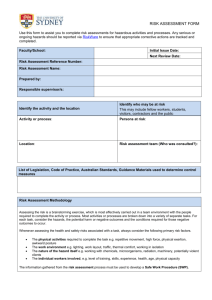
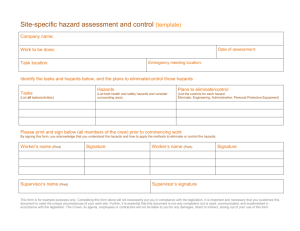
HalTech HSE Program 2010-Oct
advertisement

Haltech Testing Inc. TABLE OF CONTENTS (A) About Us Company Profile __________________________________________________ Corporate Mission Statement ________________________________________ Corporate Objectives _______________________________________________ Guiding Principles & Objectives ______________________________________ 1 2 3 4 (B) Health & Safety Policy Statement __________________________________________________ 5 Haltech Testing Inc. Guiding Principles _______________________________ 6 Petroleum Industry Guiding Principles ________________________________ 7 1.0 Introduction _____________________________________________________ 9 1.0 Introduction to Health, Safety & Environmental Program ____________ 9 1.1 Due Diligence Statement ______________________________________ 9 1.2 To Do A Hazard Assessment __________________________________ 10 1.3 Three Keys to Safety ________________________________________ 10 2.0 Responsibility for Safety and Health ________________________________ 2.1 Senior Management _________________________________________ 2.2 Supervisor _________________________________________________ 2.3 Employees ________________________________________________ 2.4 Contractors ________________________________________________ 2.5 Visitors ___________________________________________________ 11 11 11 12 12 12 3.0 Inspection Policy ________________________________________________ 3.1 Purpose ___________________________________________________ 3.2 Policy ____________________________________________________ 3.3 Responsibility ______________________________________________ List of Schedules & Forms _________________________________________ 13 13 13 13 14 4.0 Hazard Identification and Control _________________________________ 4.1 Trucking Hazard Identification, Assessment & Control _____________ 4.1.1 Hazardous Goods Identification __________________________ 4.1.2 Hazardous Goods Assessment ___________________________ . . . storage __________________________________________ . . . H2S _____________________________________________ 15 16 16 16 17 18 i Haltech Testing Inc. 4.0 5.0 4.1.3 Hazardous Goods Control _______________________________ 4.1.4 Road Hazard Assessment & Control_______________________ 4.2 Shop Hazard Identification, Assessment & Control ________________ Hazard Identification and Control - Continued 4.2.1 Machinery, Tools & Equipment __________________________ 4.2.2 Safety Equipment _____________________________________ 4.2.3 Handling of Chemicals & Airborne Contaminants ____________ 4.2.4 Cranes and Overhead Work _____________________________ 4.2.5 Welding Gases & Guns _________________________________ 4.2.6 Storage ______________________________________________ 4.2.7 Entry / Exits __________________________________________ 4.2.8 Injury or Sickness _____________________________________ 4.3 Procedures for Working On Tanks In Shop _______________________ 4.3.1 Introduction __________________________________________ 4.3.2 Procedures ___________________________________________ 4.4 Worksite Hazard Assessment & Control _________________________ 19 19 20 Safety Rules and Work Procedures _________________________________ 5.1 Safety Rules _______________________________________________ 5.2 Standard Work Procedures ____________________________________ 5.2.1 Pre-Trip Service and Safety Inspection_____________________ 5.2.2 Placards of Vehicle ____________________________________ 5.2.3 En Route Inspection and Safety Check _____________________ 5.2.4 Air Brakes ___________________________________________ 5.2.5 Driving as a Professional________________________________ 5.2.6 Employee/Contractor Training & Orientation _______________ 5.2.7 Equipment ___________________________________________ 5.2.8 Equipment, Tools and Materials __________________________ 5.2.9 Excess Head and Facial Hair _____________________________ 5.2.10 Firearms _____________________________________________ 5.2.11 Heating _____________________________________________ 5.2.12 Housekeeping/Right-Of-Way/Behavior ____________________ 5.2.13 Alcohol & Drugs ______________________________________ 5.2.14 Ladders _____________________________________________ 5.2.15 Lifting ______________________________________________ 5.2.16 Maintenance & Lockout Program _________________________ 5.2.17 Permits and Completion of Documents ____________________ 5.2.18 Personnel Safety ______________________________________ 5.2.19 Public Relations & Highway Courtesy _____________________ 5.2.20 Right to Refuse Unsafe Work ____________________________ 5.2.21 Safety Belts and Lifelines _______________________________ 5.2.22 Scaffolds and Platforms ________________________________ 5.2.23 Smoking ____________________________________________ 29 29 31 31 31 31 32 32 32 33 33 33 33 34 34 34 35 35 36 37 37 37 38 38 38 39 20 21 21 22 22 22 23 23 24 24 24 28 ii Haltech Testing Inc. 5.0 5.2.24 Tire Chains __________________________________________ Safety Rules and Work Procedures - Continued 5.2.25 Towing _____________________________________________ 5.2.26 Welding _____________________________________________ 5.2.37 WHMIS _____________________________________________ 5.2.28 Worksite Ergonomics __________________________________ 5.2.29 Modified Work _______________________________________ 5.2.30 Working in Extreme Conditions __________________________ 5.2.31 Fatigue Management ___________________________________ 39 5.3 Personal Protective Equipment ________________________________ 5.3.1 Head Wear ___________________________________________ 5.3.2 Clothing & Body Protection _____________________________ 5.3.3 Foot Wear ___________________________________________ 5.3.4 Eye Protection ________________________________________ 5.3.5 Hearing Protection_____________________________________ 5.3.6 Personal Monitors & Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus _____ 5.3.7 Special Health Considerations ___________________________ 44 44 44 44 44 45 45 45 5.4 Enforcement _______________________________________________ 46 5.4.1 Description of Driving Offences __________________________ 46 5.4.2 Description of Speeding Offences ________________________ 47 39 39 40 40 42 42 42 Code of Practice: P.P.E. Program _____________________________ 48 6.0 Legislative Compliance ___________________________________________ 6.1 Employee Responsibility _____________________________________ 6.2 Housekeeping ______________________________________________ 6.3 Working Around Moving Parts ________________________________ 6.4 Eye Protection _____________________________________________ 6.5 Respiratory Protection _______________________________________ 6.6 Working At Heights Above Ground ____________________________ 6.7 Confined Spaces ____________________________________________ 6.8 Working Alone _____________________________________________ 6.9 Hazardous Waste ___________________________________________ 6.10 Workplace Violence & Harassment _____________________________ 53 53 53 54 54 54 54 54 55 55 55 7.0 Training ______ ________________________________________________ 7.1 Employee and Contractor Training _____________________________ 7.2 Employee and Contractor Orientation ___________________________ 7.3 Driver Violations ___________________________________________ List of Schedules & Forms _________________________________________ 57 57 58 58 59 iii Haltech Testing Inc. 8.0 Communications ________________________________________________ 8.1 Communications System _____________________________________ 8.2 Safety Meetings ____________________________________________ 8.3 Project Safety Meetings ______________________________________ List of Schedules & Forms _________________________________________ 61 61 61 62 63 9.0 Accident/Incident Reporting ______________________________________ 9.1 Incident and Accident Reporting _______________________________ 9.2 Incident and Accident Investigation & Follow-Up 9.2.1 Purpose _____________________________________________ 9.2.2 Policy _______________________________________________ 9.2.3 Responsibilities _______________________________________ List of Schedules & Forms _________________________________________ 65 65 10.0 66 66 66 67 Environmental Policy ____________________________________________ 69 (C) Emergency Response Plan EMERGENCY PHONE NUMBERS _________________ pgs 75 & 76 1. Emergency Response Plan Goal _____________________ 2. Training ______________________________________ 3. Potential Emergencies_____________________________ 4. Action ________________________________________ 5. Emergency Response Plan – Spills __________________ 6. Emergency Response Plan – Fires ___________________ 7. Emergency Response Plan – H2S ___________________ 8. Emergency Response Plan – Natural Disasters _________ Emergency 1st Aid 77 77 77 78 80 81 83 84 see Procedures – MediumRisk– Tab #6 Procedures iv Haltech Testing Inc. High Risk 1. Confined Space – Entry 2. Confined Space – Leave 3. Confined Space – Prepare to Enter 4. Handling Rodents or droppings 5. Install Blinds and Blanks 6. Labeling Hazardous Products 7. Operation of Dreager Pump / Tube 8. Operating around Power lines 9. Operation of SCBA/SABA 10. P-Tank Purge 11. Pressure Problems: Troubleshooting 12. Tubular Hydrate Identification and Removal Medium Risk 1. Blow-down Float & Alarm Columns 2. Building Entry 3. Burner Lighting 4. Check Zero on Dry Flow Meter 5. Climbing Fixed Ladder on Tanks 6. Emergency First Aid and Situations 7. Flowing Oil Well: Troubleshoot 8. Fuel Gas / Utility Gas Systems: Operate 9. Gas Well: Trouble Shoot 10. Gauge Tanks Safely 11. Igniting Flare Tip 12. Lubricate Gear Mechanism on a Sr. Daniels Orfice Charger 13. Maintain Dry Flow Meter 14. Operating Daniels Junior Orfice Charger 15. Operation of Gastec Pump / Tube 16. P-Tank and Flare Stack Initial Setup 17. Putting Flow Oil Well on Stream 18. Shipping Procedures Medium Risk con’t 19. Texstream Injection Chemical Pump 20. Tool Care and Handling v Haltech Testing Inc. 21. Use of Portable Extension Ladders 22. Use of Step Ladders 23. Vent / Flair System: Troubleshoot 24. Wells Take Pressure Survey 25. Working in a Hot Environment 26. Working in Cold Weather Low Risk 1. Above Ground Storage Tank Inspection 2. Above & Below Ground Storage Tank Inspection Checklist 3. Battery Jump Start & Boost 4. Bump Testing & Calibration: Using BW Microdock II 5. Catalytic Heaters: Operate 6. Centrifuge Test for Oil BS&W cut 7. Change Dry Flow Meter Charts 8. Changing a Flat Tire 9. Cheater Cord Procedures 10. Dry Flow Meters: Troubleshooting 11. Electric Heat Trace – Operate 12. Flowing Oil Well: Perform Routine Check 13. Fuel Gas System Check 14. Fuel Gas System - Troubleshoot 15. Housekeeping 16. Inspect and Clean SCBA/SABA 17. Installation of Bolted and Threaded Connections 18. Maintaining Instrument Air Compressor 19. Performing Monthly Fire Extinguisher Check 20. Lockout Energy Sources vi Haltech Testing Inc. Haltech Testing Inc. www.haltechtesting.com 780 – 864 – 0153 COMPANY PROFILE Haltech Testing Inc. takes pride in supplying a wide variety of reliable, quality oil and gas well production testing equipment and personnel. Haltech Testing Inc. is owned and operated by Hal Keith and Lon Urness. The main office is located in Bay Tree, Alberta. The primary function is to provide exceptional well testing personnel that are trained in new well completions, frac recovery, clean-up tests, and inline production testing and sound equipment to get the job done efficiently and safely. Haltech Testing Inc. was formed in 2003 as the result of increased demand for oilfield services in the area. Haltech Testing Inc. currently operates five well testing units. (includes p-tank, flare stack and office trailer) 1 Haltech Testing Inc. CORPORATE MISSION STATEMENT To provide superior service, in a safe and cost effective manner, with sound equipment personnel, and while Environmental exceptional complying and with Industry Standards. ________(original signed)_________ Hal Keith President, Haltech Testing Inc. ________(original signed)_________ Lon Urness Sec/Treas, Haltech Testing Inc. 2 Haltech Testing Inc. Corporate Objectives 1. Provide a safe and efficient work environment. 2. Promote job security. 3. Set goals to stimulate personal and company growth. 3 Haltech Testing Inc. Guiding Principles to Achieve Our Objectives 1. Empower individuals to take ownership of ideas that improve the company’s operating policies and procedures. 2. Maintain constructive relationships between employees, peers and managers. 3. Lead by example. 4. Reinforce positive attitudes. 5. Focus on the situation or behavior, and not on the individual. 6. Meet with customers on a regular basis to ensure quality control. 4 Haltech Testing Inc. H E A L T H & S A F E T Y P O L I C Y S T A T E M E N T HALTECH TESTING INC., at all staff levels, is committed to employing responsible management practices that will result in protecting the health and safety of employees, customers, contractors and the public. To achieve this goal, HALTECH TESTING INC. will: Comply with or exceed applicable government regulations and industry standards for health, safety and environmental protection. Develop and train supervisors to ensure compliance with approved safe operating practices as they are responsible for enforcing the company health and safety program. Supervisors are responsible for enforcing the company health and safety program. Educate, train and motivate employees to conduct their activities in a safe and environmentally responsible manner. Minimize the consequences of emergency events by ensuring prompt and effective response. Require that all employees and contractors perform their duties in accordance with company standards. Develop, implement and maintain emergency response plans appropriate for our operations. Maintain regular health and safety monitoring and reporting practices. Provide on an on-going basis, sufficient resources to ensure that employees are fully informed of health, safety and environmental requirements. Be sensitive and responsive to public concerns regarding our business activities. ________(original signed)_________ ______________________________ Hal Keith President Date ________(original signed)_________ ______________________________ Lon Urness Sec/Treasurer Date 5 Haltech Testing Inc. HALTECH TESTING INC. GUIDING PRINCIPLES HALTECH TESTING INC.s’ management believes that a healthy and safe work environment for all employees and contractors is vitally important to the successful operation of our business. Employees and management must jointly make reasonable efforts to provide such a work environment. WE BELIEVE THAT: Known operational risks must be avoided or controlled to prevent injuries, work related illnesses, fires, property damage and other losses as an integral part of our business. Management and employees are jointly responsible and held accountable for ensuring, creating and maintaining a safe workplace, establishing and following health and safety programs, furnishing and using proper equipment, furnishing and using procedures and training. Employees and contractors are responsible for complying with all applicable health and safety and environmental laws and regulations and with company rules and procedures as a condition of employment. It is expected that employees and contractors will work safely and show equal concern for health and safety of their co-workers and that all incidents will be reported and investigated. Excellence in health and safety performance is achieved through the support and active participation of all employees. 6 Haltech Testing Inc. PETROLEUM INDUSTRY GUIDING PRINCIPLES FOR WORKER SAFETY We, the members of the petroleum industry have a responsibility to protect all workers engaged in its activities from personal injury and health hazards. Responsibility The prime contractor, is responsible for coordination and general supervision of all activities at the work site, including activities carried out by contractors, sub-contractors, service companies and suppliers. While all parties have a responsibility to promote safety, the prime contractor must recognize its’ leadership role in promoting worker health and safety on the basis that is has the greatest power to influence work site situations. It is the responsibility of workers and employers to refuse to perform unsafe work practices. Priority Activities will be conducted on the basis that safety of all personnel is of vital importance, whether those personnel are employed by an operating company, a contractor, a sub-contractor, a service company, or a supplier. Recognition The process of selecting contractors, sub-contractors, service companies and suppliers, and the administration of contracts, will include recognition and support of good safety performance. Support and recognition based on good safety performance will also be provided by all employers to their employees. Improvement The operating company, in cooperation with service companies within the industry will promote methods and practices that have potential for improving safety performance. 7 Haltech Testing Inc. This Page Intentionally left Blank 8 Haltech Testing Inc. 1.0 INTRODUCTION This Safety Handbook for Employees and Contractors outlines minimum safety and health expectations for employees, contractors and consultants while present at the owner’s work sites or engaged in any activity on behalf of the owners. Its contents are supplement to the Provincial Occupational Health and Safety Acts and Regulations, other applicable laws and regulations and various industry codes and documents. Standards applicable to the work being performed will be required for all contracted work or for Haltech Testing Inc.’s service orders, including those for supply and installation of materials. In the event of a conflict between the language of a contract and the guidelines, the applicable potions of the CAPP Petroleum Industry Contractor Safety Checklist shall take precedence. 1.1 DUE DILIGENCE STATEMENT DEFINITIONS ‘dangerous occurrence’ . . . . . also considered as a near-miss incident ‘driver’ . . . . . . may include operators ‘employee’ . . . . . may include contractors ‘tailgate safety meeting’ . . . . . . considered the same as a ‘worksite hazard assessment’ ‘vehicle’ . . . . . .may include trailer units and/or equipment; and ‘worksite hazard assessment’. . . . . . considered the same as a ‘tailgate safety meeting’ HAZARD: Any circumstances or conditions, which poses the risk of an incident. INCIDENT: Any unplanned and unwanted event, which results in damage or injury, or which could have resulted in damage or injury. HAZARD ASSESSMENT: See Section 4.0 of Haltech Testing Inc.’s HSE Program INSPECTION: See Section 3.0 of Haltech Testing Inc.’s HSE Program A HAZARD ASSESSMENT, also called a job safety analysis (JSA), is a careful analysis of the potential hazards associated with a particular task and/or an entire job-site. Every new job or change at a job calls for hazard assessment and controls put in place by evaluating the degree of risk and exposure. Tools to assess include Inspection and/or testing. Observation by trained individuals. Investigations of incidents and near misses. Interviewing workers and reviewing records. Analyze the risk by determining: Consequences – outcome of an incident Exposure – interaction with hazard Probability – likelihood that consequences will occur once individual is exposed Controlling the hazard to prevent harm to workers: At the source (Engineered) Between the source and the worker (administrative) and/or At the worker (PPE) 9 Haltech Testing Inc. 1.2 TO DO A HAZARD ASSESSMENT: The supervisor begins by analyzing the risks arising out of the work activities or circumstances and implement safe work procedures if the activities or circumstances create a hazard. The procedures implemented must state the number of workers involved, the steps to be followed and the safety equipment required on the Hazard Assessment Form. Look carefully at how the equipment is designed (for example, will there be special problems in very hot or extreme cold weather, or for operators who are especially short or tall)? Carefully observe someone doing their job as they normally would. List each of the basic steps involved in the task. List what might go wrong causing injury or property damage at each step. Think about as many aspects of the job as possible, mechanics, electricity, temperatures, pressures, leaks, explosives, noise, direction of movement, impacts, pinch points, stability of equipment and so on. For each potential problem, write down what should be done to prevent a problem from occurring or to minimize the damage if the problem does occur. Indicate what should be done, things to look for, positions to take and movement to make, and so on, as well as equipment maintenance and repair, and of housekeeping in the area. Give special instructions, listing what to do and how to do it, rather than general statements like, “use caution”. ** Check the lists with someone who has done the task many times, to be sure that all steps are included and all potential hazards identified. 