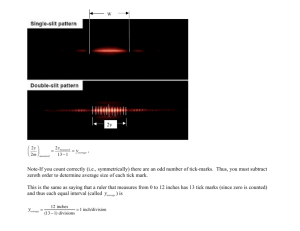
Accident report form - Synergy Education Group
advertisement

THEORY ASSESSMENT ASSESSOR GUIDE HLTAID004 Provide an emergency first aid response in an education and care setting Student Name Date Submitted Student Number ________________________________________________ _______________ _______________ Assessment Tool – Written assessment Signature of Assessor _____________________ SATISFACTORY Assessor _______________________________ NOT YET SATISFACTOY Date Assessed ___________________________ Assessment Tool – Scenarios SATISFACTORY NOT YET SATISFACTOY Assessment Tool – Observation Signature of Assessor _________________ Assessor ___________________________ Date Assessed _______________________ Signature of Assessor _____________________ SATISFACTORY Assessor _______________________________ NOT YET SATISFACTOY Date Assessed __________________________ Workshop Attendance Signature of Assessor ____________________ SATISFACTORY Assessor ______________________________ NOT YET SATISFACTOY Date Assessed __________________________ Assignment Acknowledgement I, (block capitals) __________________________________________________________________ Declare that: 1. 2. 3. I have not: Copied the work of another student; or Submitted this paper previously for another qualification at any other institute; or I have not, without clear acknowledgement of the origin of work; Directly copied any part of another person’s work (this includes information which is in an electronic form and/ or available on the internet) Summarized the work of another person (this includes articles and case reports in paper or electronic form) Used or developed an idea or derived from another person’s work I have read and understand Synergy Eduation’s Policy on plagiarism Student signature:…………………………………………………………………………………….......…………………………………………………………………… Subject: ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Due Date: ……………..…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Student Name:………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. Student Number: ……..………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ASSESSMENT INSTRUCTIONS 1. Read all of the learning material for this unit of competency before commencing. 2. Answer all the Questions for this Unit of Competency. 3. Computers may be used for the purpose of presenting the answers in a neat and professional manner. 4. If you need assistance with any of the Questions please contact your trainer, who will be happy to assist you. 5. The assessor will make arrangements to receive the completed assessment via email, USB, printed or similar. 6. All Questions and tasks must be true and correct to be assessed as satisfactory. 7. You must complete all your own work without assistance from other persons. 8. You MUST keep a copy of your assessment in case another copy is required ASSESSMENT TYPE Synergy Education will assess your ability on the unit of competency via various assessment modes. Please refer to your Student Assessment Overview Booklet if you require further information. RESUBMISSIONS Should you not achieve a satisfactory result when you first submit your written assessment, or complete the observation, you will be provided with additional opportunities to do so. Please discuss any concerns regarding assessment resubmissions with your trainer. SUBMISSIONS Please submit your answers to the Questions via one of the below methods. info@synergy.edu.au Synergy Education 35 Cougar Street, Indooroopilly Q 4068 Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/2014 Version 1.0 Section 1 Regulations, Codes of practice, Workplace procedures Scenario 1 You are working at Fun Day Childcare today and it is 9.10am. You and Jenny Jenkins a trainee, have been outside supervising playtime. Billy Bags has just fallen off the outdoor climbing frame and is lying on the ground with his left arm twisted behind him. He is crying loudly. 1. As a supervisor at Fun Day Childcare you are prepared to know how to deal with this situation because: Tick each correct answer/s The childcare centre has policies and procedures in place on what to do in cases of injury trauma and illness which you have read As part of your Childcare qualifications you were required to train as a paramedic Your centre practices emergency procedures every 12 months which includes dealing with injury and incidents You have completed your first aid course and update it every 3 years and your CPR every 12 months You google emergency care frequently 2. As a first aider you know you have to follow the first aid principles. This means you should follow – a) State and territory regulations b) ARC Guidelines c) Workplace Policies and procedures d) All of the above 3. It would be best to notify Billy’s parents as soon as possible but what would be the maximum time you have to let them know? Tick each correct answer/s 30 minutes 1 hour 24 hours 2 days 5 days 4. You will need to complete an incident report form about Billy’s accident. Tick the boxes of the details you would need to include on the incident report form Tick each correct answer/s circumstances leading to the incident what Billy had for lunch time and date the incident occurred any medication administered or first aid provided the name of any person you notified or attempted to notify 5. Complete the accident report form below: Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/2014 Version 1.0 Accident report form CLIENT’S NAME: CLIENT ORGANISATION: INCIDENT DATE: Todays Date INCIDENT TIME: DETAILS OF THE INJURY/S SUSTAINED: LOCATION OF THE INJURY/S SUSTAINED CAUSE OF INCIDENT: Fell off outdoor climbing frame TREATMENT / MEDICATION ADMINISTERED: IS MEDICAL ASSISTANCE REQUIRED: WITNESS' NAME: WITNESS’ STATEMENT WITNESS' SIGNATURE: WHERE DID THE INCIDENT OCCUR: FORM COMPLETED BY: SIGNATURE: DATE FORM COMPLETED: Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Scenario 2 Kirsty wakes up from her afternoon sleep at Fun Day Care, very irritable and the cold she seems to have had over the last couple of days is worse. When you look at her more closely you realise she has a red rash around her hairline and she has red itchy eyes. 6. You suspect that Kirsty may have measles. Number the boxes (using 1 to 4) in