ERP
advertisement

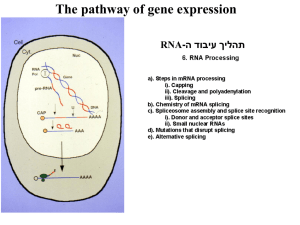
הרצאה 8 יסמין ויערה 2005 - חלק .ERP :I חלק :IIיישומי ( AIבינה מלאכותית). חלק :IIIסיום הרצאת תקשורת ותקשוב. חלק :IVהשלמות חומרה. חלק :Vדיווח/ים נושא/ים. בשיעור הבא – מבחן מסכם (לכולם יש שם וסיסמה לקושייה בתבנית הנכונה?). מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה יובל דן-גור ERP :I חלק חלק I ERP Enterprise Resource Planning פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע מה עושה ה ? ERP פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע מה עושה ה ? ERP פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע מה עושה ה ? ERP פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע ? ERP מה עושה ה ERP takes a different approach. There is only one information system in an enterprise, the ERP. All applications access common data. Real events in the business initiate transactions. Accounting is done automatically by events in sales and production. Sales can see when products can be delivered. Production schedules are driven by sales. The whole system is designed to be real-time and not historical. פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע ? ERP מה עושה ה ERP embodies what are considered the "best business practices". A company implementing ERP adapts it operations to it to achieve its efficiencies and power. The process of adapting procedures to the SAP model involves "Business Process Re-engineering" which is a logical analysis of the events and relationships that exist in an enterprise's operations. פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע ? ERP מה עושה ה Several layers: The Basis System + the heart of the system from a manager's viewpoint: the application modules. •FI Financial Accounting. •HR Human Resources •CO Controlling •PM Plant Maintenance •AM Asset Management •MM Materials Management •PS Project System •QM Quality Management •WF Workflow •PP Production Planning •IS Industry Solutions •SD Sales and Distribution פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע מה עושה ה ? ERP פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע ...הרבה כסף Approximately 65% of the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) market currently belongs to SAP, Oracle, PeopleSoft, J.D. Edwards, and Baan Worldwide ERP Market $-bil 30 35 45 58 73 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע Source: www.infotechtrends.com ERP שאלות על How long will an ERP project take?ERP vendors tell you about a three or six month average implementation time —real transformational ERP efforts usually run between one to three years What will ERP fix in my business?Integrate financial data. Standardize manufacturing processes. Standardize HR information. Will ERP fit the ways I do business? פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע ERP שאלות על What does ERP really cost? Meta Group study of (TCO) of ERP, 63 companies surveyed -the average TCO was $15 million (the highest was $300 million and lowest was $400,000). The TCO for a “headsdown” user over that period was a staggering $53,320 . When will I get payback from ERP— and how much will it be? Met Group found that it took eight months after the new system was in (31 months total) to see any benefits. But the median annual savings from the new ERP system was $1.6 million per year . פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע ERP שאלות על The Hidden Costs of ERP 1.Training 2.Integration and Testing 3.Data conversion 4.Data analysis 5.Consultants 6.Replacing Your Best and Brightest 7.Implementation Teams Can Never Stop 8.Waiting for ROI 9.Post-ERP Depression פרופ' שיזף רפאלי מחשבים ומערכות מידע חלק :IIיישומי AI 16 Artificial intelligence • Goal – To develop computers that can act like people in every way • What do humans do? – Inwardly: think, react, emote – Outwardly: move, see, feel create, innovate, invent, crack jokes – Communicate among ourselves פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 17 Developments by AI • Decision support systems – Support decision-making by humans • Expert systems – Make decision in place of an expert; – Acts as an expert assistant to a non-expert user • Neural nets • Fuzzy logic פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים מערכות מומחה Expert systems • Application