0.0_CH 4 CHARTER
advertisement

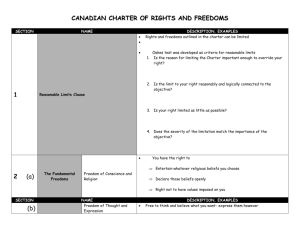
A legal , moral, or social entitlement due to all people because they are human beings. The ability to conduct one’s affairs without being hampered or frustrated. QUOTES Freedom is anarchy. Rights are freedoms expressed with responsibility Rights are something you are entitled to. Freedom is being able to express your entitlements Residential Schools THE GLOBAL MOVEMENT Human rights became a global issue after WW II UNIVERSAL DECLARATION OF HUMAN RIGHTS -backed by the UN after -“all human beings are born free & equal in dignity & rights”. -Most countries have agreed to these principles. -Problem – the only power the UN has is ‘world attention.’ -Not part of binding international law. Stalin’s Purges Apartheid Protest in China INTERNATIONAL COURTS AND TRIBUNALS 1946 International Court of Justice (Both parties had to agree) 2002 a more permanent International Criminal Court established. USA, China & others opposed (internal courts sufficient) World Abuses 1870-1996Canada’s Indian Act & Residential Schools 1900-69 Australia ‘Stolen Generation’ 1924-53 Stalin 1939-45 Holocaust 1948-94 Apartheid 1959-? Chinese occupied Tibet 1971-79 Dictatorship in Uganda 1989 Tiananmen Square China 1991-99 Civil War Sierra Leone 1992-95 Bosnian War 1994 Rwandan Genocide 2004 Darfur genocide Rwandan Genocide CANADIAN BILL OF RIGHTS – 1960 Diefenbaker Formally recognized Can. Rights held by common law. Problem – ‘No teeth’ -> Could be changed like any other law. Did not override Fed. Or Prov. laws. THE SUPREME COURT & THE RULE OF lAW CANADIAN CHARTER OF RIGHTS & FREEDOM ‘The Bill of Rights with teeth’ -> Trudeau included in Constitution. Trudeau Limiting The Charter – Reasonable Limits (Keegstra’s teachings on Holocaust) Notwithstanding Clause – Fed. & Prov. Leg. have final say (Bill 101) THE CHARTER IN ACTION association. Mobility Rights (Free movement) No extradition for death penalties, Effects of 9-11. Delwin Vriend School teacher fired for being gay by a religious private, school in Alberta Equality Rights Race, origin, colour, religion, sex, age, disability. Exceptions – Affirmative action – protects minority rights & disadvantaged. Gurbaj Singh Kirpan in school issue Fundamental Freedoms Conscience, religion, thought, belief, opinion, expression, assembly, & James Keegstra Alberta teacher who taught hatred (Holocaust) Legal Rights Arrest procedures, questioning, search & seizure. TRUANT’S GOLDEN RULE – “Life, Liberty, & Security” Do airport scanners violate your rights? Other Issues Concert goers Abortion Public cameras Pregnacy Radar cameras Gay Marriage REASONABLE LIMITS CLAUSE “Charter must be reasonable” The Oakes Test - Oakes had 8 vials of hash & $600. - Charged with trafficking; Onus was on him to prove innocence. - Supreme said small amounts is unreasonable for reverse onus. Violates “Presumption of Innocence” NOTWITHSTANDING CLAUSE Provinces wanted an assurance to protect local issues. Quebec - Bill 101 / 178 French only signs / language “Life, Liberty, Security.” The Oakes Test 1928-72 Alberta Sterilization Program 1. 2. 3. Must be important Must be rational Limits must be as minimal as possible. Oakes possessed 8 vials of hash oil 4. Must fit societies & $600 cash. objectives. Trafficking??? Personal Use??? Innocence??? Klein tried used clause to protect provinces from civil suit based on previous gov’t. FAILED!!!!! JURISDICTION & ENFORCEMENT JURISDICTION - Applies to all gov’t organizations - Ex. Gov’t Branches, corporations, banks. - Private individuals will look to Fed. & Prov. Human Rights Codes - Ex. Discrimination renting or hiring ENFORCEMENT - People can challenge gov’t positions through the Supreme Court - Charter is written in general terms so judges can interpret individual cases. - Questions to be asked by Supreme Courts: 1. Is the right covered by Charter? 2. Were these rights infringed upon by gov’t? 3. Is the violation within reasonable limits? EXAMPLE – Polygamy – Bountiful 1. Freedom of Religion 2. Arresting practicing members 3. Under-aged (forced???) marriages Video - Bountiful CANADA’S HISTORICAL BLACK EYES Banning Potlatch Illegal to hire lawyers 1960 = Right to vote Residential Schools Slavery banned in 1833 Alberta Sexual Sterilization Act Chinese Head Tax 1900s 1929 Psychiatric Hospital Patients Women = Vote 1918 1928 Komogata Maru 1914 Women not Considered “Persons” WW II War Measures Act Enemy Aliens (Deported, No land) Internment Camps Jews = No Land SUE RODRIGUEZ (August 2, 1950 – February 12, 1994) ADVOCATE FOR ASSISTED SUICIDE. - lived in Victoria, British Columbia - diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in early 1991. - fought to legalize assisted suicide; under the Criminal Code of Canada, - assisted suicide is punishable by a maximum sentence of 14 years in prison. - Her cause went to the Supreme Court of Canada, but lost. (5-4 against her.) - On September 30, 1993, she decided to take her own life with the help of an - Anonymous physician. - would become a landmark decision, Rodriguez v. British Columbia (Attorney General), - In 1994, she decided to take her own life with the help of an anonymous physician. - Svend Robinson, a New Democratic Party MP who had campaigned her cause, was also present.