ADBIO-Week3NotePacketCleavagetoSkeletonsFORSTUDENTS
advertisement

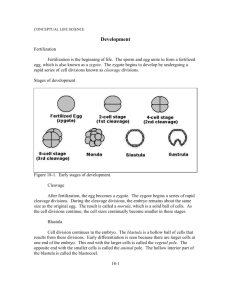
Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Week of 2/7-3/11 Notes- Advance Biology http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/odyssey/clips/ Video clips of Chicken, Pig, and Human Embryos In animals, ___________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ is the first step in a complete series of events. It is this series that finally gives rise to a full-grown organism. This is called development. In the early stages of development, the organism is called an _______________ The study of the development of an embryo is called _________________________ Although embryos develop in many different ways, the basic processes are always the same in animals. The three different processes of development include: 1. Cleavage Main focus today a. Gastrulation 2. Growth 3. Differentiation a. Morphogenesis __________________________________= First series of cells divisions after fertilization - Number of cells doubles during each division Cells _________________________________ Each division _________________________________________ ____________________= solid ball of cells resulting from early divisions of cleavage ____________________= hollow sphere formed as the cells continue to divideo A sphere only _________________________ o Filled with_______________________ o __________________________________= fluid filled inside 1 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ 2 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Activity: Examining early embryonic stages of the sea star Introduction: Echinoderms (sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers) are useful for illustrating the stages of early development for multicellular animals. Sea stars develop in an aquatic environment and develop quickly into a larva that is capable of feeding itself. Explain why you might not expect a sea star’s egg to be heavily laden with yolk: __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Directions: Obtain a whole-mount microscope slides provided. Identify the following components, structures, and stages of development listed below. Use the figure on the next page (35. 1) for help. Cleavage: Successive division of the embryo results in a two-cell, four-cell, and eight-cell stage. The next cell stage is called ________________________________-cell stage. A many-cell stage occurs after that. Cleavage occurs without an accompanying increase in size. Sketch this _______x (power) Blastula: The large number of embryonic cells of the morula arrange themselves into a blastula, a singlelayered ball with a fluid-filled cavity, called a blastocoel, in the middle. Sketch a blastula and label the blastocoel. _______x (power) 3 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Early gastrula: The cells of the blastula fold inward to form a two-layered gastrula. The cavity produced by the infolded layer of cells is the archenteron, or primitive gut, which has an opening to the outside called blastopore. The outer layer of cells is the exoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm. Sketch this stage and label the exoderm and endoderm. _______x Late gastulation: As development continues, two pouches form by out-pocketing from the endoderm surrounding the gut. These pouches become part of the coelom (body cavity), and the walls of these lateral pouches become the third germ layer, the mesoderm. _______x SCAN IN FIGURE 35.1 FROM PACKET!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 4 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Elaboration Questions: SCAN IN FIGURE 35.2 from packet (Frog development stages) 1. Examine the above drawing of the developmental stages of a frog embryo. Specifically, look at the blastula. Compare the frog blastula to that of the sea star: ____________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Compare the formation of the mesoderm in the frog to that in the sea star: ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Neurula: During neurulation in the frog, two folds of ectoderm appear. The flat layer of ectoderm between the folds is the neural tube, which will become the nerve cord and brain. An examination of the neurula in cross section shows that the nervous system develops directly above the notochord, a structure that arises from the invagination cells in the middorsal region. Do sea stars have a notochord? ________ Explain: ____________________________________ 4. List the three germ layers and the major organs that develop from each in the frog. Use your book for help: Germ Layer 1 2 3 Organs/Organ Systems Associated with Germ Layer 5. Critical thinking: Use your book to look up the definition of induction. What is induction and how does it relate to the above table? 5 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ - Arrangement of cells in the developing embryo depends on ___________________ _____________________________________________________________________ - Humans have little yolk. Why? - Amphibians, bony fish, birds, and reptiles have a large amount of yolk at __________ ______________________________________________________________ - Yolk tends to slow down ___________________________________________ o Cleavage tends to take place at end of _________________________________ o Relate this back to what you found out about frog and sea star cleavage: Gastrulation= when the blastula reaches ___________________________________________ - Cells on one side of the blastula move inward and form a two-layered embryo called the ______________________________________________________ - Opening is called the blastopore- later becomes opening of ____________________ _____________________________________ - Germ layers: o __________________________________=outer layer o __________________________________= inner layer o __________________________________= layer between As the gastrula develops, the number of cells continues to _________________________ Since the cells now grow before dividing, the embryo begins to ________________________ Cell growth alone would produce only a formless