Clinical findings
advertisement

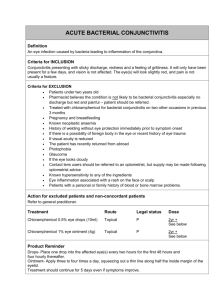
Disease of the conjunctiva China Medical University NO.4 Affiliated hospital Ophthalmology; Ophthalmology hospital of China Medical University Conjunctivitis The most common extraocular disorder Etiology: infection of microorganism physical injuries chemical injuries allergic disorder immunological disorder nutritional deficiency Conjunctivitis Classification According to the cause: bacterial, chlamydial, viral, fungal, allergic conjunctivitis According to the course: acute, subacute and chronic Conjunctivitis Clinical manifestation Symptoms – Foreign body sensation – Scratching – Burning – Fullness around the eyes – Itching and tearing – pain and photophobia Signs of conjunctivitis • • • • • • • • • • • • Hyperemia Tearing Exudation Pseudoptosis Papillary hypertrophy Chemosis Follicless Pseudomembranes Ligneous conjunctivitis Granulomas Phlyctenules Preauricular lymphadenopathy Physical sign • Hyperemia • Hyperemia Ciliary flush Secretion • Bacterial and purulent serous, mucous • Viral watery or serous • Allergic one or xerophthalmia ropy filamentous Conjunctival edema Subconjunctival hemorrhage Physical sign papillary hyperplasia: palpebral conjunctival epithelium follicular formation: accumulation of lymphocyte beneath the conjunctival epithelium Physical sign pseudomembrane or membrane : the exudation rich in fibrin from palpebral conjunctiva . Pseudomembrane: in baby and children, adenoviral, neonatal inclusion, streptococcal conj. True membrane: diphtheritic conj. Conjunctivitis Examination and diagnosis • Clinical examination • Cytologic examination smear of conjunctival and scaling smear of conjunctiva • Bacteriological examination bacterial culture and drug sensitive test • Virus isolation and its antigenic detection Conjunctivitis Principle treatment • Remove pathogenic cause, take local phamacotherapy as major, systemic treatment as supplement if necessary • 1)instillation of eyedrops 2)instillation of ointment 3)washing of conjunctival sac 4)systemic treatment • Prevention Hyperacute Bacterial conjunctivitis Hyperacute purulent conjunctivitis with the strongest infectivity and large destructibility Etiology: diplococcus gonorrhoeae adult: auto infection children: touch infection newborn: direct infection Hyperacute Bacterial conjunctivitis Clinical findings 1)incubation period: 10h-2, 3d, acute onset 2)opthalmalgia, photophobia, tearing 3)swelling of the eyelids palpebral and bulbar hyperemia and chemosis secretion: serous-bloody-purulent-nong lou yan inflammatory pseudomembrane preauricular lymphadenectasis corneal ulcer and perforation Hyperacute Bacterial conjunctivitis Diagnosis: clinical findings lab examination(Gram’ stain, G- diplococcus) Treatment: topical and systemic one is the same important Prevention be isolated to avoid infection and epidemic Bacterial conjunctivitis Acute catarrhal conjunctivitis Clinical finding:acute onset(1-3days), both eye tearing, foreign body and burning sensation conjunctival hyperemia, purulent secretion, palpebral swelling, spots of subconjunctival hemorrhage Ill process: 2 weeks Bacterial conjunctivitis Acute catarrhal conjunctivitis Bacterial conjunctivitis Chronic catarrhal conjunctivitis Etiology bacterial infection: acute-chronic or infection of bacterial with weak toxicity – non-infectious environment factors: dust, chemical smoke or gas and irritating eye drugs – complicated from other disorders Bacterial conjunctivitis Chronic catarrhal conjunctivitis Clinical finding: chronic onset, both eye itching, foreign body and asthenopia or no symptoms conjunctival hyperemia mucous secretion papillary and follicle hyperplasia Treatment: give management according to different causes Bacterial conjunctivitis Chronic catarrhal conjunctivitis Chlamydial conjunctivitis Chlamydin psittaci: Chlamydia trachomatis: antigen:ABCBa DEFGHIJK trachoma genitourinary system inclusion conjunctivitis clinical findings Acute or subacute stage(1-2mon): photophobia, tearing, foreign body sensation 1)palpebral and bulbar conjunctival hyperemia 2)ropy secretion 3)papillary hyperplasia, follicles formation 4)corneal epithelitis be cured without scar left clinical findings • Acute stage Clinical findings Chronic stage: superinfections or concomitant bacterial infections 1)Conjunctival hyperemia 2)ropy secretion 3)papillary hyperplasia, follicles in upper fornix and palpebral conjunctiva conjunctival thickening scar white luster like tenden 4)corneal epithelitis trachomatous pannus Clinical findings • Chronic stage Classification Our country I progressive stage papillae and follicles, upper