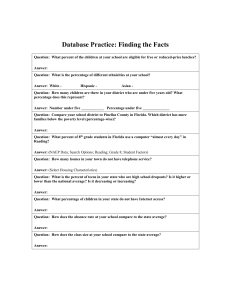
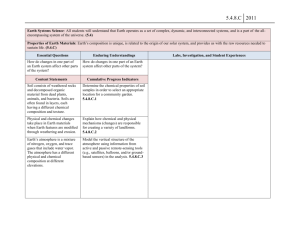
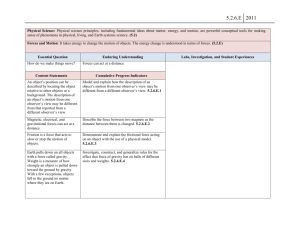
How to Compare NAEP and State Assessment Results
advertisement

How to compare NAEP and State Assessment Results NAEP State Analysis Project Don McLaughlin Victor Bandeira de Mello 35th Annual National Conference on Large-Scale Assessment June 18, 2005 overview: the questions how do NAEP and state assessment trend results compare to each other? how do NAEP and state assessment gap results compare to each other? do NAEP and state assessments identify the same schools as high-performing and lowperforming? overview: the differences results are different because standards are different students are different time of testing is different motivation is different manner of administration is different item formats are different test content is different tests have measurement error overview: the differences results are different because standards are different students are different time of testing is different motivation is different manner of administration is different item formats are different test content is different tests have measurement error overview: the focus the problem of different standards how we addressed it the problem of different students how we addressed it factors that affect validation the problem of different standards the different standards trends and gaps are being reported in terms of percentages of students meeting standards the standards are different in every state and in NAEP comparisons of percentages meeting different standards are not valid the different standards concept of population profile a population profile is a graph of the achievement of each percentile of a population the different standards a population achievement profile NAEP scale 400 500 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 Basic 200 150 1000 0 10 20 30 40 50 Percentile 60 70 80 90 100 the different standards a population achievement profile NAEP scale 400 500 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 5% 32% Basic 200 76% 150 1000 0 10 20 30 40 50 Percentile 60 70 80 90 100 the different standards a population trend profile NAEP scale 500 400 Future NAEP achievement ( 2003 + 10 Points ) Average NAEP achievement in 2003 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 Basic 200 150 0 100 0 10 20 30 40 50 Percentile 60 70 80 90 100 the different standards a population trend profile NAEP scale 500 400 Future NAEP achievement ( 2003 + 10 Points ) Average NAEP achievement in 2003 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 Basic 200 +9% +13% 150 +5% gains 0 100 0 10 20 30 40 50 Percentile 60 70 80 90 100 the different standards a population gap profile NAEP scale 400 500 NAEP Achievement of non-disadvantaged students NAEP Achievement of disadvantaged students 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 2% 13% Basic 200 13% gaps 150 1000 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Percentile 70 80 90 100 the different standards a population gap profile NAEP scale 400 500 NAEP Achievement of non-disadvantaged students NAEP Achievement of disadvantaged students 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 8% Basic 13% 200 5% gaps after a 20-point gain 150 1000 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Percentile 70 80 90 100 the different standards a population gap profile NAEP scale 400 500 NAEP Achievement of non-disadvantaged students NAEP Achievement of disadvantaged students 350 300 Advanced Proficient 250 8% Basic 200 13% 6 points larger the same 5% 8 points smaller 150 gap changes 1000 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Percentile 70 80 90 100 the different standards trends and gaps are being reported in terms of percentages of students meeting standards the standards are different in every state and in NAEP comparisons of percentages meeting different standards are not valid the different standards the solution to the problem is to compare results at comparable standards for comparing NAEP and state assessment gains and gaps in a state, score NAEP at the state’s standard the different standards NAEP individual plausible values for 4th and 8th grade reading in 1998, 2002, and 2003 and mathematics in 2000 and 2003 state assessment scores school percentages meeting standards linked to NCES school codes, in 2003 and some earlier years www.schooldata.org the different standards a school-level population gap profile Percent meeting states' primary standards 100 80 Not disadvantaged 60 40 Disadvantaged Achievement measured by state assessments 20 