mass of cells The cells in the embryo must be arranged into _________________________________, and within these structures, the cells must be specialized to ______________________________ _______________________________________ Although the cells of the gastrula are organized into distinct layers, (which were…..) they look very much alike ________________________________________________= The changing of unspecialized embryonic cells into the specialized cells, tissues, and organs that make up the organism First signs of differentiation are found on the upper surface of the __________________ 6 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ - Ectoderm cells divide, forming a neural plate that has 2 raised edges called ______________________________________________ - These slowly come together over the center of the ______________________, forming a ________________________________________________ - In the later stages of development, the neural tube forms the _____________ ____________________________________________________________ Role of neighboring cells As embryo grows, there must be coordination and communication between its tissues By late blastula or early gastrula stage, the way in which groups of cells will develop has already been determined Cells in certain regions develop along certain lines Ex: There is a particular place in frog gastrula that normally develops into an eye If this tissue is removed from the embryo and placed in a special nutrient solution: If transplanted into another frog embryo: _________________________= influence the development of neighboring cells - This process is called ________________________________________ - Scientists still don’t know exactly how this process works Check Point: Compare differentiation and cleavage: Which germ layer do you think gives rise to the human heart? Explain. 7 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ External and Internal Development Just like fertilization, development can take place inside or outside the body. Regardless of where the development occurs, the embryo needs proper nutrients, temperatures, oxygen, protection, and means of getting rid of waste. -External Development Water or land External, AquaticIn most aquatic animals, fertilization and development take _____________ __________________________________________________________________ Nourishment comes from _____________________________________________ Oxygen diffuses into ____________________________, and wastes diffuse from the ____________________________________________________ Usually little or _________________________________________________ “Mouth feeders” External, landBirds and most reptiles Large amount of _____________, and a protective ________________________ Waterproof and porous % of reptile eggs that survive less than % of bird eggs that survive…why? Do reptiles or birds lay more eggs? 8 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Internal structure of a chicken eggAs chicken embryo develops, it forms 4 membranes that lie outside the embryo itself but inside the shell= _____________________________________________ 1. ________________________________- outer most membrane- lines inside of shell and surrounds the embryo and other 3 membranes - aids in exchange of gases between embryo and environment 2. ___________________________________- saclike structure that grows out of the digestive tract of the embryo – -where exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide take place -where metabolic wastes collect 3. ____________________________- surrounds embryo contains amniotic fluid 4. _________________________- surrounds the yolk- source of food for embryo Chick development: Unlike sea stars and frogs, chicks develop on land, and there is no larval stage. Therefore, chick development is markedly different from that of sea stars and frogs because of 3 features: 1. Extraembryonic membranes 2. Large amount of yolk to sustain development 3. Hard outer shell Materials: Unfertilized chick egg Dissection prods Petri dishes water SAFETY: Wash hands after handling the egg Clean up: All parts are to go in the waste container. Wash and dry all petri dishes and dissecting tools. 9 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Directions: Get with a partner and obtain the materials above. 1. Carefully crack the egg into the petri dish filled with enough water to keep the egg moist, but not too much that the water will overflow. 2. Examine the contents of the raw egg. The egg white is called albumin. Is the albumen consistent in density and thickness? _____________________________________________________ a. These thicker masses are called chalazae. They result from the passage of the egg through the oviduct. This aids in keeping the developing embryo at the top of the yolk. 3. On the top of the yolk mass, the germinal vesicle, a small, white spot content the clear cytoplasm of the egg cell and the egg nucleus. The yolk and the germinal vesicle is the ovum. 4. Peel some of the chorion off the inside of the shell. Note how it looks and feels: ___________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ INSERT FIGURE 35.5 FROM LAB PACKET Elaboration questions: 1. What premature membrane holds the yolk together? 2. What would happen to a chick embryo of the chorioan was impermeable? 3. What would happen to the embryo of the amnion never formed? 4. Make a prediction about where the posterior and anterior end of the chick form based on the placement of the structures in this premature, unfertilized egg. Explain your reasoning. 5. How would the membranes of a human differ than those of a chick? 