IB Physics 2 Summer Reading Part 1
advertisement

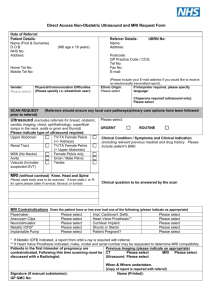
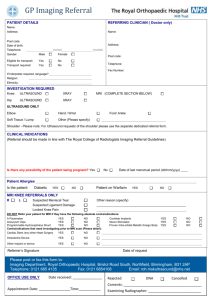
Name: IB Physics 2 Summer Reading 2015 This reading is from the Oxford IB Physics Course Companion. Note: Some of the terms used in this section are ones you have not learned about… yet. But don’t worry - we will be studying them in the coming year! C.3 Fiber Optics Structure and use of optic fibers 1) When were optic fibres first developed for communication purposes? When was the idea of sending light along a “light pipe” demonstrated? 2) What is a twisted pair? What is the major disadvantage of this method? 3) What is a coaxial cable? What is one advantage and one disadvantage of this method? 4) Describe the basic operation of optic fibers. 5) Of what 3 changes do digital signals consist? 6) Name 3 advantages of optic fibers. 7) Name the 3 types of fibers. Attenuation and dispersion 8) What is role of a repeater? 9) What is attenuation? 10) What is dipersion? 11) What is the Bel scale? 12) Why do we use decibels? What is meant by a change in power of 10 dB? 13) Write the attenuation formula and identify all variables. 14) Briefly describe how absorption causes attenuation. 15) Briefly describe how scattering causes attenuation. 16) How does scattering cause the sky to appear blue? 17) Briefly describe material dispersion. 18) Briefly describe waveguide (or modal) dispersion. 19) How do graded-index fibers correct for this effect? C.4 Imaging the body X-Rays 20) Who discovered X-rays? When? 21) What is the basic principle behind X-ray imaging? 22) When the intensity of X-rays is high, the photographic plate or sensor is exposed (darkened). With this in mind, why do bones appear white on an X-ray image? 23) How are X-rays produced? 24) What are the 4 mechanisms for removing photons in a material? (we will study the specifics during class) 25) What is attenuation? 26) State and explain the variables for the exponential intensity equation. 27) What is the difference between the linear absorption coefficient and mass absorption coefficient? 28) Why does the equation only work for monochromatic (single wavelength) X-ray beams? 29) How is the concept of “half thickness” similar to “half life” used in decay equations? 30) What is the purpose of the aluminum filter? 31) What is the purpose of the collimator? 32) What is the purpose of the grid system of lead plates? 33) What is the purpose of the two fluorescent screens? 34) What method can be used to improve contrast? 35) What are the advantages of X-rays compared to MRI scans? 36) What are the disadvantages of X-rays compared to MRI scans? 37) What are CT and CAT scans? When were they invented? 38) How do the X-ray tube and detectors operate to create an image? How is it different than a standard X-ray? 39) What are the advantages and disadvantages of this method? Ultrasound in Medicine 40) What is ultrasound? 41) What is the special property of piezoelectricity? 42) What is a piezoelectric transducer? 43) Why is a gel used between the probe and skin? 44) After a single pulse of ultrasound is sent, what happens next? 45) How can the size and location of an organ be determined? 46) What is the acoustic impedance of a material? 47) Which has a higher acoustic impedance, bone or muscle? 48) What does the ratio of reflected to initial intensity tell us? 49) Name two other uses of ultrasound that are the typical bone/tissue images. 50) Name 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of ultrasound. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) 51) What is the difference between NMR and MRI? 52) Briefly explain the concept of an MRI. 53) MRI images are good for what parts of the body? Specifically, what disorders are typically diagnosed with MRI? 54) What property of protons is important in NMR? 55) What changes occur in water when going from normal conditions to an imposed magnetic field? 56) What happens if a radio frequency of the appropriate frequency is applied? What is the name for this frequency? 57) As the protons precess, what does their changing magnetic field produce? 58) In an actual MRI, why is a gradient field added? 59) When the protons “relax” after the radio frequency is turned off, what information is gathered? 60) Name 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of MRI scans.