Libor Market Model and it implementation
advertisement

LIBOR MARKET MODEL AND ITS
IMPLEMENTATION
SUBMITTED TO FIN 519, TERM STRUCTURE MODELS
TUNG-TA CHEN
SHENG MEI,
WENJUN MEI,
YIJUN TANG
CHAO XU
PRESENTED IN THIS REPORT
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
An introduction to Libor Market Model and Term Structure Models
Derivation of Libor Market Model and Pricing of Different Contracts
Calibration of the Models with FINCAD and Bloomberg
Code Structure
Some Investigations
a. Volatility Smiles of Swaptions
b. Errors of Long Jump/Very Long Jump in Caplets Pricing
Pricing Products
a. Caption
b. Constant Maturity Swap
c. Bermudan Swaption
d. Rachet Cap
e. Trigger Swap
f. European Swaption
g. Real World Product
Extensions
a. Reduce Rank of Covariance Matrix
Conclusions
Code Base in Details
Code files are provided in Code.zip.
2 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
INTRODUCTION
TERM STRUCTURE MODELING
The real challenge in modeling interest rates is the existence of a term structure of forward rates. Fixed income
products typically depend on many points of the forward curve rather than a single point. Pricing such instruments
requires a model describing a stochastic time evolution of the entire forward curve.
There are many stochastic term structure models based on different choice of dynamics, number of factors and state
variable parameters. We will outline main approaches deveolped in the following.
BLACK MODEL
The most straight-forward and popular approach in the early days is the use of Black model with the forward
prices, primarily for pricing bond options, interest rate caps / floors, and swaptions, however this approach assumes
forward rates volatility to be either constant or time dependent. Black formula is the industry standard for valuing
caps and caplets and their market prices are quoted as Black’s implied vol.
SHORT-RATE ONE-FACTOR MODEL
The one-factor short rate models (Vasicek’s model and its extensions) use the instantaneous spot rate rt as the basic
state variable. The short rate was assumed to be a stochastic differential equation made up of a deterministic
component and a stochastic part. It has the form
drt = b(t , rt )dt + s (t , rt )dW t
A special feature of the Vasicek’s model is that the stochastic equation has a closed form solution. Even though,
short rate models gain some success in the early days. However, this one-factor model has some serious
shortcomings. For example, in one-factor short-rate, correlation between the continuously compounded rates is only
one which comes from the fact that the only non-deterministic term is the current short rate and both instantaneous
rates are driven by the existence of single source of uncertainty.
Corr (dFi (t ), dFj (t )) = 1
This is not realistic as it suggests interest rates move exactly together.
One-factor model has some serious short coming as follows:
1. There is unrealistic correlation pattern between points of the curve with different maturities.
2. There are poor calibration capabilities which can only fit a low numbers of caps and swaptions
3. It is different to express markets views and quotes in terms of model parameters because the standard way
of quoting prices on caps/floors and swaptions is in terms of Black’s model.
4. With non-zero probability, rates may become negative.
5. The short-rate model is compatible with the market model and Vasicek’s parameters ( k , q, s , x 0 ) don’t
have an immediate intuitive meaning for traders who don’t know how to relate them to Black’s market
formula.
The natural solution to overcome the one-factor models limitation and incompetence to capture the dynamics of the
interest rates would lead to development in multi-factors models.
3 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
A principal components analysis of the whole yield curve Jamshidian and Zhu (1997) found that one principal
component can explain around 70% of the total variation and three can explain around 94% of Yen, Dollar and
Deutschmark yield curves. Rebonato (1998) found that two can explain 99.1% of the total variance. However,
starting from short rate model to determine the process followed by forward rates and calibrating them to the data
seems consume a lot of time and effort, besides the mathematics become very tedious and fuss.
LIBOR MARKET MODEL
We’ve gone through the development in the interest rate models. And the most prevalent and successful model is the
framework proposed by Brace-Gatarek-Musiela (BGM, also known as the LIBOR Market Model) which is an
extension and a generalization of the Heath-Jarrow-Morton framework (HJM). Within the HJM framework the
modeled rate is the short rate. However this rate cannot be observed accurately from market data and quoted
instruments. That is why the BGM framework now prevails. Indeed it can be calibrated to the quotations of caps
and swaptions which are actively traded instruments.
We will go through the derivation of the LMM model in the following chapters.
INCOMPATIBILITY BETWEEN LIBOR AND SWAP MODELS
Theoretical incompatibility between LSM(libor swap market model) and LFM(libor forward market model)
LFM: dFi (t ) = s i (t )Fi (t )dZ i (t ), Q i ,
LSM: dS a ,b (t ) = s ( a ,b ) (t )S a ,b (t )dW t , Q a ,b
1-
Given that S a , b (t ) =
Õ
b
j= a +1
b
1
1 + t j Fj (t )
1
å t i Õ j = a + 1 1 + t F (t )
i= a + 1
j j
i
, each Fi can be lognormal under Q i and S a , b be lognormal
underQ a ,b .
Check distributions of S a , b under Q a ,b for both LFM and LSM.
Derive the LFM model Q a ,b :
dFk (t ) = s k (t )Fk (t ) ( mka ,b (t )dt + dZ ka ,b (t )
b
mka ,b =
å
(2( j £ k ) - 1)t j
j= a +1
P (t ,T j )
C a ,b (t )
max( k , j )
å
i = min ( k + 1, j + 1)
t i r k ,i s i Fi
1 + t i Fi
When computing the swaption prices as the Q a ,b expectation
C a ,b (0 )E a ,b (S a ,b (T a ) - K )+
We can use either above equation (1) or (2)
In general, S a , b coming from equation (1) is lognormal whereas S a , b coming from equation (2) is not. But here
we are showing the approximation lognormality.
4 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
LIBOR MARKET MODEL
THE DRIFTS OF DIFFERENT FORWARD RATES UNDER A SINGLE MEASURE
Given a series of time
Let the difference between the times to be
Different forward rates for these times will be
Use
zero coupon bond as the numeraire asset, the forward rate
is a martingale. However, for
which is not a martingale under the given measure. However, notice that
Fi - 1 t i - 1Pi - 1 = Pi - 2 - Pi - 1
ß
(1 + F
t
i- 1 i- 1
)P
i- 1
= Pi - 2
which is a linear combination of traded assets, thus a martingale scaled by the numeraire asset, notice that
d éê(1 + t i - 1Fi - 1 )(1 + t i Fi )ù
i
ú= t i - 1 (1 + t i Fi )dFi - 1 + t i (1 + t i - 1Fi - 1 )dFi + r i ,i - 1 s i - 1Fi - 1 s i Fdt
ë
û
which yields
and
5 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Which essentially dictates that the drift term of the forward rate must take a certain form for the non-arbitrage
relation to hold. Similarly, for
where
, we have
(1 + t
i- k
Fi - k )Pi - k
should be a martingale scaled by the numeraire asset, and
k- 1
Pi - k =
Õ (1 + t
i- l
Fi - l )Pi
l= 0
Finally we arrive at
ék
ù
d êÕ (1 + t i - l Fi - l )ú
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
which has a zero drift term for any k ³ 0
ék
ù
d êÕ (1 + t i - l Fi - l )ú=
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
ék - 1
ù
Fi - l )d (1 + t i - k Fi - k ) + (1 + t i - k Fi - k )d êÕ (1 + t i - l Fi - l )ú
êl = 0
ú
l= 0
ë
û
ék - 1
ù
+ d (1 + t i - k Fi - k ), d êÕ (1 + t i - l Fi - l )ú
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
k- 1
Õ (1 + t
i- l
The following term then must be zero
ék - 1
ù
êÕ (1 + t F )út m F dt + d (1 + t F ), d
i
l
i
l
i- k i- k
êl = 0
ú i- k i- k i- k
ë
û
and
ék - 1
ù
êÕ (1 + t F )ú = 0
i
l
i
l
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
ék - 1
ù
d (1 + t i - k Fi - k ), d êÕ (1 + t i - l Fi - l )ú
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
l= k- 1
k- 1
=
t i - k s i - k Fi - k dW i - k , Õ (1 + t i - l Fi - l ) å
t i - l s i - l Fi - ldW i - l
1 + t i - l Fi - l
l= 0
l= 0
ék - 1
ù
l= k- 1 t
s F t s F r
i - l i - l i - l i - k i - k i - k i - k ,i - l ú
= êêÕ (1 + t i - l Fi - l ) å
údt
1 + t i - l Fi - l
l= 0
êël = 0
ú
û
The drift term reduces to
ék - 1
ù
êÕ (1 + t F )út m F +
i- l i- l ú i- k i- k i- k
êl = 0
ë
û
k- 1
Õ (1 + t
l= 0
And we have the drift for Fi - k
6 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
l= k- 1
t i - l s i - l Fi - l t i - k s i - k Fi - k r i - k ,i - l
l= 0
1 + t i - l Fi - l
F
i- l i- l )å
= 0
mi - k = -
l= k- 1
t i - l s i - l Fi - l s i - k r i - k ,i - l
l= 0
1 + t i - l Fi - l
å
The process followed by Fi - k can be written as
él = k - 1 t s F s r
ù
i - l i - l i - l i - k i - k ,i - l ú
dFi - k = - êêå
úFi - k dt + s i - k Fi - k dW i - k
1 + t i - l Fi - l
êë l = 0
ú
û
Now consider Fi + k , where k ³ 1 , similar result can be obtained for
ék
- 1ù
d êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) ú
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
which is also a martingale,
ék
- 1ù
d êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) ú=
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
ék - 1
- 1ù
- 1
- 1
êÕ (1 + t F ) úd (1 + t F ) + (1 + t F ) d
i+ l i+l
i+ k i+ k
i+ k i+ k
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
ék - 1
- 1
- 1ù
+ d (1 + t i + k Fi + k ) , d êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) ú
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
ék - 1
- 1ù
êÕ (1 + t F ) ú
i+l i+l
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
The drift term is
ék
ék - 1
m F dt
- 1 ùt
- 1
- 1ù
- êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) ú i + k i + k i + k + d (1 + t i + k Fi + k ) , d êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) ú
êl = 0
ú1+ t F
êl = 0
ú
ë
û
ë
û
i+ k i+ k
k
ék
é
m
F
dt
- 1 ùt
- 1 ùk - 1 t i + k t i + l s i + l s i + k r i + k ,i + l Fi + k Fi + l
= - êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) ú i + k i + k i + k + êÕ (1 + t i + l Fi + l ) úå
dt
êl = 0
ú1+ t F
êl = 0
úl = 0 (1 + t F )(1 + t F )
ë
û
ë
û
i+ k i+ k
i+ k i+ k
i+ l i+ l
The drift term for Fi + k is thus
mi + k =
l= k- 1
t i + l s i + l Fi + l s i + k r i + k ,i + l
l= 0
1 + t i + l Fi + l
å
And the process followed by Fi + k
él = k - 1 t s F s r
ù
i + l i + l i + l i + k i + k ,i + l ú
dFi + k = êêå
úFi + k dt + s i + k Fi + k dW i + k
1 + t i + l Fi + l
êë l = 0
ú
û
In a more general form, we have specified the process followed by the forward rate
dFl = m(Fi , t )Fdt
+ s l (t )FdW
l
l
l
7 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Notice that volatility terms don’t have state-dependence.
THE STRUCTURE OF THE VOLATILITY AND CORRELATIONS
The (instantaneous) volatility of these forward rates can be formed as
é
ù+ c
s i (t ) = Fi y (T i - 1 - t ; a, b, c, d ) = Fi éêa (T i - 1 - t ) + d ù
úexp ëê- b (T i - 1 - t )ú
ë
û
û
(
)
The (instantaneous) correlations between forward rates can be formed as
(
r = exp - b t i - t j
)
MONTE CARLO
EULER FORWARD
Let’s first study the log process
é
ù
1
d ln Fl = êml (Fi , t ) - s l2 (t )údt + s l (t )dW l
ê
ú
2
ë
û
The simplest scheme would be the Euler Forward
é
ù
1
ln Fl (t + Dt ) - ln Fl (t ) = êml (Fi , t ) - s l2 (t )úDt + s l (t ) Dt f l
ê
ú
2
ë
û
where f l is a standard normal random variable. Notice the fact that s l (t ) is only time-dependent and therefore
the following integral can be evaluated analytically or numerically
C t ,t + Dt ,l =
ò
t + Dt
t
s l2 (t )dt
The Euler Forward can be rewritten as
é
ù
1
ln Fl (t + Dt ) - ln Fl (t ) = êml (Fi , t )Dt - C t ,t + Dt ,l ú+ C t ,t + Dt ,l f l
ê
ú
2
ë
û
Also, if we let sl = sgn (l - k ), where Pk is the zero coupon bond at time T k and chosen numeraire asset, we
have
l- k - 1
ml (Fi , t ) = sl
å
m=0
t k + sm Fk + sm
1 + t k + sm Fk + sm
The integral can be approximated by
8 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
r l ,k + sm s l (t )s k + sm (t )
ò
t
t + Dt
l- k - 1
ds ml (Fi , s ) » sl
å
m=0
t k + sm Fk + sm
1 + t k + sm Fk + sm
ò
t
t + Dt
ds r l ,k + sm s l (s )s k + sm (s )
PREDICTOR-CORRECTOR SCHEME
Build on the Euler Forward Scheme, the Predictor-Corrector Scheme works as follows
Let the result from Euler Forward be Fl E , and we have
mlCD =
1
2
ém F , t + m F E , t ù
êë l ( i )
ú
l
i
û
(
)
Furthermore, notice that there is at least one forward rate that has a zero drift, which is Fk , and
ln Fk (t + Dt )- ln Fk (t ) =
C t ,t + Dt ,k f k
The equation is precise for any Dt as long as C t ,t + Dt ,k is evaluated accurately. Now consider a forward rate Fl ,
whose drift only depends on Fk + s m with m = 0 L l - k - 1 , which can be computed using Predictor-Corrector
l
scheme before we compute Fl (starting from Fk ).
LONG JUMP
It is possible to use a very long jump rather than advancing the forward rates structure with a small time step. A
simpler method would be advance the forward rates such that at one step only one forward rate will be reset. This
is the long jump method. Predictor-Corrector scheme can be used, and we don’t need to worry about other forward
rates.
ln Fl (T k + 1 ) - ln Fl (T k ) =
ò
Tk + 1
Tk
æ
ö
1
÷
ds çççml Fi (s ), s - s l2 (s )÷
+
÷
÷
2
è
ø
(
)
ò
Tk + 1
Tk
dW (s )s (s )
The variance terms can be evaluated accurately just like what we did in the short time steps.
VERY LONG JUMP
If the pay-off of the contract doesn’t depend on the path of how forward rates are evolved, a very long jump is
applicable. However, notice that, if the jump step Dt is very large, it might be possible that some of the forward
rates are already reset before the time (T i - t £ D t ). It is not that problematic if we consider
ln Fl (t + Dt ) - ln Fl (t ) =
ò
t
T i Ú(t + Dt )
æ
ö
1
÷
ds çççml Fi (s ), s - s l2 (s )÷
+
÷
÷
2
è
ø
9 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
(
)
ò
t
T i Ú(t + Dt )
dW (s )s (s )
where T i Ú t + Dt = min (T i , t + Dt ). The variance/covariance terms are obtained by similar method in the
previous methods, albeit we should be careful about the integral intervals.
C ij =
ò
T i ÚT j Út + Dt
t
ds r ij (s )s i (s )s j (s )
The matrix C ij is called the TOTC (total terminal covariance).
When using the Euler scheme to evolve the yield curve, the Dt goes to zero and it slow down a numerical
calculation. However, the long jump and very long jump can reduce time since fewer steps are required and the
Monte Carlo convergence would be faster than that of Euler scheme.
But when using long jump technique, we are force to use terminal bong as numerair. The value of the numeraire
can get very small if rates become large, but the money-market account has value at least 1. For low factor models,
long jump doesn’t speed up the simulation.
REDUCE RANK OF THE COVARIANCE MATRIX
Libor Market Model involves a lot of forward rates – sometimes may be 200 forward rates, and the original
approach will require generating 200 stochastic driven factors for all these forward rates, which is costly for a
large scale Monte Carlo. Another important factor is that most of the forward rates are driven by several
important stochastic factors, which dominate their variance. These facts will lead to methods to reduce the rank of
the covariance matrix. The approach employed here is like principal component analysis.
The covariance matrix can be Eigenvalue decomposed
A = uDuT
where u contains all the Eigen vectors of the covariance matrix. Ranking the Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors by
the absolute values of Eigenvalues from the largest to smallest, it is easy to see that the variance is dominated by the
Eigenvectors of the largest Eigenvalues, here we choose 4.