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Percentile in group 70 80 90 100 the different standards comparing school-level population gap profiles Percent meeting states' primary standards 100 80 Not disadvantaged 60 40 Disadvantaged 20 Achievement measured by NAEP (thin) and state assessments (thick) 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Percentile in group 70 80 90 100 the different standards comparing school-level population gap profiles Gap in percent meeting states' primary standards 40 20 Not disadvantaged 0 Gap -20 Disadvantaged -40 Achievement measured by NAEP (thin) and state assessments (thick) -60 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Percentile in group 70 80 90 100 the different standards scoring NAEP at the state assessment standard determine the cutpoint on the NAEP scale that best matches the percentages of students meeting the state’s standard compute the percentage of the NAEP plausible value distribution that is above that cutpoint the different standards equipercentile equating Setting NAEP Scale Score for State Performance Standard 9 State Assessment Scores NAEP Scores 60% 60% Standard the different standards equipercentile equating average NAEP scale score A B C D average 205 215 225 235 220 hypothetical NAEP results in four schools in a state (actual samples have about 100 schools) the different standards equipercentile equating average NAEP scale score percent meeting state standard A B C D average 205 215 225 235 220 10% 20% 40% 50% 30% in school A, the state reported that 10% of the students met the standards the different standards equipercentile equating A B C D average average NAEP scale score 205 215 225 235 220 percent meeting state standard 10% 20% 40% 50% 30% NAEP scale score corresponding to percent meeting state standard 225 225 235 235 230 in school A, 10% of the NAEP plausible value distribution was above 225 the different standards equipercentile equating A B C D average average NAEP scale score 205 215 225 235 220 percent meeting state standard 10% 20% 40% 50% 30% NAEP scale score corresponding to percent meeting state standard 225 225 235 235 230 10% 45% 60% 30% percent above 230 on NAEP 5% If the equating is accurate, we should be able to reproduce the percentages meeting the state’s standard from the NAEP sample the different standards equipercentile equating average NAEP scale score percent meeting state standard NAEP scale score corresponding to percent meeting state standard A B C D average 205 215 225 235 220 10% 20% 40% 50% 30% 225 225 235 235 230 30% percent above 230 on NAEP 5% 10% 45% 60% error -5% -10% +5% +10% the different standards relative error in estimating cutpoints for state standards, relative error is the ratio of the observed error in reproducing school-level percentages meeting standards to that expected due to sampling and measurement error the different standards NAEP scale 325 500 mapping of primary state standards on the NAEP scale: math grade 8 in 2003 MO ME LA SC 300 NAEP Proficient AZ MA HI WY AR WA ND KY RI CA MD VT DC 275 SD ID PA NJ CT NY KS MI NV DE IL OR IN NM AK FL CO IA MT NAEP Basic W I MS TX GA OK VA 250 NC 0 225 1 2 Relative error 3 the different standards NAEP scale 325 500 mapping of primary state standards on the NAEP scale: math grade 8 in 2003 MO ME LA SC 300 NAEP Proficient AZ MA HI WY AR WA ND KY RI CA MD VT DC 275 SD ID PA NJ CT NY KS MI NV DE IL OR IN NM AK FL CO IA MT NAEP Basic W I MS TX GA OK VA 250 NC 0 225 1 2 Relative error 3 the different standards NAEP scale 325 500 MO ME LA mapping of primary state standards on the NAEP scale: math grade 8 in 2003 SC 300 NAEP Proficient AZ MA HI WY AR WA ND KY RI CA MD VT DC SD ID PA NJ CT NY KS MI NV DE 275 IL OR IN NM AK FL CO IA MT NAEP Basic WI MS TX GA OK VA 250 NC the different standards National percentile ranks of states' 2003 grade 4 reading proficiency standards National percentile rank corresponding to the standard national percentile ranks corresponding to state grade 4 reading standards in 2003 100.0 High Standards 80.0 LA NAEP Proficient Standard MO SC WY 60.0 CT MA ME CA HI PA MN 40.0 20.0 NAEP Basic Standard NY DC NV FL NMWA KY RI NH IL OH VTKS AZ AR MD IAND NJ MT (in) ID MI AK OK (de) NC WI (or) SD VA CO GA Low Standards (wv) (These state's standards are less accurately determined.) (ne) (tx) MS 0.0 1 2 Relative error in determining the placement of the standard 3 the different standards states have set widely varying standards does it matter? standards should be set where they will motivate increased achievement surely some are too high and some are too low the different standards