Air Pollution - Florida International University
advertisement

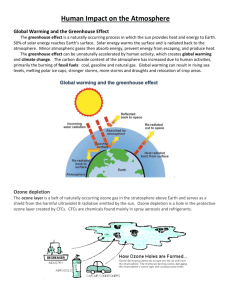
Composition Nitrogen: 78.1% Oxygen: 20.9% Other Gases: Argon : 0.9% CO2 : ~370 ppm: Green House Gas Methane: Green House Gas Ozone: blocks UV radiation Dust: solid particles in the atmosphere Water Vapor: a major player in atmospheric circulations Since water vapor is lighter than the atmosphere. Introduction of water vapor causes vertical movement (convection) in the atmosphere Structure Troposphere: 0-11 km elevation, the weather layer, temp. drops with elevation Tropopause Stratosphere 11-45 km, little vertical motion, contains ozone layer, Temp rises with elevation Stratopause Mesosphere: >45 km Ambient Air Pollution: Ground level tropospheric air pollution. It is air pollution all around us. Criteria Air Pollution: Originated with the Clean Air Act of 1970 EPA identified six most serious pollutant in the ambient air CO, O3, SO2, NO, PM (particulate matter) and Pb (Lead) VOC (Volatile Organic Pollutants): Criteria Air Pollutant These are produced in large amounts – hence higher risk Exhausts from motor vehicles account for about half of these emissions In many major cities, criteria air pollutants cause eye and respiratory irritation, head ache and other ailments. Outdoor Pollution Indoor Pollution Primary Pollution Secondary Pollution Carbon Monoxide (CO) Product of incomplete combustion of carbon Accounts for 50% of all air pollutants Accounts for 11% of all hospital admission of elderly patients for congestive heart failure Iron atom in hemoglobin in blood picks up oxygen from lungs and takes it to the cells. CO has 250 X more affinity for the iron atom compared to Oxygen Organs get less oxygen: heart and brain gets affected first Headache dizzinessfatigue, drowsiness coma death US ambient air standard for CO is 9 ppm averaged over 8 hours. If it exceeds one time in a year , the area is violating standards. Ground level Ozone Ozone O3 has three oxygen atoms Major component of photochemical smog (which also contain nitrates and nitrogen oxides) Nox + VOC (Sunlight, High Temp, stagnant air O3 Automobiles are the main producers of precursors, also power plants, aeroplanes EPA considers Ozone as the “most … intractable air pollutant in urban areas”. Effects on People: see the table Effects on Plants and trees: causes more damage to plants than all other air pollutants combined Crop loss in USA 5-10% World wide 35% of the crops grow in areas with high O3 More harmful when combined with other pollutants like acid rain Trees and forests are also adversely affected Ozone is a major component of SMOG Smog = unhealthy mixtures of air pollutants over urban areas 1. Industrial (gray air) smog = industries burn coal or oil 2. Photochemical (brown air) smog = Produced by light-driven reactions of primary pollutants & normal atmospheric compounds Irritates eyes, noses, and throats Vehicle inspection programs in the U.S. have decreased smog Nitrogen oxides (give it brown hazy color) + VOCs + heat + sunlight = O3 + other photochemical oxidants + aldehydes Industrial smog Photochemical smog 17.16 Ozone Levels Concentration (ppm) Air Quality <0.05 Good: No health impact expected 0.051 – 0.100 Moderate: Unusually sensitive people should consider prolonged exertion outdoors 0.101 – 0.150 Unhealthy for sensitive group: Active children and adults with asthma or other respiratory diseaes should avoid prolonged outdoor exertion 0.151-0.200 Unhealthy: Active children and adults and those with respiratory diseases should follow the advise above. Children should limit prolonged outdoor exertion 0.201 – 0.300 Alert Very Unhealthy: Active children and adults, and those with respiraory diseases should avoid all outdoor exertion. Others, especially children should limit outdoor exertions How to reduce Ozone pollution? Reduce NOx and VOC emissions from Automobiles 1970 CAA – emissions fell 90% But more autos and increased miles driven = high Nox and VOC New Ozone standard Low VOC and NOx does not necessarily reduce O3 Between 1990 to 1992, # of cities in US exceeding old O3 standard (<.12 ppm) fell from 97 to 56 Reduced emissions from power plants, vapor recovery nozzles in Gas stations, cleaner burning gasoline Restricting Formaldehyde emissions because Formaldehyde causes more O3 formation than other VOCs New EPA standard : 0.08 ppm – 1/3rd of US cities do not comply even with the old standard (0.12 ppm) – LA has > 0.20 ppm on 30 40 days Sulfur Gases >50 million tons of SO2 emitted worldwide 2/3rd from combustion of coal in power plants Rest mostly from Petroleum refining, smelting Natural Sources: sea water, bacteria, planktons, plants Volcanic eruption: Mt Pinatubo (1991) ejected 20 million tons – caused global cooling Sulfur dioxide (SO2) SO2 gas reacts with moisture to form sulfuric acid which causes irritation and aggravates asthma, heart disease. Mucous membrane in eye, lungs affected Forms aerosols (suspension of fine liquid or solid particles in air) of sulfuric acid (wet condition) or sulfates (dry condition) – can inflame lungs if inhaled Environmental Effects: Forms blue