. You see waves coming from the point where the stone fell. Whatever source putting out light would have waves of light energy coming out from that point 157 Just like waves coming out from that point where the stone was thrown. But you cannot see the light waves coming at you since it travels at 300,000 km/sec. 158 Waves…… Waves (light) that are traveling outward are going at 300,000 km/sec. It is one of the reasons you do not see it’s path. However, the only information we get from stars is in the form of light! This is why we need to study light. We can learn a lot about stars when we study light waves. 159 CREST CREST 160 Waves are made up of crests, nodes, troughs, amplitudes, and wavelengths. Wavelengths are also known by the greek letter Lambda. 161 Frequency…… Frequency is the number of crests or wavelengths that pass a certain point in one second. If there are more crests or wavelengths passing a certain point in one second it means that that particular wave has a lot of frequency. 162 LIGHT AND THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM. This is a chart of all the known energies. Light, an energy is in the middle of this chart. The chart itself is called the electromagnetic spectrum. Spectrum is another word for list. 163 WAVES AND CYCLES Pieces of light called photons move in a wave like fashion. A cycle is actually one wavelength. The time it takes for one cycle to occur is a period. 164 Bowling ball……. If you hang a bowling ball from the ceiling and let it swing, then one swinging back and forth motion would be a cycle.. 165 Cycles and periods….. 1 Cycle = 1 Complete wavelength The time it takes for 1 cycle = 1 period = Time it takes for one swing forward and back to where you started. 166 Cycles and frequency….. A cycle could be seen as a unit. A measure of how many cycles or wavelengths or crests that pass a certain point in one second is the frequency of that wave. Frequency is measured in Hertz. 167 Radio waves have more wavelength than gamma rays but it has much less less frequency than gamma rays. They both travel at 300,000 km/sec. 168 WAVES 1 CYCLE Transverse waves look like waves in the sea. Longitudinal waves or Compressional waves look like dominoes that fall in a row when the first one is touched. 169 WAVES ANOTHER LOOK AT A TRANSVERSE WAVE. ANOTHER LOOK AT A LONGITUDINAL OR COMPRESSION WAVE. 170 LONGITUDINAL WAVES Longitudinal or compression waves are similar to sound waves that move by passing its energy from particle to another. Like dominoes arranged in a row. 171 COMPRESSION WAVE ANOTHER EXAMPLE OF A LONGITUDINAL OR A COMPRESSION WAVE PASSING ITS ENERGY FROM ONE PARTICLE TO ANOTHER. 172 A photon, ( a piece of light!) traveling through a medium passes right through it because it has a very short wavelength and a high frequency. 173 LIGHT If you use a linear diffraction grating, which has 1000 slits/mm, (which means that each slit of plastic is closely packed) it is possible to split light into its components. Light is made up of seven colors/frequencies. They are red, yellow green, blue, indigo, and violet. 174 The visible light spectrum…. 175 Each has its own frequency, and red has more wavelength and lesser frequency than violet (purple). Purple has less wavelength and more frequency in the visible light spectrum. However all the frequencies travel at 300,000 Km/sec. 176 Burning your hand……. Radio waves have less frequency than gamma rays, which is why it is possible to block radio waves with your hand but gamma rays would burn right through your hand. 177 When light passes from a less dense area to a more dense area it bends or refracts. This is known as refraction of light. When you look at a pencil in a glass of water it is possible to see that it is broken but it is not really broken. It just appears bent or broken because of the refraction of light. 178 MORE DENSE AREA 179 WAVES AND LIGHT Going through all we have been introduced to about light: Energy causes vibrations which move in the form of waves. Waves can be described by using labels, such as crests (the top of a wave), troughs (the bottom of a wave), wavelength (which is the length from one crest to another, and amplitude (the length from the center line of a wave (node) to the top of any crest or the bottom of any trough. 180 Wavelength can also be represented by the Greek letter Lambda. A list of energies is the electromagnetic spectrum. Light is in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum since its wavelength and frequency fall into the middle range of the group of the energies. 181 Light can bend and be split up into six distinct colors. Light always travels in straight lines. 182 Light travels at 300,000 km/sec. We know that the light that comes from stars comes straight to us. It takes this light time to get to us. Light can also tell us what is in the star, by looking at the spectrum of the elements in these stars. 183 MORE REVIEW ABOUT WAVES Frequency is the number of crests that pass any point in one second, or the number of wavelengths that pass a certain point in one second. The unit is Hertz. The list of energies stretch from radio waves to gamma rays. The differences between these waves is their frequency or their wavelength. 184 The lesser the wavelength the more the frequency and vice versa. Sound energy is different in that it needs a medium to be carried. Like energy in the slinky was seen to be passing through the metal of the slinky. You cannot hear in space. Not enough atoms to carry sound energy. 185 LAB 4/5 A cycle is one forward and back movement of the pendulum. Which is a wavelength. The time it takes to do this cycle is known as a period. A robin’s pharynx vibrates about 20,000 times/sec, or 20,000 hertz. The G string of a guitar vibrates at 20 hertz. 186 Lab 4/5 has many parts. In the first part you have to make a pendulum. To make a pendulum you attach a weight at the end of a string that is measured. Tie the end without the weight to the arm of the ring stand allowing for length adjustments during the lab. Allow the pendulum to swing freely. Allow the pendulum to swing freely. Adjust the length of the pendulum’s length to the previously set out measurements. 5,10,15,20,30,35,40 and 45 cm. 187 Pull the pendulum about 45 degrees from the zero position. This is about half way between the hanging zero position and the maximum pull position. Time how long it takes to do 10 waves. Then divide that time by 10 to get the time for one wave. Make a data table with the data and plot a graph with the Lengths vs. frequency. 188 LAB 4/5 Tie a rope that is given to you to a chair and shake the rope along the floor till you can notice a clear wave. Once you have got a clear wave pattern measure the wavelength of that wave. Make a wave with a shorter wavelength and measure it. Calculate the frequency by judging how many crests passes in 10 seconds and dividing the answer by 10. 189 How to write a lab report…. Get research High light 10 items in it Put in your own words into the final notes section Start your intro story (by arranging the 10 items) This story must have a beginning, a middle and an end. 190 Next in the lab report…. Procedure Datatable/observations: do not forget units and steps etc. Conclusions: follow questions to form paragraph, introduce the data that you have to prove your answers and analyze them. 191 Lab 4/5 The third part of lab 4/5 is to conduct a flame and spectral analysis data table. Conduct the flame test on the six metallic nitrates in the test tubes. Follow all safety instructions and then look at the flame color through a spectroscope and list the colors in a data table. 