order of what you would do 2 Contact a parent or guardian to collect Kirsty and request medical confirmation of Kirsty’s illness 4 Notify parents, guardians or an authorised emergency contact of each child being educated and cared for by Fun Day Care of the occurrence (when confirmed) as soon as practicable 1 Keep Kirsty separated from the other children 3 Clean and disinfect all surfaces play equipment etc in the centre 7. Kirsty’s grandmother rings to let you know that she has taken Kirsty to the doctor and she definitely has measles. You will explain to Kirsty’s grandmother that Kirsty will not be allowed to attend Fun Day Care for: Tick each correct answer/s 1 day 10 days 14 days 4 days A week 8. You know that there are regulations about contagious disease and that other children may need to be excluded from the centre. You also know that the National Quality Framework for Early Childhood Education and Care has developed a tool/brochure to provide information on Quality Area 2: ‘Children’s Health and Safety’ which will help you with what to do. Which one of the following tools/brochures would you go to – a) Leadership and Service Management Guidelines b) Workplace Health and Safety Australia Requirements c) Staying Healthy in Childcare d) National Doctors Healthy Tips Scenario 3 Amy has enrolled in Fun Day Care and her mother has noted on her enrolment and medical form that Amy is allergic to peanuts and has an EPIPEN in case she goes into anaphylactic shock. While working with Fun Day Care you have not enrolled a child with a severe medical condition. You know that it is a requirement Education and Care Services National Regulations that the organisation must have a medical conditions policy. You need to find and read the policy before Amy commences with Fun Day Care. 9. Which of the following statements (or similar) would you find as part of the Fun Day Care’s Medical condition’s policy? Tick each correct answer/s Parent of the child is required to provide a medical management plan for the child A medical management plan is to be communicated to and followed by all Centre staff in the event of an incident relating to the child's specific health care need, allergy or relevant medical condition A risk-minimisation plan is to be developed in consultation with the parents of a child Make sure that practices and procedures are followed so that the parents are notified of any known allergens that pose a risk to a child and strategies for minimising the risk are developed and implemented Make sure that the child does not attend the Fun Day Care without the medication prescribed by the child's medical practitioner in relation to the child's specific health care need, allergy or relevant medical condition Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 10. Are you allowed to administer anaphylaxis or asthma medication to a child without authorisation, in case of an emergency? a) Yes b) No 11. Under what circumstances would you permit a child over preschool age to self-administer medication a) Authorisation for the child to self-administer medication is recorded in the medication record b) No one at the Child Care service knows how to administer the medication c) The medical conditions policy of the Child Care service includes practices for self-administration of medication. d) The child tells you they do it all the time e) a and c Scenario 4 Your Centre Director has asked you to put together a handout for parents to explain the Centre’s “Infection Control Policy”. But before you can do this you realise you need to be able to answer the questions below. 12. Different germs spread in different ways. Place the following words with the statement best describing them – Droplets, Contact, Airborne Germs such as nor virus and rotavirus can cause gastroenteritis, leading to symptoms of diarrhoea (loose stools) and/or vomiting. It may be obvious that a person can spread ________ the disease while they are unwell, but what is not so well known is that a person may still be contagious up to 10 days after the symptoms have stopped. The virus that causes measles can stay in the air for up to 2 hours after an infected ________ person has left the room. This means that people can be exposed to the virus without having direct contact with the infected person. The bacteria that cause meningococcal disease can be present in people’s throats. If an ________ infected person coughs or sneezes, the droplets they produce can infect other people nearby. 13. Which of the following strategies below are ways to break the chain of infection and stop the spread of diseases in Education and Care services Tick each correct answer/s effective hand hygiene exclusion of ill children, educators and other staff having a chain of survival immunisation cough and sneeze etiquette appropriate use of gloves completing the medical permission form 14. Why is it necessary to have policies and procedures for infection control in an education and care facility? Indicate T/F So germs can only be spread at home. __ Avoid stress and conflict between parents and educators. __ So exclusion criteria is clearly stated. __ Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 To reduce the spread of infectious disease. __ To put parents under pressure to fulfil work and other family commitments. __ 16. Which of the following circumstances below would require you or your child care director to fill in a “Child care Form - 27a – Reporting a serious injury or death” and send it to Queensland Government? Tick each correct answer/s When there is a non-accidental incident requiring medical treatment i.e. an asthma attack When a government official comes out to investigate the incident When a child has had a serious injury and medical assistance has been sought or should have been sought When the ambulance are called to assist a child in an emergency incident i.e. a broken leg When a child has been administered an epi pen When the doctor in the medical centre next door came to help with a child that was concussed and had an open head wound and was later taken to hospital by the parents Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Section 2 Workplace and Community 1. Complete the following sentences with the words below: Safe; anyone; obligation; safety; role; fundamental; workplace; all; service Duty of care is an of participants in the to ensure the health and of all persons in the workplace. Duty of care is the “ obligation that anyone working in child care, whatever the type of and whatever their , is to keep children _______________”. 