haze that blocks sunlight Causes acid deposition (acid rain) Harms stratospheric O3 Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) NO (nitric oxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), N2O (nitrous oxide) Sources: at high temp atmospheric N2 combines with O2 Motor vehicles (50%), Electric utilities (25-30%), industrial furnaces (14%) Natural sources: Lightning, soil microbes, volcanoes Same as SO2: irritation, haze, acid rain, global cooling, ozone destruction But also is precursor of Ozone formation – SO2 is not Deposited on earth acts as a plant nutrient – can be very harmful in high concentrations Particulate Matter (PM) Solids suspended in air Accounts for 10% of US air pollution Can vary in composition and size Sulfates, nitrates, metals, dust, biological matters Gaseous pollutants can condense into PMs Caused silicosis, black lung diseases (coal miners), mesothelioma from asbestos Coarser PM can be sneezed out, PM 10 is regulated by EPA, PM 2.5 even more dangerous--- can cause inflamation in Lungs. Very fine PM can cause cancer Causes Haze , lowers visibility– can cause other problems Sources: PM10 = dust from farms, mines, or roads, pollens PM2.5 = mostly from combustions– diesel motor vehicles, electric power plants, industrial operations like steel mills, fly ash Construction sites, agricultural activities, wood burning stoves Chloride salts in coastal areas EPA standard : PM10 < 50 μg/m3. PM2.5 <15 μg/m3 PM2.5 contains different chemicals in east coast comapred to west coast We don’t know which component is most harmful Sulfates, nitrates, soot, metal oxides? Controlling combustion sources Lead Causes Brain damage, nervousness, apathy Inner city children more at risk Tetraethyl Lead was used as a octane booster in gasoline Lead was used in paints Now both use banned with dramatic reduction of lead in atmosphere and in average blood levels Lead mobilized many years ago is still a problem: Old paints, solder of old water pipes, roadside soil contaminated by leaded gasoline… Other pollutants like Hg, Cd, Pb, Zn, As can be of concern near mines and smelters Volatile Organic Chemicals (VOC) Combustion sources: Motor vehicles, aeroplanes, farm machineries, lawn mowers.. Incomplete combustion, idling Evaporation during filling of gas tanks Non-combustion sources: Petroleum refineries, chemical plants Dry cleaners Paint shops, garages, print shops Bakeries – emit ethanol formed by action of yeast Sewage treatment plants, composting Natural Sources: Trees emit VOCs. 90% of VOCs in Maine is from Trees. Terpene can contribute to Ozone formation Reducing VOC emission: CAA – VOC dropped by 30% between 1970 and 1985 Acid Rain Any rain more acidic than normal rain (pH=5). Carbonic, Sulfuric and Nitric acids SO2 dissolves in water to form Sulfuric acid: main ingredient of acid rain. NOx Nitric acid. CO2 Carbonic acid Industrialized areas more affected. pH=4.2 in US Northeast In the United States, roughly 2/3 of all SO2 and 1/4 of all NOx come from electric power generation that relies on burning fossil fuels, like coal. Granitic terrains more affected than limestone terrains Affects plant growth, contaminates lakes and groundwater, man made structures, cause algal blooms, releases heavy and toxic metals from sediments Acid deposition Originates from burning fossil fuels that release sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides These compounds react with water to form sulfuric and nitric acids Acidic precipitation in the U.S. Acid Deposition: Effect of Life in Water pH Effect of Life in water 6 Snails and Crayfish begin to die 5 Fish eggs do not hatch, some fish die 4.5 to 5 Fish species like Bass and Trout begin to die 4 Many flies and frogs begin to die US emission of criteria pollutants, 2006 In 2006, the U.S. emitted 137 million tons of the 6 major pollutants Health Effects Respiratory diseases = damage to tissue (asthma, bronchitis, emphysema) ½ of all lungs examined in autopsies in US show damage Lead to lung cancer Heart disease, immune suppression, reduced mental function 1 in 5 people live with dangerously polluted air Reduced life expectancy 5-10 yrs if you live in LA (150 days of hazardous breathing) 24, 000 people/yr die in the US Los Angeles, CA Air pollution has decreased since 1970 Total emissions of the 6 monitored pollutants have declined Cap-and-trade program for SOx. Enabled the 110 most polluting power plants to buy and sell SO2 pollution rights. But CO2 emissions have been increasing Areas in the U.S. fail air quality standards Ozone Hole Ozone is harmful at Ground level At 15 km above surface UV ray reacts with Oxygen to produce Ozone. This Ozone absorbs UV ray and shields earth’s surface • 1% reduction in ozone causes 3% rise in skin cancer in light-skinned people plus increased cataract, melanoma, gene mutation, immune system damages UVA: longest wavelength: not damaging UVC: shortest wavelength: highly damaging, absorbed by oxygen UVB: intermediate wavelength: absorbed by Ozone Destruction of Ozone Ozone in the upper atmosphere can be destroyed by the exhaust of hi-altitude aircrafts and more seriously by