192 LAB 4/5 part 3 LAB 4/5 part 3, is an important experiment. It will show how it is possible to identify an element by using the light energy it gives out when heated. The light energy given off when heated can be studied by many instruments, and the information can be used to identify these metallic elements. 193 You will be given six metallic compounds. These metallic compounds have metals and nonmetals combined together. For example one of the compounds that you are going to burn is called Copper. As the name suggests there is a combination of many elements. Three in Copper Nitrate. Copper, Nitrogen and Oxygen. 194 It is possible to write these combinations using abbreviations. The abbreviation is called a chemical formula. 195 Sodium Chloride another compound is abbreviated to NaCl, which tells us that there is one atom of Sodium and one atom of Chlorine combined together to make up this molecule of the compound. The molecule is the smallest part that you can still call this compound. Water is a compound too! 196 When you see the water coming out of a tap you are really seeing billions of molecules of water that are close together pouring out of the faucet. 197 The chemical formula for water is H2O, which means there is two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen combined together to form one molecule of this compound. In the lab you are going to take a bit of each of the six compounds on to a spatula and burn it with a flame from a Bunsen burner. 198 LAB 4/5 part 3 A bunsen burner is an important tool that is used in the chemical laboratory. It can provide a safe flame to test materials. However it does produce a flame and it is dangerous of it is not handled in the correct way. Listen to all safety instructions and follow them carefully. Do not try to be adventurous! The flame that comes out of bunsen burner should be light blue in color. If it is any other color, there is an incorrect mixture of air and fuel. Contact your teacher immediately. Wear safety apron and goggles at all times when near a 199 bunsen burner that is burning. The flame is extremely hot, although it does not seem to be. The parts of the bunsen burner are kept cool by design. Long hair should be tucked under your collar or otherwise pulled back well and kept back at all times when using the flame. 200 Wet the end of the spatula, with the acid provided. Bring it into the first chemical compound. Note which compound you are using first. Bring the end of the spatula with the chemical compound stuck to it into the flame. Make sure you do not spill any chemical into the flame. 201 Note the color. Study the flame through a diffraction grating. The DG should split the light that is coming from the burning metallic element in the compound, and produce a specific spectrum. You will not have much time to see the spectrum as the flame will burn the elements quickly. So be quick to note the colors of spectrum. 202 Since we had the compound at the end of the spatula or Nichrome wire when it went into the fire, the flame color came from the compound burning. But since the compound was made from a metal and the non-metal, the non-metal is sent up into the atmosphere as a gas and the flame color came from the metal part of the compound burning. 203 Bunsen burner WATCH OUT FOR THE FLAME. IT IS HOT ONLY AT THE SPOUT THE REST OF THE BURNER IS NOT HOT TO TOUCH THE FLAME MAY TURN YELLOW DUE TO THE AIR INTAKE VALVE AT THE BOTTOM BEING OPEN. TELL THE TEACHER IF YOU SEE A YELLOW FLAME. ALWAYS WEAR PROTECTIVE GEAR! WATCH OUT FOR LONG HAIR THAT IS NOT TIED OR RESTRICTED. THERE ARE PARTS OF THE FLAME THAT ARE INVISIBLE JUST ABOVE THE TOP OF THE FLAME. A BLUE FLAME IS THE BEST FLAME AND IS REALLY HOT. THE TAP CAN BE TURNED 90 DEGREES TO OPEN. ALWAYS MAKE SURE IF IT IS OPEN OR NOT. 204 Spectral lines and what they mean. THE SPECTRAL LINES OF COLOR THAT YOU SEE THROUGH THE DIFFRACTION GRATING IS A UNIQUE PATTERN OF COLORS. EACH ELEMENT HAS ITS OWN SPECTRAL LINE OF COLOR. THEREFORE WE HAVE FOUND A WAY TO ACTUALLY IDENTIFY ANY ELEMENT BY JUST LOOKING AT THE LIGHT IT GIVES OFF WHEN IT IS BURNING. 205 I AM NOT SURE WHETHER YOU HAVE REALIZED THAT YOU HAVE FOUND A WAY TO FIND OUT WHAT ELEMENTS ARE FOUND IN STARS WHICH ARE REALLY HUGE BURNING BLOBS OF ELEMENTS! 206 THERE ARE MANY OTHER IDEAS THAT COULD BE PROVED BY LOOKING AT THE LIGHT GIVEN OFF BY ELEMENTS. BUT THIS IS VERY IMPORTANT TO OUR QUEST. IN ORDER TO KNOW WHAT IS IN A STAR WITHOUT GOING TO A STAR, WE HAVE TO ONLY LOOK AT THE LIGHT GIVEN OFF BY IT AND STUDY ITS SPECTRUM TO KNOW WHAT IS IN THE STAR! 207 208 THIS IS THE PURPOSE OF LAB 5. WE HAVE INVESTIGATED THE IDEA OF IDENTIFYING ELEMENTS USING SPECTRAL LINES OF COLOR! YOU MUST NOW WRITE UP A LAB REPORT DESCRIBING ALL THAT YOU HAVE DONE AND ESTABLISHED BY DOING THE EXPERIMENT. 208 Lab 4/5 report Introduction: Discuss/Connect the following topics: Light properties, waves, wavelength, electromagnetic spectrum and the differences between the energies, Spectral lines of energies. PROCEDURE : there are three parts 209 OBSERVATIONS: Data table, graph, rope measurements, data table from 3rd part. CONCLUSION – Discuss how elements are identified through the use of spectral lines of colors, how does this help us in establishing what is in stars. 210 DOPPLER EFFECT You must wonder how a police officer can detect how fast a car is going. Perhaps you have not gone into his car and noticed that his has a Doppler gun among his other instruments. The Doppler gun does not shoot out anything that can be seen. They shoot out energy waves (radio waves). 211 By judging the time/wave patterns from the gun to an object traveling ahead back to the gun it is possible to say whether the object is coming towards or away from the gun and how fast it is moving! 212 When a car is coming towards the Doppler gun the waves get crunched up as they bounce back from the car towards the gun. When the car is going away the waves are spread apart. 213 By looking at the differences in the wavelength (spaces between the crests), it is possible to judge the speed and direction of the car. Frequencies increase as the car approaches the gun and vice versa if the car is going away. 214 In terms of light energy, when an object that is emitting light approaches another object, the object that is being approached would experience higher frequency light energies. Remember that light is made up of six distinct frequencies. The blue end has more frequency than the red end in the spectrum of light. (ROYGBV) . 215 If an object that is giving out light approaches you at great speed you would see more blue end energies through a spectroscope as the frequencies are crunched up. This is the blue shift which means that the spectrum of light coming towards you would show a shift towards the blue end of the spectrum. 216 Since the waves are crunched up and show less wavelength and more frequency! More frequency means the blue end of the spectrum of light. 