1.3 KEYS TO SAFETY 1. Recognize the Hazard: This means having the necessary knowledge and training to be able to identify physical hazards and hazardous situations. 2. Know the Defense: This means having the necessary knowledge and training to correctly defend yourself from the hazard. You are attempting to: 1st Eliminate the potential hazard, if unable to do so then, 2nd Control the potential hazard by: 1st choice = Engineering controls (valve l, tank certification, gauges, etc) 2nd choice = Administrative controls (inspections, documentation, etc.) 3rd choice = PPE Sometimes a combination of the three is best if there is a greater level of worker safety. 3. Act in Time: This means acting in a time frame and in manner that protects yourself and others from danger. 10 Haltech Testing Inc. 2.0 RESPONSIBILITY FOR SAFETY AND HEALTH 2.1 Senior Management Ensure proper equipment is provided to do the job and laid out safely for its use, including first aid services, first aid equipment, and supplies. To develop and establish safe operating procedures and communicate these to employees. Procedures will be available. To develop supervisors competent in each of the areas of responsibility and training programs to ensure compliance with approved safe operating practices. Will ensure appropriate training for employees. Eliminate injuries by providing encouragement and support to the staff. Ensure workers report every incident and accident. The employer and/or prime contractor will post signs indicating the location of first aid service, equipment and supplies or, if posting of signs is not practicable, ensure that each worker knows the location of first aid services, equipment, supplies and procedures. Review all accidents in order to develop means of eliminating them in the future and communicate these to all employees affected. Review HSE and ERP annually. Conduct monthly safety meetings or as required and record meeting minutes. 2.2 Supervisors Supervisors appointed for supervision of well testing operations are competent in each area that is within the supervisor's area of responsibility and are responsible to maintain a safe work site including ensuring required first aid services, equipment and supplies, first aid attendants and services and that the services are adequate and appropriate. Supervisors will be trained in the safe handling, use, and storage of hazardous substances; detecting and controlling worker exposure to H2s; emergency response including well control and blowout prevention; as well as the safe operation of work site facilities. Supervisors are responsible to ensure that workers are trained in safe work practices and the health and safety program. Supervisors are responsible for training workers in safe work practices and procedures and the actions and duties of the worker under his supervision. Supervisors are responsible for informing employers and workers of the hazards and ensuring that the hazards are addressed throughout the duration of the work activities. Ensuring all regulations and safety policies are implemented, administered and enforced. Reporting and investigating all incidents, accidents, spill, near misses or hazardous conditions. Ensuring all new personnel are aware of the regulations, training requirements, site operating procedures and emergency procedures. Ensuring that all equipment (including PPE) is working properly, inspected, maintained and is capable of performing the task safely as well as the safe operation of facilities at location. Ensure worksite ERP plan is communicated to all workers, an emergency communication system in place; first aid services, equipment, supplies are on site and kept clean, dry, accessible and ready for use as well as the required number of first aiders and/or SCBA’s per worker on site and predetermined transportation services for injured or ill workers should it be required. Ensuring that all personnel under their supervision keep their certificates of safety training up-todate. Ensure that the traffic is controlled to protect workers and that workers are visible and/or physically protected. 11 Haltech Testing Inc. 2.3 Employees Each employee must read and be familiar with the contents of this booklet, signing the ‘New Personnel/Contractor Orientation Checklist’ to confirm such. Each employee must abide by the regulations contained herein. Each employee must follow company written and oral instructions to safely perform his/her job. Each employee must make themselves aware of the location of first aid services, equipment and supplies at each site. Each employee must participate in the daily maintenance of the equipment they are operating. Each employee must complete the ‘Daily Pre/Post Trip Inspection’ for Trucks/Units. Each employee must maintain a ‘Daily Log Book’ for Trucks. If the employee has any doubt regarding his/her job procedure or safety involved, he/she must consult his/her supervisor before proceeding. Each employee must report all unsafe working conditions, near-misses, incidents or safety issues immediately to his/her supervisor. Each employee must refuse to perform a task or assignment, if on reasonable and probable grounds, they believe that there exists an imminent danger to the health and safety of themselves or others. Each employee must wear appropriate PPE. Each employee must attend monthly safety meetings to discuss current safety issues. 2.4 Contractors Prior to beginning work on a Haltech Testing Inc. site, a contractor must have a minimum: Adequate comprehensive general liability insurance per occurrence and aggregate, which includes coverage for all non-owned automobile units as well as owned automobile used in the operation. Workers compensation accounts in good standing, for the jurisdictions in which the workers are employed, including coverage for all subcontractors. The project manager of Haltech Testing Inc.’s supervisor will normally request all contractors have a copy of evidence of WCB coverage for the duration of the job prior to any contactor work commencing (certificate of account showing that they have a current WCB number and/or a letter of clearance showing WCB coverage paid to certain date). This insurance must be effective on the date of service order, intermittent services agreement, or contract, and must continue in full force and effective until the services agreement, or contact, and must continue in full forces and effective until the terms of the order or contract are completed. Haltech Testing Inc. project manager should check with WCB to ensure that this coverage is in effect, prior to any work taking place by a contractor. The subcontractor must supply a copy of the company’s Health and Safety Program (Or complete Haltech Testing orientation, sign in agreement to understand and comply with Haltech Testing Inc’s Health & Safety Program). The subcontractor must comply with all permits issued by Haltech Testing Inc. The subcontractor must participate in pre-job inspections, hazard assessments, orientations, meetings and comply with all procedures laid out in this manual & Safe Practices. The subcontractor must be aware of and comply with the Occupational Health and Safety Regulations as they apply to the job as post job safety performance will be reviewed. 2.5 Visitors Visitors must immediately report to the site’s main office or control room for instructions. While on location adhere to all Government Regulations and Company Policies & Rules. Never walk about a location unescorted unless under the direction of the site supervisor or his delegate. 12 Haltech Testing Inc. 3.0 INSPECTION 3.1 Purpose To control losses of human and material resources by identifying and correcting unsafe acts and conditions. 3.2 Policy This Company will maintain a comprehensive program of safety inspections at all facilities and job sites. 3.3 Responsibilities Management is responsible for the overall operation of the program ensuring documentation. Managers are to ensure: o o o o Monthly Premises inspections Monitor supervisor/worker behavior, document quarterly Methods and Safe Work Practices, document quarterly Inspection, assessment and safety documentation Supervisors are responsible for directing formal inspections and involving the workers and units on-the-job sites that they control. Supervisors are to ensure: o To inform workers of the hazards created and ensuring that the hazards are addressed throughout the duration of the work activities. The information required includes the name of the qualified coordinator, a site drawing, which must be posted, showing project layout, first aid location, emergency transportation provisions, and the evacuation plan, and a set of work procedures designed to protect the health and safety of workers at the workplace. o Unit/Equipment inspection, recording inspections and maintenance (to be made available to equipment operators and anyone involved with inspection and maintenance). o Monitor worker behavior. o First aid kits are inspected monthly, kept clean, dry and clearly visible, with proper signage. o PPE is properly used and inspected. o Inspection, assessment and safety documentation. Workers are responsible for participating in, and contributing to, the inspection program. 13 Haltech Testing Inc. Schedules and Forms - Inspections Personal Protective Equipment Schedule _____________________ Emergency Equipment Inspection Schedule __________________ Verification of work permits Form _________________________ Daily Vehicle Inspection Form ____________________________ Truck / Equip. Inspection Form / Drivers Log _________________ Hazard Identification, Assessment & Control Form_____________ Monthly Shop Inspection Form ____________________________ Quarterly Tool Inspection Form ____________________________ 14 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.0 HAZARD IDENTIFICATION AND CONTROL Hazard identification is everyone’s responsibility. Think Now!! “What can you do to assess hazards daily?” There are several areas in which hazards present themselves on a daily basis. An assessment is to be conducted of the circumstances of the workplace, including: the number of workers who may require first aid at any time, the nature and extent of the risks and hazards in the workplace, including whether or not the workplace as a whole creates a low risk of injury, the types of injuries likely to occur, any barriers to first aid being provided to an injured worker, and the time that may be required to obtain transportation and to transport an injured worker to medical treatment. The assessment will be reviewed annually or whenever a significant change affecting the assessment occurs. The hazard assessment includes a site inspection, the number or workers, name of first aider, followed by an assessment of the hazards, and instructions to eliminate, minimize or control the hazards. Possible Hazards: Transportation: o Hauling Large loads Hazards o Loading and Unloading Products o Road Hazards Shop & Maintenance: o Machinery, Tools and Equipment o Safety Equipment o Handling of Chemicals o Overhead Work / Underneath Work o Welding Gases / Guns o Butane Lighters o Electrical Fire o Lifting o H2S o Injury or Sickness Work Site: o H2S o Hazardous gases/substances o Pressure o Tank Gauge Operation o Cell phone o Venting System o Sour Facility Safe Guard o Grounding / Bonding o Evacuation or rescue There are many more possible hazards, scrutinize your work site. 15 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.1 TRUCKING HAZARD ASSESSMENTS & CONTROL 4.1.1 Hazardous Goods Identification Haltech Testing Inc. handles many dangerous good products with the main products listed below in their proper shipping name, with the Product Identification Number (PIN). P-Tanks Propane Methanol Class 3, UN. 2924 Class 3, UN. 1075 P.G.II Class 3 UN 1230 P.G.II 4.1.2 Hazardous Goods Assessment Due to the similarities of the products the following hazard assessments will apply to all the products listed, unless otherwise identified. These products emit vapors that are both flammable and poisonous. Therefore it is important to pay close attention to this information for your protection, your fellow workers and the environment as well. Fire or Explosion May be ignited by heat, sparks or flame. Many vapors are heavier than air. Most products are lighter than water. Vapors may form explosives when mixed with air. Vapors may travel to a source of ignition and flash back. Containing vessels may explode when heated. Health First Aid Some vapors are irritating or poisonous. Methanol vapor or liquid inhalation or contact may cause severe injury or death. Fire may produce irritating, poisonous and/or corrosive gases. Run off may pollute waterways. Remove to fresh air. Apply artificial respiration if victim is not breathing. Administer oxygen if breathing is difficult (if oxygen is available and you have the proper training). Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. In case of contact with material, immediately flush skin or eyes with running water for at least 15 minutes. Keep victim warm and quiet. Methanol contact or inhalation, effect may be delayed. Get medical aid. Ensure that attending medical staff is aware of identity of products involved. 16 Haltech Testing Inc. Storage Hazardous products must be properly stored in a designated area for a hazardous substance and must be; designed and constructed to provide for the safe containment of the contents; clearly identified by signs, placards or similar means; designed and maintained to allow the safe movement of workers, equipment and material; provided with adequate ventilation and lighting; in a location not normally occupied by workers; must not be in a location such as a lunchroom, eating area, change room, clothing storage locker or passenger compartment of a vehicle; in a manner which ensures that it will not readily fall, become dislodged, suffer damage, or be exposed to conditions of extreme temperature; and labeled according to WHMIS and add MSDS sheet to binder. 17 Haltech Testing Inc. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) One of the more dangerous vapors emitted from petroleum or petroleum based products is Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S). H2S is a naturally occurring, colorless and odorless (at higher concentrations) gas that can be highly toxic. In high enough concentrations, it can paralyze the breathing control center in the brain and in the respiratory system with one breath. Workers may not be exposed to H2S as a concentration exceeding 10ppm at any time without respiratory equipment. If a work site may become immediately dangerous to life or health, follow H2S procedures to ensure that a worker wears self contained breathing apparatus or an air line respirator. Respiratory equipment must meet regulation standards as listed in PPE Code of Practice. Colorless gas. Smells like rotten eggs as between 1 ppm and approximately 100 ppm. Sense of smell is deadened after this concentration. Heavier than air, will settle in low areas, excavations, confined spaces, etc. Will readily mix with liquids and then be released when liquids are disturbed. Will cause irritation of eyes and throat at approximately 200 ppm. Will cause respiratory distress and/or lose reasoning within 2 minutes at 500 ppm. Quickly unconscious, breathing stops at approximately 700 ppm. Will cause immediate respiratory arrest at 1000 ppm. Explosive when mixed with air. 10 ppm – 8 hours without adverse effect. Above 10 ppm – breathing apparatus must be worn. As much as possible, avoid enclosed areas such as H2S process buildings, tanks, trenches or any other place where H2S may settle. Treat these areas as potential confined spaces when on a sour lease. Anytime during work where it is suspected that H2S is present, breathing apparatus must be worn and the “check in system” is to be used during the work. H2S Rescue Whenever someone is overcome by H2S or this is suspected, DO NOT RUN INTO THE AREA TO EFFECT A RESCUE. Proceed in the opposite direction, call for help and back up, don breathing apparatus, and then remove the casualty from the area. Only after you and the casualty are free of the affected area can you remove the breathing apparatus and apply artificial respiration. When the casualty exhales, avoid breathing in the exhaled H2S. A casualty who is being revived from H2S poisoning is often violent; be prepared for this. WARNING: You cannot rely on your sense of smell to determine how much H2S is present. Be safe and wear your breathing apparatus! 18 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.1.3 Hazardous Goods Control Due to the dangers surrounding the handling and transporting of the aforesaid hazardous goods (4.1.1), Haltech Testing Inc. has implemented several steps to ensure the safety of their employees and/or contractors who come in contact with these products. Haltech Testing Inc. feels that through their orientation & training, safety rules, work regulations, regular safety meetings, personal protective equipment, field supervisors, scheduled equipment and site inspections we are able to minimize the occurrence of accidents/incidents. It is imperative that the operator’s follow the safety rules and work regulations, as stated in Haltech Testing Inc.’s Health, Safety & Environmental Program, to ensure control of the hazardous good situation. The most important steps that need to be taken to attain these standards are: 1. You must ensure that all connections are made correctly. 2. Under no circumstances are you to leave the unit until completion or replacement staff has arrived and is ready to take over. 3. Do not open any valves unless you are sure that all connections have been correctly made and all safety precautions have been followed. Please take note what products you may come in contact with. Therefore if you are to transport or handle a product you are not familiar with, confirm the PIN, class, required placards and MSDS before handling the product. 4.1.4 Road Hazard Assessments & Control Every day that we share the road with other vehicles, there is the potential for an accident. We cannot stress how important it is for the driver to be alert and aware of his/her surroundings as well as other drivers actions at all times. Be aware of slow moving equipment, oversized loads and wildlife on the roadway. Vehicles should be operated in a defensive manner and Use seat belts provided. Drivers should be alert and looking for future problems before they occur. Drivers should examine their vehicles daily before using them and shall not operate any vehicle if any unsafe condition or mechanical defect is found. These conditions or defects should be reported to their supervisor for correction. Clear all windows of dirt, dew, frost, ice or snow before driving. Operated with headlights on. Do not leave tools or equipment loose in the passenger compartment of vehicles. Any vehicle having restricted rear view should be equipped with audible backup beepers or alarms. When backing into tight spots or where there may be other traffic coming, use another person as a guide. When parking a vehicle, ensure that the vehicle is set and parking brake is fully engaged. In winter, allow for extra stopping distances, especially on bridges or intersections. Drivers should try to be familiar with skid control procedures for the vehicle type. Emergency kits and extra warm clothing should be carried, especially in remote areas. 