2. An educator does not have the right, in any emergency, illness or accident, to contact emergency services or get hospital attention for a child if they are unable to contact parents/guardian or authorised person/s. Circle correct answer TRUE OR FALSE 3. What are the psychological First Aid action principles? Look Listen Feel Look Listen Link Look CPR Link Listen Feel Link Tick each correct answer/s 4. What are some of the goals of using psychological First Aid in an education or child care setting? Tick each correct answer/s Calm people Reduce distress Make people feel safe, secure and supported Help people understand the emergency and its context Re-enact the event Assist with early screening for people needing further or specialised help 5. Children in the 0 – 12 age groups may react to traumatic first aid events by Constantly talking about the event Indicate T/F ____ Re-enacting the event ____ Mood swings ____ Aggression ____ Coughing and sneezing ____ Increase in physical complaints ____ 6. In the case of an emergency, are you as child educator, allowed to give a child medication if you can get verbal permission from ? a) a grandparent (not authorised on enrolment form) b) a parent or a person (authorised on enrolment form) c) a registered medical practitioner or emergency service if a parent or person (authorised on enrolment form) cannot be contacted d) the child care centre’s director or school principal e) b) and c) Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 7. Medication may be administered to a child without an authorisation in case of an anaphylaxis or asthma emergency. TRUE OR FALSE 8. What sort of information needs to be kept private and confidential when dealing with first aid incidences. Tick each correct answer/s First aid treatment provided Time of the incident Personal details Details of medical conditions When you did your last first aid course 9. When providing first aid to anyone you need to act ethically. This means you would Tick each correct answer/s Be respectful of their privacy Keep them on their back and raise their legs Be respectful of their culture and beliefs Always get consent Provide care within you own skills and limitations Do 30 compressions and 2 breathes Scenario 5 Chloe had been playing in the covered outdoor area when she fell to the ground and started to have a seizure. This was totally unexpected and was the first time Chloe had experienced such an occurrence. The staff at Fun Day Care reacted quickly to Chloe’s convulsions and used their first aid knowledge and policies and procedures to deal with the situation. The ambulance and Chloe’s parents were called and Chloe was taken in the ambulance to be checked out at the hospital. 10. Many of the children at Fun Day Care had witnessed Chloe’s seizure and others had witnessed her being taken away in the ambulance. The children reacted to the emergency in a variety of ways and the staff decided that something needed to be done to assist the children in coping with their emotions about the incident. Indicate which of the methods below would be appropriate for Fun day Care staff to use to help the children overcome their fears and stress about Chloe’s seizure. Tick each correct answer/s Talk to the children as a group about seizures Have some children role play what happened to Chloe Pretend nothing has happened but call a psychologist to come next week and deal with the situation Allow the children to ask questions both individually and as a group Follow policies and procedures about notifying all parents and carers about the incident 11. The Fun Day Care staff had also had various reactions to Chloe’s seizure. Though they had responded very well to the emergency and were able to keep their emotions controlled in front of the children the Centre’s Director realised there was the need for a debriefing. Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Identify which of the following statements are true or false. Debriefing should be carried out three to seven days after the incident ____ Debriefing is individualised counselling ____ Debriefing is a structured voluntary discussion aimed at putting an abnormal event into perspective. ____ Debriefing is a way of helping people establish a process for recovery. ____ Debriefing stops people reacting to the incident ____ 12. Which of the following could be signs or symptoms of stress felt by some of the educators after Chloe’s seizure? Tick each correct answer/s Loss of concentration, insomnia Anxiety, nervousness Depression, anger Joint pain, irregular pulse Fatigue, headaches 13. Jessica, is a volunteer at Fun Day Care. She was shocked and amazed when she witnessed Chloe’s seizure and felt she needed to tell outsiders about what happened. After finishing work that afternoon she Tick the boxes above for the things Jessica shouldn’t have done Went onto Facebook and posted all the details about the incident, Chloe and the Centre Organised coffee with her friends so she could give them all the details of what happened because she thought it would make her feel better Put all the details about the incident, Chloe and the Centre into an email to other Childcare centres because she thought it was important they know what to do Organised a meeting with her supervisor to talk about what she should do 14. Which of the follow general signs and symptoms that suggest that a young child may be quite ill and in need urgent medical attention Tick each correct answer/s High fever Drowsiness Tiredness and decreased activity Breathing difficulty Poor circulation Poor feeding Poor urine output Red or purple rash A stiff neck or sensitivity to light Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Section 3 Anatomy and Physiology 1. Complete the table below using the following information Taken under armpit; 37.8°C (37.2°C *); 100 – 150; 20 – 25; 60 – 100; 30 – 40; 95 – 140; 38.0°C (37.5°C *); taken in mouth Standard clinical observations and other vital signs – child Approximate normal physiological ranges for a child Parameter Normal range <1 year 1 - 2 years 2 - 5 years 5 - 12 years > 12 years Standard HR (beats 110 - 160 80 - 120 clinical per min) observations Respiration 25 - 35 25 - 30 15 - 20 rate (breaths / min) Temperature Axilla _________________ - significant fever > _______________ Sublingual _____________ - significant fever > _______________ *clinically significant fever lower in infants < 3 months of age 2. Which three systems of the body work together to maintain life and provide oxygen a) Respiratory, cardiovascular, nervous b) Cardiovascular, digestive, nervous c) Skeletal, digestive, respiratory d) Lymphatic, muscular, digestive e) Lymphatic, cardiovascular, respiratory 3. Indicate if the following statements are true (T) or false (F). When listening for signs of breathing abnormal sounds may be heard such as occasional gasping called agonal respirations. ____ You should not do rescue breaths if you hear any sort of breathing sounds ____ Wheezing sounds always indicate someone is having an asthma attack ____ The alveoli air sacks in the brain that tell the body to breathe ____ You should do compressions on a baby with 2 fingers ____ You are more likely to break a babies ribs because they are more brittle from lack of calcium ____ The sternum is the bone where the ribs join at the front of the chest. ____ 4. Which of the following statements are true – Tick each correct answer/s Newborns and infants are nose breathers There is more space in the mouth taken up by the tongue, in children up to 2 years old The tongue in infants and children can easily fall back and obstruct the airway. The trachea is short and funnel-shaped and narrower Alveoli are smaller and shallower than in older children and adults Infant’s and child's cricoid cartilage (below Adams apple) is less rigid and less developed Infants and child's airway structures are more easily obstructed When doing rescue breaths on an infant their head should be kept in a neutral position Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/2014 Version 1.0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 5. Label the diagrams below - 2 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 6. Match the name of the part of the heart to its function using the list below: Right ventricle, valves, right atrium, left atrium, and left ventricle Part Function Receives blood from the body Pumps deoxygenated blood into the lung Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs Pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta which then goes to rest of body Located between upper and lower chambers and between the lower chambers and the two major arteries Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Section 4 Responding to an emergency 1. Deciding if there is an emergency situation can be difficult sometimes. Which of the following might help you to decide if there is an emergency a) Observing normal behaviour b) Strange noises, sights, or smells c) Symptoms and signs d) A barking dog e) Both b) and c) 2. Which of the following would you identify as being “possible hazards” when assisting in a First Aid emergency in an education or care setting Tick each correct answer/s Slips, trips and falls Other children Electrical hazards Hazardous substances Work equipment Physical environment 3. Complete the sentences below using the following words – Negligent; broken arm; commencement; heart attack; permission; immediate; consent; hazards; others; Duty of Care; safe and secure; illness; damage An emergency is a situation requiring action. A medical emergency is a sudden _________ such as ______________, which requires immediate medical attention. An injury is ____________________ to the body, such as a broken arm. Before approaching a casualty you must identify and minimise ____________ to ensure the safety of you and ____________. You must seek ____________ prior to the ______________ of any first aid or have written or verbal _______________form a parent or guardian if the casualty is a child (except in the case of an asthma or anaphylaxis emergency). If you start to provide first aid care for a casualty then you have established a voluntary “_______________________________” If the first aider owed a duty of care to the casualty and did not provide any care they may be found “ “ It is important to explain the process and what you are doing to the casualty to ensure they feel __________________________________ 4. When doing first aid and CPR there are some standard precautions and ways to guard against infection when doing CPR. Place the following statements or words under the most appropriate heading. Washing hands, 100 compressions/minute, use of PPE (like gloves), correct disposal of sharps, use of a mask, compressions only Standard precautions Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/2014 Infection controls doing CPR Version 1.0 5. When Billy in Scenario 1, fell off the climbing frame, how would you have initially assessed his injuries? a) Done a primary survey to assess his response and then a secondary survey including verbal questions and observation b) Asked him to stand up and see if he falls back down c) Feel all over his body from head to toe d) Move his arm around to see how much pain he is in e) Asked him about COWS 6. You find Amy, from Scenario 2, lying next to the sandpit not moving. You quickly look around to see if there any hazards and then you try to get her to respond to you by a) Shouting loudly to make her hear b) Asking her about Cows c) Shaking her firmly to wake her d) Asking her if she can hear you and other questions while squeezing her gently e) Rolling her on her side and tilting her head upwards 7. How would you know if Amy was unconscious? a) She would seem to be in a deep sleep and nothing you do would wake her b) She is totally unaware of her surroundings c) She gives no signs of response d) She will not talk or answer any questions e) All of the above 8. When you call for an ambulance you will use the number a) 999 b) 911 c) 000 d) 909 e) 090 9. If you are calling for an ambulance on a mobile phone you can also use the number a) 12456 b) 1223 c) 112 d) 221 e) 111 10. Amy is unconscious but she is breathing and the ambulance