217 Similarly if a star (an object that is giving off light energy) is giving off light and is going away from you, then what you would see through a spectroscope would be a shift towards the red end of the spectrum. Since the wavelengths would be more and there would be less frequencies. 218 DOPPLER EFFECT. The object in the smallest circle in the picture is approaching a point and as it comes closer the waves get closer and as it goes away the opposite happens. THIS IS THE DOPPLER EFFECT. In terms of stars, when studying their spectrum there is only a red shift indicating that the light energy waves coming from stars are all showing large wavelength and less frequency, and thus the stars are moving away. 219 WHEN STARS WERE BORN When you consider that all light giving objects are moving away from each other and away from a certain point in space, it must be concluded that something must have happened to produce this motion away from that point. 220 Scientists have put forward the idea that it was a really ‘big bang’ that could have started this process. I f there was a big bang then the blasted stuff must be visible at the outer edges of the universe. This has been confirmed by the radiowaves that are present at the outer edges of universe moving outward. The Doppler effect thus confirms the ‘Big Bang’! 221 THE SPECTRUM OF STARS 222 By looking at the spaces between the color lines in the spectrum it is possible to say what kind of elements are in stars. 223 It is also possible to see the amount of red shift there is in the spectrum, and thus show how far away it is and what speed it is traveling away from us. 224 WHAT DID WE FIND OUT SO FAR? WHERE ARE WE HEADED? Matter is made up of elements Light is energy, it moves in a wave and it’s included in the midst of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is a list of energies arranged according to their frequencies. 225 TWINKLE TWINKLE LITTLE STAR, HOW I WONDER WHAT YOU ARE, UP ABOVE THE SKIES SO BRIGHT, LIKE A DIAMOND IN THE SKY Just like the nursery rhyme says we often wonder what those little points of light are. In the next few weeks we are going to try and find some answer to some of our questions about stars, and increase our wonder about them! Remember we understand so much about them, not because we are able to go to a star, but because of the light that comes from stars.. 226 WHERE DO WE GO FROM HERE? Where do elements come from? How do elements form? How do elements form everything we see or don’t see around us? 227 The only information we get from stars is in the form of light or other energies. This is of great significance when we consider the enormous distances between the stars and earth. 228 The nearest star is our sun and it is 150 million kilometers away from us. It takes light 8 minutes to reach us from the sun, traveling at 300,000km/sec. The nearest star, other than the sun is called Proxima Centauri (meaning near to the sun) Light would take 2 ½ years to get to earth traveling at 300,000 km/sec! 229 The amount of distance traveled by light in one year would be known as “one light year”. Although this is the case with light energy, and we are mindful of the fact that it takes ‘time’ for the information about stars to get to us, ‘light’ is the only “solid” source of information coming to us. 230 MORE ABT THE LAST TOPIC When the light from stars are studied through a sophisticated spectroscope it is possible to tell what elements are found on these stars. We can also establish by the elements present on the stars what stage in their life they are. In any case it is safe to conclude that the same elements that we are made of are made on stars. 231 Chapter 10 232 HOW DO STARS MAKE ELEMENTS? In order to answer this question you need to understand nuclear radiation and reactions. What is an element? An element is a substance that is made of only one kind of atom, like gold which is made up of parts that look and feel the same. These parts are called gold atoms. Cobalt is another one of these elements, but it is naturally radioactive. 233 Marie Curie the discoverer of radioactivity stated that to be radioactive an element’s atoms are giving off particles and energy naturally. These particles are extremely dangerous. The particles are called Alpha and Beta. The energy that is given off is known as gamma rays. 234 An element is called naturally radioactive when it spontaneously gives off parts of its nucleus. Each nucleus of cobalt atoms contain 27 protons and 32 neutrons, however when cobalt looses either an alpha, beta, and gamma rays, it changes to another element. 235 An alpha particle is made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, so when each atoms gives up an alpha particle it is giving away parts of its nucleus. If the proton number changes then it becomes a new element. 236 In fact Cobalt looses an alpha particle and becomes Zinc! Check your periodic table and see whether this is true. Zinc has 25 protons and Cobalt had 27 protons. 237 Carbon – 14 which is a radioactive element found in our bodies changes into Nitrogen – 12, this change makes it possible for us to tell how old a ‘mummy’ is by studying the amount of carbon and nitrogen there is in the body after death! 238 HOW FAR WILL THE RADIOACTIVE PARTICLES AND ENERGY TRAVEL? 239 240 RADIOACTIVITY AND CHANGING ELEMENTS. When radioactive elements loose alpha particles they change into other elements. However, there is a rate at which they do this. 241 The time in which half of the given material of radioactive material changes is called halflife. 242 If we have 100 grams of carbon-14, in about 5000 years half of it or 50 grams of the C-14 would have changed into another element (e.g. Nitrogen – 12) 243 All living things have C-14 in them. When they die the C-14 in them starts changing into N-12. No new Carbon 14 will be added to the body. 244 If for example, we find that there is exactly 50 g of C 14 and and 50 g of N 12 in a certain ‘mummy’ in Egypt, then it is possible to ascertain that the ‘mummy’ is about 5,270 yrs. 245 This is due to the fact that one half life (since the ratio between the two elements in the ‘mummy’ is exactly half) has gone by and the half life of C 14 is 5270 yrs! This is how ancient objects are dated. It is called Radioactive dating! 246 All radioactive elements have half lives. Some have very large half lives (Plutonium has a half life of 3 billion years) There are some that have a half life less than a small part of a second! Nevertheless, it is possible to measure the half-lives of radioactive elements. 247 STARS ARE COOKING! SO HOW DO STARS MAKE ELEMENTS? IN ORDER TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION WE NEED TO UNDERSTAND TWO KINDS OF NUCLEAR REACTIONS IN WHICH RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS ARE USED. THERE ARE TWO TYPES OF NUCLEAR REACTIONS. ONE IS NUCLEAR FISSION AND WE WILL DISCUSS THAT FIRST. 248 NUCLEAR FISSION IS A NUCLEAR REACTION IN WHICH THE NUCLEUS OF THE ATOM THAT TAKES PART IN THE REACTION SPLITS APART. THE ELECTRONS ARE TOO SMALL AND DO NOT EFFECT THE OUTCOME. IT IS THE PROTONS AND NEUTRONS IN THE NUCLEUS THAT TAKE PART IN THE REACTION. 