Traditional UNIX kernels
advertisement
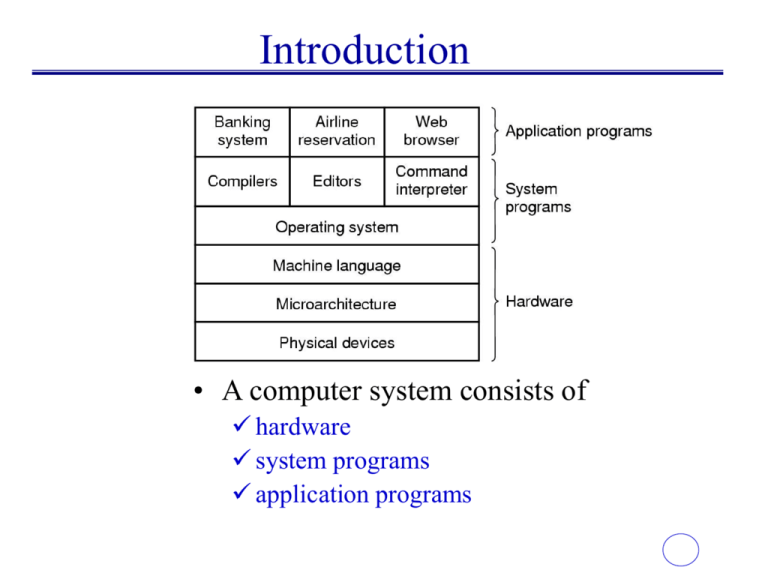
Introduction • A computer system consists of hardware system programs application programs History of Operating Systems (1) Early batch system bring cards to 1401 read cards to tape put tape on 7094 which does computing put tape on 1401 which prints output Computer Hardware Review (1) Monitor Bus • Components of a simple personal computer Type of Computers • Supercomputing: used for scientific computing • Mainframes: used to be primary form of computer, used in centralized computers, used in businesses for timesharing • Servers: computers used to connect other computers to the internet, printer, file sharing, etc. • Desktops: Personal Computers • Workstations: More powerful version of the personal computer • Handheld: Smaller operating Systems for handhelds • Real Time: Operating Systems for information that needs to be updated in real time • Embedded Systems: Systems that are found within another System History of Operating Systems • • • • • First Operating System Originally developed in AT&T Bell Labs (now know as Lucent Technologies) UNIX was taken to University of California Berkley leading to the foundation of the Berkeley Standard Distribution UNIX then opened up the computer industry to many other UNIX type operating systems and more To date, Apple MAC OS X is the most widely used desktop version of UNIX Types of Operating Systems • UNIX • Linux • Windows • MAC OS Go on to next page Linux • Free UNIX-type operating system • Linus Torvalds started creating in 1991 • Started out as MINIX then formed into Linux • Continuously updated • Popular among college students • Intended for small servers, workstations, desktops, and handhelds • Cost: Free What is Unix? A fully featured modern operating system It is available in a variety of “flavors.” It’s comprised of simple tools that perform a single function well. These tools can be used together to perform complex tasks. A Little History First: UNIX • Initial design by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie and others at AT&T's Bell Telephone Laboratories (BTL) in 1969: 32 years ago! • AT&T made the source available to Universities for research and educational use. • 1973 UNIX was rewritten in C resulting in Version 4. The C language was also originally designed and developed for use on the UNIX system by Dennis Ritchie C was evolved from 'B', developed by Thompson. Commercialization • Interactive Systems first commercial (1977) • Microsoft and SCO release XENIX (1980) • 1982 Bill Joy left Berkeley and founded Sun Microsystems. SunOS originall based on BSD 4.2 SunOS 5 (Solaris 2.X) was a collaborative effort based on System V, release 4 (SVR4). • AIX from IBM • HP/UX from Hewlett Packard Corporation • ULTRIX from Digitial Equipment Corporation, followed by DEC OSF/1. DEC purchased by Compaq Unix is Made Up of Processes • Running Programs User owned System owned Files • Regular Files: – Data – Executables <-- usually start a process • Directory Files – Contain other files and directories • Special Files Our View of the World as Users Your Shell Unix Shell A shell is a process that acts as an interface to the OS. It allows the user to run programs individually and together to accomplish a task. Simple Unix Directory Structure / usr etc local bin ... class Fred Kuhns () home grad bin ugrad ... mmscott jpeckhar... CS523S: Operating Systems var ... Your First Command Man(manual) -- Documentation is your friend • Syntax: man topic • man provides online documentation on nearly every standard command and configuration file. • Optional Syntax: man -k keyword • man man for more details Special Directories Home Directory • /home/grad/jpeckhar • ~jpeckhar • ~ • A user generally has permission to freely manipulate files within this directory and its children. • Users start with their home directory as their pwd when they login. Changing Directories • The cd(Change Directory) command is used to change directories • cd path • Paths can be relative or absolute • pwd reports present working directory • cd when entered by itself sets the pwd to the user’s home directory. Other File System Utilities • ls Lists all files in a directory • cp Copies files • mv Moves files • rm Deletes files • mkdir Makes directories • rmdir Removes directories Basic Syntax • ls ls • cp • rm cp source dest OR cp source … dir mv source dest OR mv source … dir rm file • mkdir mkdir new directory name • rmdir rmdir directory to be removed • mv Using Other Commands Syntax: command file • cat • grep Echos file contents to the screen Searches a file for a string • more Echos a file a line at a time • less Same as more but more features • wc Counts the words in a file and more • sort Sorts the contents of a file Pipes • Pipes connect stdout of one command to stdin of another comand. i.e. • ls | less • cat student_list | grep senior | sort I/O Redirection • I/O redirection allows the user to change where input to a command or output from a command goes to/comes from. • cat student_list > outfile • program < infile • program < infile > outfile Standard File Handles Every Unix process automatically comes with three file handles or descriptors. These are: Standard Input (stdin) Keyboard Standard Output (stdout) Display Standard Error (stderr) Display (unbuff)