states with higher standards have lower percentages of students meeting them Percent of students achieving primary standard (PCT) 100 PCT = 339 - 1.04 (NSE) R2 = 0.78 80 60 40 20 0 0 225 250 275 300 NAEP scale equivalent (NSE) of primary state standard 500 325 the different standards on NAEP, states with higher standards do about the as well as other states Percent proficient on NAEP (PCT) 100 PCT = 41.5 + 0.02 (NSE) R2 = 0.001 80 60 40 20 0 0 225 250 275 300 NAEP scale equivalent (NSE) of primary state standard 500 325 the problem of different students the different students the problem of different students different school coverage different grade tested absent students excluded SD/ELLs the different students different school coverage our comparisons between NAEP and state assessment results are for the same schools. NAEP weights these schools to represent the public school population in each state we matched schools serving more than 99 percent of the public school population. However, especially for gap comparisons, we were missing state assessment results for small groups whose scores were suppressed for confidentiality reasons the median percentage of the NAEP student population included in the analyses was about 96 percent the different students different grades tested in some states, assessments were administered in grades 3, 5, or 7, and we compared these results to NAEP results in grades 4 and 8 the difference in grades involved a different cohort of students, as well as a difference in curriculum content. These effects combined to reduce NAEP-state assessment correlations in some states by about 0.05 to 0.10 the different students absent students some students are absent from NAEP sessions, and some of these are not made-up in extra sessions. NAEP imputes the achievement of the absent students to be similar to that of similar students who were not absent a study by the NAEP Validity Studies Panel has found that these imputations leave negligible (if any) bias in NAEP results due to absences that study compared the state assessment scores of students absent from NAEP to the scores of students not absent the different students excluded SD/ELLs some students with disabilities and English language learners are excluded from NAEP and others are included. A teacher questionnaire is completed for each SD/ELL selected for NAEP in the past, NAEP has ignored this exclusion, and there is clear evidence that as a result, states in which NAEP exclusions increased had corresponding reports of larger NAEP achievement gains (and vice versa) the different students full population estimates the trend distortions caused by changing exclusion rates can be minimized by imputing the achievement of excluded students. in this project, comparisons between NAEP and state assessment results are based on the NAEP full population estimates [1] imputations for excluded SD/ELLs are based on the achievement of included SD/ELLs with similar questionnaire and demographic profiles in the same state [1] an appendix includes comparisons using standard NAEP estimates the different students statistically significant state NAEP gains from 1996 to 2000 grade 4 grade 8 ignoring excluded students 17 of 37 16 of 35 full population estimates 12 of 37 7 of 35 the different students statistically significant state NAEP gains and losses from 1998 to 2002 grade 4 grade 8 gains losses gains losses ignoring excluded students 18 1 8 6 full population estimates 23 0 7 2 factors that affect validation validation the question do state assessments and NAEP agree on which schools are doing better than others? the measure correlation between state assessment and NAEP school-level results validation factors that specifically affect NAEP-state assessment correlations of school-level statistics size of school NAEP samples grade level the same or different extremeness of the standard validation median school-level correlations between NAEP and state assessment results grade 4 grade 8 math reading math reading original 0.76 0.72 0.81 0.73 adjusted 0.84 0.82 0.86 0.81 validation NAEP and state assessment school means 7/8th grade math percentages meeting State standard in NAEP schools in 2003 100 90 80 70 60 % meeting 50 standard (NAEP) 40 30 20 10 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 % meeting standard (State's assessment) 80 90 100 summary two reports have been produced on 2003 NAEP-state assessment comparisons, one for mathematics and one for reading each report has an appendix with multi-page comparison profiles for all of the states the following are examples of the kinds of information included