The eigen value matrix D is like
æ
çç
ççl 1
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
ççè
l2
O
n
The total variance will be
å
l i . And Let
i= 1
10 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
l n- 1
ö
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
ln÷
÷
ø
Ds =
D = æ
çç
çç l 1
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
ççè
l2
O
l n- 1
ö
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
ln÷
÷
ø
Then a random vector that has a variance matrix of A can be obtained by
v = uDs w
where w is a Gaussian random vector that a covariance of
æ
çç
çç1
çç 1
çç
çç
O
çç
çç
çç
ççè
ö
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
1
÷
÷
÷
1÷
÷
ø
To reduce the rank, we simply set l k = k where k > R ank , which gives
v = uæ
çç
çç l 1
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çç
çè
l2
O
l R ank - 1
öæ
ö
÷
÷
çç
÷
÷
w
÷
çç 1 ÷
÷
÷
÷
çç w ÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
çç 2 ÷
÷
÷
÷
çç M ÷
÷
÷
÷
÷
çç
÷
÷
÷
÷
ç
÷
wR ank - 1 ÷
ç
÷
÷
÷
÷
ç
÷
÷
çç w
÷
÷
÷
ç
÷
è R ank ø
÷
l R an k ÷
÷
÷
÷
0 ÷
÷
÷
÷
0 ÷
ø
The number of independent random variables for each simulation will be reduced to rank.
THE PRICING OF DIFFERENT CONTRACTS
The price of a contract will be determined by the martingale method, which is
éV (T )ù
ú
= E êê
ú
N (t )
êN (T )ú
ë
û
V (t )
where V is the price of the contract and N is the numeraire asset.
To value a contract at time t, we just calculate the expected value of the contract price at a certain time scaled by the
martingale asset.
11 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
éV (T ; F )ù
i ú
V (t ) = N (t )E êê
ú
êN (T ; Fi )ú
ë
û
BOND PRICES AND SWAP RATES
Let’s make it clean that at any time T i , the price of any zero coupon bond Pj is a function of all the forward rates,
therefore we will use the zero coupon bond prices in the following sections without given out the explicit formula
for them.
Similarly, a swap that exchanges payments from T a + 1 to T b can be calculated for T from zero coupon bond
prices, which is
and therefore their explicit formulas will not be provided in the following sections.
CAPLET PRICING
Let the contract expire at T m written on the forward rate Fm + 1 , and choose any zero coupon bond Pn as the
numeraire asset. The price of the caplet is just
émax F
T
- K ,0
ê
m+1 ( m+1 )
V = Pn 0 ; Fi (0 ) E ê
ê
Pn (T m + 1 )
êë
(
(
)
)ùúN t
ú
ú
ú
û
m+1
The expectation is therefore computed by Monte-Carlo simulation.
Note that the numeraire asset is not necessarily the zero coupon bond matured at T m + 1 .
CAP PRICING
Similar to caplet, the caplet can be priced in the same way. Let T s + 1 be the first payment of the cap and T C be the
time of the last payment in the cap, the value of the cap can be written as
émax F T - K , 0
C- 1
ê
i+ 1 ( C )
V = PC (0 )N å E ê
ê
PC (T C )
i= s
êë
(
(
)
j=C - 1
Õ
j= i+ 1
ù
é1 + t F (T )ùú
t
j j
C û
úú
ëê
ú i+1
ú
û
)
The max Fi + 1 (T c )- K , 0 is the pay-off of the cap at T i + 1 , and the discount factor
j=C - 1
Õ
j= i+ 1
é1 + t F (T )ù is
j j
C ú
êë
û
used to scale the pay-off to its value at T C . Note that Fi (TC ) = Fi (T i - 1 ) for the forward rate will be reset at
T i - 1 . PC is the numeraire asset can in this case, because PC (T C ) = 1 , we have
12 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
C- 1
é
V = PC (0 )N å E êêmax Fi + 1 (T C ) - K , 0
i= 1
ë
(
j=C - 1
)Õ
j= i+ 2
ù
é1 + t F (T )ùút
j j
C û
úú i + 1
ëê
û
This makes it possible to use a very long jump to value the contract.
EUROPEAN SWAPTIONS
Let the T s + 1 be the first payment of the swap and T C be the last payment of the swap, the float leg’s value of the
swap at time T s is
N éêPs (T s ) - PC (T s )ù
ú
ë
û
The fixed leg’s value of the swap at the same time is
C
NK
å
Pi (T s )t i
i= s+ 1
The payoff of the swap is
C
é
ù
N êPs (T s ) - PC (T s ) - K å Pi (T s )t i ú
ê
ú
i= s+ 1
ë
û
The price of the swaption at time 0 is therefore
é
C
æ é
öù
ù ÷
êm ax ççN êP (T ) - P (T ) - K
ú
ú, 0 ÷
P
T
t
(
)
÷
å
C
s
i
s
i ú ÷ú
ê
çç ê s s
è ë
i= s+ 1
ê
û øú
V (0 ) = Ps (0 )E ê
ú
ê
ú
Ps (T s )
ê
ú
ê
ú
ë
û
where Ps is the numeraire asset and
C
é
æ
öù
ú
÷
V (0 ) = Ps (0 )NE êêmax çççPs (T s ) - PC (T s ) - K å Pi (T s )t i , 0 ÷
÷
÷ú
çè
ø
i= s+ 1
êë
ú
û
TRIGGER SWAP AND MULTI-LOOK TRIGGER SWAPS
This is similar to swaps, albeit the simulation should advance to each of the observe dates to check whether the
trigger is triggered or not.
RATCHET CAPS
The pricing is similar to pricing of caps, however, because the pay-off of the product is path-dependent, a very long
jump to time T C is not possible.
13 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
C- 1
é
V = PC (0 )N å E êêmax Fi + 1 (T i ) - Fi + 1 (T i - 1 ), 0
i= 1
ë
(
j=C - 1
)Õ
j= i+ 2
ù
é1 + t F (T )ùút
j j
C û
úú i + 1
ëê
û
where the value Fi + 1 (T i - 1 ) is path-dependent.
CAPTIONS
The pricing of Captions is a bit tricky. It is possible that we evaluate the pay-off of the caption at the expiration by
launching a new Monte-Carlo to evaluate the cap, or more easily, we can evaluate the pay-off of the caption by
Black-Scholes equation (for we have assumed a volatility structure and we have the forward rates), therefore we
can express the value of a caption at the expiration of the caption T C
s
V cap (T C ; Fi ) = N
å
(
)
BL Fi , s i (T c , T i - 1 ), T i - 1 - T c , K Pi (T C )t i
i=C + 2
where the function BL is
æln (F / K ) + s 2t / 2 ö
÷
ç
÷
÷
BL (F , s , t , K ) = F N çç
- KN
÷
çç
÷
÷
s
t
è
ø
æln (F / K ) - s 2t / 2 ö
÷
çç
÷
÷
çç
÷
÷
÷
çè
s t
ø
with s i (TC ,T i - 1 ) is the volatility of the forward rate from T C to T i - 1 .
The pay-off is therefore
(
V (TC ) = max V cap (TC ; Fi )- K , 0
)
and the value of the caption at time T C is
V (0 ) = PC (0 )E éêmax V cap (T C ; Fi ) - K , 0 ù
ú
ë
û
(
)
CONSTANT MATURITY SWAPS
Notice the product is path-dependent, the payment exchange at time T i is
éF (T )- SR (T ;T ,T )ùN t
i
i+a
i+b ú
êë i i
û i
where SR (T i ;T i + a ,T i + b ) is the swap rate from T i + a to T i + b . The value of the CMS can be immediately computed
given the path of the forward rates
ïì C
V = PC (0 )E ïí å
ïï i = 1
î
C
é
ùïü
êF (T ) - SR (T ;T ,T ) Õ 1 + F (T )t N t úïý
i
i+a
i+b
j
C
j
iú
êi i
j= i+1
ï
ë
ûïþ
14 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
(
)
BERMUDAN SWAPTIONS
Bermudan Swaptions have early exercise feature, and is path-dependent. The continuation value and the exercise
value can both use the same numeraire asset. If exercised at time T i , the value will be the value of the swap at time
Ti
C
é
ù
N êê1 - PC (T i ) - K å Pj + 1 (T i )t j ú
ú
j= i+1
ë
û
The continuation value is the difficult part here. Consider time T C - 1 , which is the last reset date in the swaption.
The continuation value will be zero (because there is no more continuation). The exercise value will be
V = ma x N éê1 - PC (T C - 1 ) - KPC (T C - 1 )t C ù
ú, 0
ë
û
(
)
Now consider the swaption at time T C - 2 , the continuation value will be the exercise value
(
)
CV T C - 2 , Fi (T C - 2 )
éV (T )
ù
C- 1
ê
= PC (T C - 2 )E ê
Fi (T C - 2 )ú
ú
êPC (TC - 1 )
ú
ë
û
to calculate the continuation value, a fit function with the FC - 1 (T C - 2 ) and swap rate SR (T C - 2 ;T C - 1 ,T C ) is
constructed
CV = a + bx + cy + dxy + ex 2 + fy 2
To make the fit work, we will need all the paths we’ve generated. We are fitting
PC (T i )
V (T i + 1 )
PC (T i + 1 )
to a function of Fi + 1 (T i ) and SR (T i ;T i + 1 ,TC ) for time T i . To get the continuation value for T i , and the value
of the contract at that time will be
æ
V (T i ) = max çççN
çè
C
ö
é
ù
ê1 - P (T ) - K å P (T )t ú, CV T ; F (R ), SR (T ;T ,T ) ÷
÷
÷
C
i
j+1
i
jú
i
i+1
i
i+1
C
ê
÷
÷
j= i+1
ø
ë
û
15 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
(
)
16 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
CALIBRATION
TECHNICAL DETAILS
Assume that there n forward rates fi that describe the pay-off of an interest rate derivative. The evolution of each
forward rate fi is described by the stochastic differential equation:
dfi = mi ( f , t ) fidt + s i (t ) fidW i
E [dW idW j ] = r ij (t )dt
Where r ij is the instantaneous correlation between i and j, dW i is standard Weiner process, s i (t ) is the
instantaneous volatility of forward rate and mi ( f , t ) is the drift of the forward rate. Note that the drift mi ( f , t ) for
forward rate can be calculated from the other forward rates and their instantaneous volatilities and correlations, so
the instantaneous volatilities and correlations completely describe how forward rates will evolve in the future.
The FINCAD LMM calibration functions use the following functional form for the instantaneous volatilities of
forward rates and instantaneous correlations between forward rates:
- c (t - t )
s i (t ) = ki éê{a + b(t i - t )}e i + d ù
ú
ë
û
r ij = b1 + (1 - b1 )e
- b2 t i - t j
CALIBRATION
The calibration part adjusts the parameters of the LMM as to minimize the difference between LMM internal
model values and actual prevailing market values.
We use FINCAD to calibrate the instantaneous volatilities and correlations of the LMM to quoted market data
for caplets and swaptions.
17 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Quot ed Flat Vols
for Caps/ Floors
aaVol_ Crv_ Rcap_ BL
(Fincad Funct ion)
Volat ilit y Curve of
Forward Rat es
Quot ed Black Vols
for European
Swapt ions
aaCalibrat eRcAP2_ LMM
(Fincad Funct ion)
aaCalibrat eSwapt ion2_ LMM
(Fincad Funct ion)
Calibrat ed Paramet ers for
t he Inst ant aneous Volat ilit y
Funct ion: a,b,c,d
Calibrat ed Paramet ers for t he
Inst ant aneous Correlat ion
Funct ion(bet a1,bet a2) and opt ionally,
t he inst ant aneous volat ilit y funct ion
(a,b,c,d)
Input Paramet ers int o Specific
Product Pricing
CAPLET
The first calibration is caplet.
Caplet Details
value date
effective date
18 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
8-Dec-2011
8-Mar-2012
caplet frequency
caplet or floorlet
accrual method - rate
accrual method - coupon payments
business day convention
interpolation method
bootstrapping method
quarterly
rate caplet
actual/360
actual/360
modified following business day
exponential
piecewise linear spot volatilities
We run with the initial parameters 1, 1, 1, and 1 for a, b, c and d.
Minimizer Settings
1000
maximum number of iterations
0.001
error metric tolerance
Model Parameter Range Table
lower bound
upper bound
a
b
c
d
0
0
0
0
5
5
5
5
Initial Model Parameter Table
initial value
a
b
c
d
1
1
1
1
Results
output
time taken (in seconds)
number of iterations
calibration converged
error metric
19 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Calibration
0.13
200
0
5.522686968
0.648549551
a
2.599431552
b
1.847251966
c
0.279026143
d
ADEQUATE
overall calibration result
The calibration takes 0.13 seconds to converge and using 200 iteration steps. The overall calibration is rated as
adequate. The calibrated parameters a, b, c and d for instantaneous volatility are show in the above table.
0.60
0.50
price
0.40
0.30
0.20
0.10
0.00
0
10
20
Black Price
20 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
30
caplet
Predicted
#
Price
40
50
130.00%
110.00%
90.00%
70.00%
50.00%
30.00%
10.00%
0
5
10
15
Black Vol
20
25
30
35
40
45
Predicted Vol
According to the volatility graph above, we can find that in the long term the predicted volatility matches Black
volatility better than that in short term. The error between predicted volatility and Black volatility in short term is
significant.
SWAP CURVE
Curve Settings
value date
interpolation (bootstrapping) method
spread (added to raw rates)
use money market rates?
use futures prices?
use FRA rates?
use swap rates?
calculate tenor basis curves?
21 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
8-Dec-2011
exponential discount factors
0
yes
yes
no
yes
yes
no
show all tenor basis curves?
Money Market Rates Settings
actual/360
accrual method
modified following business day
business day convention
4.00%
3.50%
3.00%
Rate
2.50%
2.00%
1.50%
1.00%
0.50%
0.00%
1-Dec-11 1-Dec-16 1-Dec-21 1-Dec-26 1-Dec-31 1-Dec-36 1-Dec-41 1-Dec-46 1-Dec-51
-0.50%
Date
Fwd Rates
Spot Rates
Observing the graph above, we can find that the difference between forward rate and spot rate is large in the near
20 years and becomes smaller in the long term. To explain the trend of spot rate curve and forward rate curve, we
start from:
æ t+ t
ö
exp çççò r (s )ds ÷
÷
÷
è t
ø
F =
t
ln (t F + 1) =
22 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
ò
t
t+ t
r (s )ds
1
¶F
t
= r (t + t ) - r (t )
t F + 1 ¶t
Then we get:
¶F
Dr
= (t F + 1)
¶r
t
Therefore, the time interval in this case is 0.25, and therefore the fluctuations in forward rates are much more
severe than spot rates.
SWAPTION
We run with the initial parameters 0.5, 2, 2, 0.5, 0.1 and 0.1 for a, b, c, d, beta1 and beta2 respectively.
Details
value (settlement) date
frequency
accrual method
interpolation method
business day convention
swaption price closed-form approximation
linear-exponential volatility parameterization
error minimization method
error metric
weighting
8-Dec-2011
quarterly
actual/360
linear
modified following business day
Hull-White
4 parameters: lognormal volatility
Levenberg Marquardt
L-2 norm or chi-squared norm
vega weighted in price space
Minimizer Settings
maximum number of iterations
error metric tolerance
Model Parameter Range Table
23 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
200
0.001
lower bound
upper bound
a
b
c
d
beta1
beta2
0
0
0
0
0
0
5
5
5
5
1
1
Initial Model Parameter Table
initial value
a
b
c
d
beta1
beta2
0.5
2
2
0.5
0.1
0.1
Results
output
time taken (in seconds)
number of iterations
calibration converged
error metric
a
b
c
d
beta1
beta2
overall calibration result
Calibration
57.094
83
0
4567705.612
0.0000
1.3703
2.2420
0.4944
0.0287
0.1100
ADEQUATE
The calibration takes 56 seconds to converge and using 83 iteration steps. The overall calibration is rated as
adequate. The following checklist tests various criteria in order to examine a calibration.
Calibration Checklist
status
24 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
calibration converged?
calibrated parameters are not too close to boundaries
all price points < 3sigma
all vol points < 3sigma
90% price points < 2sigma
90% vol points < 2sigma
price bias <= 30%
vol bias <= 30%
price residual mean <= 1sigma from 0
vol residual mean <= 1sigma from 0
no single vol point is >5% off
mean distance vol data to model is <1%
model vs data difference within given vol uncertainties
overall calibration result
25 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
pass
fail
fail
pass
fail
pass
pass
pass
pass
pass
fail
fail
pass
ADEQUATE
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
0
20
40
-0.5
60
80
100
80
100
120
price residuals
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
0
20
40
60
-0.05
-0.1
-0.15
-0.2
vol residuals
26 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
120
12.00
10.00
price
8.00
6.00
4.00
2.00
0.00
0
20
40
60
swaption #
80
100
120
90.00%
80.00%
70.00%
volatility
60.00%
50.00%
40.00%
30.00%
20.00%
10.00%
0
20
40
60
swaption #
80
100
In the short term, predicted volatility matches Black volatility better than that in the long term.
