EXPOSITORY WRITING
advertisement

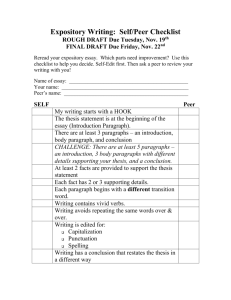
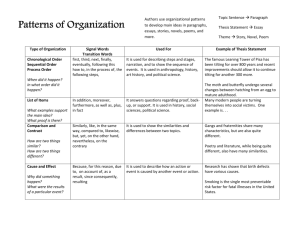
EXPOSITORY WRITING EXPOSITORY ESSAY •Expository writing explains and informs. •It presents information and does not argue for or against a point or seek to defend an opinion. •Encyclopedia articles are examples of expository writing. CHARACTERISTICS • It seeks to inform readers about a specific subject. • It presents information efficiently. • Consider who your audience is and what they will already know about the subject and thus what you still need to explain. • You do not want to bore or overwhelm your reader. CHARACTERISTICS •It tries to engage the reader’s interest. •It should instruct and inform. •It relies almost exclusively on established information. •Don’t forget to acknowledge your sources, use quotation marks correctly and document all of your sources. CHARACTERISTICS •It does not include the author’s experiences or feelings. •It does not express an opinion to be defined. The material is presented in a direct and unbiased way. CHARACTERISTICS Analysis Comparison Cause and Effect Definition Classification Process Analysis Examples TYPES OF WRITING • Cause and Effect: shows the relationship between one and another. • Process Narration: explains how an event unfolds using time or space sequencing • Compare and Contrast: compares the relevant similarities and differences between two people, places, • Problem and Solution: or objects. Compare and describes a problem and contrast essays can have a relays potential solutions point-by-point or subject by subject organization • Descriptive: depicts the attributes of a person, place, or object. Introduction to the Essay Introduction to the Essay Thesis Statement Introduction Developmental paragraphs Conclusion Thesis Statement • Expresses an opinion, attitude, or idea. • It is the main statement of the entire essay. • It should not be written as a question. • It should be expressed as a complete sentence. • It should only express only one idea toward one topic. Thesis Statement example •Not a thesis statement: - I am going to discuss the effects of smoking. •Thesis Statement: - The effects of smoking are bad for your health. Introduction •Introduces the topic and informs the reader of the topic discussed. •Generally, the introductory paragraph should include the thesis statement. •A good introductory paragraph indicates: - Causes, effects, reasons; whether it classifies, describes, narrates, or explains a process. Developmental Paragraphs •Each developmental paragraph discusses one aspect of the main topic. •The controlling idea should echo the central idea in the thesis statement. •The train of thought at the end of one paragraph should be picked up at the beginning of the next paragraph. Example • Thesis statement: - In order to make a good impression atg a job interview, you should prepare well for the interview. • Question: - How should you prepare well? Example •Answers: -Plan your answers to the possible questions the interviewer might ask. -Carefully plan and prepare what you are going to wear. -You should make sure to arrive on time. Conclusion • A conclusion can restate the main points (subtopics). • It can restate the thesis, but in different words. • It should not bring up a new topic.