state profiles state profiles of NAEP-state assessment comparisons test score descriptions and results summary standards relative to NAEP correlations with NAEP changes in NAEP exclusion/accommodation rates trends (NAEP vs. state assessment) gaps (NAEP vs. state assessment) gap trends (NAEP vs. state assessment) state profiles a state’s standards relative to its achievement distribution state profiles a state’s math trends comparison state profiles poverty gap comparison state profiles poverty gap comparison state assessment results state profiles poverty gap comparison NAEP results state profiles poverty gap comparison NAEP - state assessment state profiles a state’s poverty gap comparison other results trends gaps overall coverage subpopulation coverage school analyses sample other results: trends comparison of trends reported by NAEP and state assessments (number of states) grade 4 grade 8 math 00-03 read 98-03 math 00-03 read 98-03 state assessment reported greater gains 3 5 5 5 no significant difference 10 3 11 1 11 0 6 0 NAEP reported greater gains other results: gaps reading 2003 NAEP and state assessments tended to find similar achievement gaps math 2003 NAEP tended to find slightly larger gaps than state assessments did other results: coverage median state percentages of NAEP schools and student population matched and included in analyses grade 4 grade 8 math read math read percent of schools matched 99.1 99.1 99.2 99.2 percent of student population matched 99.5 99.6 99.8 99.8 percent of schools included in analyses 94.9 94.4 95.3 94.2 percent of students included in analyses 95.8 95.4 96.8 96.1 other results: coverage number of states and percent minority students included in the 2003 reading gap analyses grade 4 number of states black 26 students included (%) number of states hispanic disadvantage students included (%) 20 88.0 14 students included (%) number of states grade 8 99.2 13 84.5 31 91.7 28 87.9 90.1 other results: school sample percent meeting standards from state tests in NAEP schools and from state reports, 2003 State aggregate from website 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 20 40 60 State aggregate from NAEP sample 80 100 producing the report SAS programs the process find state scores for NAEP sample score NAEP in terms of state standards compute inverse CDF pair for subpopulation profiles compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and standard errors compute trends and gains compute smoothed frequency distribution of plausible values compute NAEP-state correlations SAS programs data setup the process find state scores for NAEP sample score NAEP in terms of state standards compute inverse CDF pair for subpopulation profiles compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and standard errors compute trends and gains compute smoothed frequency distribution of plausible values compute NAEP-state correlations SAS programs the process find state scores for NAEP sample population profiles score NAEP in terms of state standards compute inverse CDF pair for subpopulation profiles compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and standard errors compute trends and gains compute smoothed frequency distribution of plausible values compute NAEP-state correlations SAS programs the process find state scores for NAEP sample score NAEP in terms of state standards compute inverse CDF pair for subpopulation profiles compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and standard errors compute trends and gains compute smoothed frequency distribution of plausible values compute NAEP-state correlations SAS programs the process find state scores for NAEP sample score NAEP in terms of state standards compute inverse CDF pair for subpopulation profiles compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and standard errors compute trends and gains compute smoothed frequency distribution of plausible values compute NAEP-state correlations SAS programs the process find state scores for NAEP sample score NAEP in terms of state standards compute inverse CDF pair for subpopulation profiles compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and standard errors compute trends and gains compute smoothed frequency distribution of plausible values compute NAEP-state correlations SAS programs programs makefiles.sas standards.sas gaps.sas gaps_g.sas trends.sas trends_r.sas trends_g.sas distribution.sas correlation.sas SAS programs programs makefiles.sas standards.sas gaps.sas gaps_g.sas trends.sas trends_r.sas trends_g.sas distribution.sas correlation.sas http://www.schooldata.org/reports.asp SAS