19 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.2 SHOP HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, ASSESSMENT & CONTROL 4.2.1 Machinery, Tools and Equipment Haltech Testing Inc. will ensure that tools and equipment are performing safely and used, and operated in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions and safe work practices. If modifications are made, they must be in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. If equipment is dismantled and re-assembled, it must be checked by a qualified person and determined to be safe before operation or use. Piping systems, fittings and valves must be designed, constructed and maintained to safely withstand the anticipated internal pressures and external loads, be restrained from undue horizontal, vertical or swinging motion. Pipes must be restrained from uncontrolled movement. All equipment and safeguards must be installed, operated and maintained in a condition to be able to perform the function for which it is intended or was designed (in accordance with CSA Standard Z432-4), without compromising the health and safety of a worker. A worker must not intentionally remove, impair, or render ineffective any safeguard, except as permitted by OHS regulation. A worker must remove any equipment from service using the lock-out tag-out system when its condition or the condition of a safeguard is compromised or could affect the health and safety of a worker. Before using any machinery, tools or equipment, a worker must ensure there is no danger to other workers. Fire hazard areas are clearly identified as well as the prohibited use of an open flame or other source of ignition in the area. Guards are placed over machines or to prevent entry for your protection. KEEP THEM IN PLACE. A fixed guard must not be adjusted to be readily removable without the use of tools. Never use defective tools or tools with defective guards, turn them in and get new ones or have them tagged and repaired. Rotating parts, such as friction drives, shafts, couplings and collars, set screws and bolts, keys and keyways, and projecting shaft ends, exposed to contact by workers must be guarded. Every employee, who is required to operate a cutting torch, must be checked out by the foreman or supervisor. Do not attempt to operate a burning torch or do any work with it unless instructions are fully understood. Do not use a match to light a torch, use a friction lighter, stationary pilot flame or some suitable safe source of ignition. Always use a jack stand or axle stand when working under equipment that is supported by jacks or cranes. Always install spring brake cages when working on spring brakes, or in that area. Tire cage or another approved restraining device must be used when a person initially inflates a tire mounted on a split-rim or locking ring wheel. A person is required to use a protective screen or ensure the other workers are wearing approved eye protection when he/she are to perform electric arc welding. 20 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.2.2 Safety Equipment The shop shall have the following equipment available: First aid kit, PPE, fire extinguisher, and all other safety equipment that meets government regulations or better, kept properly supplied at regular intervals. Personal (LEL) monitor. Sufficient fire extinguishers, properly maintained. Ladders with anti-skid pads. Hook-on ladder when required for entering tanks through manhole. Fresh air blower complete with hose to introduce fresh air into tanks, when maintenance workers are required to enter a tank. One or more fire blankets. ropes and associated rescue equipment. Maxi-pot cages (spring brake cages) Jack stands. Maintenance manuals and logs. NOTE: The above is just some of the equipment that must be available, but is by no means the only equipment. It is the responsibility of the foreman or supervisor and/or employees that everyone is familiar with the safe handling and storage of that equipment. Everyone must endeavor to keep this equipment in good condition, clean and report anything missing or damaged immediately to your foreman or supervisor. 4.2.3 Handling of Chemicals or Airborne Contaminants In our work, we at times handle chemicals. Please be sure that you know the hazards involved when working with these chemicals and that you protect yourself and co-workers from harm. Some of the products you may have to work with are Methanol, glues, gaskets, kool tool, WD40, electro motive, silica sand. Be on guard at all times. It is your responsibility to use PPE and become acquainted with the way it should be handled (MSDS) and follow the instructions to the letter. If you are splashed with any chemicals, wash off with cold water immediately, and report to First Aid as soon as possible. The amount of a hazardous substance in a work area should not exceed the quantity reasonably needed for work in progress. All hazardous substance must be handled or stored in a container designed, constructed and maintained in good condition to securely handle the substance. Use proper precautions where flammable substances are present. Should a worksite environment necessitate Respiratory Protective Equipment because of exposure to airborne contaminants exceeding their occupational exposure limits or the atmosphere has an oxygen concentration of less that 19.5% by volume, Haltech Testing Inc. employees are to vacate this environment immediately unless the client has provided all the safety equipment and qualified safety personnel onsite. 21 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.2.4 Cranes and Overhead Work Every employee is warned to stand clear of crane loads. Working with cranes or booms near overhead power lines shall proceed only after making sure that no contact can occur. Before using any ladder, inspect it. See that it has proper safety feet and is free from cracks, broken rungs, and other defects. If necessary, to prevent slipping have someone hold the bottom of the ladder securely. Where practical, tie the top of the ladder securely. 4.2.5 Welding Gases & Guns Welding gases should be treated with care. Cylinders containing gases cannot be thrown around as they are under very high pressure. A valve breaking off a full bottle can create a rocket endangering everyone. The following compressed gases are commonly used in our shops: Oxygen – Oxygen supports and can greatly accelerate combustion. For this reason do not store substances which are combustible (oil, grease, rags, etc.) near oxygen cylinders, pipes or hoses. Do not smoke in an area where oxygen is stored. Oxygen, as a liquid or cold gas, may cause freeze burns. Do not touch frosted pipes and/or valves. Argon and Carbon Dioxide – Both of these gases can cause asphyxiation and death if confined, poorly ventilated areas. Argon and carbon dioxide can also cause freeze burns similar to oxygen. In liquid form these gases are extremely cold. Acetylene – This gas is highly flammable and explosive. Treat this gas with proper care. Even with copper, silver, and mercury, acetylene can at times become explosive. Keep acetylene away from sources of ignition and do not permit any accumulation of this gas. Do not leave welding guns or cutting torches inside a tank whenever you leave for a short coffee break or at lunch time. Make it a habit never to leave a gun or torch in a tank or close to the manhole for any period that you are not inside. Argon, acetylene, and other gases can kill by suffocation or explosion. For the above reason all welders and fitters are advised to wear long sleeved shirts preferably made of another material than cotton and certainly not white in color. 4.2.6 Storage Material and equipment must be placed, stacked or stored in a stable and secure manner. Stacked material or containers must be stabilized as necessary by interlocking, strapping or other effective means of restraint to protect the safety of workers. An area in which material may be dropped, dumped or spilled must be guarded to prevent inadvertent entry by workers, or protected by adequate covers and guarding. 22 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.2.7 Entry / Exits There must be a safe way of entering and leaving a workplace and a worker must not use another way if the other way is hazardous. Hazardous areas not intended to be accessible must be secured by locked doors or equivalent means of security, and are not to be entered without safe work procedures. 4.2.8 Injury or Sickness Do not try to remove foreign particles from the eye yourself. In the case of serious injury, do not move an injured person (except for safety reasons) until medical aid arrives. For the added safety of yourself and your fellow workers, acquaint yourself with the location of the following items in your work area: - first aid kit - fire extinguishers - fire blankets - nearest water outlet 23 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.3 PROCEDURES FOR WORKING ON TANKS IN SHOP 4.3.1 Introduction Most of the equipment, which is serviced in our shops, has been transporting hazardous hydrocarbon materials (explosive mixtures). It is obvious; therefore, that all our employees should realize that they should follow good safety procedures at all times and never attempt shortcuts. First and foremost, we should at all times know what dangers we are facing since knowing them can eliminate possibilities of injuries or worse. Always follow all prescribed procedures and never attempt to take a shortcut. Take the time to do a job safely. We just do not gamble with possible injury and/or death! The three ingredients necessary to create an explosion or a fire: 1st … a combustible material (gasoline, natural gas, paper, wood, etc.) 2nd… oxygen (pure or in air) 3rd … ignition (fire, spark, heat) Eliminating any one of these three will avoid a fire or explosion. Since air is present all around us and our type of work (welding, chiseling, cutting, etc.) will provide the ignition - Our best approach in almost all cases is to eliminate the combustible material. 4.3.2 Procedures Before you start any work, try to ascertain from the previous operator in what service the unit has been. NOTE: Do not completely rely on this information as always being correct for the driver may not have been aware of the last product present in that unit. Put the information received on the Unit Maintenance Log so everybody working on the unit will be aware of what to expect. Inspect the unit to see whether: Piping slopes in the proper downward direction. Equipment such as manifolds, reels, pumps, etc., where pockets of product can be trapped. Valves are operative. Space between double bulkheads can be steamed. Patches are welded over top of cracks which can cause pockets. Pads are used without vent holes. Sand and/or rust are present in the bottom of a unit. (Crude tanks are particularly bad for this and can create an extreme hazard if this is not removed before work commences.) Any other hazardous conditions. 24 Haltech Testing Inc. It is extremely important that a competent experienced person inspects the unit and report his findings. Any conditions which can possibly affect our fellow worker on this unit should also be noted in the Unit’s Maintenance Log. If, in the shop, units are being serviced, which have serviced a sour crude well, be on guard for hydrogen sulfide (H2S). (Refer to the H2S Alive Manual.) Prior to any welding being done on the barrel of the unit inside the shop, the unit must be freed of any combustible or explosive liquids or vapors. Work of a hot nature means that sparks and/or heat will be generated. For instance testing the sensors on a light petroleum unit could create a spark since a 24-volt current is used when testing. Hammering to loosen a corroded nut could create heat and/or spark, etc. In short, when in doubt whether a spark or heat could possibly occur, always take the safe route and remove the combustible and/or explosive material. In the Haltech Testing shop, in order to purge a unit from explosive liquids and/or vapors, the unit should always be steamed prior to arriving back at the Haltech Testing yard and after this, if necessary, be air purged. Continuous air blowing while the work is being done is another method of keeping a unit safe while you work on it. However, this has two disadvantages which make it not suitable as a standard procedure in Haltech Testing Inc. shop. First of all, this method brings the gases out of the tank and into the building you are working in and the possibility of it settling in pockets Second, it makes the use of an inert gas shielded welding gun inside the tank difficult. Moreover, in Haltech Testing’s shop, the above methods are not always acceptable since we want to utilize the safest possible method and there is always the possibility of a leak into a pad, resulting in trapped liquid. STEAM, simply because of its high temperature, will remove this liquid and the possibility of gaseous vapors building up again. Consequently, the only safe and proven method is always steaming and afterwards, if necessary, air purging. When a unit is steaming, be sure that as many vents and drains as possible are opened so that a good flow of steam goes through the tank. It is particularly important to have a drain open at the lowest possible point to avoid condensate build-up in the vessel. At this time all double bulkheads, lines, etc., are also steamed and purged. In certain cases where steam or condensate would damage a meter or other appendage the lines to this equipment should be disconnected as close as possible to the equipment. The appendage itself can then be aerated or carefully blown with air. 25 Haltech Testing Inc. Be sure to check for any possible hang ups of product and/or vapor. There is no set time for steaming. The type and condition of the unit as well as climatic conditions vary too greatly for a definite time. However, it should be understood that it is better to steam somewhat longer than what you initially thought necessary. A clean bore stainless steel or aluminum tank will be gas free much faster than an old corroded multi-compartment steel tank. After a unit has been completely purged of all liquids and vapors, the unit should be allowed to cool down by letting it sit for a time and/or by blowing it with air. After this, a test should be taken with an explosion meter. The meter must have a zero (0) reading when the unit is tested. Care should be taken to test all possible areas where vapors or liquids could be trapped. Apart from the compartments, areas between the double bulkheads, manifolds, pipelines, meters, inside the tunnel, legs, etc. should also be tested. If these tests show the unit is safe to work on, it can be brought into the shop. Before a worker proceeds to work on the unit, it is his responsibility to again test the unit in order to satisfy himself that the unit is completely safe. If the unit is a truck, great care should be taken that the fuel tank of the truck is properly protected against sparks either caused by a welding current and/or from cutting and welding. The battery of the truck or a trailer mounted engine should be disconnected at both terminals to avoid possible damage to the unit’s electrical system during welding. Batteries should be covered by a rag to avoid dropping sparks and exploding the hydrogen gas in the batteries. If work has to be done inside a tank unit, two (2) men (buddy system) will be assigned of which one should remain outside the unit watching the other work and be ready for assistance if this is required. When for some reason the worker inside the tank becomes incoherent or unconscious, the person outside should immediately drop a hose blowing air inside the tank and at the same time call for help. Assistance must arrive before entering the tank himself. A fire extinguisher should be handy and the person on watch should have immediate use of this device when so required. When working inside a tank, ensure that a tank ladder is used so that access and egress is facilitated. Suction and/or blowing fans should be used when working inside tank on a repair job. If a unit requires a lot of work and consequently will remain in the shop for an extended period, the unit should be regularly tested whether vapor may have built up again. Of course, a unit which was completely cut open over its full length will most likely remain safe, but when a multi-compartment unit where only one compartment is worked on, the possibility of vapors building up in the other compartments is possible, particularly in a heavily corroded tank. 26 Haltech Testing Inc. After a unit is repaired be sure that the inside of the unit is cleaned out and suitable for the product it is going to be used for. Give it that last check. In cold weather frequently a small amount of alcohol (methyl hydrate) is used to prevent valves, etc. from freezing. No hot work should be done after this procedure. In all cases: USE COMMON SENSE AND BE ALERT AT ALL TIMES. DO NOT TAKE SHORT CUTS. WHEN IN DOUBT, ASK. REALIZE WHAT HAZARDS COULD BE PRESENT AND LOOK FOR THEM. WARN YOUR FELLOW WORKER IN CASE HE DOES NOT APPROACH HIS JOB BE EXTRA CAUTIOUS. CORRECTLY. MAKE SUGGESTIONS IN CASE YOU HAVE A PRACTICAL IDEA AS TO HOW SAFETY CAN BE IMPROVED. 27 Haltech Testing Inc. 4.4 WORK SITE HAZARD ASSESSMENT & CONTROL The work sites ‘Haltech Testing Inc.’ employees must enter to perform their job have several potential hazards. These sites are not maintained by Haltech Testing Inc. but by the Oil Companies themselves. Thus, it is imperative that the Safety Rules and Work Procedures posted at each location and as stated in Haltech Testing Inc.’s Health, Safety & Environmental Program be followed stringently by the employee for their personal safety. The Worksite Hazard Assessment form is to be completed by the supervisor along with other employees upon arrival at the site and again for each change in conditions, surroundings or workers. The forms are kept on file at the office for three years. In addition, the following steps need to be taken to ensure the highest level of safety: 1. For off-site locations, fire hazard areas as well as other hazards will be identified and communicated to employees prior to commencing work activities. 2. If working alone, consider the additional hazards and make contact with your supervisor before entering the site and arrange a check-in schedule. 3. Ensure all proper PPE is onboard including SCBA prior to entering any work site, then determine the wind direction and position the unit accordingly. Assume H2S danger is present at any facility. 4. Check the H2S monitor for gas presence. If the H2S monitor exceeds 10ppm, put on SCBA immediately and notify your superior of conditions. 5. When hooked up, you must ensure that all connections are correctly made (i.e.: drop hose and grounding/bonding device, etc). 6. Under no circumstances are you to leave the unit until safe to do so. 7. Do not open any valves unless you are sure that all connections have been correctly made and all safety precautions have been followed. 8. Before leaving, perform a walk-around check of your unit before pulling away, to ensure that all valves are closed and all is ready for transport. Haltech Testing Inc.’s field supervisors are required to complete routine work site inspections to ensure the safety of their employees. Any deficiencies that cannot be rectified will be relayed to the manager. Management will proceed with corrective action. HAZARD ASSESSMENT TOOL We use the Riskex Risk Score Calculator available on Haltech Testing PC’s. 28 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.0 SAFETY RULES AND WORK PROCEDURES 5.1 Safety Rules -When driving onto a lease, take note of the wind direction (wind flag). 1. Drivers operating a tractor and trailer unit shall have a valid Class 1 License. 2. Before commencing work, ALL past experience of work including an abstract of licenses or driving record and required safety tickets must be presented to the employer. 3. No riders. Only company employees or contractors on company business are allowed to ride in company vehicles. 4. Anyone with a loss of 6 points or more on their driving record must take a “Defensive Driving Course” prior to commencing work. Failure to do so will result in employment refusal or dismissal. 5. Report all accidents/incidents, no matter how small or trivial they may seem. 6. Smoking or open flame is prohibited except in designated areas. 