Data: downloaded from Bloomberg
27 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
120
Full Swaption Vol Matrix
swap tenor (months)
volatility
1
3
6
12
24
36
48
60
84
120
180
240
1
3
option expiry (months)
6
12
24
36
48
60
12
24
36
48
60
72
84
73.350%
76.980%
63.460%
58.970%
51.465%
48.210%
50.570%
78.805%
75.165%
63.550%
56.890%
51.965%
53.365%
50.270%
78.150%
75.575%
61.770%
56.310%
52.970%
50.310%
49.290%
80.705%
70.090%
59.330%
54.665%
50.765%
48.165%
46.700%
74.720%
60.500%
52.340%
47.860%
45.570%
43.260%
42.065%
58.400%
49.570%
44.475%
41.670%
40.165%
38.760%
37.875%
46.450%
41.585%
39.025%
37.465%
36.560%
35.990%
34.975%
39.050%
36.880%
36.020%
35.070%
34.355%
34.080%
33.300%
33.230%
33.190%
32.380%
31.670%
31.380%
30.940%
30.835%
30.155%
29.775%
29.435%
29.150%
28.730%
29.125%
29.285%
29.165%
28.700%
28.400%
28.960%
28.900%
29.185%
29.175%
27.650%
27.500%
27.600%
27.700%
27.745%
27.750%
27.695%
96
108
120
180
240
300
360
46.400%
48.800%
47.775%
45.070%
44.200%
43.100%
43.940%
48.150%
47.800%
47.250%
44.280%
42.760%
42.700%
43.715%
47.900%
47.000%
46.215%
43.370%
42.355%
42.250%
42.935%
45.100%
44.725%
43.765%
40.925%
40.900%
40.275%
40.665%
40.950%
40.050%
39.335%
36.850%
36.960%
36.600%
36.995%
37.545%
36.725%
35.955%
34.100%
34.450%
34.000%
34.230%
34.300%
34.050%
34.060%
33.055%
32.930%
32.600%
32.625%
32.945%
32.650%
32.640%
31.930%
32.080%
31.500%
31.955%
28 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
84
120
180
240
30.200%
30.200%
31.185%
30.340%
30.355%
30.030%
30.240%
29.320%
29.450%
29.700%
28.820%
28.480%
27.750%
28.000%
29.000%
29.490%
29.000%
27.950%
27.615%
27.710%
27.400%
27.590%
27.555%
26.880%
26.200%
26.285%
26.100%
26.475%
Futures Prices Table (Not Used)
contract
futures price
contract
futures price
Dec-2011
Jan-2012
Feb-2012
Mar-2012
Apr-2012
May-2012
Jun-2012
Sep-2012
Dec-2012
Mar-2013
Jun-2013
Sep-2013
Dec-2013
Mar-2014
Jun-2014
Sep-2014
Dec-2014
Mar-2015
Jun-2015
Sep-2015
Dec-2015
Mar-2016
Jun-2016
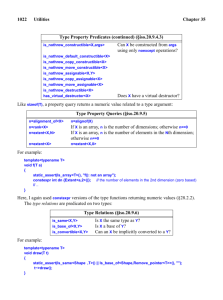
Sep-2016
Dec-2016
Mar-2017
Jun-2017
Sep-2017
Dec-2017
Mar-2018
Jun-2018
Sep-2018
Dec-2018
Mar-2019
Jun-2019
Sep-2019
Dec-2019
Mar-2020
Jun-2020
Sep-2020
Dec-2020
Mar-2021
Jun-2021
Sep-2021
97.6150
97.4750
97.3400
97.2400
97.1350
97.0450
96.9500
96.8800
96.8100
96.7550
96.6900
96.6500
96.6000
96.5650
96.5200
96.4900
96.4600
96.4250
96.3900
96.3700
96.3400
96.3100
99.4475
99.4350
99.4200
99.3900
99.3750
99.3600
99.3500
99.3500
99.3600
99.3450
99.3150
99.2400
99.1300
98.9750
98.8050
98.6200
98.4500
98.2800
98.1050
97.9150
97.7600
Single Strike Cap Data - NOT USED
cap term (months)
strike
volatility
12
24
36
48
60
72
84
1.000%
1.000%
1.000%
1.000%
1.000%
1.000%
1.000%
106.870%
87.320%
85.480%
77.940%
71.690%
66.810%
63.200%
29 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
96
108
120
1.000%
1.000%
1.000%
60.560%
58.470%
56.810%
Swap Rates Table
grid point
1Y
2Y
3Y
4Y
5Y
6Y
7Y
8Y
9Y
10Y
12Y
15Y
20Y
25Y
30Y
40Y
maturity date
12-Dec-2012
12-Dec-2013
12-Dec-2014
14-Dec-2015
12-Dec-2016
12-Dec-2017
12-Dec-2018
12-Dec-2019
14-Dec-2020
13-Dec-2021
12-Dec-2023
14-Dec-2026
12-Dec-2031
12-Dec-2036
12-Dec-2041
12-Dec-2051
Money Market Rates Table
grid point
maturity date
rate
ON
T/N
1W
2W
1M
2M
3M
4M
5M
6M
7M
8M
9M
10M
11M
12M
9-Dec-2011
12-Dec-2011
19-Dec-2011
27-Dec-2011
12-Jan-2012
13-Feb-2012
12-Mar-2012
12-Apr-2012
14-May-2012
12-Jun-2012
12-Jul-2012
13-Aug-2012
12-Sep-2012
12-Oct-2012
13-Nov-2012
12-Dec-2012
0.150%
30 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
par swap rate
0.624%
0.648%
0.758%
0.975%
1.223%
1.474%
1.689%
1.863%
2.006%
2.124%
2.315%
2.496%
2.616%
2.676%
2.712%
2.721%
0.200%
0.220%
0.276%
0.396%
0.540%
0.614%
0.682%
0.761%
0.813%
0.863%
0.916%
0.967%
1.022%
1.082%
CODE STRUCTURE
IMPLEMENTED FUNCTIONS
The following are implemented in the code:
1. Random number generators
2. Multi Dimensional Gaussian Generators, with simple cholesky decomposition, and reduced rank based on
singular value decomposition
3. Theoretical value of Caplets and Caps under the implemented Variance Structure
4. Libor Market Model based on Predictor Corrector Scheme
a. Short time step
b. Long jump
c. Very long jump
d. Automatic selection of appropriate covariance matrix for different jumps
5. Pricing of products using Libor Market Model
a. Captions
b. European Swaptions
c. Constant Maturity Swaps
d. Rachet Caps
e. Caplets
f. Caps
6. Bermudan Swaption Pricing
a. Based on least square fitting of continuation values.
IMPLEMENTATION
All the works are implemented in C++ and tested on the latest Apple Inc.’s XCode and Microsoft’s Visual C++.
Most of the classes are template classes, and we have made some requirements on how these classes should work,
what methods and properties should be implemented, and how they are initialized. Most of the classes come with at
least two type parameters, T and TSize. They are provided mainly to facilitate changing different precisions and
working with different numerical types. TSize is by default set to long, and in most cases we use double precision
(so T is set to double in most of the cases). On 64-bit platforms, long double might provider higher precision.
For all matrice, the primary index will be the row index, and the secondary index will be the column index. The
default TSize is long.
Singular Value decomposition is taken from Newmat, which can be found at
http://www.robertnz.net/nm_intro.htm
THE INTEGRAL OF THE VARIANCE
The following integral can be evaluated analytically
ò
t
t + Dt
ds r (T i ,T j )s (T i , s )s (T j , s )
for the correlation and volatility structure we’ve chosen as default, which is
31 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
s (T i , t ) = Fi y (T i - 1 - t ; a, b, c, d ) = Fi éêa (T i - 1 - t ) +
ë
(
dù
ex p éê- b (T i - 1 - t )ù
+c
ú
ú
û
ë
û
)
and
(
r ij = b1 + (1 - b1 )exp - b 2 t i - t j
)
A more general approach is to implement a numerical integrator by Simpson’s rule or similar methods. However, it
turned out that Simpson’s rule will underestimate the volatility even with 4096 sections, which is unacceptable if
the covariance needs to be recalculated for multiple times. The integral is performed in symbolic operations by
Wolfram Mathematica, and please refer to the enclosed .nb file for more details
32 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
LM M
Advancer
Variance
Structure
Forward
Rate
Sequence
TimeSequence
Covarian
ce M atrix
Product
Pricing
Gaussian
Random
Number
Generator
M odel Specification
DESCRIPTION OF CODE STRUCTURE
The most important class for the method is the LMMAdvancer, which has the following signature
template<typename TVarianceStructure,template<typename, typename,typename> class
TMultiDimensionGaussian, typename T,typename TSize = long> class LMMAdvancer
The LMMAdvancer will advance to the next time step using a TOTC style matrix (that said, it is still good to use
the LMMAdvancer for shot steps and long steps), and it checks which forward rates are reset and which are not.
For the forward rates that are already reset, the LMMAdvancer will simply carry on their last available values.
TVarianceStrucutre is the type of the variance structure, which can be inter-changed efficiently. All
TVarianceStructures have got to implement the following method:
33 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
It should be noted that a method VolatilityIntegrator(T fromT, T toT, TSize i, TSize j) must be implemented in
the class. If an analytical solution is not viable, using the numerical integrators in the header file “integrator.hpp”
might alleviate some of the painful implementations.
template<typename,typename,typename> class TMultiDimensionGaussian is the Gaussian random number
generators. It supports setting a variance matrix to it and generate corresponding random vectors. Calling
NextGroup() method on one of the instances will generate a vector of random variates according to the given
variance matrix; calling operator[] on the same instance will return the value of the vector at the given index.
Similar to TVarianceStructure, this template parameter is provided to provide more freedom in choosing different
random number generators. This is great for different factor-reducation schemes, and enable us to fast change them
without modifying the LMMAdvancer.
To save time and computational resources, the covariance matrix will be pre-computed by calling PreAdvance().
To generate the next sequence of forward rates, call SingleAdvance().
TimeSequence is the first step to start our engine. A class of TimeSequence is used for the underlying times where
the volatilities and forward rates being calculated. The times are stored in a vector, so two constructors can be
applied: the first one is push back the times one by one into the vector. The second is a copy constructor that can use
another time sequence to assign the times into a new object of this class.
Because the first time is always 0, and the therefore the first forward rate is meaningless. The second rate is not a
forward rate, but the rate from 0 to the first time spot. However, in the VarianceStructureMatrix, the first two
rates are neglected so that the matrix will stay positive definite for most of the cases.
The GetSize method for the TimeSequence and VarianceStructure however will return a size that includes these
two meaningless rates. Furthuremore, the leading 0 in the time sequence is automatically pushed into the sequence,
therefore no explicit initialization is necessary.
Several member functions are used all the way down in the program, the overloading of operator= accomplish the
assignment by another time sequence too. Other functions are used to get specific element or insert or delete element,
return the size of the time sequence and find the location of a specific time in the time sequence.
CALCULATION PROCESS
LMM Advancer is the core method to generate forward rates. The whole process of using our code to do the
product pricing is as below:
1. Establish time sequence by template<typename T,typename TSize=long> class TimeSequence times,
which is the underlying time sequence of forward rates sequence we focus on.
2. Use the time sequence to set the variance structure by template<typename T,typename TSize=long> class
VarianceStructure. When we have a varianceStructhen generate the volatility by volatility functions and
correlations.
3. Build an object by template<typename TVarianceStructure,template<typename, typename,typename> class
TMultiDimensionGaussian, typename T,typename TSize = long> class LMMAdvancer, set the time
sequence and variance structure generated in step 1) and 2) in the LMMAdvancer object.
4. Call the member function void PreAdvance() of LMMAdvancer to set the correlation of the stochastic
processes. Then do the Monte Carlo simulation by using the member function void SingleAdvance() of
LMMAdvancer, so we can get the forward rates at next time step and then use them to value any product.
34 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Variance
Parameters
Specification
Set Time
Sequence
Set Variance
Sequence
Set
Covariance
M atrix
Calculate volatility by
volatility functions,
current time, forward
rates ending time
I nitial forward
rates parameters
specification
Product
Specification
Use LM M Advancer to set
correlations
M onte Carlo using
LM M Advancer, get
the forward rates.
35 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Specific Product
Pricing
PREREQUISITES FOR DIFFERENT TEMPLATE CLASSES
MATRIX
All classes that can be used in the place of a Tmatrix must implement the following member functions:
TSize GetLength(int i) const: get the size of the matrix, i=0 will get the length of primary index and i=1
will get the length of secondary index.
T &operator()(TSize i, TSize j):, using operator(i,j) return the [i][j] element of the matrix.
const T &operator()(TSize i, TSize j) const, using operator(i,j) return the [i][j] element of the matrix.
VARIANCE STRUCTURE
T GetVolatility(TSize i,T t) const: Return the volatility of the i-th forward rate at time t
T GetCorrelation(TSize i,TSize j,T t) const: Return the correlation between the i-th forward rate and the
j-th forward rate at time t.
TSize GetSize() const
T VolatilityIntegrator
HOW DOES PRICER WORK?
Please refer to the following graph on how the pricer works.
36 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
LMMAdvancer :
T imeSequence,
VarianceSt ruct ure,
ForwardRat eSequence
LMMPricer
T rigger/ mult ilook t rigger
swaps
European
swapt ions
Rat chet caps
Const ant
Mat urit y
Swaps
Bermudan
Swapt ions
T rigger swaps
Model
Specificat ion
Swapt ion
Model
Specificat ion
Bermudan
Model
Specificat ion
Real World
Product
Rat chet caps
Model
Specificat ion
Const ant
Mat urit y
Swaps
Capt ions
Capt ions
Model
Specificat ion
Real World
Product
Model
Specificat ion
PERFORMANCE ISSUES AND ACCURACY
An initial investigation of code reveals, for N forward rates, written on N times, and if we need to generate M
paths, the number of forward rates we need to generate is approximately N 2 M . For a 30 year 3-month forward
rate simulation, 10,000 path will require approximately at least 11GB of memory, which is unrealistic for our
computers. Therefore for our Bermudan Swaption simulations, performance of the code is extremely slow.
37 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
Including PCA based method really decreases the time of the simulation by 1/7, however, for large scales
covariance matrix, the Singular value decomposition may not converge in a short enough time, and for very large
simulations, the Simple method is used.
Singular Value decomposition will also introduce other errors into the simulation, due to the fact that it is an
iterative method.
38 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
INITIAL INVESTIGATIONS
REBONATO’S SWAP APPROXIMATION
In the paper “Linking Caplet and Swaption Volatilities in a BGM/J Framework: Approximate Solutions”
written by Peter Jackel and Riccardo Rebonato in 2000, they
present an approximation for the volatility of European swaptions in a forward rate based on BGM framework
provides an analytic calculation for swaptions prices without using the need for Monte Carlo simulations.
We have seen that at the money vanilla swaptions are quoted in volatility, which means that the market uses
Black’s formula to match the price of the swaption, and the implied volatility used for quotation purposes.
Thus, if we postulate a lognormal dynamic of the swap rate under the swap forward measure which numeraire is
q- p
2
å
B pq (t ) =
2 dB p + 2 k (t )
k=1
Hence:
dS p,q
S p,q
= s p,qdW t p,q
Then, we can apply the black formula to price swaptions in the same way did for caplet because swapstions under
p, q measure is a martingale
Swaption p,q (0 ) = B p,q (0 )E p,q ((S p,q (T p ) - K )+ )
= B p,q (0 )E p,q ((S p,q (T p )N (d1 ) - K N (d2 ) )
ln(
E p,q (S p,q )
)+
K
g p,q T p
d1 =
d2 = d1 -
g p2,qT p
2
g p,q T p
2
Where E p,q (S p,q ) = S p,q (0 )
Next, we need to obtain the g p,q to apply in the black formula
dS p,q dS p,q
= s p2,qdt
S p,q S p,q
ò
Tp
0
dS p,q dS p,q
S p,q S p,q
=
39 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
ò
Tp
0
s p2,qdt = ( g p,q )2T p
The approximation formula of swap rates is decomposed in linear combination of the forward rates where the
dynamics is negligible.
q- 1
å
S p,q =
w pk ,qFk (t )
k= p
dB k + 1
w pk ,q =
q- p
2
å
2 dB p + 2 j
j=1
w in the linear combination are constant and equal to their value in 0, wpk,q (0 )
q- 1
dS p,q »
å
wpk,q (0 )dFk (t )
k= p
dS
dS
( p,q )( p,q ) =
S p,q S p,q
q- 1
å
w pk ,q (0 )w pj ,q (0 )dFk (t )dFj (t )
S p2,q
q - 1 w k (0 )w j (0 )r s s F (t )F (t )
p ,q
p ,q
kj k j k
j
= å
dt
2
S p,q
j ,k = p
j ,k = p
Supplement into above equation (3). We get
w pk ,q (0 )w pj ,q (0 )r kj s k s j Fk (t )Fj (t )
dt
ò0 jå,k = p
S p2,q
k
j
Tp
1 q- 1 w p,q (0 )w p,q (0 )Fk (0 )Fj (0 )
»
r kj (0 ) ò s k (t )s j (t )dt
å
2
0
T p j ,k = p
S p,q
( g p,q )2 »
1
Tp
T p q- 1
Above is all closed form formulas available to compute European swaptions.