has been called. While you wait for the ambulance you will – a) Leave Amy on her back and raise her feet b) Turn Amy onto her stomach and place her head to the side c) Carry her into a room and sit her on a chair with her head back d) Turn her onto her side with her head tilted slightly back e) Commence CPR Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Section 5 Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation 1. Complete the following: ________________ _______________ _____________ 2. Under what circumstances would you stop performing CPR When you need to stop the bleeding When there is no longer a pulse When the casualty starts breathing When someone else takes over When a health care professional tells you to stop When you can’t continue (e.g. exhausted) _______________ Tick each correct answer/s 3. Indicate true (T) or false (F) for the following statements CPR should be performed on a casualty who is unconscious, responsive and may be gasping occasionally CPR is a combination of 10 chest compressions and 5 rescue breaths CPR can be done using chest compressions only at 100/ minute CPR is a way of keeping blood flowing to the brain until the heart is restarted Specialised equipment called an ABC is used to try to restart the heart Cardiac arrest means a person is unresponsive, unconscious and breathing normally or moving 4. If a casualty is unconscious and left lying on their back without any airway management a) Their tongue may fall against the back of the throat and block the airway and breathing b) They may not be able to swallow or cough out foreign material c) They may feel like they are suffocating d) They may not be able to talk e) Both a) and b) 5. Airway management for an unconscious person requires Head tilt chin lift manoeuvre for adults’ Head tilt chin lift manoeuvre for children aged 1 to 8 Head tilt chin lift manoeuvre for infants’ Neutral position for adults’ Neutral position for children aged 1 to 8 Neutral position for infants’ Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Indicate T/F ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Version 1 __ __ __ __ __ __ 6. Is the following statement true or false for performing CPR on children aged 1–8 years: Use the heel of one hand only for compressions, compressing to one third of chest depth and follow the basic steps for performing CPR on an adult ____ 7. To perform CPR on infants (up to 12 months of age): Tick each correct answer/s Place the infant on their back. Do not tilt their head back or lift their chin Perform mouth-to-mouth by covering the infant’s face with your mouth – remember to use only a large breath. Do chest compressions, using two fingers of one hand, to about one third of chest depth. Follow the basic steps for performing CPR 8. An AED (automated external defibrillator) can assess whether the heart (cardiac) is shockable or non shockable. ____ 9. How would you know where to place the pads of an AED (defibrillator) in an emergency a) The defibrillator will tell you b) Follow the diagram on the outer surface of the defibrillator pads c) Look up medical books d) Use your computer e) Both a) and c) 10. Draw on the diagram where the AED pads should be placed for defibrillation on an adult: Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 11. If you needed to use a defibrillator on a child aged between 1 and 8 Indicate T/F Paediatric pads and an AED with a paediatric capability should be used ____ Paediatric capability means the voltage is higher per shock ____ Paediatric pads are placed the same way as adult pads and come with a diagram ____ You can’t use adult pads on a children because they will touch ____ If the pads are going to touch you can put one on the child’s chest and one between their shoulder blades ____ 12. When doing CPR which of the 2 body’s systems are we affecting a) Skeletal and cardio vascular b) Digestive and respiratory c) Respiratory and cardiovascular d) Skeletal and respiratory e) Both a) and b) 13. What are the benefits of using a resuscitation mask during CPR Tick each correct answer/s Reduces the chance of transmission of infectious disease Prevents direct contact between the first aider and the casualties mouth face and nose Helps to stop the first aider from coming into contact with vomit, blood and saliva Stops the casualty from talking Helps the oxygen to go to the brain Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Section 6 First aid principles, procedures and application Abdominal Injury 1. Which of the following statements describes causes of abdominal injury Tick each correct answer/s 2. Blunt trauma e.g. Bicycle accidents and falls Dehydration from lack of fluid Direct contact with a frozen surface Illness and infection – unusual pain could be a sign of appendicitis or infection Wheezing and difficulty breathing Penetrating injury – like a knife injury A child has come to you crying and complaining of a sore tummy. Earlier the child had fallen off a tricycle but had not seemed to be injured. Which of the following would you do to treat the child Tick each correct answer/s Tell them to come back if it gets any worse Assess for signs of shock Give them some food in case it is just hunger Put them in a comfortable position If signs of shock or pain is escalating call ambulance Bleeding 10. A casualty has a deep laceration on the forearm and you suspect an artery has been cut how would you identify that it is arterial bleeding? a) Dark read blood gushing from the wound b) Bright red blood dripping from the wound c) Bright red spurting from the wound d) Dark red flowing from the wound 11. What is the first aid management for an external bleeding wound? Tick each correct answer/s Apply direct pressure over the wound Use pressure immobilisation technique Apply a pad and compression bandage Wrap the wound in plastic Elevate the limb 15. Respond to the following statements using True (T) or False (F) An embedded object can be removed from any part of the body as long as you can get a good grip on the object ____ A donut bandage is only necessary for people who can’t handle the pain ____ If it is a penetrating eye wound you should leave the implement in place and immediately call the emergency services ____ Elevation is not an important step in bleeding injuries ____ If your patient is not in any pain do not worry the penetrating injury as it will eventually clear up itself ____ 16. Fill in the blanks using the words below – Danger; bleeding; amputated; foot wear; recover; remove When a body part has been you must always care for the casualty and control any bleeding before looking after the amputated part. After caring for the casualty you should then the amputated part if it does not put you in . Do not any amputated parts from gloves or , these need to be treated as the amputated part. Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/2014 Version 1.0 17. List 7 steps you would take in looking after a casualty with amputation: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 18. Respond to the following statements using True (T) or False (F) Apply pad over wound and cover with firm bandage Put amputated part in clear air tight and water tight container Wash the part to ensure no bacteria is present Place part directly on ice so it can be reconnected __ __ __ __ 19. A child has been hit in the face with a ball and has a bleeding nose. What is the first aid management of this condition? a) Lie the casualty done and place a wet towel over their face b) Have the casualty sit, place a wet towel on their neck and tilt their head back c) Have the casualty sit learning forward, pinch their nose and have them breathe through the mouth d) Have the casualty sit and blow their nose to keep it clear 20. If a nose bleed continues for more than 20 mins call and ambulance. _____ Burns 21. A burn is an injury that can be caused by: Indicate T/F Tick each correct answer/s Thermal e.g. hot liquids Frozen surfaces Electricity Chemicals Gases Friction Radiation Epilepsy 22. What is the first aid management of a burn or scald? a) Stop the burning process, cool minimum 20 minutes and cover burn with non-adhesive dressing b) Apply burn cream to the burnt area and a non-adhesive dressing c) Break blisters and remove loose skin d) Remove material that may sticking to the wound and then apply burn cream e) Cover with butter after you have cooled it for 10 minutes Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Choking and Airway Obstruction 25. Answer True (T) or False (F) to the following statements When an unconscious victim is choking they will be clutching their throat and making gasping sounds __ A partial obstruction is when there is some air movement in and out of the casualty’s lungs and they are able to cough effectively. __ A completion obstruction is when there is no air movement in or out of the lungs and the casualty is unable to cough effectively. __ A person who is choking but can still cough should be encouraged not to cough in case it hurts their throat __ 26. Place the 5 vital steps in caring for a casualty with a complete airway obstruction in correct order: If casualty is unconscious check airway and start CPR Call ambulance If obstruction does not clear give 5 chest thrusts in the centre of the chest If conscious give 5 back blows between the shoulders If obstruction still does not clear continue alternating between chest thrusts and back blows 27. Before giving back blows an infant should be a) Put in a head down position being held by the feet b) Put in a head down position across the rescuers thighs c) Shaken vigorously to dislodge the blockage d) Given a lot of water to drink e) Both a) and c) 28. In the case of choking and airway obstruction, children between 1 and 8 years of age, should be a) Treated the same way as an adult b) Treated the same way as an infant c) Only given chest thrusts d) Only given back blows Crush Injuries 29. If you found a child was pinned under a cupboard that had fallen on them you would treat them as a crush victim by? a) Using a tourniquet to stop bleeding b) Remove the cupboard as quickly as possible c) Calling the ambulance d) Leaving the cupboard on them and waiting for ambulance e) Both b) and c) Diabetes 30. Diabetes is when – a) The supply of oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues is insufficient due to the lack of effective circulation. b) There is no air movement in or out of the lungs. c) Insulin is no longer produced or not produced in sufficient amounts by the body. d) There is a complete or partial loss of consciousness after a head injury. e) The blood supply to part of the heart muscle is suddenly blocked. 31. What medication would a Type 1 Diabetic carry with them? a) EPIPEN b) Insulin c) Aspirin d) ANAPEN e) Cough Mixture Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 32. Answer True (T) or False (F) to the following statements If you know what you are doing it is okay to inject a casualty who is low in blood sugar with insulin The fastest way to help a hypoglycaemic casualty is to make them a salad sandwich Orange juice, cola, lemonade or strong cordial would assist a person currently hypoglycaemic Making a person run around the block will reduce the amount of sugar in their system __ __ __ __ Drowning 33. Fill in the gaps with the following words CPR; Resuscitated; airway; restricted; oxygen; drowning; brain; near-drowning occurs when a casualty’s breathing is because their airway is immersed win water or other liquid, interrupting the supply of to the . This can also cause other serious medical complications, even is the casualty is successfully ___________. Early rescue, clearing their casualty’s chance of surviving a and providing incident. are the vital steps that increase a 34. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of a near drowning casualty: Tick each correct answer/s Casualty’s airway is immersed in water or other liquid Coughing or difficulty breathing Vomiting No response to talk or touch No breathing normally 35. Answer True (T) of False (F) to the following statements CPR should be commenced immediately on a suspected drowning victim If a victim has water present in their mouth stop giving CPR immediately Leave the drowning victim in the water and commence CPR immediately Pump their stomach so they cough up water It is your duty of care to rescue a drowning casualty no matter what the circumstances You would need to complete a form 27A – reporting of a serious death or injury in the case of a near drowning __ __ __ __ __ __ Envenomation 36. Put against the signs and symptoms associated with the Illness or Injury. (Hint! Some signs and symptoms will be included in more than one column) SIGNS & SYMPTOMS Snake bite Spider bite Headache Puncture or scratch marks Tingling around mouth Sting Marks Abdominal Pain Limb weakness or paralysis Blurred or double vision Severe muscle cramps Difficulty breathing Sever Pain Loss of consciousness Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Jellyfish sting 37. Fill in the following blanks using the following words where appropriate using: Yes, if allergic, if severe, if heat does not help Treatment Ambulance 000 Medical aid Pressure immobilisation Ice pack or cold compress Hot water Vinegar Snake Funnel web or mouse spider Red back spider Other spiders Bee, wasp, ant Tick Dog, cat Jellyfish in tropics Jellyfish in nontropics Blue- ringed octopus Cone Shell Fish Spine Stings Stingray Epilepsy and Seizures 38. Use the following words to complete the sentences below: Abnormal; focal; 40; 2; seizures; diagnosed; disrupted; electrical activity Epilepsy occurs when the of the brain is . Epilepsy is when a person has repeated . There are different types of epileptic seizures, which can be divided into major groups. Partial or seizures start in one part of the brain and may spread to other parts of the brain. Generalized seizures are caused by activity throughout the whole brain at the same time. 39. A seizure may occur in Tick each correct answer/s a person with epilepsy almost all pregnant females almost any condition effecting the brain e.g. head injury, stroke all adults submerged in water for more than 10 minutes association with some poisons and drugs children under 5 years associated with fever 40. You must call an ambulance in which of the following circumstances of a casualty suffering a seizure? \ Tick each correct answer/s Seizure lasts more than 5 minutes Repeated seizures occur When the casualty has a sprained ankle Casualty remains unconscious for more than 5 minutes after seizure stops Casualty is pregnant When a seizure lasts less than 5 minutes and is conscious It is the casualties first seizure You feel uncomfortable dealing with a seizure Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 41. A child in your care, who is a known epileptic, suddenly suffers a major seizure. You should: Tick each correct answer/s Move the child from danger or move objects that could cause injury Hold the child’s mouth open so they can breathe Roll them into the recovery position when they stop seizing and monitor airway and breathing Hold them down so they can’t hurt themselves Reassure them as they will be dazed and confused Place a folded handkerchief between their teeth to prevent them biting their tongue 42. Is the following statement True (T) or False (F)? Febrile convulsions are usually associated with children with a fever between the ages of 6 months and 6 years. _________ Eye and Ear Injuries 43. Is this statement True (T) or False (F)? A floating object in the eye maybe removed by flushing it out with water or a saline solution. ________ 44. A child has a major eye injury where a piece of stick is poking out of the eye. Which one of the following would you do? a) Flush it with water b) Apply ointment c) Remove the stick immediately d) Wrap a bandage over the stick to hold it in place e) Get a medical professional to treat the child 45. When should you urgently call an ambulance in the case of ears injuries? Tick each correct answer/s When there is drainage coming from inside the ear. When part of the ear has been cut off When there is a ruptured ear drum When there is excessive wax build up When foreign matter like dirt or sand has got into the ear. 46. Which of the following may cause bleeding from the ear? Blast injuries Internal bleeding Head injuries Back injuries Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Tick each correct answer/s Version 1 Skeletal Injuries 47. A fracture is a) A bone that is dislodged from a joint b) A bone that is broken or bent and there is also soft tissue damage. c) A major head injury d) Where a body part is subject to a high degree of pressure from being squeezed e) Both a) and d) 48. Place the words below in the correct box for each type of skeletal injury Closed (simple); Open (compound); Complicated; Dislocation 49. Which of the following would be steps you would take for a child who has fallen off a climbing frame and you suspect a broken leg Tick each correct answer/s Keep the person still – do not move them unless there is an immediate danger Call 911 for an ambulance. Attend to any bleeding wounds first Try to straighten the broken bone Straighten the arm out so you can apply a splint to support the arm Keep the child still and provide support for the arm like a pillow or if possible a sling 50. A collar a cuff bandage is used for which of the following injuries? Head Injury Broken Ankle Collar Bone Injury Little finger injury Nose injury Tick each correct answer/s 51. Insert the missing words – Joint, doubt, position, fracture, dislocation A occurs when a bone is displaced from its normal at a . It can be difficult to tell if an injury involving a body joint is a dislocation or a fracture. If there is any you should always treat as a . Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 52. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of dislocation: Pain or tenderness Swelling inflammation or bruising Deformity Symptoms of asthma Seizure Tick each correct answer/s Head Injury 53. A concussion is… a) A brief, complete or partial loss of consciousness after a head injury b) Caused from a blast or loud noise c) Where the brain is no longer receiving oxygen d) Only caused by sporting activities e) Will cause death unless treated by a medical person 54. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of a Head Injury? Nausea and vomiting Feeling drowsy Loss on consciousness Seizure Increased appetite Blood or fluid coming from the foot Temporary confusion or memory loss Neck and Spinal Injuries 55. Which of the following are steps in assisting an unconscious casualty with a spinal injury: Tick each correct answer/s Call ambulance Move head from side to side to see if they complain of pain Follow Basic Lifesaving Support steps Handle casualty gently with no twisting and minimal head movement of head, neck and torso Turn Casualty onto their side to ensure airway is clear If airway is clear get them to stand and check for pain Do not use cervical collars or other spinal immobilisation devices unless trained Filling in a form 27a serious injury or death form 56. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of a spinal injury? Tick each correct answer/s Numbness or tingling in hands or feet Hunger Weakness or loss of movement History of incident Tenderness at injury site Thirst 57. Is this statement True (T) or False (F) Breathing is always a priority over injury Heat and Cold Related Illness 58. Factors which can cause heat illnesses are Hot conditions with high humidity Physical exertion Infection Not enough fluid to drink Drugs which affect heat regulation Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Tick each correct answer/s Version 1 Poorly ventilated environment Wearing heavy dark clothing on hot days 59. Hypothermia is when a person’s Indicate T/F Core temperature is below 35degress Celsius Core temperature is above 40 degrees Celsius Temperature is falling and the organs start to shut down Very high temperature may cause unconsciousness and death Body will stop shivering and they will become confused and have trouble speaking 60. Match the words below with each group of statements Hypothermia; Dehydration; Heat exhaustion; Heat stroke Lie person down Loosen or remove clothing Moisten skin Fan skin Give sips of water if conscious Call 000 Keep in shade Move to shelter Call Ambulance Insulate body from cold ground Remove wet clothing Wrap body and head with warm, dry cover Don’t rub or massage Rewarm with body to body contact Place in cool environment Call 000 Be ready to resuscitate Apply wrapped ice packs to neck groin and armpits Moisten skin and fan repeatedly Lips and nasal passages become dry Urination stops Kidney’s eventually fail Body can’t remove toxic substances Life threatening for elderly babies and children Minor Skin Injuries 61. Place the appropriate word - abrasion or incised wound - alongside each statement Surface layers of the skin has been broken Call an ambulance as soon as possible Clean wound with sterile gauze Use an antiseptic Apply pressure directly to the wound Remove debris Rinse the wound with sterile saline or flowing tap water Caused by sharp objects, e.g. Knives, shards of glass, slicing into the skin Could lead to significant blood loss Cover cleaned wound with non-stick sterile dressing Cover wound with a sterile dressing, continue to apply direct pressure Raise the injured area above the level of the heart Needle Stick Injuries 62. Answer True (T) of False (F) to the following statements Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1 Occurs when the skin is punctured by a used needle Always recap or snap used needles Check reporting procedures in your workplace Latex gloves will protect you against needle stick injuries HIV, Hepatitis B and C not survive outside the body Poisoning 63. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of poisoning: Nausea and vomiting Burning pain in mouth or throat Skin will be cold white and hard Blurred vision Difficulty breathing Burns at entry and exit points Loss of consciousness Tick each correct answer/s 64. For all poisoning situations you should a) Suck out the venom b) Make the casualty vomit c) Give large amounts of milk d) Call poisons information 131126 e) Raise the injured area above the level of the heart 65. 1. 2. 3. 4. Match the treatment with the type of poisoning: Swallowed Poison a) Flush skin with cool running water Poison on the skin b) Give small sips of water Inhaled Poison c) Hold eyelid open and flush with running water Poison in the eye d) Get to fresh air as soon as possible if safe to do so 1. ____ 2. _____ 3. ____ 4. _____ Shock 66. Insert the missing words – Oxygen, Insufficient, Nutrients, Circulation Shock occurs when the supply of ________ and __________ to the body’s tissues is ___________ due to the lack of effective ____________. 67. Which ONE of the following are signs and symptoms of a casualty in shock: Rapid or weak pulse; Pale, cool, sweaty skin; Feeling anxious or restless; Feeling confused; Deteriorating level of consciousness Burning pain in mouth or throat; Skin will be cold white and hard; Blurred vision; Difficulty breathing Pain or tenderness at injury site; Swelling, discolouration or bruising; Loss of power or movement in affected area Numbness or tingling in hands or feet; Hunger; Weakness or loss of movement; History of incident; Tenderness at injury site Casualty’s airway is immersed in water or other liquid; Coughing or difficulty breathing; Vomiting; No response to talk or touch 68. If a casualty is in shock you need to Control any bleeding Call ambulance If casualty is unconscious follow Basic Life Support steps Reassure casualty Assist them to rest in a comfortable position Maintain their body temperature Monitor and record vital signs Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Tick each correct answer/s Version 1 Give oxygen if available and safe to do so Complete a form 27A serious injury or death form Musculoskeletal injuries 69. Complete the words which identify the treatment for soft tissue injuries R= I= C= E= R= 70. A sprain refers to an injury involving a: A strain refers to an injury involving a: 71. Which of the following are signs and symptoms of a Sprain or Strain: Burning pain in mouth or throat Pain or tenderness at injury site Coughing or difficulty breathing Swelling, discolouration or bruising Loss of power or movement in affected area No response to talk or touch Signs and symptoms of shock Tick each correct answer/s 72. Match the correct injury with the right description: 1. Sprain A. Occurs away from the and involves torn or over stretched muscle or tendon 2. Strain B. Soft tissue injury that involves the skin and nearby tissue 3. Bruise C. Involves ligaments and other soft tissue around the joint 4. Dislocation D. Bone has been displaced from its normal position at the joint 1.___ 2.___ 3.___ 4.___ Assessor Guide – HLTAID004 © Copyright Synergy Education Group Pty Ltd Created on 03/01/14 Version 1