249 WHEN A NUCLEAR FISSION DEVICE WAS EXPLODED OVER HIROSHIMA AND NAGASAKI, JAPAN IN THE 1940’s, THE JAPANESE SURRENDERED. JAPAN GAVE UP WHEN THEY WERE SUBJECTED TO SUCH DEVASTATION. A 10 MILE RADIUS IN NAGASAKI WAS FLATTENED. NOTHING REMAINED STANDING IN THIS AREA. 250 251 “COOKING” STARS Beyond the 10 mile radius, those who survived had to deal with the radioactive dust from the mushroom cloud of dust that was tossed up from the 10 mile radius at ground zero. 252 Within the 10 mile radius what someone on ground zero area would experience is energy (RADIATION) THAT TRAVELS THE FASTEST (300,000 km/sec). THEN COMES THE TREMENDOUS SOUND BLAST(Due to the enormous amounts of air that is shoved out of the way), AND FINALLY THE PIECES OF BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, ETC. !! HOW DOES SUCH A RELEASE OF ENERGY OCCUR? 253 IN A NUCLEAR FISSION REACTION A NEUTRON IS SHOT AT A NUCLEAR FISSIONABLE MATERIAL (URANIUM) AND EACH ATOM OF URANIUM SPLITS INTO TWO PARTS. A BARIUM ATOM AND KRYPTON ATOM PART AND TWO PROTONS. ONE OF THESE PROTONS MAY CHANGE INTO ENERGY. THIS SEEMS LIKE JUST TOO LITTLE TO CAUSE ANY DAMAGE. AS A PROTON IS SMALLER THAN AN ATOM! 254 THE NUCLEAR BLAST THIS IS WHERE EINSTEIN’S EQUATION EXPLAINS WHAT HAPPENS. IN HIS EQUATION E=MC2 , THE ‘E’ STANDS FOR ENERGY, ‘M’ FOR MASS AND ‘C’ FOR THE SPEED OF LIGHT (300,000 km/sec). EVEN THE MASS OF A PROTON BECOMES SIGNIFICANT WHEN IT IS MULTIPLIED BY THE SQUARE OF THE SPEED OF LIGHT. 255 WHICH IS 300,000 X 300,000 = 900,000,000,000 X ONE PROTON’S MASS! THIS IS WHY THE BOMB DROPPED OVER NAGASAKI BECOMES SIGNIFICANTLY POWERFUL SINCE IT WEIGHED ABOUT ONE KILOGRAM. 256 CAN YOU IMAGINE HOW MUCH ENERGY WAS RELEASED DURING THAT ONE INSTANT WHEN THE REACTION STARTED AND PROTONS HIT OTHER URANIUM ATOMS? THE CHAIN REACTION STARTED AND IN ALMOST AN INSTANT ONE KILOGRAM OF MASS WAS CONVERTED INTO A TREMENDOUS AMOUNT OF ENERGY CAUSING THE DESTRUCTION. 257 WHAT ABT COOKING STARS?!! THE REACTION THAT TAKES PLACE ON STARS IS SOMETHING CALLED A NUCLEAR FUSION REACTION. IN A NUCLEAR FUSION REACTION THE NUCLEUS OF TWO ATOMS ARE FUSED TOGETHER. 258 IN ORDER FOR THIS TO HAPPEN THERE HAS TO BE ENOUGH HEAT AND PRESSURE TO CREATE THE TEMPERATURE AND OTHER CONDITIONS NECESSARY FOR FUSION TO OCCUR. SEVERAL NUCLEAR FISSION REACTIONS WOULD BE REQUIRED TO BRING ABOUT THE HEAR REQUIRED FOR FUSION OF ATOMS. THERE IS A TREMENDOUS RELEASE OF ENERGY WHEN FUSING TAKES PLACE. 259 MORE MATTER IS CONVERTED INTO ENERGY IN A NUCLEAR FUSION REACTION, THAN IN A NUCLEAR FISSION REACTION. THIS IS WHY STARS ‘SHINE’ AS THEY ARE RELEASING TREMENDOUS AMOUNTS OF ENERGY, AND AT THE SAME TIME NEW ELEMENTS ARE BEING CREATED.! 260 NUCLEAR FUSION REACTION IN A NUCLEAR FUSION REACTION ATOMS FUSE OR JOIN TOGETHER TO FORM HEAVIER ATOMS. IN THIS PICTURE ATOMS OF HYDROGEN ‘D’ AND ‘T’ JOIN TO FORM ONE NEW HELIUM ATOM AND A SPARE NEUTRON. 261 IN A STAR THE TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE IS UNIMAGINABLE AND THEREFORE THE HELIUM COULD START FUSING TO FORM HEAVIER ATOMS. THIS FORMATION OF NEW ATOMS OF HEAVIER ELEMENTS WILL CONTINUE TILL IRON STARS TO FORM IN THE CORE OF A STAR. 262 Chapter 11 263 FUSING STARS! WHAT HAPPENS TO A STAR WHEN FUSION STARTS IS THAT NEW ELEMENTS START FORMING. INITIALLY THE HYDROGEN ATOMS FUSE TO FORM HELIUM. HYDROGEN IS THE MOST ABUNDANT ELEMENT IN THE UNIVERSE AND IS FOUND EVERYWHERE. 264 WHEN A STAR IS BORN THE HYDROGEN AND OTHER ELEMENTS THAT HAVE COME TOGETHER START TO CRASH INTO EACH OTHER AT GREAT SPEED AND THROUGH FRICTION A TREMENDOUS AMOUNT OF HEAT IS PRODUCED AND NUCLEAR FISSION STARTS. THIS IN TURN STARTS FUSION REACTIONS. HYDROGEN ATOMS WHICH HAVE ONLY ONE PROTON IN ITS NUCLEUS FUSES WITH ANOTHER HYDROGEN ATOM AND MAKES A NEW ATOM WITH TWO PROTONS IN ITS 265 NUCLEUS. THIS ATOM IS NO LONGER HYDROGEN. THE HYDROGEN FUSED TO FORM HELIUM. THE ENERGY RELEASED IN THIS FUSION REACTION IS MUCH MORE THAN FISSION REACTIONS. DURING ITS LIFE THE STAR WILL START TO FUSE NUMEROUS AMOUNTS OF ELEMENTS. OUR YELLOW DWARF STAR THE SUN DOES HAVE MORE HELIUM AND THEREFORE BURNS WITH A YELLOW COLOR. 266 STARS AND BLACK HOLES STARS VARY IN SIZE, COLOR, AND TEMPERATURE. A STAR’S COLOR IS RELATED TO ITS INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL TEMPERATURE. YOU CAN TELL HOW OLD A STAR IS BY LOOKING AT THE COLOR OF THE STAR. RED, YELLOW, BLUE, AND WHITE ARE THE FOUR STAR COLORS . 267 RED STARS HAVE THE LEAST TOTAL TEMPERATURE COMPARED TO THE REST. HOWEVER THEY ARE USUALLY THE OLDEST STARS. THE YELLOW, BLUE AND WHITE STARS ARE PROGRESSIVELY HOTTER! WHITE IS THE HOTTEST STAR. BLUE STARS ARE USUALLY YOUNG STARS THAT HAVE A LOT OF HYDROGEN AND HAVE JUST STARTED FUSION REACTIONS. THEY HAVE MORE HYDROGEN ATOMS THAN ANY OTHER KIND OF ELEMENT IN THEM. 268 YELLOW STARS LIKE OUR SUN ARE FUSING HELIUM. THE HYDROGEN THAT WAS IN IT, WAS USED TO MAKE MORE HELIUM. THE RED STARS ARE IN THE FINAL STAGES OF THEIR LIVES, AND HAVE MORE OF THE ELEMENT IRON IN THEIR CORES. THIS SETS THE STAGE FOR A NOVA, DUE TO THE IMMENSE PULL OF GRAVITY DUE TO THE IRON MASS IN THE CORE. 269 A SMALL YELLOW STAR LIKE OUR SUN WOULD EXPAND, WHEN ITS CORE BECOMES IRON. IT DOES NOT HAVE AS MUCH MASS AS A LARGER STAR LIKE ‘BETELGEUSE’ IN THE ORION CONSTELLATION. IT WILL LOOSE ITS MATERIAL IN A TIMID NOVA BY EXPANDING AND LEAVING A DENSE CENTER, A WHITE DWARF STAR. 270 271 WHEN OUR YELLOW STAR TURNS RED! 272 WHERE STARS ARE BORN AND GROW A STAR IS BORN IN A PLACE WHERE THERE IS A LOT OF MASS. THERE ARE MANY PLACES IN THE UNIVERSE WHERE THERE IS A LOT OF MASS. IN THE CONSTELLATION ORION THERE IS A PLACE CALLED THE ORION’S NEBULA. IN SUCH A PLACE THE MASS IS SUBJECTED TO FORCES THAT CRUSH IT TOGETHER. THIS IS DUE TO GRAVITY THAT DEPENDS ON THE MASS THAT IS THERE. 273 WHEN THERE IS ENOUGH HEAT AND PRESSURE THERE WILL BE A SUDDEN STARTING OF THE ENGINES. NUCLEAR REACTIONS SUCH AS NUCLEAR FUSION REACTIONS RESULT IN A TREMENDOUS RELEASE OF LIGHT ENERGY. THIS IS WHEN A STAR IS BORN. 274 AS HYDROGEN FUSES WITH OTHER ATOMS, NEW ELEMENTS ARE COOKED ON THE STARS. WHEN EVER A HYDROGEN ATOM FUSES WITH ANOTHER, A NEW ATOM WITH DOUBLE THE NUMBER OF PROTONS IN ITS NUCLEUS IS FORMED. SINCE PROTON NUMBER DETERMINES THE KIND OF ATOM (ELEMENT) THAT IS FORMED, STARS DO COOK ELEMENTS! THE STARS CHANGE COLOR. A MIDDLE AGED YELLOW STAR LIKE OUR SUN HAS HELIUM.. THEN AS THE MORE HEAVIER ELEMENTS ARE FORMED, THE STAR CONTINUES TO CHANGE COLOR UNTIL IRON FORMS, AND TURNS INTO A RED COLOR STAR. THIS SIGNALS THE END OF A STARS LIFE WHEN A NOVA COULD HAPPEN. 275 LIVES OF STARS ONLY THE CORE OF THE YELLOW STAR WOULD REMAIN, AFTER THIS EXPANSION. IN THE CASE OF A LARGE RED GIANT ITS MASSIVE IRON CORES STARTS TO ATTRACT EVEN THE STARS OUTER RIM INWARDS IN AN IMPLOSION. 276 THIS IMPLOSION WOULD CAUSE SUCH A SQUEEZE THAT EVEN THE ATOMS THAT MAKE UP THE STAR WILL LOOSES ITS STRUCTURE AND ELECTRONS AND PROTONS ARE RIPPED AWAY, LEAVING A DENSE CLUMP OF NEUTRONS – A NEUTRON STAR. 277 IN AN EVEN BIGGER STAR IT IS POSSIBLE THAT THE CRUSHING GRAVITATION PULL OF ALL THE MASS WOULD KEEP EVEN LIGHT FROM ESCAPING FROM ITS CLUTCHES AND A BLACK HOLE WOULD FORM. SUCH EVENTS ARE SAID TO HAVE OCCURRED IN THE CENTER OF GALAXIES. THIS IS THE FORCE THAT CAN KEEP BILLIONS OF STARS ROTATING AROUND IT, FORMING A GALAXY OF STARS! 