06.IS_in_management_and_SIS
advertisement

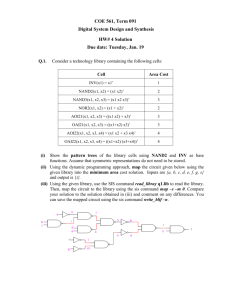
06. Information Systems (IS) in Management & Strategic Information Systems (SIS) Rev: Feb, 2013 Euiho (David) Suh, Ph.D. POSTECH Strategic Management of Information and Technology Laboratory (POSMIT: http://posmit.postech.ac.kr) Dept. of Industrial & Management Engineering POSTECH Contents 1 2 3 Information Systems in Management 1) The role of IS in Management 2) Hierarchy Level of IS in Management Strategic Information Systems 1) Introduction 2) Competitive Strategy & IT 3) Evaluation of SIS Case Study 1. Information Systems in Management 3-Axis MSS Model 1) The role of IS in Management Model IS Type = f(m, d, i) a? c? Intelligence b? Ex) TPS = f(0.1, 0.9, 0) DSS = f(0.5, 0.3, 0.2) Data 3 1. Information Systems in Management The view of Information Systems 1) The role of IS in Management View Point 1 Data Information Statistical Analysis Decision Aids Math Analysis Knowledge Reasoning View Point 2 View Point 3 H Top EIS/ESS E R P DSS IPS Middle low TPS Extreme low OAS Strategic Value Extreme top ? ? L L 4 IS Expansion H 1. Information Systems in Management Role of IS 1) The role of IS in Management View Point 4 Helper Management A Function Financing IS Accounting IS IS Management Financing Marketing Marketing IS Controller Melting Pot IS Financing IS Marketing Marketing Accounting Accounting Financing Accounting All Functions are melted 5 1. Information Systems in Management Management Hierarchy Level (1/2) 2) Hierarchy Level of IS in Management Management Triangle Extreme top Types of management Problem types to be dealt with Political strategic Unstructured Strategic Top Middle Tactical low Operational Semi – Structured and Structured Structured Extreme low Clerical 6 1. Information Systems in Management Management Hierarchy Level (2/2) Management Triangle 2) Hierarchy Level of IS in Management Use of data& Quality Types Information of Data of IS Extreme top Political decision & High-degree strategic decisional aids Top Mathematical analysis of information Decisional aids Middle low Statistical Analysis of data Information Retrieval & use for Operational purpose EIS/ESS DSS IPS MIS(s) Roles of IS Controller Strategic driver Extreme low Very important (Strong SIS) Function TPS Helper to (EDPS) Each function Little OAS 7 Importance Controller Raw data Data processing Strategic Assistant to helper to each function importance (Weak SIS) 2. Strategic Information System Strategic IT 1) Introduction ■ Technology is no longer an afterthought in business strategy, but the cause and driver ■ IT can change the way businesses compete ■ A strategic information system is any information system that uses IT to help an organization… – Gain a competitive advantage – Reduce a competitive disadvantage – Or meet other strategic enterprise objectives Information System (IS) Definition Characteristics • Support activities to the business • Mechanizes operations for better efficiency, control, and effectiveness Simply provides sufficient dependable information Doesn’t increase corporate profitability in itself • • Strategic Information System (SIS) 8 • Integral and necessary part of the business • Directly influences all aspects of marketplace profitability such as market share and earnings • Directly affects the competitive stance of the organization 2. Strategic Information System Overview of SIS 1) Introduction Paradigm Shift Globe-driven Information-driven Customer-driven Technology-driven MIT(Management Innovation Technology) Dramatic Profit Competitive Advantage SM(Super Set) SIS(Subset) OAS KM TPS (EDPS) CRM IPS & MIS EC 9 DSS ERP & BPR EIS & ESS SA MOT 2. Strategic Information System Strategy Tree (1/2) 1) Introduction ■ Use of Information Automation Information (IT, IS) Innovation ■ Automation Work Automation Automation Manufacturing Automation ■ Strategic Use of Information Strategic Information System(SIS) Strategic Use of Information (IT, IS) Non-strategic Information System (NSIS) 10 2. Strategic Information System Strategy Tree (2/2) 1) Introduction ■ Strategic Management Strategic Management (SM) Strategic Management Non-strategic Management (NSM) ■ Information Strategy Tree Work Automation Automation SIS SM Manufacturing Automation Information Innovation NSIS 11 NSM 2. Strategic Information System Competitive Strategies (1/2) 2) Competitive Strategy & IT Competitive Forces and Strategies • Businesses can develop competitive strategies to counter the actions of the competitive forces they confront in the marketplace. ■ Using Competitive Strategies – These strategies are not mutually exclusive • Organizations use one, some, or all • A given activity could fall into one or more categories – Not everything innovative serves to differentiate one organization from another • Likewise, not everything that differentiates organizations is innovative 12 2. Strategic Information System Competitive Strategies (2/2) 2) Competitive Strategy & IT ■ Cost Leadership Strategy – Reducing their costs or increasing the costs of competitors ■ Differentiation Strategy Five Competitive Strategies Cost Leadership – Developing ways to differentiate a firm’s products and services from those of its competitors Differentiation ■ Innovation Strategy – Developing unique products and services or entering unique markets or market inches Strategies ■ Growth Strategy – Expanding a company’s capacity to produce goods and services, expanding into global markets, diversifying into new products and services, or integrating into related products and services ■ Alliance Strategy – Establishing new business linkages and alliances with customers, suppliers, competitors, consultants, and other companies 13 Alliance Innovation Growth 2. Strategic Information System Ways to Implement Basic Strategies 2) Competitive Strategy & IT Basic Strategies in the Business Use of Information Technology Lower Costs ▶ Use IT to substantially reduce the cost of business processes. ▶ Use IT to lower the costs of customers or suppliers ▶ Develop new IT features to differentiate products and services. Differentiate ▶ Use IT features to reduce the differentiation advantages of competitors. ▶ Use IT features to focus products and services at selected market niches. ▶ Create new products and services that include IT components. Innovate ▶ Develop unique new markets or market niches with the help of IT. ▶ Make radical changes to business processes with IT that dramatically cut costs; improve quality, efficiency, or customer service; or shorten time to market. Promote Growth Develop Alliances ▶ Use IT to manage regional and global business expansion. ▶ Use IT to diversify and integrate into other products and services. ▶ Use IT to create virtual organizations of business partners. ▶ Develop interenterprise information systems linked by the Internet and extranets that support strategic business relationships with customers, suppliers, subcontractors, and others. Other Competitive Strategies Lock in customers and suppliers Create switching costs Raise barriers to entry Build strategic IT capabilities Leverage investment in IT 14 2. Strategic Information System Evaluation of SIS 3) Evaluation of SIS ■ When you evaluate a SIS… 1. Process automation or innovation 2. If innovation, which Hammer’s principle? 3. Which competing forces to e affected 4. Value chain activities to be reinforced 5. Type of IS 15 Note ■ MIT PPT material (SIS) – http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/sloan-school-of-management/15-565j-integrating-esystems-globalinformation-systems-spring-2002/lecture-notes/lecture02.pdf 16 Reference ■ O’Brien & Marakas, “Introduction to Information Systems – Sixteenth Edition”, McGraw – Hill, Chapter 1 ■ O’Brien & Marakas, “Introduction to Information Systems – Sixteenth Edition”, McGraw – Hill, Chapter 2 ■ Euiho Suh, “Information & Management (PPT Slide)”, POSMIT Lab. (POSTECH Strategic Management of Information and Technology Laboratory) ■ Euiho Suh, “Role of Information Systems (PPT Slide)”, POSMIT Lab. (POSTECH Strategic Management of Information and Technology Laboratory) ■ Euiho Suh, “Strategic Information Systems (PPT Slide)”, POSMIT Lab. (POSTECH Strategic Management of Information and Technology Laboratory) 17