fornix is blurred, corneal panus II regressive stage scar,a little active lesion III complete cicatricial stage scar, no active lesion and infectivity Mac Callan’s I Early stage of infiltration hyperemia and thickening early follicle and corneal panus II active stage papillae and follicles, corneal panus III precicatricial stage IV cicatricial stage Equela and complication Entropion and trichiasis Blepharopatosis Symblepharon (lower fornix) Parenchymatous xerosis of conjunctiva Chronic dacryocystitis Corneal pannus Diagnosis 1)the vessels of upper fornix and palpebral conjunctiva are blurred, congested, papillary hyperplasia or follicle formation or both 2)corneal pannus 3)scar 4)trachomatous inclusion Diagnosis on the basis of the first plus one of other three antigenic test Scar corneal pannus Treatment Topical Systemic tetracyclin, erythromycin sulfadiazine rifampin Operative: sequelae and complication Viral conjunctivitis Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis Acute onset, strong infectivity, may be sporadic or epidemic Etiology: adenovirus, type 8, 19, 29 and 37. Viral conjunctivitis Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis Clinical findings: 1)incubation period: 5-7d. 2)foreign body sensation, itching, pain, photophopia and tearing 3)palpebral edema, conjunctival hyperemia and chemosis, less and watery secretion, follicles in palpebral and fornix conjunctiva, preauricular lymphadeectasis and tenderness 4)be cured after one week exacerbate: superfial punctate keratitis Viral conjunctivitis Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis Diagnosis: Acute folliclar cinjunctivitis superfial punctate keratitis preauricular lymphadenectasis neutrophial Treatment: no specific drug 1)antiviral:topical(mainly) and systemicacyclic 2)antibiotic Viral conjunctivitis Epidemic hemorrhagic conjunctivitis Fulminant epidemic ocular infections Etiology: entero-virus type 70, picornavirus Coxsackie virus type A 24 Viral conjunctivitis Epidemic hemorrhagic conjunctivitis Clinical findings: 1)incubation period: 24hr 2)ill course: self-limited, 10d or shorter 3)ophthalmagia, foreign body sensation, photophopia and tears 4)eyelid and conjunctiva red and swollen, watery secretion, follicular hyperplasis of palpebral conjunctiva, patchy hemorrhage on bulbar conjunctiva, preauricular lymphadenectasis 5) Transient fine punctate epithelial keratitis Immunologic conjunctivitis Vernal conjunctivitis (Clinical findings) Symptom:extreme itching Sign 1)palpebral type: papillary hyperplasia in the upper palpebral conjunctiva that like oval flat cobblestone, eosinophillia in secretion 2)corneal limbal type: collid tubercles at the corneal limbus 3)mixed type: Vernal conjunctivitis Vernal conjunctivitis Treatment: 1)self-limited, no vision affected 2)general treatment: keep away proble sensitinogen 3)medical treatment: natrii cromoglycas corticosteroid Allergic conjunctivitis Immediated allergic antigen: pollen, contact lens, etc. Delayed one: various drug Clinical findings: immediate type: dermatitis of palpebral skin, blepharitis, mild infiltrative conjunctivitis Allergic conjunctivitis Lab examination: degenerative epithelial cell, few polynuclear cells and mononuclear cells in secretion Treatment: 1)find out and get rid of sensitinogen 2)corticosteroid 3)3% boric solution 4)anti-allergic agents Phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis Etiology: delayed reaction to protein of microorganism, mostly to mycobecterium tuberculosis and staphylococcus aureus Clinical findings: herpetic tubercle may appear on the bulbar conjunctiva or limbus. Pterygium Etiology: unclear, outdoor work Clinical findings: 1)hypertrophic bular conjunctiva and its subconjunctival tissue invade onto the cornea with the shape of tiangle 2)composed of head, neck, body. 3)progressive, stationary 4)differentiated with pseudopterygium Treatment: operation Pingueculae A degenerative lesion of the bulbar conjunctiva caused by the effect of ultraviolet rays Clinical findings: a kind of white–yellow amorphous subepithelial deposition near to the limbus Treatment: no needed • Pterygium Pingueculae Conjunctival concretion • Concrement on the palpebral conjunctiva • Old or those with chronic conjunctivitis • White-yellow deposit • Treatment: no need be rejected Primary benign tumors of the conjunctiva nevi Dermolipoma angioma Primary malignant tumors of the bulbar conjunctiva Squamous cell carcinoma Malignant melanoma Subconjunctival hemorrhage • Caused by vascular rupture beneath the bulbar conjunctiva or by osmotic increase of vascular wall • Treatment: 1)find out the cause 2)good explanation