10 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ 11 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Internal Development Mammals and some reptiles and sharks Placental mammals= blood vessels of the embryo’s circulatory system are in close contact with the mother’s circulatory system placenta umbilical cord Non-placental mammals= egg-laying mammals and pouched mammals (monotremes and marsuipials) Polarity Eggs and zygotes of sea urchins and other animals have definite polarity established as the egg developed within the mother ________________________________________________ During cleavage, planes of division follow a _______________________________________ relative to the poles of the zygote Polarity is defined by __________________________________________________ in the cytoplasm and yolk This distribution of yolk is the key factor ______________________________________ ______________________________________________ Usually concentrated towards 1 side of the egg= _____________________________ Opposite pole= _____________________________ Animal-vegetal axis of egg determines the __________________________________ axis of embryo Organogenesis = =more localized shape changes in both tissues and __________________________ _________________________ and ________________________________are the first organs to take shape in the embryos of frogs ______________________________= skeletal rod characteristic of all chordate embryos ______________________________= runs along anterior-posterior axis of the embryo-will become animal’s CNS 12 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ As organogenesis progresses, morphogenesis and cell differentiation continue to refine the organs that arise from the _________________________________ Mammalian development In contrast with the large, yolky eggs of birds, other reptiles, and monotremes, mammalian eggs are small and store little nutrients. -No________________________________ -Despite lack of yolk, go through a similar pattern of ________________________and _________________________________________________________________ - Ethical concerns preclude experimentation on human embryos, so knowledge about human development has been based partly on what we can extrapolate from other mammals and in vitro fertilization. THIS LEADS US TO THE TOPIC OF …… Bioethics & You: What is bioethics? Beneficence- Nonmalefecence- Autonomy- Justice- Veracity- Fidelity13 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Stations- Go through the 6 stations and fill in the following blanks. Focus on the lines that are bolded. These are the sections that you absolutely need to get done in class. The rest can be filled out using your book or internet searching skills: STATION 1Fertilization= less ambiguously referred to as ______________________________________ Process of ______________________________ fusing with a _________________________ Begins with _________________________________________________________ Ends with ___________________________________________________________ Draw a sperm and label the parts: What is an acrosome: STATION 2 Cleavage= Blastomere= Cleavage begins with a zygote, progresses through a ______________ stage and terminates at the _________ ______________________________ -Cell divisions without cell enlargement -Morula produced ( ) Same size as single cell - Cell divisions affected by ___________________________________________________________ Briefly describe the 2 cell and 4 cell stage: 14 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ In which stage does the division of blastomeres become asynchronous? Blastulation - Morula secretes ____________________________________________________ Blastomeres surround ________________________________________________________ Human embryo differentiantes into _________________________________ with inner cell mass A morula is a __________________________________________________________________ within a zona pellucid A morula usually consists of _____________ blastomeres= ____________________________________ Outer blastomeres are destined to become ______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Inner blastomeres are destined to become _______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Blastula= ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ into an epithelial monolayer. Look at the ball of cells under the microscope. This is a cross section of a frog embryo at an early stage of its growth. It shows a mass of about 64 cells that developed by cleavage from a single cell. Sketch what you see: Notice the center of the mass of cells. This hallow ball stage is called the blastula. Label this. Notice that the cells in the lower part are larger than those of the upper part. Why would this be? _____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 15 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ STATION 3 Gastrulation= Gastrulation creates 3 germ layers: Morphogenesis= Ectoderm and endoderm are made by: Mesoderm develops: Look at the slide under the microscope. This is what the ball of cells from station 2 would look like after a few days. It has developed into a gastrula. Compare the size of the two slides: _________________________ You can clearly see the three germs layers here. Sketch what you see and label the 3 germ layers: STATION 4 Architecture: 4 features of early development distinguish the Protostomes and Deuterostomes B. Spiral v. radial cleavage 1. Radial ( ): planes of division perpendicular to or include _____________________ 2. Spiral ( ): planes of division become oblique to ______ _______________________; upper cells lie in cleavage grooves between lower cells C. The blastopore becomes the ______________ and _______________________ 16 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ On the protostome side are these kind of critters: On the deutrostome side are these kinds of critters: Characteristic Protostomes Determinate Deuterostomes Indeterminate Cleavages Radial Fate of blastopore Anus Splitting of mesoderm STATION 5 Ectoderm becomes: Endoderm becomes: Mesoderm becomes: Notochord, muscle, excretory system, gonads, outer covering of internal organs, dermis, bones and cartilage, and circulatory system Coelom= 17 Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Hour: ____________ Sketch a cross section of a coelom showing the 3 germ layers An ___________________________________ does not have a body cavity A ___________________________________________ has a body cavity called a pseudocoelom located between endoderm and mesoderm Coelomate= Symmetry Gut Coelom Embryonic Germ Layers Sponges Cnidarians Flatworms Roundworms Mollusks 18