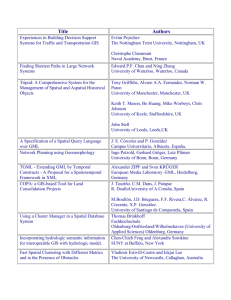
Manajemen Data & Pengguna SIG
advertisement

Matakuliah Tahun Versi : T0234 / Sistem Informasi Geografis : 2005 : 01/revisi 1 Pertemuan 10 Analisis Sistem 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • Membuat diagram / skema dari permasalahan di dunia nyata sebagai suatu model hasil analisis (C4, TIK10) 2 Outline Materi • Materi 1 : Domain data atau informasi • Materi 2 : Fungsi dan proses • Materi 3 : Prosedur beserta unjuk kerjanya 3 Analisis Sistem (1) • Analisa kebutuhan merupakan salah satu tugas RPL sebagai jembatan antara alokasi perangkat lunak tingkat sistem dengan perancangannya. • Untuk menguraikan sistem menjadi komponen- komponen dasar dengan tujuan identifikasi, evaluasi permasalahan dan kebutuhan yang diharapkan. • Agar analyst dapat menentukan fungsi-fungsi (prosedur), unjukkerja, berikut hambatan yang mungkin • Banyak metode-metode analisis yang diusulkan, dimana setiap metode memiliki sudut pandang yang unik. 4 Analisis Sistem (2) Metode-metode analisis yang beragam itu selalu berhubungan dengan prinsip-prinsip yang dikemukakan oleh Presman (1997), sbb : • Domain informasi harus dipahami dengan baik dan direpresentasikan. • Fungsi-fungsi (prosedur/proses) yang dimiliki atau akan dijalankan oleh sistem perangkat lunak harus didefinisikan. • Tingkahlaku (behavior) sistem perangkat lunak harus direpresentasikan. • Model-model informasi, fungsi, dan behavior masing-masing dituliskan (direpresentasikan) di dalam bagian (layer) yang terpisah. • Proses analisis dimulai dari informasi esensial menuju implementasi detil (dekomposisi) 5 Domain data atau informasi Dilakukan pemodelan data, untuk menjawab permasalahan : 1. Objek data primer apa yang akan diproses ? 2. Bagaimana komposisi setiap objek datanya ? 3. Atribut-atribut apa yang digunakan untuk setiap objek ? 4. Dimana tempat setiap objek ? 5. Bagaimana relasi antar objek ? 6. Bagaimana relasi antara setiap objek dengan prosesproses yang mentransformasikannya ? 6 Pemodelan Data dari Proses Spasial • • • Natural & Scale Analogue Conceptual Modelling Mathematical Modelling – Deterministics Method – Stochastic Methods – Optimization Methods Lihat Buku Referensi Utama halaman 137-140 7 Mathematical Modelling • Deterministics Method There is only one possible answer for a given set of inputs. • Stochastic Methods Recognize that there could be a range of possible outcomes for a given set of inputs, and express the likelihood of each one happening as a probability. • Optimization Methods Constructed to maximize or minimize some aspect of the model's output. 8 Construct Spatial Models for • • • Modelling Physical & Environmental Processes Modelling Human Processes Modelling the Decision-Making Process 9 Modelling Physical & Environmental Processes Examples : • GIS analysis of the potential impacts of climate change on mountain ecosystems and protected area (Halpin, 1994) • GIS analysis of forestry and caribou conflicts in the transboundary region of Mount Revelstoke and Glacier National Parks, Canada. (Brown et al. 1994) • Simulation of fire growth in mountain environments. (Vasconcelos et al., 1994) • Integration of geo-scientific data using GIS. (BonhamCarter, 1991) • Spatial interaction models of atmosphere-ecosystem coupling. (Schimel and Burke, 1993) • Geographical innovations in surface water flow analysis. (Richards et al., 1993) 10 Modelling Human Processes Examples : -Techniques for modelling population-related raster database. (Martin and Bracken, 1991) -Use of census data in the appraisal of residential properties within the UK: A Neural Network Approach (Lewis and Ware, 1997) -Design, modelling and use of spatial --An information systems in planning. (Nijkamp and Scholten, 1993) -Selecting and calibrating urban models using ARC/INFO. (Batty and Xie, 1994a, 1994b) -Introduction to the fuzzy logic modelling of spatial interaction. (See and Openshaw, 1997) -An investigation of leukemia clusters by use of a geographical analysis machine. (Openshaw et al., 1988) 11 Modelling the Decision-Making Process • • • • Outputs from process models of both human & physical systems are the raw information that will be required to assist various types of decision making. Example : Output from location-allocation model might show potential locations for a new supermarket within Happy Valley. (decision making) Map overlay is the traditional technique for integrating data for use in spatial decision making. Example : In sitting nuclear waste facilities, the criteria defining geological suitability and conservation area status can be combined using the overlay procedures outlined Chapter 6 (Main Referenced book). 12 Specific Examples • • • • Forecasting & Diffusion Location-allocation Spatial Interaction Models Multi criteria evaluation technique Forecasting : What may happen in the future under a given set of conditions. Simulating the geographical spread of a dynamic phenomenon such as forest fire requires a special type of forecasting model known as a diffusion model. A recent development in forecasting models has been to couple GIS with AI techniques such as Neural Networks (Hewitson and Crane, 1994) 13 Implementasi Model ke dalam SIG • • • • • The quality of source data for model calibration The availability of data for model validation The implementation within a GIS The complexity of modeling reality The conceptual & Technical problems of building multi-dimensional model 14 Fungsi dan proses • Untuk pemodelan Fungsional sering digunakan teknik DFD, yang merupakan metode grafis untuk menggambarkan aliran informasi dan transformasi data yang terdapat di dalam sistem. • DFD terdiri dari : DFD Level 0 (diagram konteks), DFD Level 1, Diagram Rinci. • Notasi yang digunakan : External Entity Proses data/informasi Data Store 15 Prosedur beserta unjuk kerjanya • Untuk pemodelan tingkahlaku (behavior) yang menunjukkan prosedur serta unjuk kerjanya sering digunakan teknik STD, yang merupakan metode grafis untuk menggambarkan perubahan status akibat terjadinya suatu event di dalam sistem. • Notasi yang digunakan : Status Awal event aksi Status Akhir 16 Penutup • Mahasiswa diharapkan telah mampu membuat diagram / skema dari permasalahan di dunia nyata sebagai suatu model hasil analisis . • Model hasil analisis dapat divisualisasikan dengan ERD, DFD dan STD. 17