In our initial test we have s j (t ) = k j [(a + b(t j - t ))e
- c(t j - t )
+ d ] where k j =1 a =0.05
b =0.09 c =0.44 d =0.11 b =0.1 with strike price of 6% with flat curve continuously compounded rate of 5%
We integrate above volatility function with the analytic swap price formula in the VBA and get the following
result table.
time
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
Flat 5% discount factor
0.987877
0.975900
0.964069
0.952381
0.940835
40 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
European swaption prices
5.456%
7.496%
8.910%
9.977%
10.806%
1.5
1.75
2
2.25
2.5
2.75
3
3.25
3.5
3.75
4
4.25
4.5
4.75
5
5.25
5.5
5.75
6
6.25
6.5
6.75
7
7.25
7.5
7.75
8
8.25
8.5
8.75
9
9.25
9.5
9.75
10
0.929429
0.918161
0.907029
0.896033
0.885170
0.874439
0.863838
0.853365
0.843019
0.832799
0.822702
0.812728
0.802875
0.793142
0.783526
0.774027
0.764643
0.755373
0.746215
0.737169
0.728232
0.719403
0.710681
0.702065
0.693554
0.685146
0.676839
0.668634
0.660528
0.652520
0.644609
0.636794
0.629074
0.621447
0.613913
41 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
11.457%
11.964%
12.353%
12.641%
12.840%
12.961%
13.013%
13.001%
12.933%
12.812%
12.644%
12.431%
12.178%
11.888%
11.563%
11.206%
10.819%
10.404%
9.963%
9.499%
9.013%
8.507%
7.981%
7.439%
6.880%
6.306%
5.719%
5.120%
4.509%
3.888%
3.258%
2.620%
1.974%
1.322%
0.665%
LONG JUMP AND VERY LONG JUMP WITH WRONG NUMERAIRE ASSET
We test the code and long jump/very long jump with a wrong numeraire asset. The priced product is caplet, which
has a theoretical price because we know the volatility of the forward rates for sure.
The following contract is used: Caplet that matures on 0.75 years, written on 0.25 years’ forward rate
F (0.75 , 1.0 ) . The strike price is 0.05. Assuming a flat term structure of 0.05. Assuming the following
parameters for volatility and correlation:
a = 0. 09
b = 0. 44
c = 0. 11
d = 0. 05
b1 = 0
b 2 = 0. 1
The theoretical value for this caplet is 0.000739054. For very long jump and long jump, both 10,000 paths are
generated (though not stored). The numeraire asset is chosen to be zero coupon bond that matures at 0.75.
The following graph provided a glimpse of the results. The average result for long jump is 0.0007385, while for
very long jump the result is 0.0007400. The long jump is more accurate at an error of 0.08%, while the very long
jump’s result is slightly more inferior at 0.13%. However, notice the standard deviation of long jump’s result is
3.6 ´ 10 - 6 , while for very long jump the result is slightly better at 2.7 ´ 10 - 6 .
42 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
0.000746
0.000744
0.000742
0.00074
0.000738
0.000736
0.000734
0.000732
0.00073
0.000728
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Short Jump 0.000740.000740.000730.000740.000740.000740.000730.000740.000730.00074
Long Jump 0.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.00074
Theoretical 0.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.000740.00074
43 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
PRICING RESULTS
Please see the following table
Product
Pricing
Swap
beggin
g
Swap
end
Exercise
date/Termi
nal date
tenor
Simulati
on
Pricin
g
Time
European
Swaption
Trigger
Swaption
Ratchetcaps
Bermudan
Swaption
Const Maturity
Swap
Caption
0.0570392
1
5
1
0.25
5000
1.46
0.0573001
1
5
0.25,0.5,0.75
0.25
5000
4.304
0.25
0.25
5000
5000
67.761
37.161
0.25
5000
10.419
0.0019846
0.0555382
1
0.0052545
44 | Libor Market Model and It’s Implementation
5
2
DETAILS OF THE CODE FILES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Namespace Index ........................................................................................................................................... 2
Hierarchical Index .......................................................................................................................................... 3
Class Index ..................................................................................................................................................... 4
File Index ........................................................................................................................................................ 5
TermStructure ............................................................................................................................................. 6
Class Documentation .....................................................................................................................................10
TermStructure::_srandInitializer ...............................................................................................................10
TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T > .......................................................................................................12
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > ......................................................................................14
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer< TVarianceStructure, T, TSize > .....................................................17
TermStructure::CapletInfo< T > ................................................................................................................19
TermStructure::CapletPricer< TLMMAdvancer, T, TSize > ....................................................................21
TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T > ..........................................................................................................23
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > .................................................................................25
TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T > ..............................................................................................29
TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver< T, TSize > .......................................................................................31
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ..............33
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T,
TSize > ......................................................................................................................................................41
TermStructure::LMMPathPool< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ...............43
TermStructure::LMMPricer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ....................47
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed< TMatrix, T, TSize > .........................................................................51
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper< T, NPrimary, NSecondary, TSize > .....................................................54
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize > ..............................56
TermStructure::Polynomial< T, TOrder > .................................................................................................59
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix< T, TSize > ...............................................................................................61
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize > ....................................64
TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize >.............................................................................................................66
TermStructure::TimeSequence< T, TSize > ..............................................................................................69
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder< T, TSize > ...................................................................................72
TermStructure::VarianceStructure< T, TSize >.........................................................................................74
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix< T, TVarianceStructure, TSize > ............................................78
File Documentation .......................................................................................................................................80
BermudanSwaption.hpp ............................................................................................................................80
BlackScholesPricer.hpp .............................................................................................................................81
capletInfo.hpp ............................................................................................................................................82
ForwardRateSequence.hpp ........................................................................................................................83
functor.hpp ................................................................................................................................................84
functorFitter.hpp ........................................................................................................................................85
Integrator.hpp ............................................................................................................................................86
leastSquareSolver.hpp ...............................................................................................................................87
LMMAdvancer.hpp ...................................................................................................................................88
LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp .........................................................................................................89
LMMPathPool.hpp ....................................................................................................................................90
LMMPricer.hpp .........................................................................................................................................91
main.cpp ....................................................................................................................................................92
matrix.hpp..................................................................................................................................................93
matrixChildren.hpp ....................................................................................................................................94
matrixdecomposition.hpp ..........................................................................................................................95
xlv | Code File Details
matrixOperations.hpp ................................................................................................................................96
mstester.cpp ...............................................................................................................................................97
polynomial.hpp ..........................................................................................................................................99
pricertestmain.cpp ...................................................................................................................................100
randomNumberGenerators.hpp ...............................................................................................................102
SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp ......................................................................................................103
srandInitializer.cpp ..................................................................................................................................104
srandInitializer.hpp ..................................................................................................................................105
standardFunctions.hpp .............................................................................................................................106
swap.hpp ..................................................................................................................................................107
timeSequence.hpp ....................................................................................................................................108
timeSequenceHolder.hpp .........................................................................................................................109
varianceStructure.hpp ..............................................................................................................................110
Index ............................................................................................................................................................111
xlvi | Code File Details
1 | Code File Details
NAMESPACE INDEX
NAMESPACE LIST
Here is a list of all namespaces with brief descriptions:
TermStructure ...................................................................................................................................... 6
2
CLASS INDEX
CLASS HIERARCHY
This inheritance list is sorted roughly, but not completely, alphabetically:
TermStructure::_srandInitializer ............................................................................................................ 10
TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T > .................................................................................................... 12
TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T > ................................................................................................ 23
TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T > .................................................................................... 29
TermStructure::Polynomial< T, TOrder > ...................................................................................... 59
TermStructure::CapletInfo< T > ............................................................................................................ 19
TermStructure::CapletPricer< TLMMAdvancer, T, TSize > ................................................................. 21
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > .............................................................................. 25
TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver< T, TSize > .................................................................................... 31
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ........... 33
TermStructure::LMMPathPool< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ............ 43
TermStructure::LMMPricer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ................. 47
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian,
T, TSize >........................................................................................................................................ 41
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed< TMatrix, T, TSize > ...................................................................... 51
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper< T, NPrimary, NSecondary, TSize > .................................................. 54
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize > .......................... 56
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix< T, TSize > ............................................................................................ 61
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize > ................................. 64
TermStructure::TimeSequence< T, TSize > ........................................................................................... 69
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder< T, TSize > ................................................................................ 72
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer< TVarianceStructure, T, TSize > ........................................... 17
TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize > .................................................................................................. 66
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > .................................................................... 14
TermStructure::VarianceStructure< T, TSize > ..................................................................................... 74
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix< T, TVarianceStructure, TSize > ......................................... 78
3
CLASS INDEX
CLASS LIST
Here are the classes, structs, unions and interfaces with brief descriptions:
TermStructure::_srandInitializer (A class maintains that srand() is called only once ) ............... 10
TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T > (Common requirement for all functors ) ........................ 12
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > ........................................................................... 14
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer< TVarianceStructure, T, TSize > ....................................... 17
TermStructure::CapletInfo< T > ...................................................................................................... 19
TermStructure::CapletPricer< TLMMAdvancer, T, TSize > ........................................................ 21
TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T > (Error Function ) ................................................................. 23
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > (A Sequence of Forward Rate Based on a
Given Time Sequence ) ........................................................................................................................ 25
TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T > (Inverse Error Function ) ....................................... 29
TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver< T, TSize > (Least Square Solver based on two matrices ) 31
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >
(LMMAdvancer is the method to move a set of forward rates ) ..................................................... 33
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer< TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > ............................................................................................ 41
TermStructure::LMMPathPool< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > (A
class to generate a pool of paths from LMMAdvancer; ) ................................................................ 43
TermStructure::LMMPricer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize > .... 47
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed< TMatrix, T, TSize > (Transpose of a Matrix ) ................... 51
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper< T, NPrimary, NSecondary, TSize > (Wrap a C++ matrix,
T[][] to a matrix satisfies the requirements of the matrix ) ............................................................. 54
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize > (A
Reduced-rank Gaussian Generator utilizing SVD. Rank is defaul to 4 ) ....................................... 56
TermStructure::Polynomial< T, TOrder > (A Polynomial ) ........................................................... 59
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix< T, TSize > (A matrix using double pointer as the storage ) ...... 61
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize > (A Gaussian
Generator based on CholeskyDecomposition ) ................................................................................. 64
TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize > (Swap Contract ) ...................................................................... 66
TermStructure::TimeSequence< T, TSize > (Time Sequence. The times that all the data are
based on ) ............................................................................................................................................. 69
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder< T, TSize > (A structure that has a time sequence in it ) 72
TermStructure::VarianceStructure< T, TSize > (A variance structure. Please refer to the doc for
more details on the theories ) .............................................................................................................. 74
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix< T, TVarianceStructure, TSize > (Initiate an
instantaneous covariance matrix from a variance structure ) ......................................................... 78
4
FILE INDEX
FILE LIST
Here is a list of all files with brief descriptions:
BermudanSwaption.hpp .................................................................................................................... 80
BlackScholesPricer.hpp ..................................................................................................................... 81
capletInfo.hpp ..................................................................................................................................... 82
ForwardRateSequence.hpp ............................................................................................................... 83
functor.hpp .......................................................................................................................................... 84
functorFitter.hpp ................................................................................................................................ 85
Integrator.hpp .................................................................................................................................... 86
leastSquareSolver.hpp ....................................................................................................................... 87
LMMAdvancer.hpp ........................................................................................................................... 88
LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp ............................................................................................... 89
LMMPathPool.hpp ............................................................................................................................ 90
LMMPricer.hpp ................................................................................................................................. 91
main.cpp .............................................................................................................................................. 92
matrix.hpp ........................................................................................................................................... 93
matrixChildren.hpp ........................................................................................................................... 94
matrixdecomposition.hpp .................................................................................................................. 95
matrixOperations.hpp ........................................................................................................................ 96
mstester.cpp ........................................................................................................................................ 97
polynomial.hpp ................................................................................................................................... 99
pricertestmain.cpp ............................................................................................................................ 100
randomNumberGenerators.hpp ..................................................................................................... 102
SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp ............................................................................................. 103
srandInitializer.cpp .......................................................................................................................... 104
srandInitializer.hpp .......................................................................................................................... 105
standardFunctions.hpp .................................................................................................................... 106
swap.hpp ........................................................................................................................................... 107
timeSequence.hpp ............................................................................................................................. 108
timeSequenceHolder.hpp ................................................................................................................. 109
varianceStructure.hpp ..................................................................................................................... 110
5
NAMESPACE DOCUMENTATION
TERMSTRUCTURE NAMESPACE REFERENCE
CLASSES
class BermudanSwaption
class BlackScholesPricer
class CapletInfo
class CapletPricer
class ForwardRateSequence
A Sequence of Forward Rate Based on a Given Time Sequence. class AbstractFunctor
a common requirement for all functors. class LeastSquareSolver
Least Square Solver based on two matrices. class LMMAdvancer
LMMAdvancer is the method to move a set of forward rates. class LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer
class LMMPathPool
A class to generate a pool of paths from LMMAdvancer;. class LMMPricer
class SimpleMatrix
A matrix using double pointer as the storage. class MatrixWrapper
Wrap a C++ matrix, T[][] to a matrix satisfies the requirements of the matrix. class
MatrixTransposed
Transpose of a Matrix. class Polynomial
A Polynomial. class SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian
A Gaussian Generator based on CholeskyDecomposition. class PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian
A Reduced-rank Gaussian Generator utilizing SVD. Rank is defaul to 4. class _srandInitializer
A class maintains that srand() is called only once. class ErrorFunction
Error Function. class InverseErrorFunction
Inverse Error Function. class Swap
Swap Contract. class TimeSequence
Time Sequence. The times that all the data are based on. class TimeSequenceHolder
A structure that has a time sequence in it. class VarianceStructure
A variance structure. Please refer to the doc for more details on the theories. class
VarianceStructureMatrix
INITIATE AN INSTANTANEOUS COVARIANCE MATRIX FROM A VARIANCE
STRUCTURE. FUNCTIONS
template<typename TFunctor , typename T , typename TSize > T Integrator_simpson (T start, T end,
TFunctor fx, TSize M=1024)
A simple Simpson integrator.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void LUDecomposeTo (const
TFromMatrix &input, TToMatrix &L, TToMatrix &U)
LU Decomposition.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void LUDecomposeTo (const
TFromMatrix &input, TToMatrix &result)
LU Decomposition. The L and U matrix is put into result, assuming diagonal elements of L is 1.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void CholeskyDecomposeTo (const
TFromMatrix &a, TToMatrix &b)
Cholesky Decomposition.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void SingularValueDecomposeTo (const
TFromMatrix &a, TToMatrix &u, TToMatrix &d, TToMatrix &v)
6
Singular Value Decomposition.
template<typename TInputMatrix , typename TLoadMatrix , typename TResultMatrix , typename
TTempMatrix > void LUDecompositionSolve (const TInputMatrix &input, const TLoadMatrix
&load, TResultMatrix &result, TTempMatrix &tempStorage)
template<typename TLeftMatrix , typename TRightMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > void Multiply
(const TLeftMatrix &l, const TRightMatrix &r, TResultMatrix &result)
Matrix multiplication.
template<typename TLeftMatrix , typename TRightMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > void Plus
(const TLeftMatrix &l, const TRightMatrix &r, TResultMatrix &result)
matrix plus
template<typename TLeftMatrix , typename TRightMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > void Minus
(const TLeftMatrix &l, const TRightMatrix &r, TResultMatrix &result)
matrix minus l - r
template<typename T , typename TOrder > Polynomial< T, TOrder > GenerateBasis (TOrder order)
FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TFROMMATRIX , TYPENAME TTOMATRIX >
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::CHOLESKYDECOMPOSETO (CONST
TFROMMATRIX & A, TTOMATRIX & B)
Cholesky Decomposition.
