phonemic awareness - DeVonya Sherrice Preston, M. Ed
advertisement

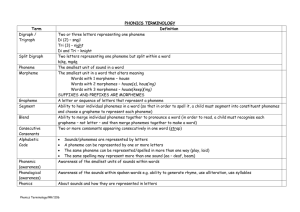
Providing Learning Innovations and Curriculum Solutions Strengthening Our Teaching Skills in Reading & Writing Mary Mount Easter Institute Bogota, Columbia April 6 – 9, 2014 Olivia Broxey, Ph.D. DeVonya Preston, M.ED. Providing Learning Innovations and Curriculum Solutions Phonics & Phonemic Awareness English Consonants and Vowel Sounds Part I Objectives • Participants will be able to: – identify the five major components of an effective reading program – pronounce letter-sound correspondences for all English consonants and vowels – employ a variety of instructional routines The Big Five: Essentials for Reading Success: Components of Reading Phonemic Awareness Comprehension Vocabulary Phonics/Phonological Awareness Fluency The Big Five: Essentials for Reading Success: Components of Reading Phonemic Awareness • An awareness of phonemes in the speech stream. Instruction that teaches children to hear, identify, and manipulate the 44 individual soundsphonemes- found in the English language. Phonics • The relationship between the letters(graphemes) of written language and the sounds(phonemes) of spoken language. Fluency • The ability to read a text accurately, quickly and with expression Vocabulary Comprehension • The learning of meaning and pronunciation of words • Acquiring strategies to understand, remember and communicate what is read. • The reason for reading What is a Phoneme? A Phoneme This is the smallest unit of sound in a How many phonemes can word. you hear in cat? Sheep? • A phoneme you hear • A grapheme you see A word always has the same number of phonemes and graphemes! A grapheme These are the letters that represent the phoneme. The grapheme could be 1 letter, 2 letters or more! We refer to these as sound buttons. t igh ai In the English Language… • There are 44 phonemes • Represented by 26 letters • A letter can sometimes represent more than one sound. Ex. a sounds differently in the following words: at, ate, all, was. • There are hundreds of spellings that can be used to represent the phonemes. Only the most common need to be taught. Phonemic Awareness • the knowledge that words are made up of a combination of individual sounds. • For example, – the word cat is made up of three sounds (phonemes) /c/a/ and /t/. – If a child knows that cat, car, and caboose all have the same sound at the beginning of the word, she has phonemic awareness. – In other words, she is aware that the /c/ sound (phoneme) begins each of those three words. Phonics/ Phonological Awareness • Phonics is the relationship between a specific letter and its sound, only as it relates to the written word. • For example, if a child does not recognize. – the word chant, he might break the word apart into pieces, such as /ch/ /a/ /n/ /t/ Then, the child combines those sounds to create the word chant. Phonics Instruction Consists of: • Identifying sounds in spoken words • Recognizing the common spellings of each phoneme. • Blending phonemes into words for reading. • Segmenting words into phonemes for spelling. What is Systematic and Explicit Phonics Instruction? • Systematic phonics instruction provides direct teaching of a set of letter-sound relationships in a clearly defined sequence. • Explicit instruction provides teachers with precise directions so that the relationship between letters and sounds are made clear to the students. Understanding the English Alphabetic Code Consonants and Vowels Consonants • Consonants can be categorized according to –How they are produced –Where they are produced in the mouth –Whether they are voiced or unvoiced. Consonants • The 5 major categories of consonants based on their manner of articulation include the following: – Plosives (stops) /b/,/p/,/d/,/t/, – Fricatives /f/,/v/,/th/ /z/ – Nasals /m/,/n/,/ng/ – Liquids /l/,/r/ – Glides /w/,/y/,/h/ Vowels • 19 of the 44 English phonemes are vowel phonemes. • The consonants w and y often act as vowels. – Y acts as a vowel when it appears at the end of a word or syllable. – W acts as a vowel when it is used in combination with another vowel. Vowels Diphthongs /oi/ (boil, boy), /ou/ (house,cow) These are vowel sounds that are formed by a gliding action in the mouth. R-controlled vowels /ar/ (chair), /ur/ (fern, bird, hurt), /ar/ (park) The letter r affects the sound of the vowel that precedes it in many ways. Vowels • Schwa (alone, happen, direct, gallop, circus) Not all linguists consider this a separate sound. The schwa is also known as as murmur or neutral sound. Up to 22 different spellings of the schwa sound have been identified. The Letter Sounds Song Good vs. Bad Song A Song B English Consonants: Jigsaw 1. Within your groups, SELECT ONE LETTER. 2. Go to www.rachelsenglish.com to watch your Sound(s) video(s). 3. Meet with EXPERT group to review information and plan your 3 minute lesson. 4. Go back to your TEACHING group and share your findings. Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 S and Z S and Z S and Z Y Y Y J J J G G G R R R Providing Learning Innovations and Curriculum Solutions Phonics: Instructional Routines and Center Activities English Consonants and Vowel Sound Part II Providing Learning Innovations and Curriculum Solutions Phonemic Awareness: Instructional Routines and Center Activities English Consonants and Vowel Sounds Part III