CFCs(Chlorofluorocarbons) which were used as a refrigerant and in aerosol spray cans (e.g., Freon) 40 billion lbs of CFC produced since 1931 and 90% of this released to the atmosphere The released CFC either dissolves in seawater or go into Troposphere where they remain for many decades and are harmless Some of the CFC escape to stratosphere, absorb UV ray and releases Chlorine which act as a catalyst to break Ozone molecule Destruction of Ozone Chlorine + Ozone = ClO(Chlorine Monoxide) + O2 A single chlorine atom can destroy 100,000 ozone molecules ozone hole is more pronounced in polar regions In polar stratosphere, extreme cold removes nitrogen compounds, which normally inactivate chlorine, from the stratosphere Release of reactive chlorine is also catalyzed by fine ice crystals in stratosphere At present both the Arctic and Antarctic are affected by ozone hole Sulfate aerosols as from Mt Pinatubo also destroys Ozone layer Ozone Hole UV rays reaching Antarctica each spring has increased from 20 to 200% every year since 1980s Production of algae and bacteria in contact with seawater has decreased by 15% since the late 1980s Marine Phytoplanktons are severely stressed This in turn, will affect animals higher in the food chain. Ozone Hole Ozone Hole over Antarctica and N. America Present scenario Montreal Protocol (1987, 1990) Signed by more than 70 nations Stipulates phasing out of CFCs and other ozone depleting compounds by 2000 Hesitancy on part of China Substitutes not totally safe Latest data indicate that ozone hole is not expanding CO2 needs to be added to the list! Not regulated as a pollutant under the U.S. Clean Air Act. But most emissions are CO2 A greenhouse gas Contributes to global climate change In the US… Sources of C02 US emissions 1. 40 % Petroleum products 2. 34 % coal 3. 20 % natural gas Greenhouse Effect In a greenhouse, light enters but IR cannot escape CO2 in atmosphere allows light rays to enter but traps IR CO2 % in atmosphere has increased from 280 ppm in pre-Industrial time to present day value of 375.64 ppm (2003 data) Rise in atmospheric CO2 in the last two decades Greenhouse Effect: Is it Real? How much CO2=How much rise of T? More T = more evaporation = more cloud = Less Temp… Real rise or natural fluctuation? Data for the last 10ka indicate upto 6 °C fluctuation Little ice age (1450 – 1850) Global Temperature Rise Methane (CH4) concentration ppb Other Greenhouse Gases Methane, water vapor, nitrous oxide Rice paddy, extraction of fossil fuel, raising of live stock (bovine flatulence) cause increase in methane Cutting of forests kills CO2 sink Some effects might be opposite of CO2: SO2 Temperate regions more resilient Colder climate will have longer growing season Marginal areas to be hard hit More flooding, heat waves… Greatest air pollution problem: Global Warming • www.nelson.wisc.edu/outreach/energy2006 Evidence to Support Global Warming Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) An international panel of scientists and government officials established in 1988 Generated reports on the synthesis of scientific information concerning climate change 4th Assessment report 2007 Documents observed trends in surface temperature, precipitation patterns, snow and ice cover, sea levels, storm intensity The IPCC concluded that it is more than 90% likely that most global warming is due to humans The Debate over climate change is over 84% of people surveyed think humans contribute to global warming Predicts future changes Temperatures will rise 0.2 degree Celsius per decade Greenhouse Effect: Problems Rise of temperature : Drier climate? Melting of Ice Caps: ultimate reduction of soil moisture (up to 40%) If all the ice melted sea level will rise by 75m inundating 20% of the Earth’s land area. No Florida!! Even a partial melting of Antarctica ice cap will raise sea level by 3 to 6m. Fear of calving from Ross Ice Shelf Rising sea levels IPCC predicts mean sea level to be 18-59 cm (7-23 in) higher than today’s at the end of the 21st century Predictions from two models By 2030, Illinois will have a climate like Missouri’s. By 2090, it will have a climate like Oklahoma’s. Green = Canadian model Blue = Hadley model Halting emissions • California’ s Global Warming Solutions Act • Cut greenhouse gas emissions 25% by 2020 • 10 NE states launched the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) in 2007 • cap-and-trade program for C emissions from power plants Fig. 15-22, p. 371 Kyoto Protocol Conference: Dec 1-11, 1997 in Kyoto, Japan Six Greenhouse gases were targeted (CO2, CH4, NOx, CFC- substitutes) Their emission to be reduced below 1990 levels as follows: EU: 8%, US: 7%, Japan 6% The reduction will be done in a 5 year period between 2008-2012 Emission can be traded in global market Creation of carbon sinks like afforestation can be balanced against emission Developing countries to benefit from “clean” technology The protocol will be open for signature in March, 1998, has to be ratified by countries producing 55% of the emissions: reached in 2004 after Russia signed it. Entered into force: Feb 16, 2005 US pulled out of it in 2001