Definition at line 82 of file matrixdecomposition.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TORDER >
POLYNOMIAL<T,TORDER> TERMSTRUCTURE::GENERATEBASIS (TORDER
ORDER)
Definition at line 56 of file polynomial.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TFUNCTOR , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE >
T TERMSTRUCTURE::INTEGRATOR_SIMPSON (T START, T END,
TFUNCTOR FX, TSIZE M = 1024)
A simple Simpson integrator.
Definition at line 9 of file Integrator.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TFROMMATRIX , TYPENAME TTOMATRIX >
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LUDECOMPOSETO (CONST TFROMMATRIX &
INPUT, TTOMATRIX & L, TTOMATRIX & U)
LU Decomposition.
Definition at line 13 of file matrixdecomposition.hpp.
7
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TFROMMATRIX , TYPENAME TTOMATRIX >
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LUDECOMPOSETO (CONST TFROMMATRIX &
INPUT, TTOMATRIX & RESULT)
LU Decomposition. The L and U matrix is put into result, assuming diagonal elements of L is 1.
Definition at line 47 of file matrixdecomposition.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TINPUTMATRIX , TYPENAME TLOADMATRIX ,
TYPENAME TRESULTMATRIX , TYPENAME TTEMPMATRIX > VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::LUDECOMPOSITIONSOLVE (CONST TINPUTMATRIX &
INPUT, CONST TLOADMATRIX & LOAD, TRESULTMATRIX & RESULT,
TTEMPMATRIX & TEMPSTORAGE)
Definition at line 139 of file matrixdecomposition.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLEFTMATRIX , TYPENAME TRIGHTMATRIX ,
TYPENAME TRESULTMATRIX > VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::MINUS (CONST
TLEFTMATRIX & L, CONST TRIGHTMATRIX & R, TRESULTMATRIX &
RESULT)
matrix minus l - r
Definition at line 26 of file matrixOperations.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLEFTMATRIX , TYPENAME TRIGHTMATRIX ,
TYPENAME TRESULTMATRIX > VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::MULTIPLY
(CONST TLEFTMATRIX & L, CONST TRIGHTMATRIX & R,
TRESULTMATRIX & RESULT)
Matrix multiplication.
Definition at line 8 of file matrixOperations.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLEFTMATRIX , TYPENAME TRIGHTMATRIX ,
TYPENAME TRESULTMATRIX > VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::PLUS (CONST
TLEFTMATRIX & L, CONST TRIGHTMATRIX & R, TRESULTMATRIX &
RESULT)
matrix plus
Definition at line 14 of file matrixOperations.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TFROMMATRIX , TYPENAME TTOMATRIX >
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::SINGULARVALUEDECOMPOSETO (CONST
TFROMMATRIX & A, TTOMATRIX & U, TTOMATRIX & D, TTOMATRIX & V)
Singular Value Decomposition.
8
Definition at line 106 of file matrixdecomposition.hpp.
9
CLASS DOCUMENTATION
TERMSTRUCTURE::_SRANDINITIALIZER CLASS REFERENCE
A class maintains that srand() is called only once.
#include <srandInitializer.hpp>
STATIC PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
static void SafeInitialize ()
Safely call srand() without worrying that it is already called.
STATIC PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
static int IsInitializerd = 0
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
A class maintains that srand() is called only once.
Definition at line 10 of file srandInitializer.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
STATIC VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::_SRANDINITIALIZER::SAFEINITIALIZE ()
[INLINE, STATIC]
Safely call srand() without worrying that it is already called.
Definition at line 15 of file srandInitializer.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
INT TERMSTRUCTURE::_SRANDINITIALIZER::ISINITIALIZERD = 0
[STATIC]
Definition at line 13 of file srandInitializer.hpp.
10
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILES:
11
srandInitializer.hpp
srandInitializer.cpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::ABSTRACTFUNCTOR< T > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
a common requirement for all functors.
#include <functor.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
virtual T operator() (const T &x) const =0
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::ABSTRACTFUNCTOR< T >
a common requirement for all functors.
A common requirement for all functors. Operator() is required.
Definition at line 9 of file functor.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > VIRTUAL T
TERMSTRUCTURE::ABSTRACTFUNCTOR< T >::OPERATOR() (CONST T & X)
CONST [PURE VIRTUAL]
Implemented in TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T > (p.29), TermStructure::Polynomial<
T, TOrder > (p.60), and TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T > (p.23).
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
12
functor.hpp
13
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE > CLASS
TEMPLATE REFERENCE
#include <BermudanSwaption.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
BermudanSwaption (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &times, TSize swapEnterIndex=0, TSize
swapEndIndex=0)
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
TSize SwapEnterIndex
The time index that the swap starts, the first payment is this time +1.
TSize SwapEndIndex
the time index that the swap ends.
T Strike
Strike Rate of the Swap.
T Notional
Notional amount, defaults to 1.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE >
Definition at line 11 of file BermudanSwaption.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
14
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE
>::BERMUDANSWAPTION (TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TIMES, TSIZE
SWAPENTERINDEX = 0, TSIZE SWAPENDINDEX = 0) [INLINE]
Definition at line 14 of file BermudanSwaption.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE >::NOTIONAL
Notional amount, defaults to 1.
Reimplemented from TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize > (p.68).
Definition at line 21 of file BermudanSwaption.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE >::STRIKE
Strike Rate of the Swap.
Reimplemented from TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize > (p.68).
Definition at line 20 of file BermudanSwaption.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE >::SWAPENDINDEX
the time index that the swap ends.
Reimplemented from TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize > (p.68).
Definition at line 19 of file BermudanSwaption.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::BERMUDANSWAPTION< T, TSIZE
>::SWAPENTERINDEX
The time index that the swap starts, the first payment is this time +1.
Reimplemented from TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize > (p.68).
Definition at line 18 of file BermudanSwaption.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
15
16
BermudanSwaption.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::BLACKSCHOLESPRICER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, T,
TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
#include <BlackScholesPricer.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer< TVarianceStructure, T,
TSize >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
T PriceCaplet (const ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > &f, const TVarianceStructure
&varianceStructure, T Strike, TSize ChooserIndex, TSize CurrentTimeIndex=0)
T PriceCap (const ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > &f, const TVarianceStructure
&varianceStructure, T Strike, TSize EndIndex, TSize EnterIndex=0, TSize CurrentTimeIndex=0)
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TYPENAME T,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::BLACKSCHOLESPRICER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, T,
TSIZE >
Definition at line 12 of file BlackScholesPricer.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TYPENAME T,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::BLACKSCHOLESPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, T, TSIZE >::PRICECAP (CONST
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & F, CONST
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE & VARIANCESTRUCTURE, T STRIKE, TSIZE
ENDINDEX, TSIZE ENTERINDEX = 0, TSIZE CURRENTTIMEINDEX = 0)
[INLINE]
17
Definition at line 32 of file BlackScholesPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TYPENAME T,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::BLACKSCHOLESPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, T, TSIZE >::PRICECAPLET (CONST
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & F, CONST
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE & VARIANCESTRUCTURE, T STRIKE, TSIZE
CHOOSERINDEX, TSIZE CURRENTTIMEINDEX = 0) [INLINE]
Definition at line 20 of file BlackScholesPricer.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
18
BlackScholesPricer.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETINFO< T > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
#include <capletInfo.hpp>
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
T ResetTime
T PaymentTime
T Strike
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETINFO< T >
Definition at line 7 of file capletInfo.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > T TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETINFO< T
>::PAYMENTTIME
Definition at line 11 of file capletInfo.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > T TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETINFO< T
>::RESETTIME
Definition at line 10 of file capletInfo.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > T TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETINFO< T
>::STRIKE
Definition at line 12 of file capletInfo.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
19
capletInfo.hpp
20
TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETPRICER< TLMMADVANCER, T, TSIZE >
CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
#include <capletInfo.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
T Price ()
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
CapletInfo Info
TSize NumberOfTrials
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLMMADVANCER, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETPRICER<
TLMMADVANCER, T, TSIZE >
Definition at line 16 of file capletInfo.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLMMADVANCER , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETPRICER< TLMMADVANCER,
T, TSIZE >::PRICE () [INLINE]
Definition at line 22 of file capletInfo.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLMMADVANCER , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CAPLETINFO TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETPRICER<
TLMMADVANCER, T, TSIZE >::INFO
Definition at line 20 of file capletInfo.hpp.
21
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TLMMADVANCER , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::CAPLETPRICER<
TLMMADVANCER, T, TSIZE >::NUMBEROFTRIALS
Definition at line 21 of file capletInfo.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
22
capletInfo.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::ERRORFUNCTION< T > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
Error Function.
#include <standardFunctions.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
virtual T operator() (const T &x) const
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::ERRORFUNCTION<
T>
Error Function.
Definition at line 12 of file standardFunctions.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > VIRTUAL T
TERMSTRUCTURE::ERRORFUNCTION< T >::OPERATOR() (CONST T & X)
CONST [INLINE, VIRTUAL]
Implements TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T > (p.12).
Definition at line 15 of file standardFunctions.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
23
standardFunctions.hpp
24
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > CLASS
TEMPLATE REFERENCE
A Sequence of Forward Rate Based on a Given Time Sequence.
#include <ForwardRateSequence.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void SetTimeSequence (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &times)
Set the forward rate to a time sequence.
const TimeSequence< T, TSize > & GetTimeSequence () const
Get the underlying time sequence.
const T & ForwardRateAt (TSize i) const
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
T & ForwardRateAt (TSize i)
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
T & operator[] (TSize i)
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
const T & operator[] (TSize i) const
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
const ForwardRateSequence & EstablishDiscountFactors () const
Establish Discount Factors.
bool IsDiscountFactorEstablished () const
T DiscountFactorAt (TSize fromT, TSize base=0) const
Get the discount factors at Time_i.
T SwapRate (TSize fromT, TSize toT) const
TSize GetSize () const
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
T CurrentTime
Current Time.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >
A Sequence of Forward Rate Based on a Given Time Sequence.
Forward Rate Sequence is the defined as the F_i for a time T_i, and a time span Tau_i. The rate is
from T_{i-1} to T_{i}, therefore the first rate in the sequence is meaningless because it is F_0
Definition at line 14 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
25
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::DISCOUNTFACTORAT (TSIZE FROMT, TSIZE BASE = 0) CONST
[INLINE]
Get the discount factors at Time_i.
Definition at line 74 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> CONST
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE&
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::ESTABLISHDISCOUNTFACTORS () CONST [INLINE]
Establish Discount Factors.
Definition at line 59 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> CONST T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::FORWARDRATEAT (TSIZE I) CONST [INLINE]
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
Definition at line 39 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::FORWARDRATEAT (TSIZE I) [INLINE]
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
Definition at line 44 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::GETSIZE ()
CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 88 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> CONST
TIMESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::GETTIMESEQUENCE () CONST [INLINE]
Get the underlying time sequence.
26
Definition at line 34 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> BOOL
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::ISDISCOUNTFACTORESTABLISHED () CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 69 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR[]
(TSIZE I) [INLINE]
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
Definition at line 49 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> CONST T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR[]
(TSIZE I) CONST [INLINE]
Get the forward rate from Time_{i-1} to Time_i.
Definition at line 54 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::SETTIMESEQUENCE (TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TIMES) [INLINE]
Set the forward rate to a time sequence.
Set the forward rate to a time sequence, the forward rates already in the sequence will be
flushed
Definition at line 28 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::SWAPRATE
(TSIZE FROMT, TSIZE TOT) CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 79 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE
>::CURRENTTIME
27
Current Time.
Definition at line 24 of file ForwardRateSequence.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
28
ForwardRateSequence.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::INVERSEERRORFUNCTION< T > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
Inverse Error Function.
#include <standardFunctions.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
virtual T operator() (const T &x) const
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::INVERSEERRORFUNCTION< T >
Inverse Error Function.
Definition at line 30 of file standardFunctions.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > VIRTUAL T
TERMSTRUCTURE::INVERSEERRORFUNCTION< T >::OPERATOR() (CONST
T & X) CONST [INLINE, VIRTUAL]
Implements TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T > (p.12).
Definition at line 33 of file standardFunctions.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
29
standardFunctions.hpp
30
TERMSTRUCTURE::LEASTSQUARESOLVER< T, TSIZE > CLASS
TEMPLATE REFERENCE
Least Square Solver based on two matrices.
#include <leastSquareSolver.hpp>
STATIC PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
template<typename TInputMatrix , typename TLoadMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > static void Fit
(const TInputMatrix &input, const TLoadMatrix &Load, TResultMatrix &result)
Fit the Square.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::LEASTSQUARESOLVER< T, TSIZE >
Least Square Solver based on two matrices.
Solve for lease square fit, the solver is LUDEcomposition Solver
Definition at line 13 of file leastSquareSolver.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TINPUTMATRIX , TYPENAME TLOADMATRIX ,
TYPENAME TRESULTMATRIX > STATIC VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::LEASTSQUARESOLVER< T, TSIZE >::FIT (CONST
TINPUTMATRIX & INPUT, CONST TLOADMATRIX & LOAD,
TRESULTMATRIX & RESULT) [INLINE, STATIC]
Fit the Square.
PARAMETERS:
31
input
the input matrix.
load
the load.
result
where the result will be stored. Please pre-locate the space
Definition at line 22 of file leastSquareSolver.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
32
leastSquareSolver.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
LMMAdvancer is the method to move a set of forward rates.
#include <LMMAdvancer.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void InitiateForwardRateSequence ()
Ask LMMAdvancer to iniate its own forward rates storage.
void SetForwardRateSequence (ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > &f)
Set the LMMAdvancer's current forward rates to f, a new next sequence will be generated.
void SetTimeSequence (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &ts)
Set the time sequence.
const TimeSequence< T, TSize > & GetTimeSequence () const
get the time sequence
TimeSequence< T, TSize > & GetTimeSequence ()
get the time sequence
void Set (TVarianceStructure &vs, TimeSequence< T, TSize > &ts)
Set the variance structure.
ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > & CurrentSequence ()
Return the current forward rate sequence for CurrentTime.
ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > & NextSequence ()
Return the next forward rate sequence for CurrentTime + TimeStep.
const ForwardRateSequence< T,
TSize > & CurrentSequence () const
Return the current forward rate sequence for CurrentTime.
const ForwardRateSequence< T,
TSize > & NextSequence () const
Return the next forward rate sequence for CurrentTime + TimeStep.
void PreAdvance ()
Ready the Gaussian random vector generator.
void SingleAdvance () const
Generate the next sequence without calling PreAdvance(), assuming Gaussian Number Generator is
ready.
void Advance ()
void PushAdvancerToTimeStep ()
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
TSize AnchorIndex
The forward rate that has a zero drift/ the numeraire zero coupon bond's maturity index.
T CurrentTime
Current Time.
33
T TimeStep
Time Step.
PROTECTED MEMBER FUNCTIONS
TSize _getStartIndex () const
A method to find which fowward rates are already reset.
void ComputeC ()
Compute Variance Matrix.
PROTECTED ATTRIBUTES
TimeSequence< T, TSize > * _timeSequence
The underlying time sequence.
TVarianceStructure * _varianceStructure
The underlying variance structure.
ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > * _forwardRateSequence
The current forward rates, forward rates at time CurrentTime;.
ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > * _nextSequence
The generated forward rates, forward rates at time CurrentTime + TimeStep.
TMultiDimensionGaussian
< SimpleMatrix< T, TSize >, T,
TSize > _gaussian
The Gaussian Generator.
SimpleMatrix< T, TSize > CVector
The variance matrix for Gaussian Generator.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE =
LONG>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >
LMMAdvancer is the method to move a set of forward rates.
The forward rates at time CurrentTime + TimeStep are generated by Gaussian Generator
Definition at line 14 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
34
TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::_GETSTARTINDEX () CONST
[INLINE, PROTECTED]
A method to find which fowward rates are already reset.
Definition at line 28 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::ADVANCE () [INLINE]
Ready the gaussian number generator and generate the next forward rate sequence.
Repeatedly calling this method may cost a lot because matrix decomposition in Gaussian
number generators will be called repeatly. Consider calling PreAdvance() and
SingleAdvance() separately.
Definition at line 183 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::COMPUTEC () [INLINE,
PROTECTED]
Compute Variance Matrix.
Definition at line 38 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::CURRENTSEQUENCE ()
[INLINE]
Return the current forward rate sequence for CurrentTime.
Definition at line 102 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
CONST FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
35
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::CURRENTSEQUENCE () CONST
[INLINE]
Return the current forward rate sequence for CurrentTime.
Definition at line 112 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
CONST TIMESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>& TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::GETTIMESEQUENCE () CONST [INLINE]
get the time sequence
Definition at line 86 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TIMESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>& TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::GETTIMESEQUENCE () [INLINE]
get the time sequence
Definition at line 91 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::INITIATEFORWARDRATESEQUENCE () [INLINE]
Ask LMMAdvancer to iniate its own forward rates storage.
