Political Parties in the United Kingdom
advertisement

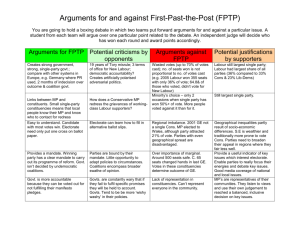
Political Parties / Elections in the United Kingdom 2010 General Election: Hung Parliament/Coalition Government Conservatives: 306 seats (gain of 98 seats) ; 36.1% of vote Labour: 258 seats (loss of 91 seats) ; 29.0% of vote Liberal Democrats: 57 (loss of 5 seats); 23% of vote Other Parties: 28 seats (loss of 1 seat); 11.9% of vote Foundations of the Party System Two-plus system 2 dominant parties (Labour + Conservative) Party system reflects class identification (main social identifier in UK) Also, ideological (Liberal Democrats) + Regional parties (Scottish National Party, Welsh Plaid Cymru) 2010 - Labour + Conservative only won 65% of popular vote, but have 87% of seats in Commons Labour Party Largest/strongest party on the “left” of political spectrum Traditionally labor unions have provided majority of funds for the party Former Labour Leaders Gordon Brown + Tony Blair Current Labour Leader: Ed Millibrand Tony Blair’s “Third Way” Moderate “New Labour” Party Centrist alternative to “Old Labour” Party on left and Conservative Party on right Initiated by Blair in late 1990s: – Acceptance of market economy by Labour Party – Devolution Conservative Party (Tories) Dominant party in Great Britain between WWII and late 1990s Main party on the right 98% of all Conservative seats are in England Conservative Leader/Prime Minister: David Cameron Thatcher’s Reforms (1980s) Privatized business and industry – Sold many government-owned enterprises to private sector Cut back on social welfare programs Strengthened national defense (staunch anti-communist) Resisted complete integration into the European Union (EU) – “Euroskeptics” – feel EU threatens British sovereignty – Rejected single currency (Euro) Liberal-Democratic Party Alliance between the Liberal and Social Democratic Parties during the 1980s Supports social programs, integrated Europe (EU) Currently part of coalition government with Conservatives Liberal Democratic Leader/Deputy PM: Nick Clegg Other Parties Scottish National Party Plaid Cymru – Welsh nationalist party (Wales) Sinn Fein – political arm of the IRA (Irish Republican Army) Elections Members of Parliament (MPs) are the only national officials that British voters select Elections must be held at least every 5 years, but Prime Minister may call them earlier Power to call elections very important – Prime Ministers always call elections when they think that the majority party has the best chance to win Elections II “Winner-take-all” system Single-member district plurality system Parties select a candidate to run in each district “First-past-the-post” winner Elections III MPs do not have to live in the district in which they are running, therefore party selects who runs in what districts = parties powerful Party leaders run from safe districts – districts that the party almost always wins Effects of FPTP/WTA System Voting Patterns Conservative Party: – Middle and upper classes – Educated – Residents of England, mostly rural and suburban areas Labour Party: – Working class – Residents of urban / industrial areas – “Third Way” centrist policies/devolution made Labour Party appealing to Scots, Welsh, and the poor U.S. vs. British Elections United States – Parties are less powerful – Members must live in districts – Party leaders run in their respective districts – Citizens vote for three officials on national level – Between 30 and 60% of the eligible voters actually vote – First-past-the-post, singlemember districts; virtually no minor parties get representation Great Britain – Party determines who runs where – Members usually don’t live in their districts – Party leaders run in “safe districts” – Citizens vote for only one official on the national level – About 65-75% of the eligible voters actually vote (number was less in 2001 & 2005) – First-past-the-post, singlemember districts; some representation from minor parties, but still less than if they had proportional representation Conservative Party (Tories) Weakened by division of party in late 1990s: – Traditional Wing – values noblesse oblige and elitism, supports Britain’s membership in EU – Thatcherite Wing – strict conservatives, support full free market “Euroskeptics” – feel EU threatens British sovereignty