worm vocab only - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
advertisement

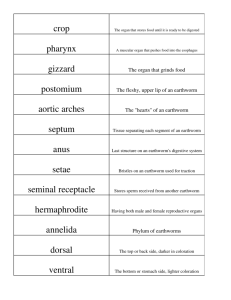
WORM VOCAB ONLY One of the external bristles on annelids ______________ Seta (Setae) A pair of nerve clusters that serve as a brain at the anterior end Cerebral ganglia of some invertebrates _________________ A thickened section around clitellum an earthworm’s body that ______________ produces mucous for reproduction In a flatworm, a cell that collects nitrogen waste and excess body water for the excretory system and excretes it through the skin ______________ Flame cell An organism that produces both male and female gametes (sperm & eggs) _________________ hermaphrodite An infolding of the intestinal wall of an earthworm that increases surface area to absorb more nutrients ________________ typhlosole Fleshy flap of skin that overhangs the mouth of an earthworm and senses light/dark ________________ prostomium A NON-CELLULAR LAYER in parasitic round worms that protects them from the host’s digestive and immune system cuticle (also seen in earthworms)_________________ A structure in a female or hermaphrodite Seminal receptacle that receives sperm ________________ A continuous sheet of FUSED CELLS that covers the external surface of a fluke or tapeworm & protects the worm from the host’s digestive and immune system __________________ tegument Tubule through which some invertebrates (like segmented and round worms) eliminate nitrogen waste _________________ nephridia Dividing walls that separate the coelom into compartments in an earthworm ________________ septa Type of circulatory system in which blood is contained in vessels______________ closed Type of development in which young start as an immature larva and must undergo metamorphosis to become adults indirect _______________ Type of reproduction in which offspring are produced by combining genetic material from 2 parents ________________ sexual Muscular part that pulls food into the digestive system______________ pharynx 5 pair of muscular tubes which connect the dorsal and ventral blood vessels and force blood Aortic arches through the circulatory system ________________ A knob shaped organ bearing hooks and suckers that lies at the anterior end of a tapeworm ________________ scolex One of the many body segments of a tapeworm containing reproductive organs proglottid ______________ The structure that stores soil waiting to be crop digested in earthworms _________________ A muscular region in the digestive tract of earthworms that crushes and grinds food gizzard ________________ The host in which the adults of a parasitic worm live and reproduce ______________ Primary host A disease characterized by muscle pain and stiffness caused by a parasitic blood fluke of schistosomiasis the genus Schistosoma _________________ A carbohydrate found in the cocoons of earthworms and the exoskeletons of some chitin arthropods ________________ Structure that stores sperm made to give away to other worms ______________ Seminal vesicles Type of coelom seen in earthworms in which the body cavity is lined on both sides by mesoderm _________________ Eucoelom or “true” coelom Flatworm phylum that includes Planaria, Platyhelminthes flukes, and tapeworms ________________ Ring around the body of an earthworm that produces mucous for reproduction clitellum ______________ Traction bristles on the ventral surface of an earthworm _________________ setae Round worm phylum that includes Ascaris, pinworms, hookworms, and filarial worms________________ Nematoda Reproductive organ that produces eggs ______________ ovary A disease caused by a parasitic round worm of the genus Trichinella; characterized by muscle pain and stiffness trichinosis _________________ Opening for digestive waste in an earthworm ________________ anus Reproductive organ that produces sperm testes ______________ ganglia A cluster of nerve cells_______________ Segmented worm phylum which includes earthworms and leeches ________________ Annelida Development in which offspring hatch or are born with a similar shape as the adult form and must just grow bigger ______________ direct Type of symmetry in which dividing the animal produces bilateral 2 mirror images _______________ Ability to regrow lost body parts regeneration ________________ Type of reproduction in which offspring are produced from the genetic material of only asexual one parent______________ Body system that removes nitrogen waste and maintains the balance of ions/water excretory _______________ Digestive organ in an earthworm where intestine nutrients are absorbed ________________ Shared one opening digestive/circulatory space seen in Planaria Gastrovascular ______________cavity Joining of sperm and egg outside the mother’s body_______________ External fertilization Maintaining the balance of water and ions in the body _______________ osmoregulation Concentration of a “brain” and sensory organs at the anterior end of an cephalization animal______________ Outside body covering on an animal_______________ integument Body system that exchanges gases with the environment________________ respiratory Line that runs from the male genital pore to the clitellum along which sperm Sperm groove travels______________ Type of coelom seen in flatworms with no space around the internal organs_______________ acoelom Opening for sperm leaving an earthworm to Male genital pore be given away ______________ coelom Space around body organs ______________ Organism with spiral determinate cleavage whose blastopore becomes its mouth ________________ protostome Oligochaeta Class to which earthworms belong ______________ Organisms without a backboneinvertebrates _______________ Kind of circulatory system in which blood is NOT contained in vessels open and flows loose inside the coelom ____________ Type of coelom in which there is NO space and mesoderm Acoelom fills the area between ectoderm ____________________ and endoderm Type of coelom in which mesoderm Is found lining the outside body wall and surrounding the gut __________________ eucoelom Type of coelom in which mesoderm lines the outside body wall but is pseudocoelom NOT found around the gut ____________________ Body system for removing nitrogen waste excretory ____________________ Body system for transporting nutrients and oxygen around circulatory in body ____________________ Body system that exchanges respiratory gases with the environment __________________ Body system that maintains the balance of water/ions (osmoregulation) excretory __________________ Body system for receiving info nervous about the environment and responding ________________ Body system for obtaining nutrients ____________________ digestive Body system that produces offspring reproductive __________________ Body system that moves the organism or moves substances inside the body muscular __________________ Body system that provides skeletal support and protection ______________________ Body system that makes hormones endocrine which control other body systems ________________ Body system that deals with integumentary what covers the animal __________________ Type of cleavage pattern in which cells stack on top of each other and Indeterminate decide later on what they will become ______________ radial cleavage A skeleton formed by putting fluid into the coelom space __________________ Hydrostatic skeleton Cleavage pattern in which cells twist as they divide and decide Determinate early what they will become ____________________ spiral cleavage Waste produced in body cells by the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids and handled by the excretory system Nitrogen waste _______________________________ Label the directions DORSAL A.__________________ POSTERIOR D_______________ ANTERIOR __________________B VENTRAL ___________________ C Animation from: http://bestanimations.com NAME THE TYPE OF COELOM Pseudocoelom Images from: Eucoelom http://www.lander.edu/RSFOX/310images/310bilatImage.html Acoelom NAME THE TYPE OF SYMMETRY Radial Bilateral Images from: http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/labs/radial.jpg http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/labs/bilateral.jpg http://vilenski.org/science/safari/animals/other/classify_animals.html Asymmetry