278 STAGES OF A STAR’S LIFE. IN AN EXTREMELY LARGE RED GIANT STAR THE RESULTING SUPERNOVA WOULD SPREAD THE MATTER THAT WAS IN THE STAR INTO THE UNIVERSE. A LARGE SUPER RED GIANT WOULD CAUSE AN EVEN MORE SIGNIFICANT IMPLOSION (WHICH IS AN EXPLOSION THAT GOES INWARD) AND THE RESULTING MATTER BECOMES SO DENSE THAT IT WOULD NOT ALLOW EVEN LIGHT TO ESCAPE FROM ITS PULL. THIS WOULD RESULT IN THE FORMATION OF A BLACK HOLE. BLACK HOLES ARE NOT VISIBLE BUT THE MATTER THAT IS BEING PULLED INTO IT CAN BE RECORDED. BETELGEUSE IN THE ORION CONSTELLATION IS A PRIME CANDIDATE FOR THIS KIND OF A SITUATION. FOR ALL WE KNOW BY NOW IT HAS OCCURRED AND WE ARE STILL WAITING FOR THE LIGHT FROM THAT SUPERNOVA TO REACH US. ORION ALSO HAS A NEBULA WHERE YOUNG STARS HAVE JUST BEGUN TO LIGHT UP! 279 THE CONSTELLATION ORION HAS IN ITS MIDST, A PLACE WHERE STARS CAN BE BORN! ITS CALLED THE ORION’S NEBULA. 280 281 NEBULA’S ARE PLACES WHERE THERE IS ENOUGH MATERIAL TO START A STAR. 282 YOUNG STARS. YOUNG STARS THAT ARE ALMOST BLUE IN COLOR. THIS IS DUE TO THE STAR HAVING A LOT OF HYDROGEN IN THEM. 283 A MIDDLE AGED STAR! THE MIDDLE AGED STAR WHICH HAS A YELLOWISH RED TINGE IS BURNING ITS HELIUM CONTENT. ALL ITS HYDROGEN HAS BEEN USED UP AND IT CAN ONLY USE ITS HELIUM MASS. 284 285 286 WHAT DID WE SEE TILL NOW? For your Journal: If you travel from earth into outer space what might you pass first? Next? How do you account for day and night? Summer and Winter? Why are kilometers often inadequate for measuring distances in space? What do you use in their place? 287 WHAT WE DID TILL NOW AND WHERE WE ARE GOING……… These are the ideas we know now: 1. Stars have elements, 2. Stars send out elements when they die, like what is going on in the picture of 1996AA-C supernova in the next slide! 288 SUPERNOVA 1196AA.C 289 Could these elements that are sent out by stars get together and form earth like planets and new stars. A star is like a phoenix (from mythology) that can rise from its own ashes! What could help in bringing these elements come together to form planets and stars? 290 Chapter 12 291 In order to understand ARISTOTLE how matter that was 384-322BC thrown out by stars could form planets, you must consider what ‘motion’ is. Ancient greek philosophers, 3000 years ago, like Aristotle, Ptolemy, Aristarchus, and Eratosthenes, studied motion. 292 What puzzled them was how anything could move in space, what makes anything move, could anything move on its own, and what exactly is motion? They realized the importance of trying to understand motion. Aristotle proposed the idea that things that did not have life could not really move if there was no ‘force’ used. This set in motion 2000 years of misconception about motion. 293 AN IDEA! Folks at that time came up with the idea that a man called ‘Atlas was actually carrying earth on his shoulder, and if you tickled his armpits earth would fall into the eternal pit! Someone even suggested that if he was given a long enough lever he could move earth himself! Do you know who that was? 294 For about 2000 years people followed the ideas of Aristotle and Ptolemy until Copernicus arrived into the arena of science. He lived at a time that was beginning to be called the Renaissance when a lot of ideas were being hatched and old beliefs were being changed. Copernicus put forward the idea that the sun was the center of the solar system and the earth was a planet traveling around it. “If earth were moving where could heaven and hell be? Where would ‘Atlas’ be, now that he had no job!?” These were some questions that people may have asked during that time. 295 NICHOLAS COPERNICUS(1473-1543 296 To imagine an idea that was out of the ordinary, was frightening, even today. It would take more than just providing proof to make such changes in ideas. Copernicus would not publish his ideas and got a book that had all his ideas given to him when he was on his death bed. He never went against the wishes of the people of the day. 297 Galileo provided the mathematical and conceptual proof for the ideas that Copernicus presented. The first idea he resolved was that it was possible to have motion without force. He had already used a telescope that he built himself and seen the moons of Jupiter. He had to explain what made these moons and Jupiter itself to move by themselves 298 It is important to note that since Copernicus, the earth centered universe idea has been rejected. Shortly after Galileo’s time people such as Johannes Kepler and Tycho Brahe, had already established a lot about the night sky and the movements of the planets. 299 Galileo’s first task was to prove that it is possible to have motion without force. The words ‘motion’, ‘mass’, and ‘force’ will take on a new meaning by the time we see what Galileo and Newton did for us regarding the study of motion. The three concepts are related. Motion is universal, so therefore it occurs everywhere. There is nothing that does not move. This is not a generalized notion. 300 Where would there be no motion at all? 301 When you are sitting at your table on your chair, are you moving? Obviously not!?? Actually you are, if you consider the billions of atoms that you are made up off that have electrons that buzz around the nucleus at close to 300,000 km/sec. Also, if you consider that you are on the earth that revolves at 30 m/sec and goes around the sun at 330,000 km/hr, you are moving!! 302 GALILEO SEES THE LIGHT! THIS HEADING COULD PROBABLY HAVE BEEN THE HEADLINES FOR THAT DAY WHEN GALILEO DISCOVERED THAT THERE WERE OTHER SATELLITES REVOLVING AROUND OTHER PLANETS. GALILEO WOULD HAVE LOOKED OUT AT THE STARS EXACTLY AS SHOWN IN THE PICTURE. HE BUILT THE TELESCOPE HIMSELF. THE PAPER SHOWN ALONGSIDE, IS IN HIS OWN HAND AND SHOWS WHAT HE HAD NOTED DOWN WHEN HE SAW THE FOUR MOONS OF THE PLANET JUPITER.. 303 THE ENTIRE SOLAR SYSTEM REVOLVES AROUND THE MILKY WAY GALAXY’S CORE . SINCE THE ‘BIG BANG’ THE GALAXY ITSELF IS MOVING AWAY FROM SOME POINT IN SPACE AT CLOSE TO THE SPEED OF LIGHT! IF THIS IS THE CASE THEN THERE IS NOTHING THAT IS NOT MOVING! HOWEVER, THERE IS ONE PLACE WHERE THERE WOULD NOT BE ANY MOTION. THAT IS A PLACE WHERE THE TEMPERATURE IS EXTREMELY LOW. 304 THIS TEMPERATURE MUST BE MEASURED IN A SPECIAL SCALE, (WHICH HAPPENS TO BE THE STANDARD UNIT OF MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE) THE KELVIN SCALE. IN OTHER WORDS THE PLACE THAT IS SUBJECTED TO 0 KELVIN OR –273O CELSIUS WOULD HAVE NOTHING MOVING. INCLUDING THE ELECTRON THAT IS ZIPPING AROUND THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM. AT 0 KELVIN THE ELECTRON WOULD NO LONGER BE ABLE TO RESIST THE PULL OF THE NUCLEUS AND IT WILL BE PULLED INTO THE NUCLEUS. THIS WOULD RESULT IN THE ATOM LOOSING ITS SPACE BETWEEN THE NUCLEUS AND THE ELECTRONS. 305 THIS WOULD MEAN THAT THE ENTIRE ATOM WOULD LOOSE ALL ITS VOLUME AND BE REDUCED TO A MINISCULE PORTION OF ITS ORIGINAL SIZE. IN OTHER WORDS IF YOU WERE TO TAKE A MOUNTAIN AND REDUCE ITS TEMPERATURE TO 0 KELVIN THEN IT WOULD BE REDUCED TO A MICROSCOPIC SIZE! 306 WHAT DOES THIS ALL MEAN? IT IS CLEAR THAT MOTION IS REALLY VERY NECESSARY TO IMAGINE OUR UNIVERSE THE WAY IT IS. WITHOUT MOTION THE UNIVERSE WOULD LOOK AND FEEL VERY STRANGE?!?? NEXT YOU NEED TO CONSIDER THAT MOTION IS RELATIVE. 307 THIS MEANS THAT IF YOU WERE TO SEE A BIRD FLY IN THE SKY AND NOTICE AT THE SAME TIME A PLANE THAT FLIES ABOVE THE CLOUDS IT IS POSSIBLE TO THINK THAT THE BIRD IS FLYING FASTER THAN THE PLANE. IT SEEMS THAT WAY BECAUSE THERE IS NO REFERENCE POINT BEYOND THE PLANE TO COMPARE ITS MOTION TO, AS OPPOSED TO THE BIRD THAT HAS ALL THE TREES AND OTHER MATERIAL THAT IS ON THE GROUND THAT WE CAN COMPARE THE BIRD’S FLIGHT TO. 308 THEREFORE MOTION MUST BE RELATED TO A BACKGROUND OR REFERENCE POINT, TO ACTUALLY KNOW THAT MOVEMENT IS TAKING PLACE.! THE EARTH IS MOVING BUT THIS IS IMPOSSIBLE TO SEE TILL IT PASSES CLOSE TO ANOTHER PLANET. IT WOULD BE DIFFICULT TO COMMUNICATE WHAT YOU KNOW ABOUT MOTION WITHOUT MEASUREMENT. THE SIMPLEST WAY TO MEASURE MOTION IS TO USE SPEED. 