7. Intoxicating liquor or drugs and persons under their influence are strictly forbidden while on the job or on client location or Haltech Testing’s facility. 8. Do not show up for work still under the influence of alcohol from the night before. 9. Always use headlights and clearance lights when driving. 10.All company vehicles will be driven at or below the posted speed limits. For example: if the posted speed is 100 kms/hr, drive 90 kms/hr. All gravel roads maximum is 70 kms/hr. 11.Always respect all contractor and client road signs (speed limits, regulatory signs) 12.Tire wear and inflation pressure will be checked regularly as well as oil and radiator levels. Employees are not permitted to perform tire disassembly or reassembly as tire services must be performed by a professional. 13.Check vehicles daily by walking around vehicle to give an eye inspection and record it. Unit is to be grounded with a cable before commencement of inspection. 14. As part of preventative maintenance on Haltech Testing Inc.’s units, drivers will report all necessary repairs to the supervisor and record it in the “Unit Repair & Maintenance Log”. Operators have the responsibility of ensuring that the “Unit Repair & Maintenance Log” is checked before leaving the yard with any unit to be familiar with the unit they will be operating. 15. Operators must not work under vehicles with PTO engaged and without clocking tank vents. 16. Vehicles must be kept clean inside and outside. Ensure nothing obstructs the safe operation of equipment. 17. Employees shall ensure that company vehicles contain safety flares, first aid kit, a fire extinguisher and a flashlight (and seasonal emergency kit). 18. Employees shall ensure that all company vehicles and trailers have fully operating clearance, parking and signal lights, and are repaired as necessary. 19. Misuse of company property or equipment will bring automatic dismissal. 20. Supervisors will hold a tailgate (hazard assessment) meeting before starting work to inform employees of any safety hazards and the control or elimination of the hazard, record site personnel and first aiders, and to ensure general compliance with safe work procedures. 21. Never ride on a load that is in the process of being winched. Never be on top of an unsecured load, between the load and the pipe racks or tubs, or in any other area made hazardous by potential pipe/load movement. Pipes must be loaded on or unloaded from a truck one layer at a time. 22. Never walk under a suspended load. 29 Haltech Testing Inc. 23. All trucks must be properly grounded when necessary. 24. Never leave your vehicle unattended while hooking up (unhooking) or loading (unloading) at any site. 25. If a leak occurs, isolate as fast as possible and notify your supervisor or the appropriate site authority. 26. Understand your responsibility and duties including Emergency Response Plan. 27. Use safe fueling procedures. 28. Always put on tire chains while parked on a level area BEFORE driving into a slippery or muddy area. Chain up on both drive axles. 29. When following a truck that has a large or heavy load, wait until that vehicle has reached the top of the hill before proceeding up the same hill. 30. Never stand between a vehicle and the loading or docking area. 31. Always wear weather appropriate clothing, close fitting clothing and confined or short cut head and facial hair. Avoid wearing piercings, dangling neckwear, jewelry, or other similar items. 32. Drivers must at all times be aware of other workers around them when backing up, loading or unloading. 33. ALWAYS drive defensively. Be aware of careless actions of others. 34. Experienced employees share the responsibility for instructing new employees in matter of conduct and working safely. Improper activity or behavior will be reported and investigated. 35. Conduct which may be termed “practical joking”, “scuffling” or “horseplay” is forbidden because of the risk of serious injury. No activity that could result in a hazard to yourself or to any other person. 36. PPE to be worn in all designated areas. 37. Regular monitoring and/or hot work permits are required to control ignition sources. 38. All lights are to be clean before leaving the yard as needed. 39. All highway traffic regulations are to be strictly followed. 40. Decks on trucks and trailers are to be kept clean at all times. 41. Place stands or blocking under equipment before work commences. 42. Use the lock-out system on trucks, trailers, equipment or tools before any servicing or repairs take place. 43. Compressed air or steam must not be used for blowing dust, chips, or other substances from equipment, materials and structures if any person could be exposed to the jet, or to the material it expels or propels. 44. Obey all Haltech Testing Inc. and customer safety policies. 45. Haltech Testing Inc. employees are never involved in pipeline pigging. 46. WORK SAFELY. EMPLOYEE DISCIPLINE POLICY: SUSPENSION OR DISMISSAL DEPENDENT UPON SEVERITY OF INFRACTION. 30 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.2 STANDARD WORK PROCEDURES 5.2.1 Pre-Trip Service and Safety Inspection 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Check oil, coolant and belt tension Start motor and allow engine to properly warm up. Check all instrument panel gauges. Hook up airlines before backing under trailer where applicable. Check 5th wheel/hitches on all equipment, including converters, making sure it is properly locked and that all spindle locks operate properly where applicable. 6. Check air system and all brakes for adjustment. 7. Turn on and check lights including signal light – lenses should be clean and without damage. 8. Ensure that there is adequate air pressure in all tires and physically inspect the wheels, wheel nuts, and oil seals. 9. Note any damage to equipment on appropriate reports and report to your supervisor and report in the Maintenance Log. 10. Check your safety equipment. It is your responsibility to ensure that the equipment your unit carries operates properly. 11. Check that all licenses, registration, certification and permits are in your unit. 12. Conduct a thorough visual check of the complete unit. “Walk Around Check”. 13. Ensure windows and mirrors are clean and unobstructed. 14. Ensure that your unit has not sustained recent damage. It is your responsibility to ensure that all damage is noted with your supervisor prior to your departure. 15. Ensure that your trailer is properly equipped with the appropriate number of placards (if required) and labeling . 5.2.2 Placarding of Vehicle 1. Placards identifying the class of dangerous goods being transported must be displayed on: i. Cargo tanks and tanks containing dangerous goods or residues of dangerous goods from a previous load requiring a placard. ii. Vehicles containing more than 500 kgs (1,100 lbs) or more than 5 containers (combined) of all other classifications of dangerous goods. 5.2.3 En Route Inspection and Safety Check To be carried out approximately every 1.5 to 2 hours on pavement and every 1 to 1.5 hours on gravel. The first en-route inspection is to occur within the first hour of starting your trip. 1. Pull completely off the road into a safe location. 2. Begin your en-route inspection by walking down the driver’s side of your unit against the flow of traffic. 3. Physically check the tires. 4. Visually check for oil and coolant leaks. 31 Haltech Testing Inc. 5. Check all wheels, wheel nuts, feel hubs for excessive heat and check oil levels in sight glasses. 6. Inspect air hoses and connections. 7. Clean windshield, lights and license plates when necessary. 8. Complete a thorough visual inspection of your equipment. 9. Drain air tanks periodically to ensure air system is free from moisture and freezing at least every 24 hours. 10. Check oil and coolant levels. 11. Ensure load remains secure. 5.2.4 Air Brakes 1. Drivers shall regularly check all brakes on the unit to ensure that they remain in proper working order. 2. You must have full system pressure to operate your brakes properly. It is your responsibility to ensure that the full system pressure has been achieved prior to operating your vehicle. 5.2.5 Driving as a Professional To be a professional driver requires much more than just the skill to operate a motor vehicle. It requires a “professional attitude” that promotes safe, courteous driving and pride in a job well done. It also requires that maintenance of vehicles and equipment is one of the driver’s top priorities. Always consider the “consequences of your actions”. Safety is extremely important in our industry – we must conduct ourselves as true professionals at all times. 5.2.6 Employee and Contractor Training and Orientation Haltech Testing Inc. recognizes that initial safety training is one of the most important aspects of a safety program. In pursuit of achieving corporate objectives and superior results employees are continuously encouraged and supported to upgrade their professional skills. All employees of Haltech Testing Inc. are required to have the mandatory work permits – TDG, WHMIS, H2S Alive, G.O.D.I. (for truck drivers), Fatigue Management and First Aid. If the potential employee does not possess the above permits Haltech Testing Inc. will arrange for the permits. The recruiting and hiring of new drivers is critical to the success of Haltech Testing Inc. As such Haltech Testing Inc. has developed a program to ensure that all new drivers are interviewed, screened, tested and trained by qualified Haltech Testing Inc. staff. All prospective employees (driving for the company) are required to submit a current drivers abstract and resubmit abstracts on a yearly basis. Upon hiring the employee will submit a 3 year employment history and copies of all relevant safety tickets. All employees will fully disclose any violations, incidents and accidents they have prior to employment as well as while in the employ of Haltech Testing Inc. regardless of whether the violation occurred during work hours or during time off. All sub-contractors and independent contractors are also subject to the same qualification and training procedures. (Refer to part 7.0.) 32 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.2.7 Equipment All trucks must be equipped with: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Approved directional lighting Properly operating braking system H2S personal detector #1 first aid kit Fire extinguisher All required documentation 5.2.8 Equipment, Tools and Materials No worker shall use any tool without proper training in its correct use unless supervised by a worker competent in the use of that took, equipment or appliance. 1. All contractor supplied equipment and tools required to complete the task undertaken must be in good working order. 2. Any tools damaged or in need of repair must be tagged “Unserviceable” and should not be used until repaired or replaced. 3. All portable lamps, extension cords and electrical tools must have proper ground and be certified for the electrical classification of the work area in which they are to be used. Explosion proof equipment should be used in situations where combustion or explosion is possible. 4. Before leaving pneumatic tools unattended bleed air pressure from the airline. 5. When using electrical tools in a wet area use a ground fault interrupter (GF) circuit breakers on the power line or check that equipment insulation is sound using an insulating platform and wear rubber gloves to minimize shock hazard. 5.2.9 Excess Head and Facial Hair Haltech Testing Inc. employees and contractors must be clean-shaven, mustaches neatly trimmed and sideburns trimmed to not extend below the ear lobe. Head hair should be cut to above the collar or tied back or contained above the collar with a hair net. Anyone failing to comply with this policy will be refused access to the work site and may be subject to disciplinary action. 5.2.10 Firearms No employee shall carry any firearms on themselves or in their vehicles on any Haltech Testing Inc. sites. 33 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.2.11 Heating Within Haltech Testing Inc. of P/L right-of-way, contractor built or supplied tool sheds, field offices, temporary work structures or shanties must not be heated with open electric heaters or other nonexplosion proof devices without approval from a Haltech Testing Inc. representative. All rigid gas and propane lines for temporary heating must be connected by a tradesman with a valid gas fitter’s ticket. 5.2.12 Housekeeping/Right-of-Way Behavior All employees shall ensure that good housekeeping practices are continuously observed at Haltech Testing Inc. work sites. All exits and emergency equipment must be kept clear of obstructions. Work sites must be left in an orderly fashion at the end of each workday and at the end of the job. Posted signs, including pipeline right-of-way speed limits must be adhered to. Ensure that survey markers, line locates or paint marks are not obscured by materials, vehicle, and equipment movement or spoil piles from excavations. Floors, platforms, ramps, stairs and walkways available for use by workers must be kept in good repair and kept free of slipping and tripping hazards. Material storage should be on level ground and materials that may be blown about by the wind should be secured or covered by a tarp. Combustibles at work sites shall be stored in a covered, well-ventilated shed located a safe distance from other material storage and identified with appropriate warning signs. All rubbish or excess building materials must be collected in bins/barrels and taken to an approved disposal site or area designated by Haltech Testing Inc. representative. Never let waste blow off a right-of-way or lease onto landowner’s property or into ditches. Hazardous wastes or WHMIS controlled products must be disposed of properly. Burning is not permitted at Haltech Testing Inc. sites without permission of the Haltech Testing Inc. representative. The contractor is responsible for supplying proper sanitary facilities and potable water for their employees at work sites. 5.2.13 Alcohol and Drugs Possession of or being under the influence of illegal drugs, controlled substances or alcoholic beverage is strictly prohibited on Haltech Testing Inc. work sites. Abuse of or use of will be cause for removal from the work site. A worker must ensure that legitimate use of over the counter medications or prescription drugs does not impair one’s ability to perform their job. No employee or contractor shall distribute, possess, or consume alcohol or illegal drugs on any work site occupied by the Company or in any Company vehicle or equipment. No employee or contractor, including on call workers, shall report to work or be at work under the influence of any drug or substance that may or will affect his/her ability to work safely. No employee or contractor shall misuse prescription or nonprescription medication while at work. All workers must report to their supervisor any medication that may affect their ability to safely perform their job. No employee shall refuse testing or substance abuse evaluations. 34 Haltech Testing Inc. Drug and Alcohol Testing A third party will be used to administer the testing provisions if deemed necessary. The worker to be tested will be accompanied by a supervisor. Testing and test results will be conducted in a manner that protects the privacy and dignity of the individual. Testing may be done: Incident: Of an employee for alcohol and/or drugs when impairment or drug and/or alcohol use may have been a factor. Reasonable Suspicion Testing: When a company supervisor or other official makes observations which form a reasonable basis for suspecting that the employee is in breach of this policy. Reasonable Suspicion is based in observations concerning appearance, behavior, speech, body odors and/or possession of alcohol, drugs or paraphernalia. Pre-employment: Employees in safety sensitive positions may be tested prior to working. Consequences of Failure to Comply: An employee who fails to comply with this policy may be disciplined or terminated as deemed appropriated in regards to nature of the violation, the existence of prior violations, the response to prior corrective programs and the seriousness of the violation. Employees who test positive on an illegal drug or alcohol tests over the alcohol level of .04 will be removed from duty and suspended without pay and/or terminated. 5.2.14 Ladders Portable ladders must meet all regulatory requirements and shall as a minimum be: 1. CSA approved and equipped with safety feet on hard surfaces or spike feet for soft surfaces. 2. Ladder must be inspected before use on each shift, and after any modification, and any condition that might endanger workers must be remedied before the equipment is used. 3. In good condition, never painted, and must be marked for the grade of material used to construct the ladder and the use for which the ladder is constructed. 4. Tied off at the top with tag lines or held by another worker and extending at least 1 m beyond the top of the bearing point. 5. Nonconductive if being used for electrical work. Never climb or step onto small piping, tubing or electrical conduits. 6. Overlap upper and lower sections of extension ladders by at least three rungs. 7. Set the base of the ladder at least one quarter of the vertical length from the base of the wall or structure and the operator is never to use the last two rungs. 8. Not be used if there is another safe way to enter or leave an area. 9.If work cannot be done from a ladder without hazard to a worker, a work platform must be provided. A worker must not carry up or down a ladder, heavy or bulky objects or any other objects which may make ascent or descent unsafe. 5.2.15 Lifting Haltech Testing Inc. recommends mechanical lifting, lowering, pushing, pulling, carrying, handling or transporting any load in excess of 20 kg (44 lbs) whenever possible. In any case, avoid lifting anything over 50 lbs. without assistance. When lifting any object plant your feet securely, lower your body by bending at the knees (never bend from the waist), firmly grip the object to the lifted position and lift with your leg muscles while avoiding any twisting of your back. When lifting jagged or sharp edged objects be sure to use gloves to protect your hands. Get assistance from a coworker to lift anything heavier or awkward. 35 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.2.16 Maintenance Program Maintenance records must be kept available to equipment operators and inspecting personnel, including but not limited to the name of manufacturer, the type of equipment, the date put into service, when and for what purpose the equipment has been used, the date of the last inspection and name of the inspecting person, any damage suffered, and the date and nature of all repairs and maintenance. Tools & Equipment Maintenance The operator of any vehicle/mobile equipment shall be directly responsible for the safe operation of that equipment. The operator shall examine his/her equipment before initial daily use and thereafter as required. When the operator has reasonable cause to believe that the equipment is not in proper running order, he/she shall take action to ensure that the equipment is repaired before use with lockout tag-out system and procedures. Manufacturer’s specifications are to be adhered to in service, repair, testing, adjustment, or inspection. A log of inspections and maintenance will be immediately available to the equipment operator and to any other person involved with inspection and maintenance of equipment. Records will be retained until six months after the sale of a piece of equipment. Lockout /Tagout If an employee must interact with a machine (other than normal operating mode) in a manner which may have the potential to cause injury to oneself or others, then he or she must lockout the machine. It is the responsibility and right of an employee to lockout and ensure the control of energy whenever he/she has a need to place any part of their body in a position on or near machinery/equipment where unexpected movement, release of stored energy, energizing of electrical systems, of the flow of gases, fluids or other materials and could have the potential to injure oneself or others. Covers, guards and stop buttons are not to be used as lockout devices. Only devices which allow for eliminating the possibility of release of energy are to be used to service, repair, test, adjust or inspect the equipment safely. Employees will be trained in lockout procedures. Where lockout tags are used, the person who initiated the lockout on the machine must be in control of removing the lockout. Only the employer may authorize another competent employee to remove a lockout tag from equipment or machinery if necessary only after verifying that no worker will be in danger due to the removal. AT NO TIME SHOULD MACHINERY/EQUIPMENT BE LEFT IN AN UNSAFE CONDITION WITHOUT BEING TAGGED OUT. • Identify the machinery or equipment… • Shut off the machinery or equipment… • Label & Identify and de-activate all energy… • Apply a lock/tag… • Test it… See Lockout/Tagout Procedure. 