Definition at line 61 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::NEXTSEQUENCE () [INLINE]
Return the next forward rate sequence for CurrentTime + TimeStep.
36
Definition at line 107 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
CONST FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::NEXTSEQUENCE () CONST
[INLINE]
Return the next forward rate sequence for CurrentTime + TimeStep.
Definition at line 117 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::PREADVANCE () [INLINE]
Ready the Gaussian random vector generator.
Gaussian rando vector generator will require some kind of costly decompositions, and by
calling PreAdvance(), the action will be taken
Definition at line 128 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::PUSHADVANCERTOTIMESTEP
() [INLINE]
Definition at line 189 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::SET (TVARIANCESTRUCTURE &
VS, TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TS) [INLINE]
Set the variance structure.
Definition at line 96 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
37
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::SETFORWARDRATESEQUENCE
(FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & F) [INLINE]
Set the LMMAdvancer's current forward rates to f, a new next sequence will be generated.
Definition at line 67 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::SETTIMESEQUENCE
(TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TS) [INLINE]
Set the time sequence.
Definition at line 76 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::SINGLEADVANCE () CONST
[INLINE]
Generate the next sequence without calling PreAdvance(), assuming Gaussian Number Generator is
ready.
Definition at line 134 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>*
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::_FORWARDRATESEQUENCE
[PROTECTED]
The current forward rates, forward rates at time CurrentTime;.
Definition at line 22 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
38
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<SIMPLEMATRIX<T,TSIZE>, T, TSIZE>
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::_GAUSSIAN [PROTECTED]
The Gaussian Generator.
Definition at line 26 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>*
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::_NEXTSEQUENCE
[PROTECTED]
The generated forward rates, forward rates at time CurrentTime + TimeStep.
Definition at line 24 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TIMESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>* TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::_TIMESEQUENCE [PROTECTED]
The underlying time sequence.
Definition at line 18 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE* TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::_VARIANCESTRUCTURE [PROTECTED]
The underlying variance structure.
Definition at line 20 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
39
TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::ANCHORINDEX
The forward rate that has a zero drift/ the numeraire zero coupon bond's maturity index.
Definition at line 74 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::CURRENTTIME
Current Time.
Definition at line 122 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
SIMPLEMATRIX<T,TSIZE> TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::CVECTOR [PROTECTED]
The variance matrix for Gaussian Generator.
Definition at line 58 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::TIMESTEP
Time Step.
Definition at line 124 of file LMMAdvancer.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
40
LMMAdvancer.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMBERMUDANSWAPTIONPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >
CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
#include <LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer<
TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
T PriceBermudanSwaption (Swap< T, TSize > &contract, TSize NumberOfPath=10000)
PROTECTED ATTRIBUTES
LMMPathPool
< TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T,
TSize > _pathpool
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMBERMUDANSWAPTIONPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >
Definition at line 10 of file LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
41
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMBERMUDANSWAPTIONPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICEBERMUDANSWAPTION (SWAP< T, TSIZE > & CONTRACT, TSIZE
NUMBEROFPATH = 10000) [INLINE]
Definition at line 15 of file LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> LMMPATHPOOL<TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE>
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMBERMUDANSWAPTIONPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::_PATHPOOL [PROTECTED]
Definition at line 13 of file LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
42
LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
A class to generate a pool of paths from LMMAdvancer;.
#include <LMMPathPool.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void ReleasePool () const
std::vector< std::vector
< ForwardRateSequence< T,
TSize > * > > const * GetPool () const
Get all the paths at once.
void SetLMMAdvancer (LMMAdvancer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T,
TSize > &advancer)
Set the underlying LMMAdvancer.
ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > & operator() (TSize pathID, TSize TimeIndex)
Get the generated ForwardRateSequence for pathID and TimeIndex. Note the function doesn't require
adjusting TimeIndex for currentTimeIndex.
const ForwardRateSequence< T,
TSize > & operator() (TSize pathID, TSize TimeIndex) const
Get the generated ForwardRAteSequence for path ID and timeIndex. Note the function doesn't require
adjusting TimeIndex for currentTimeIndex.
void Generate () const
Generate the path pool.
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
TSize NumberOfPath
Number of Path need to be generated.
TSize CurrentTimeIndex
Current Time Index, Where all the Forward Rates start.
TSize EndIndex
End of the index, where the forward rates all ends.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >
43
A class to generate a pool of paths from LMMAdvancer;.
To Generate NumberOfPath paths for an index range. This pool is provide to reduce the number
of LMMAdvancer's PreAdvance(), which is time consuming because of different
decompositions.
Definition at line 13 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::GENERATE () CONST [INLINE]
Generate the path pool.
Definition at line 56 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>
STD::VECTOR<STD::VECTOR<FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE> *> >
CONST* TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::GETPOOL () CONST [INLINE]
Get all the paths at once.
Definition at line 30 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE PATHID,
TSIZE TIMEINDEX) [INLINE]
Get the generated ForwardRateSequence for pathID and TimeIndex. Note the function doesn't
require adjusting TimeIndex for currentTimeIndex.
Definition at line 46 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
44
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE PATHID,
TSIZE TIMEINDEX) CONST [INLINE]
Get the generated ForwardRAteSequence for path ID and timeIndex. Note the function doesn't require
adjusting TimeIndex for currentTimeIndex.
Definition at line 51 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::RELEASEPOOL () CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 18 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::SETLMMADVANCER (LMMADVANCER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE > & ADVANCER) [INLINE]
Set the underlying LMMAdvancer.
Definition at line 35 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::CURRENTTIMEINDEX
Current Time Index, Where all the Forward Rates start.
Definition at line 42 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
45
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::ENDINDEX
End of the index, where the forward rates all ends.
Definition at line 44 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPATHPOOL<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::NUMBEROFPATH
Number of Path need to be generated.
Definition at line 40 of file LMMPathPool.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
46
LMMPathPool.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
#include <LMMPricer.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::LMMPricer< TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void SetLMMAdvancer (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &ts, TVarianceStructure &variance)
ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > & InitialForwardRateSequence ()
const ForwardRateSequence< T,
TSize > & InitialForwardRateSequence () const
T PriceEuropeanSwaption (const Swap< T, TSize > &swap, const T &strike, TSize chooserIndex,
TSize N=1000000)
T PriceTriggerSwap (const Swap< T, TSize > &swap, const T &strike, TimeSequence< T, TSize >
&chooserTime, TSize N=1000000)
T PriceConstMaturitySwap (const T &fwp, Swap< T, TSize > &swap, const TSize swap_b, const
TSize swap_a, const T &strike, TSize N=50000)
T PriceRatchetcaps (const T &fwp, TSize N=50000)
T PriceCaplet (T time_now, T time_beg, T time_end, T K, TSize N=50000)
T PriceSwap (Swap< T, TSize > &swap, const T time_now, const TSize swap_b, const TSize swap_a,
const T strike, TSize N=50000)
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
LMMAdvancer
< TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T,
TSize > UnderlyingAdvancer
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >
47
Definition at line 11 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::INITIALFORWARDRATESEQUENCE () [INLINE]
Definition at line 23 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST FORWARDRATESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>&
TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::INITIALFORWARDRATESEQUENCE () CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 27 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICECAPLET (T TIME_NOW, T TIME_BEG, T TIME_END, T K, TSIZE N =
50000) [INLINE]
Definition at line 149 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICECONSTMATURITYSWAP (CONST T & FWP, SWAP< T, TSIZE > &
48
SWAP, CONST TSIZE SWAP_B, CONST TSIZE SWAP_A, CONST T & STRIKE,
TSIZE N = 50000) [INLINE]
Definition at line 77 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICEEUROPEANSWAPTION (CONST SWAP< T, TSIZE > & SWAP, CONST
T & STRIKE, TSIZE CHOOSERINDEX, TSIZE N = 1000000) [INLINE]
Definition at line 31 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICERATCHETCAPS (CONST T & FWP, TSIZE N = 50000) [INLINE]
Definition at line 114 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICESWAP (SWAP< T, TSIZE > & SWAP, CONST T TIME_NOW, CONST
TSIZE SWAP_B, CONST TSIZE SWAP_A, CONST T STRIKE, TSIZE N = 50000)
[INLINE]
Definition at line 171 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::PRICETRIGGERSWAP (CONST SWAP< T, TSIZE > & SWAP, CONST T &
STRIKE, TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & CHOOSERTIME, TSIZE N =
1000000) [INLINE]
49
Definition at line 49 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER<
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE
>::SETLMMADVANCER (TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TS,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE & VARIANCE) [INLINE]
Definition at line 17 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TEMPLATE<
TYPENAME, TYPENAME, TYPENAME > CLASS
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, TYPENAME T = DOUBLE, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>
LMMADVANCER<TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN,
T,TSIZE> TERMSTRUCTURE::LMMPRICER< TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN, T, TSIZE >::UNDERLYINGADVANCER
Definition at line 16 of file LMMPricer.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
50
LMMPricer.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE > CLASS
TEMPLATE REFERENCE
Transpose of a Matrix.
#include <matrixChildren.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
MatrixTransposed ()
defualt constructor
MatrixTransposed (const TMatrix< T, TSize > &matrix)
initiate from a matrix
const T & operator() (const TSize &i, const TSize &j) const
Get the i,j element.
T & operator() (const TSize &i, const TSize &j)
Get the i,j element.
TSize GetLength (int i)
Get the length.
PROTECTED ATTRIBUTES
TMatrix< T, TSize > * _underlyingMatrix
The underlying matrix.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE >
Transpose of a Matrix.
Definition at line 7 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE
>::MATRIXTRANSPOSED () [INLINE]
defualt constructor
51
Definition at line 14 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE
>::MATRIXTRANSPOSED (CONST TMATRIX< T, TSIZE > & MATRIX)
[INLINE]
initiate from a matrix
Definition at line 19 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE
>::GETLENGTH (INT I) [INLINE]
Get the length.
Definition at line 34 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG> CONST
T& TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE
>::OPERATOR() (CONST TSIZE & I, CONST TSIZE & J) CONST [INLINE]
Get the i,j element.
Definition at line 24 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG> T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED< TMATRIX, T, TSIZE
>::OPERATOR() (CONST TSIZE & I, CONST TSIZE & J) [INLINE]
Get the i,j element.
Definition at line 29 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
52
TEMPLATE<TEMPLATE< TYPENAME T1, TYPENAME T2 > CLASS
TMATRIX, TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = UNSIGNED LONG>
TMATRIX<T,TSIZE>* TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXTRANSPOSED<
TMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::_UNDERLYINGMATRIX [PROTECTED]
The underlying matrix.
Definition at line 11 of file matrixChildren.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
53
matrixChildren.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXWRAPPER< T, NPRIMARY, NSECONDARY,
TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
Wrap a C++ matrix, T[][] to a matrix satisfies the requirements of the matrix.
#include <matrix.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
MatrixWrapper (T(&underlying)[NPrimary][NSecondary])
Default Constructor.
T & operator() (TSize i, TSize j)
Get the i,j element.
const T & operator() (TSize i, TSize j) const
Get the i,j element.
TSize GetLength (int i) const
Get the length.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, INT NPRIMARY, INT NSECONDARY, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXWRAPPER< T,
NPRIMARY, NSECONDARY, TSIZE >
Wrap a C++ matrix, T[][] to a matrix satisfies the requirements of the matrix.
Definition at line 115 of file matrix.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, INT NPRIMARY, INT NSECONDARY, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXWRAPPER< T, NPRIMARY,
NSECONDARY, TSIZE >::MATRIXWRAPPER (T(&)
UNDERLYING[NPRIMARY][NSECONDARY]) [INLINE]
Default Constructor.
Definition at line 121 of file matrix.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
54
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, INT NPRIMARY, INT NSECONDARY, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXWRAPPER< T,
NPRIMARY, NSECONDARY, TSIZE >::GETLENGTH (INT I) CONST [INLINE]
Get the length.
Definition at line 135 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, INT NPRIMARY, INT NSECONDARY, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> T& TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXWRAPPER< T, NPRIMARY,
NSECONDARY, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I, TSIZE J) [INLINE]
Get the i,j element.
Definition at line 125 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, INT NPRIMARY, INT NSECONDARY, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST T& TERMSTRUCTURE::MATRIXWRAPPER< T,
NPRIMARY, NSECONDARY, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I, TSIZE J) CONST
[INLINE]
Get the i,j element.
Definition at line 130 of file matrix.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
55
matrix.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
A Reduced-rank Gaussian Generator utilizing SVD. Rank is defaul to 4.
#include <SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian (TSize rank=4)
Constructors. Rank is defalt to 4.
void SetRank (TSize rank)
Set the rank of the.
void SetVarianceMatrix (TVarianceMatrix &_varianceMatrixinput)
Set Variance Matrix.
void NextGroup () const
Generate Next Random Vector.
const T & operator() (TSize i, TSize j) const
Get the i-th element of the generated vector.
const TSize GetLength (int i) const
Get the size of the generated vector.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >
A Reduced-rank Gaussian Generator utilizing SVD. Rank is defaul to 4.
Definition at line 60 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN
(TSIZE RANK = 4) [INLINE]
Constructors. Rank is defalt to 4.
56
Definition at line 75 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::GETLENGTH (INT I) CONST [INLINE]
Get the size of the generated vector.
Definition at line 122 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::NEXTGROUP () CONST [INLINE]
Generate Next Random Vector.
Definition at line 101 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I, TSIZE J) CONST
[INLINE]
Get the i-th element of the generated vector.
Definition at line 117 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::SETRANK (TSIZE RANK) [INLINE]
Set the rank of the.
Definition at line 80 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::PCABASEDMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::SETVARIANCEMATRIX
(TVARIANCEMATRIX & _VARIANCEMATRIXINPUT) [INLINE]
57
Set Variance Matrix.
Definition at line 85 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
58
SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::POLYNOMIAL< T, TORDER > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
A Polynomial.
#include <polynomial.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::Polynomial< T, TOrder >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
Polynomial (const TOrder &order=0)
virtual T operator() (const T &x) const
T & operator[] (const TOrder &i)
const T & operator[] (const TOrder &i) const
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TORDER = SIZE_T>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::POLYNOMIAL< T, TORDER >
A Polynomial.
A Polynomial of
Definition at line 13 of file polynomial.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TORDER = SIZE_T>
TERMSTRUCTURE::POLYNOMIAL< T, TORDER >::POLYNOMIAL (CONST
TORDER & ORDER = 0) [INLINE]
Definition at line 25 of file polynomial.hpp.
59
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TORDER = SIZE_T> VIRTUAL T
TERMSTRUCTURE::POLYNOMIAL< T, TORDER >::OPERATOR() (CONST T &
X) CONST [INLINE, VIRTUAL]
Implements TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T > (p.12).
Definition at line 30 of file polynomial.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TORDER = SIZE_T> T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::POLYNOMIAL< T, TORDER >::OPERATOR[] (CONST
TORDER & I) [INLINE]
Definition at line 42 of file polynomial.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TORDER = SIZE_T> CONST T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::POLYNOMIAL< T, TORDER >::OPERATOR[] (CONST
TORDER & I) CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 50 of file polynomial.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
60
polynomial.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
A matrix using double pointer as the storage.
#include <matrix.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
SimpleMatrix (TSize length1=1, TSize length2=1, const T &defaultT=0)
Constructors.
SimpleMatrix (const SimpleMatrix &anotherMatrix)
copy constructor
SimpleMatrix & operator= (const SimpleMatrix &anotherMatrix)
operator=
SimpleMatrix & Resize (const TSize &i, const TSize &j)
Resize the matrix. The matrix's contents will be released.
TSize GetLength (int i) const
Get the length.
virtual ~SimpleMatrix ()
DEstructor.
T & operator() (TSize i, TSize j)
Get the i,j element.
const T & operator() (TSize i, TSize j) const
Get the i,j element.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >
A matrix using double pointer as the storage.
Definition at line 7 of file matrix.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::SIMPLEMATRIX (TSIZE
LENGTH1 = 1, TSIZE LENGTH2 = 1, CONST T & DEFAULTT = 0) [INLINE]
Constructors.
61
Definition at line 38 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::SIMPLEMATRIX (CONST
SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE > & ANOTHERMATRIX) [INLINE]
copy constructor
Definition at line 43 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> VIRTUAL
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::~SIMPLEMATRIX ()
[INLINE, VIRTUAL]
DEstructor.
Definition at line 97 of file matrix.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::GETLENGTH (INT I)
CONST [INLINE]
Get the length.
Definition at line 90 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I,
TSIZE J) [INLINE]
Get the i,j element.
Definition at line 102 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> CONST T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I,
TSIZE J) CONST [INLINE]
Get the i,j element.