309 HOW FAST ARE WE MOVING? IF YOU CAN FIND OUT WHAT THE SPEED OF EARTH’S ORBIT AROUND THE SUN, THEN YOU DESERVE CREDIT! HOW FAST DOES A GALAXY MOVE? IS OUR GALAXY MOVING? IF OUR GALAXY IS MOVING THEN WE MUST BE MOVING TOO WITH IT! 310 SPEED IS DISTANCE DIVIDED BY TIME. THEREFORE SPEED IS A RATE. A RATE IS ANY QUANTITY DIVIDED BY TIME. BY VIRTUE OF BEING DIVIDED BY TIME ANY PRODUCT BECOMES A RATE. LAB 6 – IN THE PHYSICS 500 LAB CALCULATE THE SPEED FOR THREE DIFFERENT RACES. EACH RACE MUST BE RUN THREE TIMES SO WE CAN GET AN AVERAGE SPEED. THE DATA TABLE WILL LOOK LIKE THIS: RACE 1 – TRIAL DIST TIME SPEED 1 26m 5sec 26/5 = 5.1m/s 2 26m 4sec 26/4 = 6.2m/s etc. etc…. Avg. spd? 311 IN THE NEXT PART OF THE SAME LAB WE SHALL STUDY THE SPEED OF DOMINOES KEPT AT DIFFERENT SPACES FROM EACH OTHER. THE DATA TABLE WOULD LIKE THIS: DIST TRL1 TRL2 T3 AVG. SPEED TIME D/T 0.5cm 1s 1.5 1.25 1.25s. 5cn/1.25s 1.0cm 2s 2.3 2.5s 1.5cm 3s ETC….. IN THIS DATA TABLE THE DISTANCE REFERS TO THE SPACE BETWEEN THE DOMINOES IN EACH TRAIL. REPEAT EACH DIST TWICE SO YOU CAN HAVE AN AVERAGE TIME. 312 INTRO TOPICS: MOTION (DISCUSS THE TOPIC AND USE NOTES) MEASURING MOTION – SPEED – DIST/TIME PROCEDURE – 2 PARTS – PART 1 PHYSICS 500 – RACES PART 2 DOMINO SETUP OBSERVATION – 2 DATA TABLES GRAPH – DIST / SPEED X’ / Y” CONCLUSION: A. DEFINITION OF SPEED B. WHAT EFFECTS THE SPEED OF THE DOMINOES C. WHAT WAS THE MAXIMUM SPEED FOR THE DOMINOES D. WHICH SPACING RESULTED IN THE FASTEST SPEED? WHY? 313 Moving from measuring motion to trying to understand how motion could occur without the use of force is a natural step. MOVING FROM MEASURING MOTION TO TRYING TO UNDERSTAND HOW MOTION COULD OCCUR WITHOUT THE USE OF FORCE IS A NATURAL STEP. ALTHOUGH COPERNICUS HAD GIVEN US THE VIEW THAT THE EARTH WAS NOT THE CENTER OF THE UNIVERSE. IT WAS NOT UNTIL GALILEO'S THAT THIS WAS CONSIDERED POSSIBLE. THE GREATEST DILEMMA SINCE THE DAYS OF ARISTOTLE AND PTOLEMY WAS THAT THE EARTH COULD NOT BE MOVING AS IT WOULD REQUIRE AN ENORMOUS AMOUNT OF FORCE TO ACCOMPLISH. AS SOON AS THIS ISSUE WAS RESOLVED IT WAS POSSIBLE TO IMAGINE EARTH MOVING. GALILEO SET OUT TO PROVE THAT IT WAS NOT NECESSARY TO HAVE FORCE APPLIED CONSTANTLY TO HAVE MOTION OCCUR , ONCE MOTION HAD BEGUN. HE MADE SEVERAL RAMPS ON WHICH HE STUDIED AND MEASURED MOTION. THIS RAMP WAS SHAPED LIKE A CURVED SEMICIRCLE. IF A METAL BALL WAS RELEASED AT THE TOP OF THIS SMOOTH RAMP IT COULD BE SEEN THAT THE BALL WOULD TRAVEL TO THE OPPOSITE END AND REACH THE SAME HEIGHT ON THE OTHER SIDE. IF YOU WERE TO EXTEND THE SIZE OF THE RAMP TO BE 314 SUCCESSFULLY LONGER IT WOULD STILL HAVE THE SAME IF THE RAMP WERE STRETCHED TO INFINITY THEN THAT BALL WOULD CONTINUE MOVING AT THE SAME SPEED THAT IT STARTED WITH, UNLESS IT COMES INTO CONTACT WITH ANOTHER FORCE. IN OTHER WORDS THE BALL WOULD KEEP MOVING FOREVER. THUS EVEN THE EARTH DOES NOT NEED ANY FORCE TO KEEP IT MOVING ONCE IT HAS STARTED TO MOVE. GALILEO WAS ABLE TO PROVIDE EXPERIMENTAL AND VISUAL PROOF THAT THIS WAS HAPPENING. HOWEVER HE WAS NOT ABLE TO EXPLAIN WHY THIS PHENOMENON WAS TRUE. IT TOOK THE GENIUS OF ISAAC NEWTON TO EXPLAIN WHY THIS HAPPENS. INERTIA IS A CONCEPT THAT DID NOT EXIST TILL NEWTON. THAT AN OBJECT COULD KEEP MOVING FOREVER IN SPACE WITH NO FRICTIONAL FORCES OR ANY OTHER FORCE WAS PROVED BEYOND DOUBT BY GALILEO BUT WHAT MAKES AN OBJECT DO THIS? IF YOU CONSIDER THE MANY ACTIVITIES WE DID IN CLASS I.E. THE RULER AND THE FINGER CATCH, THE COIN AND CARD TRICK, THE HOOP AND COIN TRICK, THE TABLECLOTH AND CHINA TRICK, ALL POINT TO THE EXISTENCE OF INERTIA WHICH IS THE ABILITY OF ANYTHING WITH MASS TO REMAIN AT REST OR KEEP MOVING WHEN NO OTHER FORCE IS APPLIED. 315 SPACE MOVEMENT THERE IS NOTHING PUSHING THE ASTRONAUTS OR THE SPACE STATIONS, THEY WILL KEEP MOVING UNTIL ANOTHER FORCE COMES INTO CONTACT WITH IT. IN OTHER WORDS THERE IS NO NEED TO KEEP GIVING FORCE TO AN OBJECT THAT IS ALREADY MOVING WHEN THERE IS NO OTHER FORCE. THE OBJECT WILL MOVE IN A STRAIGHT LINE FOREVER! THANK GOODNESS FOR GRAVITY! 316 LAB 7 IN THIS LAB WE ARE DOING A SET OF SIX ACTIVITIES TO INVESTIGATE FORCES. AT THE END OF THE SIX ACTIVITIES A DATA TABLE MUST BE MADE, LISTING THE STATION, THE OBSERVATIONS, AND THE FORCES THAT WERE NOTICED AT EACH ACTIVITY STATION. THE CONCLUSION QUESTIONS TO THE LAB WERE A) WHAT FORCES WERE IN PLAY AT EACH STATION B) WAS THERE ONLY ONE FORCE ACTING AT ANY STATION THAT YOU WERE AT. 317 ACCELERATION! WHEN GALILEO WENT TO THE TOWER OF PISA AND DROPPED TWO IRON BALLS, ONE WHICH WAS MUCH BIGGER THAN THE OTHER, HE DID NOT INTEND TO SHOW THAT THEY BOTH WOULD REACH THE GROUND AT THE SAME TIME. ON THE OTHER HAND HE WAS TRYING TO SHOW THAT THEY WOULD BOTH BE ACCELERATING TOWARDS THE GROUND AT THE SAME RATE. IN ORDER TO UNDERSTAND WHAT HE WAS TRYING TO PROPOSE, THE CONCEPT OF ACCELERATION MUST BE CLEAR. ACCELERATION IS THE CHANGE IN SPEED IN A GIVEN PERIOD OF TIME. BUT IT IS ALSO A RATE OF A RATE: ACC = SPEED/TIME = D/T/T= m/s/s WHENEVER YOU DIVIDE ANY QUANTITY BY TIME YOU HAVE A RATE. SO WHEN ACCELERATION IS CALCULATED YOU ARE DIVIDING SPEED (WHICH IS A RATE) BY TIME, THEREFORE ACCELERATION IS A RATE OF A RATE. 318 1ST LAW OF NEWTON TRIES TO EXPLAIN HOW MOTION COULD OCCUR WITHOUT FORCE. JUST AS GALILEO HAD PREDICTED. NEWTON’S 1ST LAW HOWEVER GAVE THE REASON TO WHY MOTION WITHOUT FORCE IS POSSIBLE. INERTIA IS THE ABILITY OF OBJECTS WITH MASS TO KEEP IN MOTION OR REMAIN AT REST, UNLESS ACTED UPON BY ANOTHER FORCE. IN THIS DEFINITION IT IS QUITE CLEAR THAT IS IS INERTIA (THAT ABILITY THAT MATTER HAS IF IT HAS MASS ) THAT ACTUALLY CAUSES MOTION TO OCCUR WITHOUT CONTINUALLY APPLYING FORCE. THE WORDS MASS, INERTIA, AND FORCE MUST BE USED IN ORDER TO UNDERSTAND AND DEFINE NEWTON'S 1ST LAW. 2ND LAW OF MOTION : DESCRIBES WHAT HAPPENS TO MOTION WHEN FORCE IS APPLIED. THE FIRST RELATIONSHIP TO UNDERSTAND IS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN FORCE AND MOTION. WHEN THERE IS MORE MOTION THERE MUST HAVE BEEN MORE FORCE APPLIED. FOR EXAMPLE IF YOU PUSH A TOY CAR WITH A TOUCH OF YOUR FINGER THEN YOU WOULD FIND IT MOVING JUST A BIT, HOWEVER IF YOU PUSHED WITH ALL YOUR FINGERS WITH MORE FORCE YOU WOULD MAKE IT MOVE MUCH FASTER. 319 WHAT NEWTON SAYS….. 320 AND NEWTON SAYS…..! 321 AND NEWTON SAYS…! 