Input and Output
advertisement

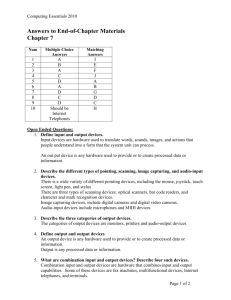
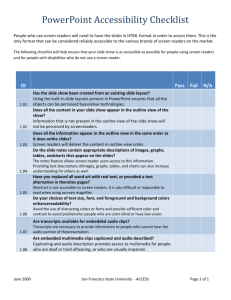
Chapter 6 Input and Output Professor Michael J. Losacco CIS 1150 – Introduction to Computer Information Systems Overview Chapter 6 Define Input Describe Keyboard Entry Discuss Pointing Devices Describe Scanning Devices Discuss Image and Audio Capturing Devices Define Output 2/26 2 Overview Chapter 6 Discuss Monitor Features and Types Define Printing Features and Types Discuss Audio Devices Discuss Video Devices Define Combination Input/Output Devices Discuss Ergonomics 3/26 3 What is Input? Chapter 6 Translate Words, Sounds, Images, Actions Into a Form that the System Unit Can Process Input Devices Include: Keyboards Mice and Pointing Devices Scanning Devices Audio-input devices 4/26 4 Keyboard Entry Chapter 6 Traditional Notebook Virtual Tablets, Smartphones Thumb Smartphones, Handhelds Predictive Text Predict Word Being Typed as It’s Typed 5/26 5 Pointing Devices Chapter 6 Mouse Trackball, Trackpad Touchscreen Game Pad, Joystick Simulation 6/26 Pointing Devices Chapter 6 Stylus Handwriting Recognition Translates Handwritten Characters Graffiti 7/26 Scanning Devices Chapter 6 Optical Flatbed Document Portable Card Readers Magnetic 8/26 Scanning Devices Chapter 6 Bar Code Readers Uses Laser Beam to Read Bar Codes Vertical Lines / Spaces of Different Widths RFID Readers Reads Tag Via Radio Waves Uses Manage Inventory Toll Payments 9/26 Scanning Devices Chapter 6 Character and Mark Recognition Devices Magnetic-ink Character Recognition OCR (Optical-character Recognition) Characters’ Shapes Determined Converted Into Editable Text OMR (Optical-mark Recognition) 10/26 Image Capturing Devices Chapter 6 Digital Cameras Records Images Digitally Digital Video Cameras Records Motion Digitally Webcam 11/26 Audio-Input Devices Chapter 6 Convert Sound To Digital Human Voice, Music Voice Recognition Systems Use Microphone Sound Card Special Software Contextual Use Challenges ESL, Women, Accents, Children 12/26 Mobile Data Collection Chapter 6 Collect Data Where Transaction Occurs Capture Data Directly From Source Data Transfer Wireless / Docking Station Advantages Saves Time Lowers Labor Cost Reduces Errors Available Sooner for Analysis 13/26 What is Output? Chapter 6 Processed Data or Information Types Text Graphics Audio Video 14/26 Monitors Chapter 6 AKA Screen or Display Features Resolution Pixel (Picture Element) Dot Pitch Contrast Ratio Size Aspect Ratio 15/26 Monitors Chapter 6 Flat-panel Monitors Most Widely Used Today Thinner More Portable Require Less Power to Operate Liquid Crystal Display TFT-LC AMOLED 16/26 Monitors Chapter 6 E-book Readers Kindle, Nook Digital/Interactive Whiteboards High-definition Television (HDTV) LCD – Brighter Screen, Longer Life Plasma – Rich Color, Low Lighting, Wide Angle LED – Thinner, Bright Lighting, Less Power 17/26 Monitors Chapter 6 Bit Depth Number of Bits Used to Store Pixel Data Determines Number of Colors Displayed 32-bit Video Card 232 = 4.3 Billion Colors 18/26 Printers Chapter 6 Hardcopy Features Resolution DPI (Dots per Inch) Color Speed PPM (Pages per Minute) Memory Duplex Printing 19/26 Printers Chapter 6 Ink-jet Laser Personal or Shared Cloud Thermal Plotters 20/26 Audio and Video Devices Chapter 6 Speakers and Headsets Portable Media Players AKA Digital Media Players Apple iPod, Creative Zen Mobile Digital Television (Mobile DTV) Watch TV on Computer, Smartphone 21/26 Combination Devices Chapter 6 Multifunctional (MFD) Scan, Print, Fax, Copy Internet Telephones Voice-over IP (VoIP) AKA Internet Telephony Vonage MagicJack Skype 22/26 Combination Devices Chapter 6 Robots Artificial Intelligence (AI) Simulate Human Senses, Thought Processes, Actions Robotics Perception System Industrial Mobile Household 23/26 Combination Devices Chapter 6 Virtual Reality Headgear and Gloves Simulate Three-dimensional Environment Stereoscopic Screens Sensors Collect Data About Hand Movements Create Immersive Experience 24/26 Ergonomics Chapter 6 Human Factors Related to Things People Use Fit the Task to the User to Avoid: Eyestrain and Headache Back and Neck Pain Repetitive Strain Injury Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 25/26 Careers in IT Chapter 6 Technical Writer Prepare Instruction Manuals, Technical Reports Translate Technical Information Easily Understandable Instructions or Summaries Communications / Journalism / English Degree Specialization in, or Familiarity with, a Technical Field Annual Salary of $41,000 - $78,000 26/26