Definition at line 107 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> SIMPLEMATRIX&
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR= (CONST
SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE > & ANOTHERMATRIX) [INLINE]
62
operator=
Definition at line 56 of file matrix.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> SIMPLEMATRIX&
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMATRIX< T, TSIZE >::RESIZE (CONST TSIZE & I,
CONST TSIZE & J) [INLINE]
Resize the matrix. The matrix's contents will be released.
Definition at line 74 of file matrix.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
63
matrix.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
A Gaussian Generator based on CholeskyDecomposition.
#include <SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void SetVarianceMatrix (const TVarianceMatrix &_varianceMatrixinput)
Set Variance Matrix.
void NextGroup () const
Generate Next Random Vector.
const T & operator() (TSize i, TSize j) const
Get the i-th element of the generated vector.
const TSize GetLength (int i) const
Get the size of the generated vector.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX, TYPENAME T, TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >
A Gaussian Generator based on CholeskyDecomposition.
Definition at line 12 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::GETLENGTH (INT I) CONST [INLINE]
Get the size of the generated vector.
Definition at line 52 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID
64
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::NEXTGROUP () CONST [INLINE]
Generate Next Random Vector.
Definition at line 30 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> CONST T&
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I, TSIZE J) CONST
[INLINE]
Get the i-th element of the generated vector.
Definition at line 47 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME TVARIANCEMATRIX , TYPENAME T , TYPENAME
TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN<
TVARIANCEMATRIX, T, TSIZE >::SETVARIANCEMATRIX (CONST
TVARIANCEMATRIX & _VARIANCEMATRIXINPUT) [INLINE]
Set Variance Matrix.
Definition at line 23 of file SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
65
SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
Swap Contract.
#include <swap.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
Swap (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &times, TSize swapEndIndex=0, TSize swapEnterIndex=0)
Initiate a swap.
T Price (const ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize > &forwardRate, TSize pricingPoint=0) const
Price a swap based on the given forward rate sequence. PricingPoint is the time index that the swap is
priced.
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
T Strike
Strike Rate of the Swap.
TSize SwapEnterIndex
The time index that the swap starts, the first payment is this time +1.
TSize SwapEndIndex
the time index that the swap ends.
T Notional
Notional amount, defaults to 1.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >
Swap Contract.
66
Define a swap contract. The enter index is when the swap is entered, The first payment shoudl
occur at enterindex + 1. The end index is the time of the last payment.
Definition at line 14 of file swap.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >::SWAP (TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >
& TIMES, TSIZE SWAPENDINDEX = 0, TSIZE SWAPENTERINDEX = 0)
[INLINE]
Initiate a swap.
PARAMETERS:
times
TimeSequence of the swap
swapEndeIndex
the time idnex of the last payment
swapEnterIndex
the time index of the first payment - 1
Definition at line 22 of file swap.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >::PRICE (CONST
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & FORWARDRATE, TSIZE
PRICINGPOINT = 0) CONST [INLINE]
Price a swap based on the given forward rate sequence. PricingPoint is the time index that the swap is
priced.
Definition at line 36 of file swap.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >::NOTIONAL
67
Notional amount, defaults to 1.
Reimplemented in TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > (p.15).
Definition at line 34 of file swap.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >::STRIKE [MUTABLE]
Strike Rate of the Swap.
Reimplemented in TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > (p.15).
Definition at line 28 of file swap.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >::SWAPENDINDEX
the time index that the swap ends.
Reimplemented in TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > (p.15).
Definition at line 32 of file swap.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::SWAP< T, TSIZE >::SWAPENTERINDEX
The time index that the swap starts, the first payment is this time +1.
Reimplemented in TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize > (p.15).
Definition at line 30 of file swap.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
68
swap.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE
REFERENCE
Time Sequence. The times that all the data are based on.
#include <timeSequence.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
TimeSequence ()
Default Constructor.
TimeSequence (const TimeSequence &anotherTimeSequence)
Copy constructure.
TimeSequence & operator= (const TimeSequence &anotherTimeSequence)
operator =
TimeSequence & PutTime (const T &time)
Add another time to the sequence.
T TimeDifference (TSize i) const
Get the time difference/interval which is T_{i-1}-T_i.
T GetTime (TSize i) const
Get the time.
TSize GetSize () const
GEt the size of the time sequence.
TSize GetIndex (T t)
Get the index of the time sequence.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >
Time Sequence. The times that all the data are based on.
Most of times, all classes will maintain a poitner to the same copy of a TimeSequence. It should
be seldomly changed after initialization. The first in the time sequence will always be zero, and
will be automatically pushed into the sequence when it is created. So don't push zero into the time
sequence.
Definition at line 13 of file timeSequence.hpp.
CONSTRUCTOR & DESTRUCTOR DOCUMENTATION
69
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::TIMESEQUENCE ()
[INLINE]
Default Constructor.
Definition at line 21 of file timeSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::TIMESEQUENCE (CONST
TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & ANOTHERTIMESEQUENCE) [INLINE]
Copy constructure.
Definition at line 27 of file timeSequence.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::GETINDEX (T T)
[INLINE]
Get the index of the time sequence.
Definition at line 66 of file timeSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::GETSIZE () CONST
[INLINE]
GEt the size of the time sequence.
Definition at line 61 of file timeSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::GETTIME (TSIZE I)
CONST [INLINE]
Get the time.
Definition at line 56 of file timeSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TIMESEQUENCE&
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::OPERATOR= (CONST
TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & ANOTHERTIMESEQUENCE) [INLINE]
operator =
70
Definition at line 33 of file timeSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TIMESEQUENCE&
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::PUTTIME (CONST T &
TIME) [INLINE]
Add another time to the sequence.
Definition at line 44 of file timeSequence.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE >::TIMEDIFFERENCE
(TSIZE I) CONST [INLINE]
Get the time difference/interval which is T_{i-1}-T_i.
Definition at line 51 of file timeSequence.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
71
timeSequence.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCEHOLDER< T, TSIZE > CLASS
TEMPLATE REFERENCE
A structure that has a time sequence in it.
#include <timeSequenceHolder.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder< T, TSize >:
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
virtual const TimeSequence< T,
TSize > & GetTimeSequence () const
Get the underlying time sequence.
virtual void SetTimeSequence (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &times)
Set the underlying time sequence.
PROTECTED ATTRIBUTES
TimeSequence< T, TSize > * _timeSequence
The underlying time sequence.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCEHOLDER< T, TSIZE >
A structure that has a time sequence in it.
A structure that has a time sequence in it. Many products and pricers need
TimeSequence<T,TSize>, and this provides a common utility to fciliate the programming. Note
that TimeSequence<T,TSize> can be modified in these classes
Definition at line 14 of file timeSequenceHolder.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
72
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> VIRTUAL CONST
TIMESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>& TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCEHOLDER<
T, TSIZE >::GETTIMESEQUENCE () CONST [INLINE, VIRTUAL]
Get the underlying time sequence.
Definition at line 21 of file timeSequenceHolder.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> VIRTUAL VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCEHOLDER< T, TSIZE
>::SETTIMESEQUENCE (TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TIMES) [INLINE,
VIRTUAL]
Set the underlying time sequence.
Definition at line 26 of file timeSequenceHolder.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>
TIMESEQUENCE<T,TSIZE>* TERMSTRUCTURE::TIMESEQUENCEHOLDER<
T, TSIZE >::_TIMESEQUENCE [PROTECTED]
The underlying time sequence.
Definition at line 18 of file timeSequenceHolder.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
73
timeSequenceHolder.hpp
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE > CLASS
TEMPLATE REFERENCE
A variance structure. Please refer to the doc for more details on the theories.
#include <varianceStructure.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void SetTimeSequence (TimeSequence< T, TSize > &ts)
Set time sequence.
T GetVolatility (TSize i, T t) const
get volatility for a forward rate i at time t
T GetCorrelation (TSize i, TSize j, T t) const
get the correlation between two forward rates
TSize GetSize () const
get the number of forward rates
T VolatilityIntegrator (T fromT, T toT, TSize i, TSize j) const
Integrate the volatility from time fromT to ToT.
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
std::vector< T > Phis
The Phis.
Ta
Other parameters other than Phis.
Tb
Tc
Td
T beta1
T beta2
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >
A variance structure. Please refer to the doc for more details on the theories.
Definition at line 8 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
74
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE
>::GETCORRELATION (TSIZE I, TSIZE J, T T) CONST [INLINE]
get the correlation between two forward rates
Definition at line 59 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::GETSIZE () CONST
[INLINE]
get the number of forward rates
Definition at line 65 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::GETVOLATILITY
(TSIZE I, T T) CONST [INLINE]
get volatility for a forward rate i at time t
PARAMETERS:
i
the index of the forward rate
t
the time of the desired volatility
Definition at line 51 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE
>::SETTIMESEQUENCE (TIMESEQUENCE< T, TSIZE > & TS) [INLINE]
Set time sequence.
Definition at line 40 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE
>::VOLATILITYINTEGRATOR (T FROMT, T TOT, TSIZE I, TSIZE J) CONST
[INLINE]
Integrate the volatility from time fromT to ToT.
Definition at line 70 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
75
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::A
Other parameters other than Phis.
Definition at line 38 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::B
Definition at line 38 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::BETA1
Definition at line 38 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::BETA2
Definition at line 38 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::C
Definition at line 38 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::D
Definition at line 38 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> STD::VECTOR<T>
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTURE< T, TSIZE >::PHIS
The Phis.
Definition at line 36 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
76
varianceStructure.hpp
77
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE > CLASS TEMPLATE REFERENCE
Initiate an instantaneous covariance matrix from a variance structure.
#include <varianceStructure.hpp>
PUBLIC MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void SetVariaceStructure (TVarianceStructure &underlying)
T operator() (TSize i, TSize j) const
TSize GetLength (int i) const
PUBLIC ATTRIBUTES
T CurrentTime
PROTECTED ATTRIBUTES
TVarianceStructure * _underlyingStructure
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T, TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG>CLASS
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE >
Initiate an instantaneous covariance matrix from a variance structure.
Definition at line 81 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
MEMBER FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE ,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TSIZE
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE >::GETLENGTH (INT I) CONST [INLINE]
Definition at line 98 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE ,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
78
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE >::OPERATOR() (TSIZE I, TSIZE J) CONST
[INLINE]
Definition at line 93 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE ,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> VOID
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE >::SETVARIACESTRUCTURE
(TVARIANCESTRUCTURE & UNDERLYING) [INLINE]
Definition at line 87 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
MEMBER DATA DOCUMENTATION
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE ,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> TVARIANCESTRUCTURE*
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE >::_UNDERLYINGSTRUCTURE
[PROTECTED]
Definition at line 84 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T , TYPENAME TVARIANCESTRUCTURE ,
TYPENAME TSIZE = LONG> T
TERMSTRUCTURE::VARIANCESTRUCTUREMATRIX< T,
TVARIANCESTRUCTURE, TSIZE >::CURRENTTIME
Definition at line 86 of file varianceStructure.hpp.
THE DOCUMENTATION FOR THIS CLASS WAS GENERATED FROM THE
FOLLOWING FILE:
79
varianceStructure.hpp
FILE DOCUMENTATION
BERMUDANSWAPTION.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "timeSequence.hpp"
#include "timeSequenceHolder.hpp"
#include "swap.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize >
NAMESPACES
80
namespace TermStructure
BLACKSCHOLESPRICER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
"timeSequence.hpp"
"timeSequenceHolder.hpp"
"ForwardRateSequence.hpp"
"standardFunctions.hpp"
"cmath"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer< TVarianceStructure, T, TSize >
NAMESPACES
81
namespace TermStructure
CAPLETINFO.HPP FILE REFERENCE
CLASSES
class TermStructure::CapletInfo< T >
class TermStructure::CapletPricer< TLMMAdvancer, T, TSize >
NAMESPACES
82
namespace TermStructure
FORWARDRATESEQUENCE.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "timeSequence.hpp"
#include <vector>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize >
A SEQUENCE OF FORWARD RATE BASED ON A GIVEN TIME SEQUENCE.
NAMESPACES
83
namespace TermStructure
FUNCTOR.HPP FILE REFERENCE
CLASSES
class TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T >
A COMMON REQUIREMENT FOR ALL FUNCTORS. NAMESPACES
84
namespace TermStructure
FUNCTORFITTER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
NAMESPACES
85
namespace TermStructure
INTEGRATOR.HPP FILE REFERENCE
NAMESPACES
namespace TermStructure
FUNCTIONS
86
template<typename TFunctor , typename T , typename TSize > T
TermStructure::Integrator_simpson (T start, T end, TFunctor fx, TSize M=1024)
A simple Simpson integrator.
LEASTSQUARESOLVER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "matrix.hpp"
#include "matrixdecomposition.hpp"
#include <iostream>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver< T, TSize >
LEAST SQUARE SOLVER BASED ON TWO MATRICES. NAMESPACES
87
namespace TermStructure
LMMADVANCER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
"matrix.hpp"
"ForwardRateSequence.hpp"
"SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp"
<vector>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::LMMAdvancer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T,
TSize >
LMMADVANCER IS THE METHOD TO MOVE A SET OF FORWARD RATES.
NAMESPACES
88
namespace TermStructure
LMMBERMUDANSWAPTIONPRICER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "LMMPricer.hpp"
#include "LMMPathPool.hpp"
#include "leastSquareSolver.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer< TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >
NAMESPACES
89
namespace TermStructure
LMMPATHPOOL.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include <vector>
#include "LMMAdvancer.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::LMMPathPool< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize
>
A CLASS TO GENERATE A POOL OF PATHS FROM LMMADVANCER;.
NAMESPACES
90
namespace TermStructure
LMMPRICER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "swap.hpp"
#include "BermudanSwaption.hpp"
#include "LMMAdvancer.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::LMMPricer< TVarianceStructure, TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >
NAMESPACES
91
namespace TermStructure
MAIN.CPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
<iostream>
"matrix.hpp"
"randomNumberGenerators.hpp"
"matrixdecomposition.hpp"
"matrixOperations.hpp"
"matrixChildren.hpp"
"polynomial.hpp"
"SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp"
DEFINES
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
FUNCTIONS
double t (const Polynomial< double > &p, double x)
int main (int argc, char const *argv[])
DEFINE DOCUMENTATION
#DEFINE _USE_MATH_DEFINES
Definition at line 2 of file main.cpp.
FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
INT MAIN (INT ARGC, CHAR CONST * ARGV[])
Definition at line 19 of file main.cpp.
DOUBLE T (CONST POLYNOMIAL< DOUBLE > & P, DOUBLE X)
Definition at line 15 of file main.cpp.
92
MATRIX.HPP FILE REFERENCE
CLASSES
class TermStructure::SimpleMatrix< T, TSize >
A matrix using double pointer as the storage. class TermStructure::MatrixWrapper< T, NPrimary,
NSecondary, TSize >
WRAP A C++ MATRIX, T[][] TO A MATRIX SATISFIES THE
REQUIREMENTS OF THE MATRIX. NAMESPACES
93
namespace TermStructure
MATRIXCHILDREN.HPP FILE REFERENCE
CLASSES
class TermStructure::MatrixTransposed< TMatrix, T, TSize >
TRANSPOSE OF A MATRIX. NAMESPACES
94
namespace TermStructure
MATRIXDECOMPOSITION.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
<cmath>
"matrix.hpp"
"newmat10/newmat.h"
"newmat10/newmatap.h"
"newmat10/include.h"
NAMESPACES
namespace TermStructure
FUNCTIONS
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void TermStructure::LUDecomposeTo
(const TFromMatrix &input, TToMatrix &L, TToMatrix &U)
LU Decomposition.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void TermStructure::LUDecomposeTo
(const TFromMatrix &input, TToMatrix &result)
LU Decomposition. The L and U matrix is put into result, assuming diagonal elements of L is 1.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void
TermStructure::CholeskyDecomposeTo (const TFromMatrix &a, TToMatrix &b)
Cholesky Decomposition.
template<typename TFromMatrix , typename TToMatrix > void
TermStructure::SingularValueDecomposeTo (const TFromMatrix &a, TToMatrix &u, TToMatrix
&d, TToMatrix &v)
Singular Value Decomposition.
template<typename TInputMatrix , typename TLoadMatrix , typename TResultMatrix , typename
TTempMatrix > void TermStructure::LUDecompositionSolve (const TInputMatrix &input, const
TLoadMatrix &load, TResultMatrix &result, TTempMatrix &tempStorage)
95
MATRIXOPERATIONS.HPP FILE REFERENCE
NAMESPACES
namespace TermStructure
FUNCTIONS
template<typename TLeftMatrix , typename TRightMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > void
TermStructure::Multiply (const TLeftMatrix &l, const TRightMatrix &r, TResultMatrix &result)
Matrix multiplication.
template<typename TLeftMatrix , typename TRightMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > void
TermStructure::Plus (const TLeftMatrix &l, const TRightMatrix &r, TResultMatrix &result)
matrix plus
template<typename TLeftMatrix , typename TRightMatrix , typename TResultMatrix > void
TermStructure::Minus (const TLeftMatrix &l, const TRightMatrix &r, TResultMatrix &result)
matrix minus l - r
96
MSTESTER.CPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
<iostream>
"matrix.hpp"
"matrixdecomposition.hpp"
"leastSquareSolver.hpp"
"BermudanSwaption.hpp"
"swap.hpp"
"LMMPricer.hpp"
"varianceStructure.hpp"
"SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp"
"LMMPathPool.hpp"
"LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp"
"BlackScholesPricer.hpp"
<fstream>
DEFINES
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
FUNCTIONS
template<typename T > std::ostream & outputTo (std::ostream &stream, T &m)
void t ()
int main (int argc, char const *argv[])
DEFINE DOCUMENTATION
#DEFINE _USE_MATH_DEFINES
Definition at line 1 of file mstester.cpp.
FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
INT MAIN (INT ARGC, CHAR CONST * ARGV[])
Definition at line 85 of file mstester.cpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > STD::OSTREAM& OUTPUTTO (STD::OSTREAM
& STREAM, T & M)
Definition at line 18 of file mstester.cpp.
VOID T ()
97
Definition at line 31 of file mstester.cpp.
98
POLYNOMIAL.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include <map>
#include "functor.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::Polynomial< T, TOrder >
A POLYNOMIAL. NAMESPACES
namespace TermStructure
FUNCTIONS
99
template<typename T , typename TOrder > Polynomial< T, TOrder >
TermStructure::GenerateBasis (TOrder order)
PRICERTESTMAIN.CPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
<cmath>
<iostream>
<fstream>
<cstdlib>
<string>
<vector>
<sstream>
"srandInitializer.hpp"
"randomNumberGenerators.hpp"
"matrix.hpp"
"matrixdecomposition.hpp"
"timeSequence.hpp"
"varianceStructure.hpp"
"SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp"
"LMMAdvancer.hpp"
"LMMPricer.hpp"
"newmat10/newmat.h"
"newmat10/include.h"
DEFINES
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
FUNCTIONS
template<typename T > std::ostream & outputTo (std::ostream &stream, T &m)
int main (int argc, char const *argv[])
DEFINE DOCUMENTATION
#DEFINE _USE_MATH_DEFINES
Definition at line 1 of file pricertestmain.cpp.
FUNCTION DOCUMENTATION
INT MAIN (INT ARGC, CHAR CONST * ARGV[])
Definition at line 40 of file pricertestmain.cpp.
TEMPLATE<TYPENAME T > STD::OSTREAM& OUTPUTTO (STD::OSTREAM
& STREAM, T & M)
100
Definition at line 28 of file pricertestmain.cpp.
101
RANDOMNUMBERGENERATORS.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "srandInitializer.hpp"
#include "standardFunctions.hpp"
#include <cmath>
DEFINES
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
DEFINE DOCUMENTATION
#DEFINE _USE_MATH_DEFINES
Definition at line 1 of file randomNumberGenerators.hpp.
102
SIMPLEMULTIDIMENSIONGAUSSIAN.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
"matrixdecomposition.hpp"
"randomNumberGenerators.hpp"
<vector>
<cmath>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize >
A Gaussian Generator based on CholeskyDecomposition. class
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize >
A REDUCED-RANK GAUSSIAN GENERATOR UTILIZING SVD. RANK IS
DEFAUL TO 4. NAMESPACES
103
namespace TermStructure
SRANDINITIALIZER.CPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "srandInitializer.hpp"
104
SRANDINITIALIZER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::_srandInitializer
A CLASS MAINTAINS THAT SRAND() IS CALLED ONLY ONCE.
NAMESPACES
105
namespace TermStructure
STANDARDFUNCTIONS.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include <cmath>
#include "functor.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T >
Error Function. class TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T >
INVERSE ERROR FUNCTION. NAMESPACES
106
namespace TermStructure
SWAP.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "timeSequence.hpp"
#include "timeSequenceHolder.hpp"
#include "ForwardRateSequence.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize >
SWAP CONTRACT. NAMESPACES
107
namespace TermStructure
TIMESEQUENCE.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::TimeSequence< T, TSize >
TIME SEQUENCE. THE TIMES THAT ALL THE DATA ARE BASED ON.
NAMESPACES
108
namespace TermStructure
TIMESEQUENCEHOLDER.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include "timeSequence.hpp"
CLASSES
class TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder< T, TSize >
A STRUCTURE THAT HAS A TIME SEQUENCE IN IT. NAMESPACES
109
namespace TermStructure
VARIANCESTRUCTURE.HPP FILE REFERENCE
#include <vector>
CLASSES
class TermStructure::VarianceStructure< T, TSize >
A variance structure. Please refer to the doc for more details on the theories. class
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix< T, TVarianceStructure, TSize >
INITIATE AN INSTANTANEOUS COVARIANCE MATRIX FROM A VARIANCE
STRUCTURE. NAMESPACES
110
namespace TermStructure
INDEX
_forwardRateSequence
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 39
_gaussian
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 39
_getStartIndex
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 35
_nextSequence
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 39
_pathpool
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPrice
r, 43
_timeSequence
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 40
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder, 75
_underlyingMatrix
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed, 55
_underlyingStructure
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix, 81
_USE_MATH_DEFINES
main.cpp, 94
mstester.cpp, 99
pricertestmain.cpp, 102
randomNumberGenerators.hpp, 104
_varianceStructure
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 40
~SimpleMatrix
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix, 64
a
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
Advance
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 35
AnchorIndex
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 40
b
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
BermudanSwaption
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption, 15
BermudanSwaption.hpp, 82
beta1
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
beta2
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
BlackScholesPricer.hpp, 83
c
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
capletInfo.hpp, 84
CholeskyDecomposeTo
TermStructure, 7
ComputeC
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 35
CurrentSequence
111
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 35, 36
CurrentTime
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 28
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 40
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix, 81
CurrentTimeIndex
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 47
CVector
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 41
d
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
DiscountFactorAt
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 26
EndIndex
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 47
EstablishDiscountFactors
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 26
Fit
TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver, 31
ForwardRateAt
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 26
ForwardRateSequence.hpp, 85
functor.hpp, 86
functorFitter.hpp, 87
Generate
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 45
GenerateBasis
TermStructure, 7
GetCorrelation
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 77
GetIndex
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 72
GetLength
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed, 54
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper, 57
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGa
ussian, 59
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix, 64
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussi
an, 66
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix, 80
GetPool
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 45
GetSize
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 26
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 72
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 77
GetTime
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 72
GetTimeSequence
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 27
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 36
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder, 75
GetVolatility
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 77
Info
TermStructure::CapletPricer, 21
InitialForwardRateSequence
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 49
InitiateForwardRateSequence
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 36
Integrator_simpson
TermStructure, 7
Integrator.hpp, 88
IsDiscountFactorEstablished
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 27
IsInitializerd
TermStructure::_srandInitializer, 10
leastSquareSolver.hpp, 89
LMMAdvancer.hpp, 90
LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer.hpp, 91
LMMPathPool.hpp, 92
LMMPricer.hpp, 93
LUDecomposeTo
TermStructure, 7, 8
LUDecompositionSolve
TermStructure, 8
main
main.cpp, 94
mstester.cpp, 99
pricertestmain.cpp, 102
main.cpp, 94
_USE_MATH_DEFINES, 94
main, 94
t, 94
matrix.hpp, 95
matrixChildren.hpp, 96
matrixdecomposition.hpp, 97
matrixOperations.hpp, 98
MatrixTransposed
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed, 53, 54
MatrixWrapper
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper, 56
Minus
TermStructure, 8
mstester.cpp, 99
_USE_MATH_DEFINES, 99
main, 99
outputTo, 99
t, 100
Multiply
TermStructure, 8
NextGroup
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGa
ussian, 59
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussi
an, 67
112
NextSequence
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 37
Notional
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption, 15
TermStructure::Swap, 70
NumberOfPath
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 47
NumberOfTrials
TermStructure::CapletPricer, 22
operator()
TermStructure::AbstractFunctor, 12
TermStructure::ErrorFunction, 23
TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction, 29
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 45, 46
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed, 54
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper, 57
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGa
ussian, 59
TermStructure::Polynomial, 62
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix, 64
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussi
an, 67
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix, 81
operator[]
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 27
TermStructure::Polynomial, 62
operator=
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix, 65
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 72
outputTo
mstester.cpp, 99
pricertestmain.cpp, 102
PaymentTime
TermStructure::CapletInfo, 19
PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGa
ussian, 58
Phis
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 78
Plus
TermStructure, 8
Polynomial
TermStructure::Polynomial, 61
polynomial.hpp, 101
PreAdvance
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 37
Price
TermStructure::CapletPricer, 21
TermStructure::Swap, 69
PriceBermudanSwaption
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPrice
r, 43
PriceCap
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer, 17
PriceCaplet
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer, 18
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 49
PriceConstMaturitySwap
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 50
PriceEuropeanSwaption
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 50
PriceRatchetcaps
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 50
pricertestmain.cpp, 102
_USE_MATH_DEFINES, 102
main, 102
outputTo, 102
PriceSwap
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 50
PriceTriggerSwap
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 51
PushAdvancerToTimeStep
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 37
PutTime
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 73
randomNumberGenerators.hpp, 104
_USE_MATH_DEFINES, 104
ReleasePool
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 46
ResetTime
TermStructure::CapletInfo, 19
Resize
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix, 65
SafeInitialize
TermStructure::_srandInitializer, 10
Set
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 38
SetForwardRateSequence
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 38
SetLMMAdvancer
TermStructure::LMMPathPool, 46
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 51
SetRank
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGa
ussian, 59
SetTimeSequence
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 27
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 38
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder, 75
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 77
SetVariaceStructure
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix, 81
SetVarianceMatrix
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGa
ussian, 60
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussi
an, 67
SimpleMatrix
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix, 63, 64
SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian.hpp, 105
SingleAdvance
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 38
113
SingularValueDecomposeTo
TermStructure, 9
srandInitializer.cpp, 106
srandInitializer.hpp, 107
standardFunctions.hpp, 108
Strike
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption, 15
TermStructure::CapletInfo, 19
TermStructure::Swap, 70
Swap
TermStructure::Swap, 69
swap.hpp, 109
SwapEndIndex
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption, 15
TermStructure::Swap, 70
SwapEnterIndex
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption, 15
TermStructure::Swap, 70
SwapRate
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence, 27
t
main.cpp, 94
mstester.cpp, 100
TermStructure, 6
CholeskyDecomposeTo, 7
GenerateBasis, 7
Integrator_simpson, 7
LUDecomposeTo, 7, 8
LUDecompositionSolve, 8
Minus, 8
Multiply, 8
Plus, 8
SingularValueDecomposeTo, 9
TermStructure::_srandInitializer, 10
IsInitializerd, 10
SafeInitialize, 10
TermStructure::AbstractFunctor
operator(), 12
TermStructure::AbstractFunctor< T >, 12
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption
BermudanSwaption, 15
Notional, 15
Strike, 15
SwapEndIndex, 15
SwapEnterIndex, 15
TermStructure::BermudanSwaption< T, TSize >,
14
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer
PriceCap, 17
PriceCaplet, 18
TermStructure::BlackScholesPricer<
TVarianceStructure, T, TSize >, 17
TermStructure::CapletInfo
PaymentTime, 19
ResetTime, 19
Strike, 19
TermStructure::CapletInfo< T >, 19
TermStructure::CapletPricer
Info, 21
NumberOfTrials, 22
Price, 21
TermStructure::CapletPricer< TLMMAdvancer,
T, TSize >, 21
TermStructure::ErrorFunction
operator(), 23
TermStructure::ErrorFunction< T >, 23
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence
CurrentTime, 28
DiscountFactorAt, 26
EstablishDiscountFactors, 26
ForwardRateAt, 26
GetSize, 26
GetTimeSequence, 27
IsDiscountFactorEstablished, 27
operator[], 27
SetTimeSequence, 27
SwapRate, 27
TermStructure::ForwardRateSequence< T, TSize
>, 25
TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction
operator(), 29
TermStructure::InverseErrorFunction< T >, 29
TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver
Fit, 31
TermStructure::LeastSquareSolver< T, TSize >,
31
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer
_forwardRateSequence, 39
_gaussian, 39
_getStartIndex, 35
_nextSequence, 39
_timeSequence, 40
_varianceStructure, 40
Advance, 35
AnchorIndex, 40
ComputeC, 35
CurrentSequence, 35, 36
CurrentTime, 40
CVector, 41
GetTimeSequence, 36
InitiateForwardRateSequence, 36
NextSequence, 37
PreAdvance, 37
PushAdvancerToTimeStep, 37
Set, 38
SetForwardRateSequence, 38
SetTimeSequence, 38
SingleAdvance, 38
TimeStep, 41
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer<
TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >, 33
114
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer
_pathpool, 43
PriceBermudanSwaption, 43
TermStructure::LMMBermudanSwaptionPricer<
TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >, 42
TermStructure::LMMPathPool
CurrentTimeIndex, 47
EndIndex, 47
Generate, 45
GetPool, 45
NumberOfPath, 47
operator(), 45, 46
ReleasePool, 46
SetLMMAdvancer, 46
TermStructure::LMMPathPool<
TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >, 44
TermStructure::LMMPricer
InitialForwardRateSequence, 49
PriceCaplet, 49
PriceConstMaturitySwap, 50
PriceEuropeanSwaption, 50
PriceRatchetcaps, 50
PriceSwap, 50
PriceTriggerSwap, 51
SetLMMAdvancer, 51
UnderlyingAdvancer, 51
TermStructure::LMMPricer<
TVarianceStructure,
TMultiDimensionGaussian, T, TSize >, 48
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed
_underlyingMatrix, 55
GetLength, 54
MatrixTransposed, 53, 54
operator(), 54
TermStructure::MatrixTransposed< TMatrix, T,
TSize >, 53
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper
GetLength, 57
MatrixWrapper, 56
operator(), 57
TermStructure::MatrixWrapper< T, NPrimary,
NSecondary, TSize >, 56
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGaus
sian
GetLength, 59
NextGroup, 59
operator(), 59
PCABasedMultiDimensionGaussian, 58
SetRank, 59
SetVarianceMatrix, 60
TermStructure::PCABasedMultiDimensionGaus
sian< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize >, 58
TermStructure::Polynomial
operator(), 62
operator[], 62
Polynomial, 61
TermStructure::Polynomial< T, TOrder >, 61
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix
~SimpleMatrix, 64
GetLength, 64
operator(), 64
operator=, 65
Resize, 65
SimpleMatrix, 63, 64
TermStructure::SimpleMatrix< T, TSize >, 63
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian
GetLength, 66
NextGroup, 67
operator(), 67
SetVarianceMatrix, 67
TermStructure::SimpleMultiDimensionGaussian
< TVarianceMatrix, T, TSize >, 66
TermStructure::Swap
Notional, 70
Price, 69
Strike, 70
Swap, 69
SwapEndIndex, 70
SwapEnterIndex, 70
TermStructure::Swap< T, TSize >, 68
TermStructure::TimeSequence
GetIndex, 72
GetSize, 72
GetTime, 72
operator=, 72
PutTime, 73
TimeDifference, 73
TimeSequence, 72
TermStructure::TimeSequence< T, TSize >, 71
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder
_timeSequence, 75
GetTimeSequence, 75
SetTimeSequence, 75
115
TermStructure::TimeSequenceHolder< T, TSize
>, 74
TermStructure::VarianceStructure
a, 78
b, 78
beta1, 78
beta2, 78
c, 78
d, 78
GetCorrelation, 77
GetSize, 77
GetVolatility, 77
Phis, 78
SetTimeSequence, 77
VolatilityIntegrator, 77
TermStructure::VarianceStructure< T, TSize >,
76
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix
_underlyingStructure, 81
CurrentTime, 81
GetLength, 80
operator(), 81
SetVariaceStructure, 81
TermStructure::VarianceStructureMatrix< T,
TVarianceStructure, TSize >, 80
TimeDifference
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 73
TimeSequence
TermStructure::TimeSequence, 72
timeSequence.hpp, 110
timeSequenceHolder.hpp, 111
TimeStep
TermStructure::LMMAdvancer, 41
UnderlyingAdvancer
TermStructure::LMMPricer, 51
varianceStructure.hpp, 112
VolatilityIntegrator
TermStructure::VarianceStructure, 77