36 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.2.17 Permits and Completion of Documents There are several documents that are essential to our business. Employees must submit all requested documents deemed necessary by Haltech Testing Inc. in a timely fashion and in neat, legible writing. These documents are identified below: 1. Field Tickets 2. Time Sheets and Invoices 3. Worksite Hazard Assessments 4. Unit Inspections 5. Driver log books (hours of service) 6. Pre-trip and post-trip inspection reports (Kenworth’s) 7. Unit maintenance logs 8. Others as applicable Until the above are properly and accurately completed and filled in, the operator’s pay cannot be processed. 5.2.18 Personnel Safety All personnel involved in the produced fluids from (possible sour) wells shall: 1. Know the dangers and effects of hydrogen sulfide gas or any other chemical hazard or biological hazards on site. Ceiling level exposure to a substance listed in Schedule 1 Table 2 of the Occupational Health and Safety Code is not to be exceeded at any time. 2. Be properly trained in the use of respiratory equipment. 3. Be clean shaven at all times. This is to facilitate the effective sealing of a faceplate should respiratory protective equipment be required. 4. A worker must perform a negative pressure seal check before each use of a respirator. The contractor shall ensure that his employees are supplied with and wear all the necessary personal protective equipment required for the job as specified by regulatory requirements and in Haltech Testing Inc.’s Health and Safety Program. 1. Wear approved hard hat while being in the vicinity or on any worksite. 2. Ensure employees are protected from traffic hazards. 3. At all times wear appropriate clothing. 4. Smoking is prohibited except in designated areas. 5. Entrance to any lease must be double checked with supervisor if the flare is out, if there is any evidence of any gas leaks, and/or the H2S monitor detects a reading above 10ppm. The lease operator will be notified if any of these conditions exist. 5.2.19 Public Relations and Highway Courtesy All vehicles have equal rights on the highways. The way our units are operated will reflect upon our image. While we gain the respect of the public on the road, it is equally important that this image be conveyed while off the road – whether at coffee shops or an inspection station. Be conscious at all times that you represent Haltech Testing Inc. wherever you are! 37 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.2.20 Refuse Unsafe Work Any worker has the right to refuse unsafe work. If you think that the work you do or the piece of equipment you use is unsafe you can stop this work immediately by citing your legal right to refuse unsafe work. Once you refuse to continue, procedures exist for rectifying the situation. Contact your supervisor or health and safety representative to find out how to correct the unsafe situation. Do not continue to work until you have been advised that the situation has been corrected. The supervisor will investigate the matter immediately ensuring that any unsafe condition is remedied or if in his or her opinion the report is not valid, must so inform the person who made the report. 5.2.21 Safety Belts and Lifelines and Rescue Equipment Safety harnesses, rescue gear, ropes and equipment must be inspected visually and physically by qualified workers after each use, or when used for training purposes. When it is impractical to provide work platforms and guardrails, all workers shall wear a CSA approved safety harness with a safety line, or wear a lanyard when: a) Working on temporary work platforms 2.4 m (7.8 ft) or greater above the nearest permanent safe level. b) When work is being done over operating equipment or equipment hazards such as protruding valves, or over water or open tanks. c) When working from a temporary structure at a height of more than 6 m above a permanent safe level d) When working from a ladder at a height of more than 2.4 m above the nearest permanent safe level where, because of the nature of the work, that person is unable to use at least one hand to hold onto the ladder. Use a safety rope or lanyard which is no more than 2m long and tied off so a worker can fall no more than 2m. Harness/fall arrest systems must meet three criteria: 1. They must be used only for the purpose for which they were designed. 2. All metal components must be built to withstand 4000 lbs. strain (17.8kN). 3. The rope or lanyard must be built to withstand the impact of a falling worker (TEN times the worker’s body weight). Safety harness must meet the design specifications outlined in CSA Standard Z259.10-M90. Anyone working on an elevated scaffold must have their safety harness tied into a lifeline, which is fastened to the top of the structure where the worker is working and extends freely to the ground. 5.2.22 Temporary Structures - Scaffolds and Platforms For working above 3 meters, scaffolding must be in place – ladders cannot be used. Scaffolding must be secured from accidental movement. All scaffolds, platforms and ladders used by the contractor shall be constructed, maintained and used in compliance with the applicable OH&S regulations & manufacturers specifications and erected by qualified personnel to minimum specs. While erecting scaffold, mark or designate it as “unsafe”. Scaffolding should only be designated as “safe” to use once erection and bracing is complete and mudsills/base plates, work decks, handrails 38 Haltech Testing Inc. and toe boards and sectional pining are installed and checked, the scaffold has been tied to permanent structure and outriggers are in place (when scaffold is above 4m high). Do not enter a temporary structure unless it has been inspected and you are authorized to use it and you have been trained and instructed in its safe and proper use. 5.2.23 Smoking Smoking is allowed only in designated areas. Only safety matches or lighters with enclosed or covered mechanisms are permitted on the site. Strike anywhere matches or open mechanism disposable lighters are prohibited on field locations. 5.2.24 Tire Chains Drivers are expected to use good judgment on deciding when to install tire chains, before getting into trouble. When chaining up ensure to chain both drive axles. 5.2.25 Towing In extreme conditions, if the unit is loaded, it must be unloaded into another unit before it is towed. When a unit gets stuck, where possible, the driver MUST notify their supervisor BEFORE the unit is towed. The towing vehicle must be capable of towing the stuck unit in a safe manner. A cotton towrope or nylon webbed tow strap with no metal eyelets is the preferred equipment for towing. The towrope or strap must be in good repair, load rated and of sufficient strength to safely carry out the towing operation. If towropes or straps are unavailable, chains and cables may be acceptable if they are in good repair, load rated and of sufficient strength to safely carry out the towing operation. CHAINS AND CABLES MUST NOT BE JERKED DURING THE TOWING PROCEDURE. If a clevis is used it must be the threaded pin type and have the load rated capacity and sufficient strength to safely carry out the towing operations. UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES will ropes or straps equipped with metal hook and chain tail ends or any other type of clevis be permitted. 5.2.26 Welding If a hot work permit is issued for welding the amount of general structural fabrication etc. within the area tested for flammable hazards should be kept to a minimum. This general fabrication should be done outside of the area subject to the permit wherever possible. The contractor shall use only competent, licensed welders to operate cutting and welding equipment. All welders must wear fire resistant coveralls, proper welding gloves and eye protection. When welding on anything other than mild, uncoated steel, respiratory protection is also required. Gas welding hoses must be equipped with appropriate flame arresters or check valves. Gas cylinders must have valve cover caps put in place when the cylinders are not in use. Always turn gas flow off at the tank and the torch. Any raising or lowering of cylinders with a crane or hoist should be done with a rope cylinder cradle, not a cradle fashioned from chains, cables, ropes or a sling. A hot work permit is required for work such as welding, grinding and oxygen cutting. Areas for structural steel and pipe fabrication require welding screens to protect any nearby workers from welding flash. When welding, fire extinguishers should be easily accessible to the welder. Hot tapping or stress relieving require detailed procedures, pre-job discussion between the Haltech Testing Inc. 39 Haltech Testing Inc. representative and must be placed on the material being welded and closely adjacent to the arc unless an alternative method is approved. Welding machines must be turned off at the end of each day’s work or when left unattended. 5.2.27 WHMIS All workers have the “Right to Know” about all substances (WHMIS regulated or not) at the work site. Management will consult with employees to ensure an effective WHMIS program, which addresses applicable WHMIS Requirements including education and training, and is reviewed annually, or more frequently if required by a change in work conditions or available hazard information. Management must approve any new hazardous products prior to purchase. Only controlled products permitted by Haltech Testing Inc. management shall be used on a Haltech Testing Inc. site. All controlled products must be properly (WHMIS) labeled. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for all materials must be provided. All workers working near or with a WHMIS regulated material must: 1. Understand the product’s short and long term health effects. 2. Understand the proper environment, use, storage and handling of the product. 3. Know what personal protective equipment to use, if any. 4. Know and be able to administer the necessary first aid. 5. Understand procedure for disposal of hazardous waste. All WHMIS labels must be clear, easy to read and prominently displayed on the product container. If a product arrives without a WHMIS supplier label or with an incomplete one, the product cannot be used. Let the Supervisor know about the problem. The product can be returned to the supplier. Alternately, it can be stored while the Company gets the right label and has it applied. However, a placard is required to identify these stored products until proper labels are obtained and applied. Workplace Labels are labels applied at the workplace. They are used on: Controlled products that are made at the workplace for use there, such as solvents that are redistilled. Controlled products that are transferred from the supplier’s containers or from Bulk storage to workplace containers. To replace supplier labels that have been damaged. On-site bulk storage containers if the supplier has not provided a supplier label. Workplace labels have only three pieces of information: 1. Name of the product. 2. Information on how to use the products safely. 3. Reference to the MSDS for further information. 5.2.28 Worksite Ergonomics The purpose of the ergonomic program is to focus on the well-being of workers by evaluating, preventing, and managing work-related hazards or risks associated with musculoskeletal injury’s (MSI’s) and educating workers who may be exposed to the possibility of MSI in specific measures 40 Haltech Testing Inc. to eliminate or reduce that possibility. Training includes identification of factors that could lead to a MSI, the early signs and symptoms of MSI and their potential health effects, and preventive measures including, the use of altered work procedures, mechanical aids, and PPE where applicable. Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI): MSI means an injury or disorder of the muscles, tendons, ligaments, joints, nerves, blood vessels or related soft tissue including a sprain, strain, and inflammation, that may be caused or aggravated by work. They are also known as Cumulative Trauma Disorders or Repetitive Motion Injuries. Activities that may cause MSI’s include: Frequently repeating an activity or motion (e.g., turning valves, using a keyboard, or mouse). Awkward, static, or prolonged positioning of the body (e.g., working at the computer or driving). Forceful exertion (e.g., lifting, pushing, pulling). Exposure to vibration (e.g., using hand tools or operating heavy vehicles). Prolonged exposure to heat or cold. Symptoms of MSI’s are: Stiffness Tingling/Numbness Pain Swelling Fatigue Workstation/Area Analyses: Analyses are conducted to review any concerns; equipment needs, and work area changes. These analyses look at the job tasks, work practices, workstation design, equipment, and environmental factors such as temperature, lighting, and noise. Consequently, recommendations to modify the workstation/area may be made. These analyses also identify potential risk behaviors that may require changes or modifications to existing work habits to prevent an injury or illness. The employer will consult with workers who have signs or report symptoms of MSI and workers who perform similar tasks to identify work related causes and if necessary take corrective measures to prevent further injury. The effectiveness of measures take to minimize MSI will be reviewed annually and deficiencies will be corrected. Hazard Prevention and Control: Symptoms of MSI as well as prevention will be included in employee orientation. A worker to be assigned to work which requires specific measures to control the risk of MSI, will be trained in the use of those measures, including procedures, mechanical aids and personal protective equipment. Hazard prevention and control is also accomplished by modifying and/or rotating jobs, physically changing the workstation/area, adjusting tools, or monitoring the work environment to ensure over exposure does not occur. This process eliminates or reduces the risk factors associated with injuries or illnesses occurring in the workplace. See the attached “Ergonomics Checklist” for additional preventative measures. Breaks to Reduce Strain: Tedious work (e.g., data entry) requires 3 to 5-minute breaks every hour. Driving or operating heavy equipment for long periods require breaks every 1 to 2 hours. 41 Haltech Testing Inc. In addition to breaks, short “mini-breaks” of stretching, hand exercises, shoulder shrugs, or neck rotations will improve circulation and reduce stress on the body. Alternating job tasks also helps prevent discomfort and fatigue. Reporting MSI Signs and Symptoms: Early detection of signs and symptoms can prevent the progression and severity of MSI’s it is the worker’s responsibility to report MSI signs, symptoms, or concerns. If symptoms of musculoskeletal injury are reported, prompt review of the activities of that worker and workers doing similar tasks will be conducted and necessary corrective action taken to avoid further injury. 5.2.29 Modified Work When an employee is injured and modified work is recommended by the physician, Haltech Testing Inc. will make every reasonable effort to provide suitable temporary modified employment as set out in the WCB program. Participants placed on modified work will be expected to provide feedback in order to improve the program. 5.2.30 Working in Extreme Conditions A worker should not be exposed to levels that exceed those listed in the screening criteria for heat or cold stress exposure in the heat or cold stress and strain section of the ACGIH Standard. If not practicable, reduce the exposure of workers to levels below those listed in the screening. If exposure is likely, Haltech Testing Inc. will include a heat or cold stress in the hazard assessment to determine the hazards and develop and implement a heat or cold stress exposure control plan. If a worker shows signs or reports symptoms of heat or cold stress, the worker must be removed from the hot or cold environment and receive first aid. 5.2.31 Fatigue Management Haltech Testing will promote awareness of the impact of fatigue on human performance and promote a work environment that allows for effective implementation of fatigue counter measures. Workers will arrive at the worksite fit and ready for work ensuring they have received adequate rest and nutrition prior to arrival. (22 hours awake can be equal to 0.08 blood alcohol level.) Workers fatigued are unable to work safely and may present a hazard to themselves and others and are required to report problems with fatigue to the supervisor and also alert co-workers of their signs of fatigue. Fatigue can lead to the following conditions, effects, or behaviors which increases the risk of incident. Inability to see properly Slower reflexes and reactions microsleeps (brain goes to sleep for up to 60 seconds and worker blacks out) automatic behavior (routine tasks without conscious thoughts) inability to make good decisions inability to concentrate, solve problems decreased alertness inability to remember things just done, seen, or heard 42 Haltech Testing Inc. inability to notice things the worker would usually notice more mistakes than usual poor logic and judgment inability to respond quickly or correctly to changes inability to communicate well inability to handle stress moodiness (giddy, depressed, irritable, impatient, restless) Supervisors will assess if fatigue is a hazard and make recommendation to management. 43 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.3 PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is to protect employees from the risk of injury by creating a barrier against workplace hazards. Personal protective equipment is not a substitute for good engineering or administrative controls or good work practices, but should be used in conjunction with these controls to ensure the safety and health of employees. Personal protective equipment will be provided, used and maintained when it has been determined that its use is required and that such use will lessen the likelihood of occupation injury and/or illness. 5.3.1 Head Wear Approved hard hats must be worn on all Haltech Testing Inc. work sites and must meet CSA Standard Z94.1-92 and be marked as such. If lateral impact to the head is likely, appropriate industrial protective headwear that meets legislative requirements must be worn. 5.3.2 Clothing & Body Protection Workers are responsible for providing clothing needed for protection against the natural elements, general purpose work gloves, and appropriate footwear including safety footwear, and safety headgear and coveralls. Clothing must be long sleeved shirts and full length pants. Wear no jewelry. Flame resistant coveralls/outerwear will be worn when working on jobs near existing wells, plants, batteries, rigs or pipelines. It is recommended that under layers of clothing next to the skin be made of flame resistant fabric or 100% natural fibers that will not melt when exposed to heat. Fire resistant clothing is defined as having inherently fire resistant fibers, second flash fire and will not support combustion. Outerwear excessively contaminated with hydrocarbons must be changed and laundered as it will pose a fire hazard and result in skin irritation. Nylon clothing is strictly prohibited. Do not clean clothing by blowing with compressed air or washing in gasoline, kerosene, or a solvent. Properly fitting arm, leg, torso or skin protective equipment that is appropriate to the work hazard or work site must also be worn if this type of injury is likely. Additional high visibility apparel meeting the Type 1 or Type 2 criteria of WCB Standard Personal Protective Equipment Standard 2-1997 must be worn by a worker exposed to the hazards of vehicles traveling at speeds in excess of 30 km/h or if exposed to the hazards of mobile equipment, high visibility apparel meeting at least the Type 3 criteria. 