that acts as an expert CAPTURES HUMAN EXPERTISE IN LIMITED DOMAINS OF KNOWLEDGE • It gives recommendations – – – – about customer credit engineering problems legal situations sifting for the exception פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 18 19 Expert System types (1) • KNOWLEDGE BASE: Model of Human Knowledge • RULE - BASED EXPERT SYSTEM : AI System Based on IF - THEN Statements (Bifurcation); Rule Base: Collection of IF - THEN Knowledge • SEMANTIC NETS: Uses Property of INHERITANCE to Organize, Classify Interrelated Characteristics פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 20 Expert System types (2) • AI SHELL: Programming Environment of Expert System • INFERENCE ENGINE: Search Through Rule Base – FORWARD CHAINING: Uses Input; Searches Rules for Answer – BACKWARD CHAINING: Begins with Hypothesis, Seeks Information Until Hypothesis Accepted or Rejected פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 21 Expert Systems limitations • Often Reduced to Problems of Classification • Can be Large, Lengthy, Expensive • Maintaining Knowledge Base Critical • Many Managers Unwilling to Trust such Systems פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 22 Top-down in ExSys • פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי ביה”ס למנהל עסקים ,אונ’ חיפה 23 Simple example • If the animal hops and the object is tall, then the animal is a kangaroo. • If the animal is gray and large, then the animal is an elephant • The animal is tall. The animal is gray. The animal is large. • Solve by back chaining: What is the animal? פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 24 Parts of an expert system • Inference engine – Knows which rules to execute • Rule base – List of rules • Fact base – Set of facts we provided פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 25 Other points to be made (1/2) • Symbolic processing – Forget bits, bytes, and data structures — think of ‘symbols’ • Applicability – Rules are specific – Inference engine is general פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 26 Other points to be made (2/2) • Expert system shell – – – – Provides inference engine Helps create rule and fact base General tool for a wide variety of problems Gives user capability to answer: » How did you determine that answer? פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 27 ES Examples online • CLIPS: an ES shell made by NASA. Visit at: – http://www.jsc.nasa.gov/~clips/CLIPS.html • Try JESS monkey-and-bananas online, at : – http://www.scs.ryerson.ca/~dgrimsha/java/c820a198/ • Try the whale expert system, at: – http://www.vvv.com/ai/demos/whale.html • Winning AI financial and manufacturing applications: – http://www.brightware.com/company/awards/index.html פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 28 רשתות נוירונים פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי ביה”ס למנהל עסקים ,אונ’ חיפה 29 Neural Nets - back to biology פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי ביה”ס למנהל עסקים ,אונ’ חיפה רשתות נויורונים Neural Nets • Designed to simulate the brain • Neurons, synapses • Useful when – Problem is difficult – An expert can’t say exactly how a decision is arrived at – Past situations (descriptions and decisions) are available • Ideal for massively parallel computers פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 30 31 Neurons, Synapses, Axons, Dendrites פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי ביה”ס למנהל עסקים ,אונ’ חיפה 32 And again... פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי ביה”ס למנהל עסקים ,אונ’ חיפה 33 ?Credit decisions פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי ביה”ס למנהל עסקים ,אונ’ חיפה יישומי רשתות נורונים Applications of neural nets • • • • • • • Character recognition Credit card fraud detection Petroleum exploration Financial forecasting Loan approval Missile guidance Parking a truck פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 34 רשתות נוירונים לעומת מערכות מומחה • Neural networks are flexible tools in a dynamic environment. • Neural networks have the capacity to learn rapidly and change quickly • Rule based systems are limited to the specific situation for which they were designed; פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 