lecture 1 - Knowledge Representation & Reasoning at UIUC!
advertisement

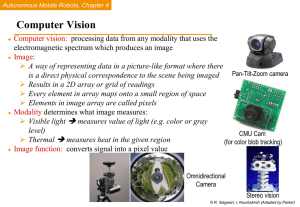
CS 440 / ECE 448 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Fall 2006 Instructor: Eyal Amir TAs: Deepak Ramachandran (head TA), Jaesik Choi Today • Artificial Intelligence – Motivation – the dream – Long-term goals – Short-term applications • What you will learn – Tools, concepts, thought – What you should know • Administration of this class What is Artificial Intelligence? • Examples: – Game playing? (chess) – Robots? (Roomba) – Learning? (Amazon) – Autonomous space crafts? (NASA) • What should AI have? Example: Shakey (1971) Example: Mobile Robots (2001) Example: (2005) DARPA Grand Challenge Example: (2005) DARPA Grand Challenge Motivation of AI • • • • Autonomous computers Embedded computers Programming by telling Human-like capabilities – vision, natural language, motion and manipulation • Applications: learning, media, www, manipulation, verification, robots, cars, help for disabled, dangerous tasks Long-Term Goals • Computers that can accept advice • Programs that process rich information about the everyday world • Programs that can replace experts • Computer programs that can decide on actions: control, planning, experimentation • Programs that combine knowledge of different types and sources • Programs that learn Short-Term Goals • Inferring state of the world from sensors – Vision – Natural-language text • • • • Planning & decision making Diagnosis & analysis Learning, pattern recognition Knowledge & reasoning – acquire, represent, use, answer questions What This Course Covers • Major techniques used in artificial intelligence – Vision – Probabilistic reasoning – Learning – Knowledge representation - logic & probability – Logical reasoning – Robotic control, Stimulus-Response – Planning and sequential decision making Today’s Handouts • • • • • • Syllabus and Dates Readings Midterms, Final exam Home assignments Project assignments Class website: http://reason.cs.uiuc.edu/cs440 Project: Autonomous Car • Project divided into milestones: – – – – – Vision Tracking Reactive control High-level control Combination • Teams of 4-6 people – send team composition to TAs • After the end of semester... Project continues until the DARPA Urban Competition (Dec 2007). What you should know • • • • • Matrix Algebra Probability and Statistics Logic Data structures C++ What You Will Know • Matlab • LISP / Prolog • Building and reasoning with complex probabilistic and logical knowledge • Build autonomous agents • Create vision/sensing routines for simple detection, identification, and tracking • Create programs that make decisions autonomously or semi-autonomously Administration of This Class • Homeworks every week – see homework #0 given today • • • • Handouts given in class Homeworks collected: beginning of class Homeworks returned within a week 7 days flexible grace period – once spent, 20% off for every late day More Administration • Cheating policy: – 0 on first occurrence, F on second – Honor code • Grading formula: – 3hr credit = Mid1(20%)+Mid2(20%)+Final(20%)+HW(20%)+Proj(20%) – 4hr credit = Mid1(15%)+Mid2(15%)+Final(15%)+HW(15%)+Proj(40%) – Extra credit for class participation (3%) • Project grading – Grade given to group every milestone (5 milestones total) – Adjusted grade to individual contribution • Final exam only on last 1/3 material Office Hours • Eyal: Thu 4pm-5pm – SC 3314 • TAs (Deepak, Jaesik): Tue 3pm-5pm – SC 0207 • Communication: – Newsgroup: class.cs440 on nntp.cs.uiuc.edu – Special requests: ta440@cs.uiuc.edu