5.3.3 Foot Wear CSA approved – CSA standard Z195-02 – Class 1 footwear is mandatory for anyone required to work, supervise, inspect or visit a field work site. CSA approved boots can be identified by the green triangle on them. All boots must have a raised heel. Shoes are inadequate. 5.3.4 Eye Protection CSA approved –standard Z94.3-92, Z94.3-99, Z94.3-02 – eyewear with side shields or face shields will be worn on all job sites. The use of contact lenses or prescription eyewear is acceptable provided that safety goggles are worn for added protection. Under no circumstances will contact be permitted while using respiratory protections. If wearing contact lenses poses a hazard to the worker, he/she must be advised of the hazard and the alternatives to wearing contact lenses. In instances where the eyes may be exposed to hazardous chemicals, eyewash facilities shall exist. 44 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.3.5 Hearing Protection A noise assessment will be conducted where workers may be exposed to noise levels in excess of the occupational exposure limits. Every possible effort will be made to reduce the noise to which workers are exposed. Whenever noise hazards in excess of either 85 dBA Lex daily noise exposure level or 140 dBC peak sound level, all persons entering the area will be informed and must wear hearing protection (meeting the requirements of CSA Standard Z94.2-02). Should an assessment confirm workers are exposed to excessive noise, a management program with detailed procedures will be developed which will include noise measurement, education and training, engineered noise control, hearing protection, posting of noise hazard areas, hearing tests, annual program review (as per BC OHS Part 7 Section 7). If noise level reduction to or below noise exposure limits is not practicable, noise exposure will be reduce to the lowest level practicable and warning signs posted in the noise hazard areas and the Haltech Testing Inc. will ensure that hearing protection is worn effectively in noise hazard areas and will give workers who are exposed to noise that exceeds noise exposure limits an initial hearing test as soon as practicable after employment starts, and a test once every 12 months after the initial test. Hearing tests will be administered by a hearing tester authorized by the Board. (test results will be sent to the Board when required). When we have no control over noise at the client’s site, employees will abide by the client’s safety program instruction regarding noise and hearing protection. Records will be kept of the annual hearing test results for each worker for as long as the worker is employed with us, and not released to anyone without the written permission of the worker. Records will also be kept of the education and training provided to workers, and the results of noise exposure measurements taken. 5.3.6 Personal Monitors & Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus Sites which have the potential to develop flammable, toxic or explosive atmospheres require the use of personal monitors (H2S, DO, LEL) and the availability of a self-contained breathing apparatus. All employees shall be fitted and trained in the proper use of these monitors and apparatus’s prior to coming on site. All workers must use the appropriate respiratory equipment provided. (See Code of Practice.) 5.3.7 Special Health Considerations Anyone with special health considerations – for example, epilepsy or allergies to wasp or bee stings – should supply specific first aid specialty items required on site to treat reasonably foreseeable emergencies resulting from such special health considerations. These workers must let other workers and/or first-aid personnel know of their special health requirements. 45 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.4 ENFORCEMENT 5.4.1 Description of Driving Offences (As of May 2005) No driver’s license Wrong class license/fail to obey condition/restriction Operate motor vehicle without license in possession Fail to produce driver’s license to peace officer Fail to produce vehicle registration to peace officer Fail to produce vehicle insurance to peace officer Possess invalid driver’s license Operate unregistered motor vehicle or trailer License plate not properly displayed License plate expired on MV or trailer License plate not attached/legible or visible Possess mutilated/altered document Drive while license is suspended/cancelled Operate over dimensioned MV on hwy contrary to permit or traffic safety act Unauthorized dumping/unloading of goods on a highway Transport goods not properly secured/loose load Fail to report to inspection station Fail to stop at stop sign Fail to obey traffic control device Fail to maintain drivers log book Fail to produce drivers log book Exceed allowed driving hours False log book Brake lights not working Signal lights not working Inadequate brakes – out of adjustment Trailer brakes non-compliant Inadequate mirrors Fail to wear seat belt Overload – divisible load – 5000 kg or less Overload – divisible load – Over 5000 kg Overload – permitted load – 5000 kg or less Overload – Road ban/Restricted bridge 5000 kg or less Overload – Road ban/Restricted bridge over 5000 kg $230.00 230.00 115.00 172.00 172.00 172.00 345.00 230.00 115.00 230.00 115.00 345.00 COURT COURT 575.00 345.00 230.00 287.00 172.00 345.00 345.00 345.00 345.00 57.00 115.00 172.00 172.00 57.00 115.00 $24 per 100 Kg $40 per 100 Kg $29 per 100 Kg $29 per 100 Kg $40 per 100 Kg 46 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.4.2 Description of Speeding Offences The specified penalties payable in respect of contraventions of section 15 (2)(p) and ® of the Traffic Safety Act and sections 53(5) © and 70 of the Use of Highway and Rules of the Road Regulation are those set out below: K/Hr Over Limit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Fine Amount 57.00 59.00 62.00 64.00 66.00 69.00 71.00 73.00 75.00 78.00 80.00 82.00 85.00 87.00 89.00 103.00 110.00 113.00 120.00 124.00 129.00 136.00 140.00 147.00 150.00 K/Hr Over Limit 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Fine Amount 156.00 161.00 166.00 172.00 177.00 187.00 194.00 203.00 211.00 219.00 228.00 236.00 247.00 255.00 264.00 273.00 281.00 290.00 299.00 307.00 316.00 325.00 333.00 432.00 351.00 47 Haltech Testing Inc. Haltech Testing Inc. Baytree, Alberta Code of Practice PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT 1. Policy 2. Purpose 3. Responsibilities 1. Managers/Supervisors 2. Employees 3. Office of Health and Safety 4. PPE Distribution 5. Program Components 1. Hazard Assessment & Equipment Selection 2. Protective Devices 1. Eye and Face Protection 2. Head Protection 3. Hearing Protection 4. Foot Protection 5. Hand Protection 6. Personal Monitors 7. Self Contained Breathing Apparatus 3. Cleaning / Maintenance / Storage 4. Training 5. Recordkeeping 6. Implementation 48 Haltech Testing Inc. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT PROGRAM CODE OF PRACTICE 1. POLICY The objective of the Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Program (includes respirator protective equipment) is to protect employees from the risk of injury by creating a barrier against workplace hazards. Personal protective equipment is not a substitute for good engineering or administrative controls or good work practices, but should be used in conjunction with these controls to ensure the safety and health of employees. Personal protective equipment will be provided at no cost to the worker, (unless otherwise agreed), used, and maintained when it has been determined that its use is required and that such use will lessen the likelihood of occupational injury and/or illness. 1.1. The Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) places responsibilities on employers to implement certain basic health and safety requirements regarding the provision and use of PPE. Haltech Testing Inc. Is committed to effectively applying them. 1.2. PPE can be defined as all equipment (including clothing affording protection against the weather) which is intended to be worn or held by a person at work and which protects against one or more risks to their health or safety. 1.3. Under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations, employers are required to carry out workplace risk assessments, so enabling them to select the most appropriate means of reducing any identified risks to an acceptable level. Employers should eliminate or minimize the risks as close as possible to the source of the risk, thereby protecting everyone in the workplace. PPE should always be regarded as the ‘last resort’ for protection from risk as it only protects the wearer and can be compromised, e.g. by not being worn or being used incorrectly. The use of PPE must not itself endanger the worker. 1.4. This Code of Practice has been developed under Haltech Testing Inc.’s Health and Safety Policy and has the same authority as that policy. It sets out guideline on how to manage the provision, use and maintenance of PPE and applies to all workplaces and work activities where PPE is required. 2. PURPOSE To develop a proactive management response where PPE is deemed necessary to protect the health and safety of employees. To ensure compliance with legislative requirements. To establish and maintain a PPE risk assessment process, with documented records where appropriate. 3. RESPONSIBILITIES Notwithstanding the health and safety responsibilities outlined within Section 2 of Haltech Testing Inc.’s HSE Program the following specific responsibilities apply with regard to the provision and use of PPE. 49 Haltech Testing Inc. 3.1 Managers/Supervisors Managers/Supervisors are responsible on a day to day basis for ensuring the implementation of this Code for the staff within their control and ensuring CSA approved PPE (Section 5.2). In particular they must: 3.1.1. Familiarize oneself with the content of this Code, and actively inform staff. 3.1.2. Ensure that specific assessments are carried out for both the risk to be protected against and the different types of PPE that could be used to protect an individual from that risk. On this basis the suitability of the selected PPE against the risk will be assessed, thereby ensuring any PPE provided is suitable for the intended purpose and that the use of PPE does not itself endanger the worker. Simply and obvious assessments that can easily be explained need not be recorded, however more complex assessments should be recorded and kept readily accessible to those who need to know the results. These assessments should be periodically reviewed, including consideration as to whether more suitable PPE has subsequently become available. 3.1.3. Ensure that employees receive suitable and sufficient information, instruction and training with regard to PPE supplied. 3.1.4. Take all reasonable steps to ensure the full and proper use, storage in a manner that prevents contamination, maintenance that keeps it sanitary, examination, repair and replacement of PPE. This may involve taking disciplinary measures in accordance with Haltech Testing Inc.’s disciplinary procedures, where employees fail to use PPE correctly. [Note: Much of this may be delegated to the PPE user, however a supervisory and monitoring role is retained to ensure actions are carried out.] 3.1.5. Periodically carry out recorded audits of any PPE held by team members (see Inspection Form Chapter 3). This shall include an inspection of the equipment and sanitary storage accommodation provided along with annual testing by a qualified tester. 3.2. Employees Employees have personal responsibilities to ensure the effectiveness of any safe system of work provided. In particular they must: 3.2.1. Ensure that PPE provided is used, maintained and cleaned in accordance with the training, instruction and information received. Refrain from wearing protective equipment outside of the work area where it is required if to do so would constitute a hazard. 3.2.2. Take all reasonable steps to return PPE to storage accommodation provided for it after use. If not possible, to take all reasonable steps to safeguard the conditions that may affect their ability to wear or use PPE. 3.2.3. Regularly examine PPE before and after use and report any defect, damage or loss to their manager/supervisor. 3.2.4. Inform their manager/supervisor of any medical conditions that may affect their ability to wear or use PPE. 50 Haltech Testing Inc. [Note: Non-compliance with 3.2 of this Code is a disciplinary matter and may be dealt with in accordance with Haltech Testing Inc.’s disciplinary procedures.] 3.3. Haltech Testing Inc. Health and Safety Manager 3.3.1. Haltech Testing Inc.’s Health and Safety Manager has the responsibility to support and monitor the process of provision and use of PPE. In particular PPE provision and use will be targeted during inspections and audits and a periodic review of this Code shall be carried out (i.e. annually). 4. PPE DISTRIBUTION 4.1. All PPE provided by Haltech Testing Inc. shall be used only as a last resort when it is certain that the task is necessary and there is no safer way to accomplish or deal with residual risk. It shall comply with the following general rules: a) Be supplied free of charge. b) Be suitable for the task intended and adequately control the risk involved. c) Take into account any ergonomic requirements and the state of health of the person(s) who may wear it. [The aim shall always be to choose PPE that will give minimum discomfort to the wearer, as uncomfortable equipment is unlikely to be worn properly.] d) Be capable of fitting the wearer correctly and be compatible with any other items of PPE that may be worn at the same time. e) Does not contribute to increasing any other risk such that overall risk increases. f) Be readily available for use. 4.2. Suitable representatives of the workforce intended to wear items of PPE shall be involved in its selection and specification to ensure its suitability. 4.3. Where individuals experience problems in wearing selected PPE medical advice may be sought as to whether the individual can tolerate wearing the PPE. 5. PROGRAM COMPONENTS 5.1. HAZARD ASSESSMENT & EQUIPMENT SELECTION 5.1.1. A risk survey for the use of PPE when carrying out visits has been carried out and is attached as Appendix B. This identifies risks that may be presented to different parts of the body, which PPE may help overcome. This survey shall be reviewed annually or more frequently as needs dictate. It is essential that any provision and standard of PPE be based on the results of risk assessment. PPE and Respiratory PPE selection must be approved in accordance with OHS and CSA standards. 5.2. PROTECTIVE DEVICES 5.2.1. Eye and face protection requirements: standard issue safety goggles meeting CSA Standard Z94.3-92, Z94.3-99, Z94.3-02. 5.2.2. Head protection: hard hat meeting CSA Standard Z94.1-92. 5.2.3. Hearing protection: CSA Standard Z94.2-02 5.2.4. Foot protection: CSA Standard Z195-02 steel toed work boots. 5.2.5. Hand protection: light to heavyweight Nitrile coated gloves meeting CSA Standards. 5.2.6. Personal monitors: capable of detecting H2S, CO, LEL. 5.2.7. Respiratory Protective Equipment (SCBA): CSA Standard Z94.4-02. 51 Haltech Testing Inc. 5.3. CLEANING / MAINTENANCE / STORAGE 5.3.1. Haltech Testing Inc.’s uses emergency self contained breathing apparatus’ (SCBA) and they are to be cleaned and disinfected after each use, the air will be changed out (of a quality that meets the requirements of Table 1 of CSA Standard Z180.1-00 and does not contain a substance in a concentration that exceeds 10 percent of its occupational exposure limits) and flow tested annually by a competent professional to maintain proper operations. H2S Alive training procedures for inspection of SCBA’s to ensure that respiratory protective equipment that is not used routinely but is kept for emergency use is inspected at least once every calendar month by a competent worker to ensure it is in satisfactory working condition. 5.3.2. The Personal Gas Monitors will need recalibrating every six months or if disposable monitors are used, they will need to be replaced every two years. 5.3.3. Issued respirators must be stored in a clean and safe environment to prevent contamination and damage which may compromise the protective effect of the respirator. They shall be stored in a manner that will protect against the following: contamination, dust, sunlight, extreme temperatures, excessive moisture and damaging chemicals. They will be stored in the designated cabinet. (Scheduled inspection of compressed air cylinders and maintenance and repairs for each selfcontained breathing apparatus will be in accordance with the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-Z94.4-02.) 5.4. TRAINING 5.4.1. Prior to individuals using any PPE for the first time they shall receive adequate information, instruction and training in its use. A competent person shall carry out training and fit testing, with suitable records kept. It must make the user aware of why PPE is needed; when it is to be used, repaired or replaced; cleaning and maintenance requirements; and the PPE’s limitations. 5.5. RECORDKEEPING 5.5.1. A recorded fit testing, instruction and issue of PPE, repair and replacement procedure shall operate. PPE shall be repaired or replaced if damaged or subject to wear and tear such that its integrity is affected. Additionally identified items of PPE will be replaced automatically after certain time periods to assure their integrity – time period may vary dependant on factors such as good practice and manufacturer’s recommendations. An example of a suitable type of record sheet is attached at Appendix A – any such local records should contain similar information. 6. IMPLEMENTATION 6.1. All existing employees will be advised about this Code through normal channels and the Code will be made readily available in the office. 6.2. Health and safety awareness training will include input on PPE. 6.3. Copies of the Code will be distributed to Heads of Business Units. 52 Haltech Testing Inc. 6.0 LEGISLATIVE COMPLIANCE The federal government, in cooperation with provincial governments, has developed a comprehensive set of regulations to enhance safety. An employee safety representative is appointed to assist in resolving health and safety issues. When a Safety Committee is formed (with 20 or more employees), planned inspections and pertinent safety issues will be addressed in this way. One must be able to prove that all reasonable steps have been taken to comply with the regulations. The Occupational Health & Safety Act, Regulations and Code is available for reference. 6.1 Employee Responsibility A. the health and safety of: I) employees in the work place. II) those workers not engaged in the work of that employer but present themselves at the work site where the work is being carried out. B. that workers engaged in the work of the employer is aware of their responsibilities and duties under the Act and Regulations. Every worker shall, while engaged in an occupation: A. take reasonable care to protect the health and safety of himself and other workers present while hi is working and; B. cooperate with his employer for the purpose of protecting the health and safety of: I) himself II) other workers engaged in the work of the employer and III) other workers not engaged in the work of that employer IV) but not present at the work site at which the work is being carried out. 6.2 Housekeeping It is the responsibility of the employer and the employee to ensure that housekeeping is done on a daily basis, ensure that: Floors are kept clean of debris, oil and grease Aisles, doorways and exits are to be kept clear of all obstacles. 6.3 Working Around Moving Parts Where there is danger of contact with moving parts of machinery or in any work process where a similar hazard exists: close fitting clothing shall be worn head and facial hair shall be cut or tied back dangling neck wear, jewelry or other similar items shall not be worn. 53 Haltech Testing Inc. 6.4 Eye Protection Properly fitting goggles shall be worn when engaged in work where there is potential eye hazard from flying objects. Wear your goggles when mixing chemicals, scraping paint and hammering. 