322 GO ROCKET GO! ROCKETS BUILT BY USING CONSTRUCTION PAPER AND FILM CANISTERS WERE DONE TO SHOW THE 3RD LAW OF NEWTON THAT ALL FORCES ACT IN PAIRS. THERE IS NO FORCE THAT IS FOUND BY ITSELF. THUS WHEN THE FILM CANISTER WITH THE ALKA SELTZER TABLET AND THE WATER IS ENCLOSED THE RESULTING GAS PRODUCTION CAUSES THE FORCE TO ACT DOWNWARDS AND THE FLOOR PUSHES UP WITH EQUAL FORCE AND THE ROCKET GOES UP! 323 HOW CAN WE TELL SOMEONE WHERE WE ARE IN SPACE? THE VIDEO IS ABOUT HOW PEOPLE CAME TO USE LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE AND WHY IT WAS SO IMPORTANT FOR PEOPLE TO KNOW HOW TO MOVE FROM ONE END OF THE EARTH TO THE OTHER. UNLESS THERE WAS A WAY OF MEASURING HOW FAR AND WHERE YOU WERE GOING IT WOULD BE IMPOSSIBLE TO TRAVEL ANYWHERE WITH ANY CERTAINTY. JOHN HARRISON WAS A CARPENTER WITH A SPECIAL GENIUS FOR UNDERSTANDING HOW TO MEASURE TIME IN A VERY PRECISE MANNER WITH THE INSTRUMENTS THAT WERE AVAILABLE TO HIM AT THAT TIME. BEING ABLE TO MEASURE TIME EXACTLY HELPED IN ESTABLISHING WHERE YOU WERE IN THE OCEAN BY LOOKING AT THE TIME AND WHERE THE SUN WAS WHEN YOU WERE TRYING TO SEE WHERE YOU WERE. LONGITUDE IS THE LINES GOING EAST AND WEST, AND LATITUDE IS LINES GOING NORTH AND SOUTH. YOU CAN EVEN HAVE A CELESTIAL SPHERE AND HAVE LINES OF LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE ON IT! 324 SUMMING UP. EVERYTHING IS IN MOTION EXCEPT AT 0 KELVIN. INSIDE STARS ELEMENTS ARE BEING CREATED. THESE ELEMENTS ARE CREATED BY FUSION/FISSION REACTIONS. STARS UNDERGO NOVA/SUPERNOVAS AND SEND OUT THE MATERIAL THAT THEY ARE MADE UP OF. WHEN THEY SEND OUT MATERIAL THE STUFF THAT IS REMAINING BECOMES NEW SMALLER STARS, FORM MATERIAL THAT COULD BECOME NEW STARS. WHEN STARS EXPLODE THEY GO THROUGH A PERIOD OF IMPLOSION AND THEN EXPLOSIONS WHEN THEY EXPLODE THEY GO OUTWARD AT A CERTAIN SPEED. SPEED CAN BE CALCULATED BY DIVIDING DIST BY TIME. THE INERTIA THAT THIS MATERIAL HAS DUE TO ITS MASS ENABLES IT TO KEEP MOVING IN SPACE UNTIL IT COMES ACROSS SOME OTHER FORCE. THE MOTION ASSOCIATED WITH THIS MATERIAL THAT IS COMING OUT OF STARS IS MEASURED IN TERMS OF SPEED AND ACCELERATION. 325 ACCELERATION DEPENDS ON TWO FACTORS. MASS AND FORCE. ACCELERATION IS DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO FORCE SO IF THERE IS MORE FORCE THERE WILL BE MORE ACCELERATION. SIMILARLY MASS IS INDIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO ACCELERATION. If THERE IS MORE MASS THERE WILL BE LESS ACCELERATION. ALSO THE AMOUNT OF MASS DETERMINES THE AMOUNT OF INERTIA AND THE GRAVITY. IN OTHER WORDS MORE MASS, MORE INERTIA, AND MORE GRAVITY. SPEED IS A RATE THAT MEASURES THE AMOUNT OF DISTANCE COVERED, AND THE ACCELERATION IS THE AMOUNT SPEED CHANGES IN A CERTAIN TIME. CELESTIAL SPHERES AND LONGITUDES AND LATITUDES HELP US SHOW WHERE THIS MATTER IS IN THE UNIVERSE AND HOW WE CAN FIND IT. FORCES ALWAYS ACT IN PAIRS. WHEN THERE IS ONE FORCE THERE WILL BE AN EQUAL AND OPPOSITE FORCE. “TANK” ABOUT IT! IF A MOUSE AND AN ELEPHANT WERE TO COLLIDE WITH YOU IN SPACE, WHERE ALL THINGS ARE WEIGHTLESS, WHICH ONE WOULD HURT MORE, THE MOUSE OR THE ELEPHANT? WHY? NEWTON REALIZED THAT THE SUN PULLS ON THE EARTH WITH THE FORCE OF GRAVITY AND CAUSES THE EARTH TO MOVE IN ORBIT AROUND THE SUN. DOES THE EARTH PULL EQUALLY ON THE SUN? DEFEND YOUR ANSWER. 326 Chapter 13 327 What did you see when you looked at salt powder through a microscope? What did the little cubes represent? Crystals are made up of compounds joining together to form special 3 - dimensional shapes. Compounds themselves are made up of elements. 328 A lot of crystals together form a piece of mineral. Minerals can be pretty, shiny, flaky and dull. In the smashed rock dust that you saw under a microscope there were three distinct mineral crystals. You cannot see the crystal structure since there were only a few molecules of compounds attached together. 329 There many minerals. More than 2000 combinations of elements producing all different varieties of minerals. They generally fall into 2 categories. Those that have silicate in them and those that do not! The non-silicate variety of mineral can be further divided into ,halides, carbonates, sulfates, oxides, 330 331 WE WILL BE STUDYING THESE MINERALS AND HOW TO IDENTIFY THEM. 332 MINERALS HAVE MANY CHARACTERISTICS OR DISTINGUISHING FEATURES THAT MAKE THEM UNIQUE. EACH ROCK MAY CONTAIN MANY MINERALS MIXED TOGETHER. MINERALS ARE USUALLY FOUND IN DEFINITE CRYSTAL SHAPES. FOR EXAMPLE SALT IS FOUND TO BE IN CUBED CRYSTALS. SALT OR HALITE ROCKS ARE COMMON IN CERTAIN PARTS OF THE WORLD. 333 HARDNESS SCALE The hardness scale is one of the methods of identifying minerals. 1.Talc 8. Topaz 2.Gypsum 9. Corundum 3.Calcite 10. Diamond 4.Flourite 5.Apatite 6.Feldspar (orthoclase) 7.Quartz. 334 TEST 1 – COLOR. ALTHOUGH COLOR IS THE EASIEST TEST TO CONDUCT IT WILL PROBABLY BE THE MOST UNRELIABLE SINCE THERE MAY BE MANY MINERALS THAT HAVE THE SAME COLOR. ALSO THERE COULD BE MINERALS THAT COME IN SEVERAL COLORS. BUT IT IS A START. YOU CAN NARROW IT DOWN! TEST 2 – TEXTURE. THE FEEL OF THE MINERAL. TEST 3 – STREAK. USE A STREAK PLATE TO CONDUCT THIS TEST. FIRMLY RUB THE MINERAL ON A STREAK PLATE TO PRODUCE POWDER ON THE PLATE. IF IT HAS A DARK STREAK IT IS PROBABLY HAS A LOT OF METALS IN IT. TEST 4 – LUSTER. THE AMOUNT OF LIGHT THAT REFLECTS OF THE MINERAL IS A DISTINCTIVE FEATURE OF THAT MINERAL. IN THE CASE OF SOME THERE IS A METALLIC LUSTER, AND IN OTHERS GLASSY AND DULL ETC. DESCRIBE TO THE BEST OF YOUR KNOWLEDGE WHAT THE LUSTER IS. USE AN APPROPRIATE ADJECTIVE TO DESCRIBE THE LUSTER. 335 TEST 5 - HARDNESS. USE THE MOTH'S HARDNESS SCALE TO INDICATE THE HARDNESS. TEST 6 – CLEAVAGE. WHEN THE MINERAL HAS DEFINITE FACES IN WHICH IT BREAKS OFF THEN IT HAS CLEAVAGE. FOR EXAMPLE SOME MINERALS COME IN CUBES, OTHERS IN 8 FACE SHAPED CRYSTALS. DEPENDING ON THESE FACES THE MINERALS CLEAVAGE IS DETERMINED. TEST 7 – FRACTURE. THIS INDICATES WHETHER HOW THE MINERAL BREAKS. IF IT BREAKS IRREGULARLY THEN IT HAS FRACTURE. DENSITY – MEASURE THE MASS AND THE VOLUME OF THE MINERAL. MEASURE THE VOLUME OF THE MINERAL BY USING THE METHOD TO MEASURE THE VOLUME OF IRREGULAR SOLIDS. 336 Actually testing for minerals is harder than you think. If you can scratch the mineral with your nail and it leaves a mark, the hardness will be between 0 to 2. If a copper penny leaves a mark the hardness is probably between 2 and 3. If a hard nail leaves a mark but the a nail nor a penny leaves a mark then the hardness is probably between 5 and 6. 337 If your mineral leaves a mark on glass then the mineral’s hardness is probably between 7 and 8. 338 Chapter 14 339 THE CRUST OF THE EARTH IS BROKEN INTO PLATES. THESE PLATES ARE KNOWN TO MOVE. CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY GIVES A REASON FOR THE MOVING CRUST. THE CRUST COULD BE MOVING BY CONVECTION CURRENTS IN THE MANTLE AND OUTER CORE. CONVECTION CURRENTS ARE THE MOVEMENT OF HOTTER MATERIAL UPWARD AND COLDER MATERIAL DOWNWARD DUE TO CHANGE IN DENSITY OF THESE MATERIALS. FOR EXAMPLE HOT AIR RISES ON EQUATORIAL REGIONS OF THE EARTH DUE TO HOT AIR HAVING LESS DENSITY AND THEN WHEN IT RISES TO A CERTAIN ELEVATION IT COOLS DOWN AND SINKS DUE TO ITS HIGH DENSITY WITH THE ATOMS IN THE AIR COMING CLOSER TOGETHER. THIS CYCLE IS REPEATED AND CAUSES AND CONVECTION CURRENT. CONVECTION CURRENTS ARE THE MACHINES THAT DRIVE THE CONTINENTAL PLATE MOVEMENT. CONTINENTAL PLATE MOVEMENT CAN ALSO BE SEEN BY THE MOVEMENT OF T HE CONTINENTS AND THE SIMILARITY OF GEOGRAPHICAL AND LIVING FEATURES IN CONTINENTS THAT ARE FAR APART. 340 FISSURES ARE HOLES IN THE CRUST OF THE EARTH AND COULD LEAD DEEP DOWN TO MAGMA PITS WHICH ARE LARGE RESERVOIRS OF MAGMA. THE HOT GASES THAT COME OUT OF FISSURES ARE USUALLY SULFUR DI OXIDE AND CARBON GASES. THERE IS ALSO POSSIBILITY OF STEAM DEPENDING ON THE AMOUNT OF WATER CONTENT IN THE ROCK STRATA. THEY ARE SUPERHEATED GASES AND CAN BE AT SEVERAL HUNDRED DEGREES. CONTINENTAL PLATE MOVEMENT IS THE SOURCE OF VOLCANIC ACTIVITY. THIS MOVEMENT CAUSES THE FORMATION OF FISSURES, THROUGH WHICH MAGMA OR HOT GASES COULD COME UP. SINCE THESE GASES AND MAGMA ARE KEPT UNDER SUCH PRESSURE. WHEN THIS MATERIAL IS RELEASED THROUGH A FISSURE THERE IS A TREMENDOUS RATE OF FLOW OUTWARD THROUGH THE FISSURE. 