Lesson 5 & 6 - CA Sri Lanka
advertisement

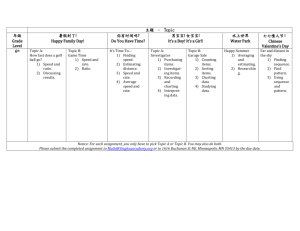
MGT 30725 PROJECT MANAGEMENT LESSON 5 AND 6: PROJECT PLANNING – TIME AND COST PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT Conducted By: Dr. Madhu Fernando, PMP, DBA, MEng. 1 PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT Project Time Management Process Plan Schedule Management Define Activities Sequence Activities Estimate Activity Resources Estimate Activity Duration Develop Schedule Control Schedule 2 PLAN SCHEDULE MANAGEMENT Process of establishing the policies, procedures, and documentation for planning, developing, executing, managing, and controlling the project schedule. 3 DEFINE ACTIVITIES The Process of identifying and documenting the specific actions to be performed to produce the project deliverables. 4 SEQUENCE ACTIVITIES The Process of identifying and documenting the relationships among the project activities. 5 ESTIMATE ACTIVITY RESOURCES The Process of estimating the type and quantities of the material, human resources, or equipment, or supplies required to perform each activity. 6 ESTIMATE ACTIVITY DURATION The Process of estimating number of work periods required to complete individual activities with estimated resources. 7 PROJECT ESTIMATING TECHNIQUES Estimating method Analogous estimating Parametric estimating Three-point estimating Bottom-up estimating Description Generally used at the start of the project when not much is known. Compares the current project with past similar projects. A quick and relatively easy method of estimating, although not terribly accurate. Used for estimates that are quantitatively based, such as dollars per square foot or number of installations per day. A relatively simple method, but not every activity or cost can be estimated quantitatively. Accounts for uncertainty associated with estimating by determining an optimistic (best case, represented by O), most likely (represented by M), and pessimistic (worst case, represented by P) scenario. The most likely estimate is weighted most heavily. The equation is (O + 4M + P) / 6 Used when there is significant detail about the activity. A detailed assessment of the resources, capabilities, and amounts are used to determine an accurate duration or cost estimate. This is the most accurate method but also the most timeconsuming and expensive form of estimating. DEVELOP SCHEDULE The Process of analyzing activity sequences, durations, resource requirements and schedule constraints to create a project schedule. 9 CRITICAL PATH METHOD AND PERT TECHNIQUES Practice : CPM Calculation PERT Calculation Individual Exercises CONTROL SCHEDULE The Process of monitoring the status of project activities to update project progress and manage changes to the schedule baseline to achieve the plan. 11 PROJECT COST MANAGEMENT Project Cost Management involves developing the cost baseline, project budget and control changes. 1. Estimate Cost 2. Determine Budget 3. Control cost ESTIMATE COST – TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES Expert judgment Analogous estimating Parametric estimating Bottom-up estimating Three point estimating COST PLANNING – DETERMINE BUDGET Cost budgeting also uses similar tools and establish the project budget by aggregating cost of the activities to a total budget. The approved budget will provide the cost baseline for the project. CONTROL COST Approved project budget provides the baseline for the project cost. Any changes to the cost baseline must be monitored and approved only with an approved change request Tools and Techniques: Earned value management Forecasting To-complete Performance index (TCPI) Performance reviews Variance analysis Project management software CONTROL COST WITH EARNED VALUE TECHNIQUE Earned Value Management Formulas for performance measurement BAC = Budget at Completion PV = Planned Value AC = Actual Cost EV = Earned Value CV = Cost Variance CV = EV- AC SV = Schedule Variance SV = EV – PV CPI = EV/AC SPI = EV/ PV