6.5 Respiratory Protection Occupational Health & Safety legislation requires that appropriate respiratory protective equipment (RPE) be worn when a worker is, or may be exposed to an immediately dangerous to life or health atmosphere, when oxygen concentration drops below 19.5%, or when an air-born contaminant exceeds the occupational exposure limit. Filter type respirators ARE NOT TO BE USED IN HYDORGEN SULPHIDE OR OXYGEN DEFICIENT ATMOSPHERES. All contractors’ employees shall be properly trained in the use, care and limitations of this equipment before it is used. 6.6 Working At Heights Above Ground Level An employee shall ensure that where it is possible for a worker to fall a vertical distance greater than 3.5 meters from a temporary work area of 1.2 meters from a permanent work area, the worker is protected from falling by: a guard rail around the work area safety belt or harness securely attached to an anchor point 6.7 Confined Space Where a worker is to enter a confined space the employer shall ensure that the confined space is: ventilated sufficiently to maintain an oxygen content of 18% must be isolated from pipes or supply lines containing harmful substances he must be attended by at least one other worker stationed at or near the entrance to the area who is equipped and capable of rescue 6.8 Working Alone Before a worker is assigned to work alone, the manager must develop and implement a written procedure for checking the well-being of a worker assigned to work alone under conditions which present a risk of disabling injury if the worker might not be able to secure assistance in the event of injury. A worker required to work alone and any person assigned to check on the worker must be trained in the procedure. The supervisor must identify any hazards to that worker and must take reasonable measures to eliminate any hazards, and if it is not practicable to eliminate the hazard, to minimize the risk from the hazard. The procedure for checking a worker's well-being must be developed with safety 54 Haltech Testing Inc. management involvement including the time interval between checks and the procedure to follow in case the worker cannot be contacted, including provisions for emergency rescue. If a worker is working alone at a work site and assistance is not readily available if there is an emergency or the worker is injured or ill, the employer must provide effective radio, telephone or other electronic communication with scheduled contact between a worker who works alone and the designated person to make and record the scheduled contact with the employee working alone and capable of assisting the worker in an emergency or if the worker is injured or becomes ill. If electronic communications are unreliable at a worksite, the supervisor or designated co-worker will visit the worker at prescheduled intervals and at the end of the shift. The work alone procedure will be review annually or as required. 6.9 Hazardous Waste A hazardous material is defined as any biological, chemical or physical agent or material exhibiting any of the following characteristics: explosive; compressed gas; flammable; combustible liquid; reactive or oxidizing; toxic or infectious; radioactive; corrosive; and/or environmental hazard. A controlled product becomes hazardous waste and disposal will be arranged by the manager. You must ensure each container is properly labeled to be disposed of at the appropriate hazardous waste facility. 6.10 Workplace Violence and Harassment Haltech Testing Inc.’s policy on workplace violence and Harassment is to strive to provide a healthy and open work environment and strictly prohibits harassment or violent behavior. Violence means the attempted or actual exercise by a person of any physical force so as to cause injury to a worker, and includes any threatening statement or behavior which gives a worker reasonable cause to believe that he or she is at risk of injury. A risk assessment will be performed if a risk of injury to workers from violence arising out of their employment. The risk assessment will consider previous experience in that workplace, occupational experience in similar workplaces, and the location and circumstances in which the work takes place. If a risk of injury to workers from violence is identified by an assessment, procedures will be established to eliminate or minimize the risk to workers from violence and affected workers will be informed. Employees who feel they are, or have been subjected to harassment or workplace violence, or if they have been a witness to either situation, should take the following steps: Clearly inform the alleged harasser or person engaging in violent behavior that his/her behavior towards you is offensive and unwelcome and to stop such behavior. If the behavior continues, or if you feel you cannot talk to or do not want to talk to the alleged harasser, or the conduct is of a serious nature, or causes you to feel unsafe, go directly to management to discuss the situation. Complaints may be filed in either written 55 Haltech Testing Inc. form (by letter) or verbally. A health professional should be consulted if exposed to workplace violence. Haltech Testing Inc. will seriously address and investigate the complaint. At the conclusion of the review and any investigation conducted (and documented), Haltech Testing Inc. will take appropriate action, which may include immediate discharge of the offender if Haltech Testing Inc. determines that harassment or violent behavior has occurred. Haltech Testing Inc. seeks to preserve confidentiality regarding matters alleged in the complaint to the extent that such confidentiality does not conflict with efforts to review, investigate and otherwise address the complaint, take remedial or other action in response to the report, and/or prevent further harassment or other inappropriate behavior. Retaliation against persons who bring a complaint of harassment or violence is strictly prohibited. 56 Haltech Testing Inc. 7.0 TRAINING 7.1 EMPLOYEE AND CONTRACTOR TRAINING Haltech Testing Inc. recognizes that initial safety training is one of the most important aspects of a safety program. The applicant will be thoroughly interviewed and if management feels they are a potential employee a background check will be initiated. Upon completion of a positive background check, Haltech Testing Inc. management will invite the potential employee to an orientation where general instruction, safety policies and procedures, guidelines and proper equipment operations will be covered. Finally, the new personnel will work under the direct supervision of a competent worker who will demonstrate new tasks until such time the new employee/contractor becomes competent enough to operate equipment and perform job tasks safely. Only authorized personnel will operate equipment. The position will be offered with a three (3) month probation period. All sub-contractors and independent contractors are also subject to the same qualification and training procedures. Employees and contractors must be trained in safe work practices as well as field oriented training (by an approved training agency that provides the first aid training to candidates for a certificate in emergency first aid, standard first aid or advanced first aid.) which may include, but is not necessarily limited to; First Aid, CPR, H2S Alive, Respiratory Protection, G.O.D.I. (or an applicable Canadian driving training course acceptable to the Board, or have completed driver training providing skills and knowledge for safe driving equivalent to or better than those required), Fatigue Management, WHMIS and TDG. A worker who successfully completes the training by an approved agency must meet the standards for a certificate in all required training. Designated first aid personnel must be at least 16 years old, has successfully completed the first aid training course or first aid examination developed or approved by the Board, has a first aid certificate in good standing at the required level issued by the Board or a person recognized by the Board, and meets any other requirements determined by the Board for designation as a first aid attendant. Employees will remain under supervision until he/she is deemed competent to safely perform work duties and procedures. Employees will operate only the equipment for which they have been authorized and are trained. Employees will also be trained or orientated in Basic Safety Awareness, PPE, Inspection, Lockout Tag System, Hazard Assessment, symptoms of MSI, Drug and Alcohol policy, the proper completion of bills of lading (tickets), dangerous goods documents, time cards, driver’s daily logs and all other relevant record keeping items. Proof of training in the following courses must be provided to a Haltech Testing Inc. Copies of the safety tickets will be placed in the driver’s file. Course Name Certificate Issued By Training Duration (Hrs) Renewal (Yrs) H2S Alive 8 3 TDG 4 3 WHMIS 8 3 FIRST AID 2 OR 3 57 Haltech Testing Inc. 7.2 EMPLOYEE AND CONTRACTOR ORIENTATION When an employee or contractor reports to work at a Haltech Testing Inc. site, which is new to them, their immediate supervisor will outline the following: General employment information; Haltech Testing Inc. Health and Safety Policy and Guiding Principles. Rules. Workers responsibilities for safety and health and company disciplinary policy as it relates to health and safety. Work attire, PPE, expectations around provision, care, maintenance and use. Assignment of duties and Housekeeping expectations. Initial safety training requirements and safety meetings. Emergency Response Plan (Fire prevention and Emergency Evacuation) First aider, supplies, equipment and procedures. Specific job hazards they may encounter, including fire, first aid, prohibited or restricted areas at the site, H2S, flammable or hazardous substances and hazardous waste. How to report an incident, a near miss or a job hazard. Workplace Violence and Harassment Policy, Ergonomics and Drug and Alcohol Policy Lockout Tag System If the employee is inexperienced, who their supervisor will be, and the length of time they are expected to work under direct supervision of the individual. Any other safety or environmental particulars about the site that the employees may not be expected to be familiar with or have encountered before. Contractor’s employees shall have all training necessary to safely perform the tasks they are assigned and safely use the equipment they are operating. 7.3 REPORTING OF DRIVING VIOLATIONS All prospective and current employees will fully disclose to Haltech Testing Inc. any and all driving violations and accidents the employee has been involved in either during work hours and/or during personal time. These violations are any that occurred while driving a Haltech Testing Inc. vehicle or any other vehicle. Management will periodically review all driver violations and will take corrective steps when the violations necessitate that step. At the discretion of management the steps can and will include additional driver training or, depending on the severity and number of violations could result in the termination of employment. All information collected on all drivers will be maintained in the individual drivers file for a period of 5 years. Upon hiring the employee will provide Haltech Testing Inc. with a current drivers abstract, a complete 3 year employment history as well as a completed application form or resume. All these items will be retained in the drivers file in the office as per regulation. Management will use these items to research the prospective employee before hiring and to do checks when deemed necessary by certain circumstances. The employee is responsible for ensuring that Haltech Testing Inc. receives an annual drivers abstract that will be placed in the drivers file. Management may request additional abstracts during the yearly period if they deem it necessary. 58 Haltech Testing Inc. Forms – Training Verification of Mandatory Work Permits ____________________ New Personnel Competency Checklist _______________________ New Personnel/Contractor/Orientation Checklist_______________ Verification of Orientation ________________________________ Verification of On-the-Job Training _________________________ Verification of Supervisor Training _________________________ Employee Discipline Consult Form _________________________ 59 Haltech Testing Inc. This Page Intentionally left Blank 60 Haltech Testing Inc. 8.0 COMMUNICATION 8.1 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Haltech Testing Inc. understands the importance of communication between themselves and their employees. Employees of Haltech Testing Inc. are encouraged to speak with management, in person or by phone or by writing, at any time, to discuss issues of concern. Haltech Testing Inc. encourages employees to write up an ‘Improvement Opportunity’ as to resolve issues of concern. The employee and the supervisor will try to resolve the complaint between themselves as soon as possible. The employee or the supervisor may refer an unresolved complaint to a health and safety representative to be investigated jointly. The persons who investigate the complaint will inform the employee and the employer of the results of the investigation. If the complaint is justified, the employer, on being informed of the results of the investigation, will inform the persons who investigated the complaint of how and when the employer will resolve the matter. If the person who investigated the complaint conclude that a danger exists, the employer shall, on receipt of a written notice, ensure that no employee use or operate the machine or thing, work in the place or perform the activity that constituted the danger until the situation is rectified. 8.2 Safety Meetings Safety meetings will be held monthly, with a requirement that all employees attend. Any employee that does not attend a scheduled safety meeting without an acceptable reason may be suspended for 1 (one) day without pay. The meetings are a valuable tool for management and employees alike to communicate any areas of concern. At this time management will bring forth key topics, responsibilities and whom they affect and employees bring their concerns. The following points should be addressed in the meeting: 1. Identify supervisory personnel. These people should be available throughout the job to give direction and organize. 2. Outline job procedure. 3. Discuss safety hazards (including any new hazardous products prior to purchase). 4. Instruct on the use of personal protective equipment. 5. Instruct on Emergency Procedures: a. Enact a buddy system when hazard is suspected or known. b. Define the escape route in the event of an accident. c. Define the assembly area. 6. Ensure proper safety precautions are taken, safety equipment and PPE, signage, WHMIS labeling, and proper use of controls. 7. ERP drills and consult with workers to maintain a current ERP (once a year). 8. Detail personal assignments. A good safety meeting will reduce the number of job problems, reduce equipment losses and minimize personnel injuries. The safety meeting must be conducted with all the personnel on location present. It is to be performed by the supervisor in charge of the job. 61 Haltech Testing Inc. 8.3 Project Safety Meetings A system of managing projects consisting of: Pre-project meeting – These are held between contractors and Haltech Testing Inc. representatives to review all aspects of work performed, including project safety management. Regular contractor safety meeting – These are held between the contractor and his employees while engaged in work for Haltech Testing Inc. Haltech Testing Inc. representatives may occasionally attend. These are usually documented on the Haltech Testing Inc. weekly contractor safety meeting form. Worksite Hazard Assessment or Safe Work Permit (also known as tailgate safety meetings or Job Safety Analysis) – These are held between the foreman, supervisor or contractor, and with the employees to review safety requirement, job procedures, hazards and employee questions or concerns. It must be documented on a Haltech Testing Inc. Worksite Hazard Assessment form. It is a method of authorizing specific work to be done at a job site or location. All hazards are noted, communicated to all workers on site, and the required precautions are assigned to individuals. The permit is normally valid for only a specific time period before re-testing and/or re-issuing is required. Quarterly Management field visits to ensure HS&E Program compliance. Recorded on Site Visit Form. Annual Management meeting (to include management and employee participants) to review and update HS&E Program and any recommendations, ERP, procedures and any injuries, accidents or incidents. Definitions: SCBA – Self Contained Breathing Apparatus, usually Scot brand Air Packs, the standards for selection, use and care of respiratory protective equipment are outlined in the document (Respiratory Protection Guidelines) available from a Haltech Testing Inc. representative. Haltech Testing Inc. has available brand specific checklists for daily and monthly maintenance of supplied air respiratory protection. TDG – Transportation of Dangerous Goods – Refers to current Acts and Regulations. UEL – Upper Explosive Limit – The maximum concentration of vapor in air at which the propagation of flame occurs on contact with the source of ignition. LEL – Lower Explosive Limit WCB – Workers’ Compensation Board – A non-government board which administers the fault free accident fund. Haltech Testing Inc. requires workers compensation coverage with all WCB accounts for the jurisdiction in which the workers are employed, in good standing, including coverage for all sub-contractors, for the entire duration of the job. 62 Haltech Testing Inc. Forms – Communications Improvement Opportunity _____________________________________ Worksite Hazard Assessment Form _______________________________ Safety Meeting Record _________________________________________ Site Visit Record ______________________________________________ 63 Haltech Testing Inc. This Page Intentionally left Blank 64 Haltech Testing Inc. 9.0 INCIDENT / ACCIDENT REPORTING & INVESTIGATION 9.1 INCIDENT AND ACCIDENT REPORTING Regardless of time of day, any employee, contractor or consultant involved in or witness to an injury, incident or near miss must report details to a Haltech Testing Inc. representative immediately. Management receiving the report must investigate the unsafe condition and must ensure that any necessary corrective action is taken. If there are fatalities or serious incidents, make every reasonable effort to prevent alteration of the scene and/or stop work until unsafe conditions are resolved. Any occurrence involving an injury to a worker or having potential for property loss of damage over $1,000.00 reportable to any regulatory agency, or which result in any damage or injury to a third party’s property or person must be investigated by the manager. Notifications to the WCB and Department of Labor (Occupational Health and Safety) or the client for injuries or and incidents requiring reporting must be complied to in a timely manner. Medical aid must be reported to the manager and lost time injuries also require WCB reporting by the employee and the employer. These forms must be completed in addition to the Haltech Testing Inc. incident report form. Any first aid injuries must be recorded on a first aid report form (found in the first aid kit) and submitted to the office for file. The contractor is required to designate one of the on-site work crew as the on-site safety supervisor. The contractor’s safety representative shall keep copies of all permits issued (hot work permits, etc.) and shall return a copy to Haltech Testing Inc.’s representative when work covered by the permit is complete. The employer of the person who has charge, management or control of a Dangerous Good is to report when there is a dangerous occurrence involving a spill, a bulk containment of dangerous goods is damaged, there is an explosion or fire, OR a person has been killed or injured (requiring hospitalization) in an accident involving dangerous goods. A Dangerous Occurrence is to be reported within 30 days with Transport Dangerous Goods. Also, using form found in Part 15 of the Federal OH&S Regulations where investigation of a hazardous occurrence resulting in a disabling injury to an employee, electric shock, toxic atmosphere, or oxygen deficient atmosphere that caused an employee to lose consciousness, or the implementation of rescue, revival, or other similar emergency procedure, or a fire or explosion. A copy of the report will be submitted to the safety representative; and within 14 days after the hazardous occurrence, to a health and safety officer at the regional office or district office (Occupational Health and Safety). March 1 each year a written report with the number of accidents, occupational diseases, and other hazardous occurrences affecting any employee in the 12 month period ending on December 31 should be submit to the Minister using the form found in Part 15 of the Regulations. 