341 IF THERE IS A LOT OF GASES AND STEAM TRAPPED WITHIN THE MAGMA THEN THE RELEASE OF ENERGY IS MORE VIOLENT AND WE SEE PRELATIC EVENTS. A PYROCLASTIC EVENT IS ASSOCIATED WITH STRATA VOLCANOES WHICH SEND OUT LAVA BOMBS AND SUDDEN RELEASE OF SPOUTS OF MAGMA ACCOMPANIED BY MASSIVE EARTH MOVEMENTS. MT. ST. HELENS WAS A GOOD EXAMPLE OF THIS KIND OF VOLCANO. TAR PITS ARE THOSE AREAS WHERE TAR HAS BEEN RELEASED THROUGH FISSURES/VENTS IN THE EARTH’S CRUST THROUGH WHICH TAR WHICH IS FORMED FROM ANCIENT SEDIMENTS COME UP TO THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. PUMICE IS THE LAVA ROCK THAT FORMS WHEN THERE IS A LOT OF AIR POCKETS IN THE MAGMA. IT IS A LIGHT IGNEOUS ROCK. GRANITE IS FOUND FORMED IN SITES WHERE THE MAGMA COOLED UNDERGROUND SLOWLY. BASALT AND RHYOLITE ARE IGNEOUS ROCKS THAT HAVE FORMED FAIRLY QUICKLY AFTER VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS. OBSIDIAN IS ANOTHER IGNEOUS ROCK THAT FORMS VERY QUICKLY ON THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. 342 SUDDEN RELEASE OF ENERGY CAUSES EARTHQUAKES. (P,S, AND L). PRIMARY WAVES BEHAVE LIKE DOMINOES HITTING ONE ANOTHER AND THE ENERGY TRAVELING FORWARD PASSING FROM ONE PIECE OF MATTER TO THE OTHER. SECONDARY WAVES ARE LIKE WAVES AND UNDULATE. THEY CAUSE AN UP AND DOWN MOTION OF THE MATTER AS ENERGY PASSES THROUGH IT. LARGE WAVES ARE VERY COMPLICATED WAVES OF ENERGY THAT CAUSE A SIDE WAYS AND UP AND DOWN MOVEMENT. L- WAVES CAUSE THE MOST DAMAGE. S-WAVES CANNOT PASS WELL THROUGH LIQUIDS. P- WAVES COULD PASS THROUGH MOST MATERIAL. EARTHQUAKE WAVES CAN BE USED TO ESTABLISH THE PARTS OF THE EARTH. THE EARTH HAS FOUR DISTINCTIVE REGIONS IN IT. THE CRUST IS WHAT WE LIVE ON, BELOW IT IS THE MANTLE, BELOW THE MANTLE IS THE OUTER CORE AND IN THE CENTER IS THE INNER CORE.. THIS CAN BE ESTABLISHED BY TRACING THE PATH OF P AND S WAVES AS THEY TRAVEL THROUGH THE EARTH. P-WAVES TRAVEL THROUGH THE EARTH WITH A CERTAIN PATTERN. AS THEY PASS THROUGH THE MANTLE THEIR SPEED INCREASES STEADILY UNTIL IN THE REGION OF THE CORE ITS SPEED IS THE MOST. THIS INDICATES TO US THAT THERE ARE DISTINCTIVE AREAS OF DENSITY. THE INNER CORE BEING THE MOST DENSE AND THE OUTER CORE NEXT, AND THE LEST DENSE IS THE MANTLE. SECONDARY WAVES DO NOT PASS THROUGH THE OUTER CORE BECAUSE IT CONTAINS MATERIAL THAT IS LIQUIDIZE IN COMPOSITION. 343 WHENEVER THERE ARE ANY EMERGENCIES IN A STATE OR CITY THE OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT TAKES OVER THE SITUATION TO HANDLE IT. THE IDEA IS TO HAVE A CENTRAL OFFICE AND OFFICER HANDLING THE SITUATION. WE LEARNT FROM THE MOVIE ‘VOLCANO’ THAT PRECEDING VOLCANIC ACTIVITY THERE IS ALWAYS SEISMIC ACTIVITY. BY SEISMIC ACTIVITY WE MEAN THAT THE EARTH SHAKES OR QUAKES. THIS SHAKING CAN BE RECORDED ON A RICHTER SCALE. IN RUNS FROM 1 TO 10 . 1 BEING THE LEAST POWERFUL AND 10 THE MOST POWERFUL. THERE ARE OTHER MEASURES AND UNITS BUT THIS IS THE MOST COMMON ONE. EARTH TREMORS AND GAS RELEASE ARE PRELIMINARY INDICATORS OF POSSIBLE VOLCANIC ACTIVITY. 344 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS CONGLOMERATE, BRECCIA, SANDSTONE (CLASTIC – ROCKS WITH PIECES OF ROCK EMBEDDED, THESE ROCKS HAVE VARIOUS SIZES OF SEDIMENT IN THEM, CONGLOMERATE HAVING THE LARGEST PIECES AND SANDSTONE HAVING THE SMALLEST PIECES) SHALE, SILTSTONE, LIMESTONE ARE OTHER EXAMPLES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. LIMESTONES HAVE FORMED FROM SEDIMENTS IN OCEANS. SHALE AND SILTSTONE ARE MADE UP OF VERY FINE SEDIMENTS. SEDIMENTS FORM THROUGH TWO KINDS OF WEATHERING. WEATHERING IS THE BREAKING DOWN OF ROCKS INTO SMALLER, AND SMALLER PIECES. MECHANICAL WEATHERING IS THE BREAKING DOWN ROCKS BY MECHANICAL MEANS. WATER IS THE ONLY COMPOUND THAT EXPANDS WHEN IT FREEZES. WATER GETS INTO CRACKS IN THE ROCKS AND DURING COLD WEATHER FREEZES, EXPANDS AND BREAKS DOWN ROCK. OTHER KINDS OF AGENTS THAT CAUSE MECHANICAL WEATHERING IS WIND ACTION AND GRAVITATIONAL FORCES THAT BRING ROCKS DOWN ON OTHER ROCKS AND BREAK THEM UP. THESE SEDIMENTS THAT ARE FORMED ARE CARRIED BY MOVING WATER. THE FASTER THE MOVEMENT OF WATER THE MORE SEDIMENT THAT IS CARRIED. THEREFORE A RIVER LIKE THE MISSISSIPPI COULD CARRY A LOT OF SEDIMENT. THIS SEDIMENT IS THEN DEPOSITED DEPENDING ON THE SPEED OF THE CURRENT. AS IT NEARS THE DELTA, THE RIVER SLOWS AND DEPOSITS THE HEAVIER SEDIMENT AND THEN FINALLY AS IT ENTERS THE OCEANS IT SLOWS DOWN COMPLETELY AND DEPOSITS THE VERY FINE 345 SEDIMENTS. THE SEDIMENT THEN LIES THERE AND HAS MANY OTHER LAYERS OF SEDIMENTS THAT IS PILED UP ON TOP OF IT. OVER THE YEARS (MILLIONS) THESE LAYERS GET COMPACT AND CEMENTED AND FORM SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. SEDIMENT THAT PILES UP IN OCEANS FORM LIMESTONE. THESE ROCKS CONTAIN REMAINS OF OCEANIC CREATURES. PLACES WHERE LIMESTONE IS FOUND WERE UNDER THE OCEAN AT SOME TIME DURING THERE LIFE. 346 Metamorphic Rocks 347 The Rock Cycle 348 GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE. PRECAMBRIAN, PALEOZOIC, MESOZOIC, AND CENEZOIC ARE THE FOUR ERAS THAT EARTH’S AGE IS DIVIDED INTO. PRECAMBRIAN STRETCHED FROM THE BIRTH OF THE PLANET TO THE START OF THE MESOZOIC ERA WHICH IS ABOUT 4 BILLION YEARS. IT ENDS WITH THE APPEARANCE OF SINGLE CELLED ORGANISMS IN AN EARTH THAT WAS MOSTLY COVERED BY OCEANS. DURING THE EARLY PRECAMBRIAN ERA THE EARTH COOLED FROM A SEETHING MASS OF MOLTEN MATERIAL TO FORM THE DISTINCTIVE LAYERS OF THE EARTH WITH A HARD CRUST SEALING IN THE MANTLE AND THE OUTER AND INNER CORES. THIS SEALING IN CAUSES THE FORMATION OF FISSURES AND VOLCANIC ACTIVITY BECOMING RAMPANT. THE MANY VOLCANOES PRODUCE GASES SUCH AS CARBON DIOXIDE (CO2), SULFUR DIOXIDE (SO2), AND WATER. THE STEAM WOULD CONDENSE INTO RAIN WHICH COVERED THE LAND AREA AND CREATED THE VAST OCEANS. HOWEVER THE RAIN WAS MIXED WITH THE GASES AND FORMED ACID RAIN. THE ACID RAIN AND WATER CAUSES A LOT OF WEATHERING AND FORMATION OF SEDIMENTS. THE PALEOZOIC ERA THAT IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWS THE END OF THE PRECAMBRIAN PERIOD IS SIGNIFICANT IN THAT IT SHOWS THE FIRST EXPLOSION OF LIVING ORGANISMS THAT ARE COMPLEX AND IS THEREFORE KNOWN AS THE CAMBRIAN EXPLOSION. THE FIRST PERIOD IN THE PALEOZOIC ERA IS THE CAMBRIAN PERIOD. PERIODS ARE SMALLER DIVISIONS OF TIME WITHIN THE FOUR ERAS. PLANTS ALSO GREW IN ABUNDANCE AND VARIETY. BY THE END OF THE PALEOZOIC ERA AND THE PERMIAN PERIOD THE FIRST ORGANISMS TO EXIST ON LAND EMERGE. THE PALEOZOIC ERA ALSO WITNESSED THE FIRST OF MANY MASS EXTINCTIONS AND TRILOBITES WHICH WERE IN SUCH GREAT ABUNDANCE DURING THE EARLY PART OF THE MESOZOIC ERA DIED OUT COMPLETELY BY THE END OF IT! 349 B + THE MESOZOIC ERA THAT IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWED SHOWED THE APPEARANCE OF HUGE CREATURES THAT STAYED ON THE LAND AND WERE CARNIVORES. WARM BLOODED ANIMALS STARTED TO APPEAR. THE FISH THAT FIRST APPEARED IN THE PALEOZOIC ERA BECAME FOR ADAPTED IN THE OCEANS WITH LARGE SIZES SURVIVING. AT THE END OF THE MESOZOIC WE ARE CONFRONTED WITH THE SECOND MAJOR EXTINCTION AND THE LARGE LAND ANIMALS COMPLETELY DISAPPEAR. THE MOST MODERN ERA IS THE CENOZOIC ERA. THIS IS THE ERA IN WHICH HUMAN BEINGS DEVELOPED AND ONLY TOWARDS THE VERY END OF THE CENOZOIC ERA. 350