programs: setup makefiles.sas for state st get NAEP plausible values for subject s, grade g, and year y get state assessment data for NAEP schools (from NLSLASD) merge files to get example02.sas7bdat and example03.sas7bdat SAS programs: setup makefiles.sas *******************************************************************************; * Project : NAEP State Analysis *; * Program : MakeFiles.SAS *; * Purpose : make source file for workshop at LSAC 2005 *; * *; * input : naep_r403 NAEP Reading grade 4 2003 data *; * naep_r402 NAEP Reading grade 4 2002 data *; * XX state XX assessment data *; * YY state YY assessment data *; * *; * output : example02 - 2002 data *; * example03 - 2003 data *; * *; * Author : NAEP State Analysis Project Staff *; * American Institutes for Research *; * *; *******************************************************************************; SAS programs: setup standards.sas compute NAEP equivalents of state standards based on school level state assessment scores in NAEP schools macro %stan(s,g,y,nlevs) output Stansgy file with state standard cutpoints on NAEP sample StanR403 s g y varname level cut stderror percent R 4 03 Rs5t0403 2 164.2 3.2 91.9 R 4 03 Rs5t0403 3 205.8 1.1 68.9 R 4 03 Rs5t0403 4 264.9 1.8 9.4 SAS programs: setup standards.sas generate school level file with percentages meeting levels by reporting category, with jackknife statistics macro %StateLev(file,s,g,y) macro %NAEP_State_Pcts(s,g,y,group) macro %Sch_State_Pcts(standard,s,g,y) output StPcts_standard_sgy with school stats for first/recent standard, by category macro %Criterion(standard,s,g,y) output criterion_ standard_sgy with criterion values for cutpoints SAS programs: gaps gaps.sas compute and plot subpopulation profiles (inverse CDF) and compute mean NAEP-state gap differences and respective standard errors, by regions of the percentile distribution macro %gap(s,g,lev,y1,y2,group1,group2) where y1 y2 lev group1 group2 is the earlier years (need not be present) is the later year is the standard for which the gap is being compared is the 5-char name of the focal group is the 5-char name of the comparison group SAS programs: gaps gaps.sas output: inverse CDF for comparison pairs ICDFr4__03group1group2 mean NAEP-State gap differences and SEs by regions of the percentile distribution DiffGapsMINtoMAXgroup1group2R4__03.XLS DiffGapsMINtoMEDgroup1group2R4__03.XLS DiffGapsMEDtoMAXgroup1group2R4__03.XLS DiffGapsMINtoQ1_group1group2R4__03.XLS DiffGapsQ1_toQ3_group1group2R4__03.XLS DiffGapsQ3_toMAXgroup1group2R4__03.XLS SAS programs: gaps gaps.sas output: population profiles STATE_PV_03.gif STATE_BW_03.gif NAEP_PV_03.gif NAEP_BW_03.gif NAEP_STATE_PV_03.gif NAEP_STATE_BW_03.gif state achievement profile state achievement profile NAEP achievement profile NAEP achievement profile NAEP/state gap profile NAEP/state gap profile d SAS programs: gaps gaps.sas output: population profiles NAEP_PV_03.gif NAEP achievement profile SAS programs: gaps gaps_g.sas plot subpopulation profiles and place them on a four-panel template to include in report macro %pop_profile set SAS/Graph options macro %plot_gaps plot graphs using options macro %createtemplate create four-panel template macro %replaygaps place graphs in template SAS programs: gaps gaps_g.sas SAS programs: trends trends.sas compute difference between state and NAEP and respective standard errors output data file trends_sy including both NAEP and NAEP state standard measures trends_r.sas compute gains and respective standard errors output data file summary_s SAS programs: trends trends_g.sas plot NAEP and state assessment trends by grade and place them on a two-panel template to include in report compute t for testing significance of differences in gains between NAEP and state assessment SAS programs: correlations correlation.sas compute NAEP-state correlations and standard errors macro %corrs(standard,s,g,y,group) output CorrsY_standard_groupsgy file with state standard RtR4032 RtR4032 RtR4032 correlation 0.60 0.73 0.43 standard error 0.11 0.06 0.10 SAS programs: distribution distribution.sas create file with plausible value frequency distribution output distribution_sgy file 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 SAS programs all programs and data files are available for download at http://www.schooldata.org/reports.asp including files with the imputed scale scores for excluded students we used in the report NAEP State Analysis Project American Institutes for Research Victor Bandeira de Mello Don McLaughlin Victor@air.org DMcLaughlin@air.org National Center for Education Statistics Taslima Rahman Taslima.Rahman@ed.gov