65 Haltech Testing Inc. 9.2 INCIDENT AND ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION AND FOLLOW-UP 9.2.1 Purpose To investigate accidents / incidents so that causes can be determined and corrective actions can be implemented to prevent reoccurrence. 9.2.2 Policy In this Company, the following types of incidents shall be fully investigated: 1. Accidents that result in injury requiring medical attention or report of a musculoskeletal injury. 2. Accidents that cause property damage or interrupt operations with potential loss. 3. When there is a release of dangerous goods that represent a danger to health, life, property, or the environment. 4. Incidents that have the potential to result in (1) or (2) or (3) above, such as close calls or near misses. All incidents that fall under Section 13 of the Occupational Health and Safety Act must be reported to OH&S and to WCB or other regulatory agencies as defined by the OH&S Act. 9.2.3 Responsibilities 1. All employees shall report all incidents or near misses as soon as possible to their immediate supervisor and assist in the investigation when requested. 2. Supervisors shall conduct initial investigations and report to management promptly. 3. Management shall determine the need for, and if necessary, shall direct investigations. They shall also determine root causes and recommend corrective action. 4. The manager shall review all reports, determine the corrective action to be taken, record it in the action log, and ensure that such action is implemented by noting observations of changes or documenting interview with workers to confirm same. 5. Administration shall retain record of all incidents, accidents and first aid records for a minimum of three years from the date the incident is recorded. 66 Haltech Testing Inc. Forms – Incident / Accident Reporting Incident or Near-Miss Report _____________________________ Automobile Accident & Cargo Claim Report _________________ Witness Statement ______________________________________ WCB Worker’s Report of Injury __________________________ Accident / Incident Investigation Report _____________________ WCB Employer’s Report of Injury _________________________ 67 Haltech Testing Inc. This Page Intentionally left Blank 68 Haltech Testing Inc. 10.0 ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY Haltech Testing Inc. is dedicated to establishing harmony and balance between the performing of service to the oilfield sector and the environment in order to achieve a sustainable social and natural environment. 69 Haltech Testing Inc. This Page Intentionally left Blank 70 Haltech Testing Inc. EMERGENCY RESPONSE PLAN 71 Haltech Testing Inc. 72 Haltech Testing Inc. TABLE OF CONTENTS EMERGENCY PHONE NUMBERS _________________________________ 75 & 76 1. Emergency Response Plan Goal _____________________________ 2. Training _____________________________________________ 3. Potential Emergencies _____________________________________ 4. Action _________________________________________________ 5. Emergency Response Plan – Spills __________________________ 6. Emergency Response Plan – Fires ___________________________ 7. Emergency Response Plan – H2S ___________________________ 8. Emergency Response Plan – Natural Disasters _________________ Emergency 1st Aid 77 77 77 78 80 81 83 84 see Procedures – MediumRisk– Tab #6 73 Haltech Testing Inc. 74 Haltech Testing Inc. Emergency Contacts THE Baytree 24 Hr. – Hal Keith 780-864-0153 Cell 780-353-3763 Home Baytree 24 Hr. – Lon Urness 780-864-5881 Cell 780-353-2259 Home Baytree 24 Hr – Micah Meunier 780-864-0140 Cell Blueberry PRIMARY 24 Hr – Esther Mann EMERGENCY 780-864-0312 Cell NUMBER IS AMBULANCE FAIRVIEW GRANDE PRAIRIE SPIRIT RIVER DAWSON CREEK FORT ST JOHN FORT NELSON 780-835-6100 780-532-9511 780-864-2453 250-782-2211 250-785-2079 250-774-2344 AIR AMBULANCE NORTH CARIBOO AIR (FSJ) NORTHERN AIR (Grande Prairie) STARS (Grande Prairie) 888-735-9464 800-661-1911 888-888-4567 (Call 911) RCMP FAIRVIEW GRANDE PRAIRIE SPIRIT RIVER DAWSON CREEK FORT ST JOHN FORT NELSON 780-835-2211 780-538-5700 / 538-5701 780-864-3533 250-784-3700 250-787-8140 250-774-2777 911 DANGEROUS GOODS INCIDENTS - ALBERTA ENVIRONMENT 800-222-6514 E.R.C.B. (Oil & Gas Incidents) 780-538-5138 INDUSTRIAL ACCIDENTS 780-538-5249 DISASTER SERVICES 800-272-9600 POISON CONTROL CENTER 800-332-1414 DANGEROUS GOODS INCIDENTS - BC P.E.P. (Environment or Oil & Gas Incidents) INDUSTRIAL ACCIDENTS 800-663-3456 780-538-5249 75 Haltech Testing Inc. FIRE DEPARTMENT FAIRVIEW SPIRIT RIVER WORSLEY ALARM BONANZA ALARM DAWSON CREEK POUCE COUPE FORT ST JOHN FORT NELSON 780-835-4372 780-864-4111 780-685-3811 780-353-3911 250-782-9898 250-786-5794 250-785-4333 250-774-2222 FIRE MASTER GRANDE PRAIRIE 780-539-4400 HOSPITAL FAIRVIEW WORSLEY HEALTH UNIT GRANDE PRAIRIE SPIRIT RIVER DAWSON CREEK FORT ST JOHN FORT NELSON 780-835-6100 780-685-3927 780-538-7100 780-864-3993 250-782-8501 250-262-5200 250-774-8100 WCB 866-922-9221 888-621-7233 WCB WCB - Alberta - BC FORESTRY ALBERTA BC 780-427-3473 FISH & WILDLIFE 800-642-3800 HYDRO FAIRVIEW GRANDE PRAIRIE BC 780-835-2206 780-538-7000 888-769-3766 OILSPILL CO-OP (Area T- Alberta) ALPINE ENVIRONMENT Sherry Paul 780-538-0050 FIRST AID UNIT ALBERTA - IND. AMBULANCE BC – ON-SITE ADV. MEDICAL SERV. 866-611-9911\ 866-402-2339 PORTABLE BREATHING AIR TRAILER FIRE MASTER STANDARD SAFETY WEL INDUSTRIES – Wayne L 780-539-4400 780-529-4017 780-864-1276 76 Haltech Testing Inc. 1. EMERGENCY RESPONSE PLAN GOAL Haltech Testing Inc.’s goal is to reduce injuries, save lives and reduce costs if disaster strikes. Fist aid equipment and supplies are to be clearly visible, maintained in a clean, dry and serviceable condition, in a container that protects the contents from environment and is clearly labeled. Site personnel must know what needs to be done and how to get it done together. How we respond could determine the extent of personal injury, public health threats, equipment loss and environmental damage. Therefore, Haltech Testing Inc. will provide employees with training which will include scenarios of potential emergencies in the oilfield industry. Every reasonable effort must be made to control the hazards while the condition is being corrected or an emergency response is being carried out. There are times when the emergency procedures may be dangerous to the safety or health of workers. Be sure that only those workers competent in correcting the condition and the minimum number of workers necessary are exposed to the hazard. 2. TRAINING Haltech Testing Inc. is committed to providing adequate training to ensure that employee or contractor safety is not compromised. All participants in the Emergency Response will take the following basic training and records will be kept on file. Basic Safety Awareness and orientation PPE The use and the care of fire fighting equipment Rescue and Evacuation (for supervisors) (Including simulated rescue or evacuation exercises and regular retraining, appropriate to the type of rescue or evacuation that may be required.) Standard First Aid (including immobilization of the injured and procedures to call for transportation of injured workers) WHMIS H2S Alive TDG 3. POTENTIAL EMERGENCIES An emergency may be the result of process upsets, uncontrolled reactions, fires, explosions, threats, unplanned releases of hazardous materials, natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods and winter storms. Potential emergencies include: Injury to worker Fire (may involve hazardous materials) Release of Hazardous or Controlled Product (leak / spill) Climate/Natural Disasters (forest fire) 77 Haltech Testing Inc. Mechanical or process problems that can be solved routinely or by technical knowledge alone are not considered emergencies. Emergency Equipment & Fire Protection Plan Haltech Testing Inc.’s worksite is built to code and is equipped with smoke/fire alarms, exit signs and fire extinguishers. Emergency Equipment for each unit also includes: First Aid supplies with Eye Wash Shower Fire fighting supplies Cell Phone H2S detector and SCBA when required Survival Kit (seasonal) Spill soak up pads Emergency Contact List 4. ACTION 1. Recognize the Problem & Sound Alarm 2. Evaluate the Hazard 3. Take Control 4. Call Out for Help 5. Take Action 6. Make Record and Follow Up Following notification of a possible emergency, the supervisor in place and Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor must evaluate the situation, the effect on personnel in the area and the effect on other areas, including the community and the environment. 1. Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor has two choices: Initiate routine response and/or cleanup procedures for relatively small, nonthreatening emergencies or; Activate the ERP thereby activating the Emergency Response Team. 78 Haltech Testing Inc. 2. First Aid Procedures see Tab #6 – Medium Risk If someone is injured: 3. STAY CALM, assess the situation carefully. First ask yourself “Is it safe to assist the victim or will rescuers be at risk?” If it is safe, call for help and administer first aid. Then communicate with supervisor and they will arrange for rescue or evacuation. If safety is questionable, immediately contact Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor and wait for instruction. Next, consider the following questions: What equipment must be shut down? Should the area be isolated? Fires involving gas require isolation. Is evacuation necessary? Are surrounding area’s at risk? What kind of resources and assistance are needed? What key management personnel should be notified? The supervisor and Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor have the responsibility for coordinating all response measures and have the authority to commit resources in an imminent or actual emergency situation. Emergency Alerting Procedures Upon discovery of any apparent emergency situation (spill, fire, explosion, personal injury, etc.), contact Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor at the following number: Hal Keith: Lon Urness: Micah Meunier Home: 780-353-3763 Home: 780-353-2259 Cell: Cell: Cell: 780-864-0153 780-864-5881 780-864-0140 The following information is required to effectively deal with the emergency: Caller’s name Location of the emergency Nature of the emergency Number and severity of injuries Other relevant information Alerting Environmental Agencies It is the responsibility of the Environmental Compliance Manager to contact (and record that contact) with environmental regulatory agencies of any reportable accidental spill or release. Contact Hal of Haltech Testing Inc.’s at the office, 780-864-0153 or have the office staff contact a supervisor. 79 Haltech Testing Inc. 5 EMERGENCY RESPONSE PLAN – SPILLS Responsibilities Haltech Testing Inc. has a responsibility to ensure that operations are carried out in a manner that is safe and protects the environment. Haltech Testing Inc. is committed to taking every precaution to control, store, handle, use and dispose of hazardous materials and substances. Haltech Testing Inc. and its contractors will comply with all environmental regulations and monitor operations to ensure that preventive measures are in place to minimize risk. Supervisor is to do a head count immediately upon evacuating and report to Haltech Testing Manager and notify emergency responders as necessary. Manager is to notify emergency responders as necessary, or municipality and province as required. General Chemical Spill Response Techniques In ideal situations, emergencies are assessed, contained and corrected quickly by the discoverer. Reality suggests that these actions take time and often require a team of responders. Identify the spilled material (MSDS) as quickly as possible. Contact Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor immediately. After assuring that the area is safe, remove any victims from the spill area as soon as possible. Obtain assistance in isolating the area from the workers. Obtain and put on appropriate personal protective equipment. Eye, face and hand equipment are recommended at a minimum. Begin a containment process. Turn off pumps, close valves and dike the spill with absorbent. Now the emergency requires careful assessment. Fires, vapor clouds, ruptured pipes or chemical reactions may dictate the need for evacuation. IF SO, CALL HALTECH’S OPERATIONS MANAGER and EVACUATE THE AREA; if not, consider the next step. Listen to directions from Haltech Testing Inc.’s Operations Supervisor. Seek specific manual or MSDS advice on your next action. You may want to pump the material to containment, flush it to the waste water system, neutralize it in place or simply absorb all free liquid. Place all absorbed or neutralized material in approved 55 gallon drums in preparation for removal (pending approval of method by Environmental Manager or their designate). Initiate decontamination of the area. Remember that soap and water may work best. Under no circumstances should you use any other decontamination solution without permission by the Environment Manager or their designate. Decontaminate yourself at an appropriate location. Use soap and water or a neutralizing solution approved by the Environment Manager. Clean PPE or dispose of it with the drummed waste material. 80 Haltech Testing Inc. 6 EMERGENCY RESPONSE PLAN - FIRES At Haltech Testing Inc.’s Shop/Office Sound Alarm Call 911 Evacuate to muster area Call Haltech Testing Manager Supervisor is to do a head count immediately upon evacuating and report to Haltech Testing Manager. Other Fire Discovery and Alerting If at another site, we are required to IMMEDIATELY report ANY fire discovered, within a forested area, to Lands and Forest Services. All fire reports are to be directed to: Fire Master Grande Prairie 780-539-4400 IMMEDIATE reports must also occur where accidental equipment fires occur. Forest look-out towers cannot always identify resulting smoke as an equipment fire. Unnecessary deployment of Forest Service Resources could be prevented by reporting such fires immediately. In the event that the Forest Service cannot be contacted, IMMEDIATE contact should be made with Haltech Testing Inc.’s office, personnel in the field or at home. Supervisory personnel will then ensure that the information is forwarded to Lands and Forest Services, preferably at the local fire district level. When calling, the person should be prepared to provide the Forest Service with the following information: Name Telephone number Fire location (as detailed as possible) Time of discovery Any fire or weather details observed Fuel type (ie. timber, slash, grass) Wind direction Potential danger to men and equipment Action being taken Suppression When a fire occurs: 1. Sound Alarm. Notify the rest of the crew and cease operations. 81 Haltech Testing Inc. 2. Designate one member of the crew to IMMEDIATELY REPORT the fire to the Lands & Forest Service. This person shall remain available to communicate details of the fire and suppression activity being taken and required. 3. The remaining crew shall begin suppression actions IMMEDIATELY. 4. Proper PPE for firefighting (Firefighter’s Protective Clothing for Protection Against Heat and Flame.) must be worn if required to approach the seat of a fire or enter a structure or other hazardous area during an emergency. 5. The person in charge of the crew during suppression operations will continue to supervise the effort until Lands & Forest Service personnel arrive on the site. The person in charge will designate someone to document: How and where the fire originated The time of discovery The time initial suppression action was taken The time remainder of crew arrived on the fire scene The time equipment arrived or was set up (cats, pumps, etc.) The crew MUST continue fire suppression action or other assigned duties until relieved by Lands & Forest Services. 82 Haltech Testing Inc. 7 EMERGENCY RESPONSE PLAN - H2S EXPOSURE Introduction H2S can be found in many job-sites, not just petroleum industry operations. It may accumulate wherever a mixture of hydrocarbons and sulphur are found. Oil and gas fields and tank cars have the potential to contain significant amounts of the gas. Beside these locations, there are a variety of organic sources where H2S can be found, including such unlikely spots as ships’ holds, mine shafts, pulp mills, swamps and sewers. H2S is a natural by-product of organic decay. Locations of H2S No job site can be excluded as a potential source since every sector of the oil and gas industry can be contaminated by H2S. The point of release on any site is important to know so you can take appropriate action to avoid the gas. Wind direction is critically important because it affects the ability to detect the gas, influences the level of concentration and obviously determines the rate of movement of the gas both on site and towards the surrounding areas. Identifying areas where the gas will likely be found is another useful strategy for determining specific sources. Look for traps formed by buildings or natural landform depressions that can become specific danger spots in an incident. Since H2S is heavier than air it will tend to settle or concentrate in low lying areas. Emergency Medical Response to H2S Exposure Emergency Response First Aid Rescue Step One: Evacuate immediately Step Two: Sound the alarm Step Three: Assess the situation Step Four: Protect rescue personnel Step Five: Rescue victim Step Six: Revive victim Step Seven: Get medical aid Supervisor is to do a head count immediately upon evacuating and report to Haltech Testing Manager. Manager to dispatch assistance immediately and report as is required by municipality or province as required. 83 Haltech Testing Inc. 8 EMERGENCY RESPONSE PLAN - NATURAL DISASTER Earthquake Do Not Run outside. The possibility of being struck by falling debris is far more prevalent leaving a building during an earthquake. Do get under a desk or other solid protection such as a heavy table. Alert everyone else in the area. Avoid doorways. Protect yourself from exploding windows or falling debris. Remain under a solid structure till the earthquake subsides. If in your vehicle, pull over as soon as is safe, and stay in your vehicle. Do evacuate to muster area when shaking has subsided. Supervisor is to do a head count immediately upon evacuating and report to Haltech Testing Manager. Notify emergency responders as necessary. Tornado Do Not Run outside. The possibility of being struck by debris is far more prevalent. Alarm everyone else. Do get underground if possible or into the most interior small room (bathroom). Stay away from windows and doors. If in your vehicle, get as far away from the tornado as possible or drive to a building, preferable with a basement to get protection. Do evacuate to muster area when tornado has passed. Supervisor is to do a head count immediately upon evacuating and report to Haltech Testing Manager. Notify emergency responders as necessary. Winter Storm Carry winter survival kit. If road conditions have become impassable, stay at the office or on location and remain warm. If on the road and you become stranded, Do Not leave your vehicle to try to walk to safety in a blizzard. Avoid over exertion and exposure Stay in your car Keep fresh air in your car Run your motor sparingly Use a candle for heat instead of the car’s heater Set out a warning light or flares Put on the dome light (but don’t wear down your battery) Exercise your limbs vigorously Keep watch for traffic or searchers 84