Lailaigib Lifecycle Of A Star
advertisement

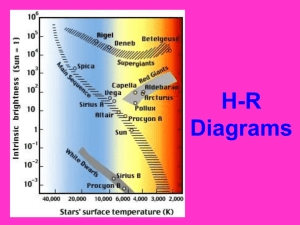
Stars are started by NEBULA: Cloud of gas and dust Hydrogen makes up 97% of a Nebula. Helium makes up 3% of a Nebula All other elements makes up less than 1% of a Nebula A high mass and low mass star starts off the same way. Near the end of the death of the High Mass Star runs out of hydrogen it swells and grows cooler, different than a low mass star. The evolutionary difference is that the High Mass Star passes through a pulsating Yellow Giant phase before it becomes a Red Giant. At the end of a low mass star the helium stars too burn out and it goes back to the core http://library.thinkquest.org/3103/nonshocked/topics/highmassstar/h ighmassstars.html http://astronomyonline.org/Stars/LowMassEvolution.asp A Protostar is a baby star or pre-star Notes the formation of stars A Protostar is surrounded by a lot of gas and dust that blocks the light, but allows through large amounts of far infrared. http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/P/protostar.html This is when the Protostar gains enough mass to begain fusion. All main sequence stars fuse Hydogen Notes life cycle of a star Stars live out the majority of their lives in a phase termed of the Main Sequence. Once getting nuclear fusion, stars shine energy into space http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/labs/star_life/starlife_sequence.html http://library.thinkquest.org/05aug/00108/mainsequence_frameset.htm A neutron star is about 20 km in diameter and the mass of about 1.4 times that of the Sun. This means that a neutron star is so bigger that on Earth, one teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons. Its small size and high density, a neutron star possesses a surface gravitational field. http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/science/know_l1/pulsars.html http://www.universetoday.com/wpcontent/uploads/2008/05/foxneutronartwork.jpg White dwarfs form from the collapse of stellar cores which nuclear fusion has stopped, and are exposed to space following the loss of the old star's bloated outer envelope, typically as a planetary nebulahttp://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedi a/W/whitedwarf.html http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/W/whited warf.html Star with the mass of 25 to 50 times the sun from black holes after a supernova. the left over core of the star is so dense that it causes a gravitational collapse. Act two high mass stars http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black_hole A white dwarf cools off over trillions of years until it no longer emits light Act one small to medium mass http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/B/blackdw arf.html