35 רשתות נוירונים לעומת מערכות מומחה – Expert systems are rule-based computer programs. – Expert systems are good for applications with logical separators between decisioninfluencing factors. – Since ES have explicit rules, it is easy to understand how their decisions are made. – But expert systems are difficult to build because the rules don't always exist and the "expert" information is difficult to acquire. פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 36 37 Fuzzy logic • Regular logic – Answer is false or true (i.e., 0 or 1) • Fuzzy logic – Answer ranges from 0 to 1 but can be anywhere in between (i.e., means maybe yes, maybe no) • Another “rule-based” development • Closer to the way people think פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 38 Fuzzy logic: example • Think of “youngness” • Not just “young” or “old”; there are degrees פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 39 Applications of fuzzy logic • • • • Elevators Automobile cruise control Washing machines Camera auto-focus Fuzzy Logic? באיזו מידה יש יישום ניהולי ל Virtuality”“ מומלץ לקרוא ולחשוב על פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 40 מקורותReferences • Spielberg’s AI film and web site • Buchanan’s brief history of AI: http://www.aaai.org/Pathfinder/bbhist.html • John McCarthy’s “What is AI?” http://www-formal.stanford.edu/jmc/whatisai/whatisai.html • AI Trends and Controversies http://www.computer.org/intelligent/articles/AI_controversies.htm פרופ’ שיזף רפאלי אונ’ חיפה,ביה”ס למנהל עסקים 41 The Internet and accompanying Technologies Part 5 מחשבים ומערכות מידע חלק :IIIסיום הרצאת תקשורת ותקשוב 43 Primary Usesשימושים עיקריים מחשבים ומערכות מידע 44 EDI מחשבים ומערכות מידע Networks allow client/server computing שרת-טכנולוגיית לקוח Can distribute functions among machines Client Terminal Display Client PC Stand-alone PC מחשבים ומערכות מידע Editing data fields Error checking Help screens Calculations Query processing Server Host Host Server File server 45 46 CLIENT • • • • USER POINT - OF - ENTRY COMPUTER / WORKSTATION / LAPTOP USER INTERACTS WITH CLIENT THRU GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE (GUI) • ENTER & RETRIEVE DATA • ANALYZE & REPORT * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 47 SERVER • • • • * COMPUTER SATISFIES USER’S NEEDS NOT VISIBLE TO USER PROCESSING ACCESS TO DATABASES מחשבים ומערכות מידע 48 INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDER (ISP) COMMERCIAL ORGANIZATION WITH PERMANENT CONNECTION TO INTERNET SELLS TEMPORARY CONNECTIONS TO SUBSCRIBERS * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 49 INTERNET CAPABILITIES CAPABILITY FUNCTIONS SUPPORTED E -MAIL PERSON -TO-PERSON MESSAGING; DOCUMENT SHARING USERNET NEWSGROUPS ELECTRONIC BULLETIN BOARDS CHATTING INTERACTIVE CONVERSATIONS TELNET LOG ON ONE COMPUTER, WORK ON ANOTHER GOPHERS LOCATE TEXT USING HIERARCHY OF MENUS ARCHIE SEARCH DATABASES FOR FILES AVAILABLE FOR DOWNLOADING WAIS LOCATE FILES IN DATABASES USING KEYS FTP TRANSFER FILES FROM COMPUTER TO COMPUTER WORLD WIDE WEB HYPERTEXT LINKS TO RETRIEVE/FORMAT/DISPLAY INFORMATION מחשבים ומערכות מידע 50 INTERNET ADDRESS ggalileo@univpisa.edu.it INDIVIDUAL OR ORGANIZATION NAME HOST COMPUTER DOMAIN LOCATION מחשבים ומערכות מידע 51 WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW) • STANDARDS TO STORE, RETRIEVE, FORMAT, DISPLAY INFORMATION • CLIENT-SERVER ARCHITECTURE • GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE • DYNAMIC LINKS TO OTHER DOCUMENTS (“hot links”) • EXPLOSION IN BUSINESS USE * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 52 WWW ADDRESS http//www.datamation.com GO TO WEB WEB SITE NAME TYPE OF ORGANIZATION מחשבים ומערכות מידע 53 E-Commerce Part 6 מחשבים ומערכות מידע 54 ELECTRONIC COMMERCE DOING BUSINESS ELECTRONICALLY • AUTOMATION OF BUSINESS - TO -BUSINESS • TRANSACTIONS * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 55 ? NEW BUSINESS MODELS מחשבים ומערכות מידע 56 E-Business on the Internet • Business-to-consumer (B2C) – Amazon, Dell • Business-to-business (B2B) – Freemarkets, CommerceOne Verticalnet • Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) – Ebay, QXL • Consumer-to-Business (C2B) – Priceline, Accompany, LastMinute מחשבים ומערכות מידע 57 INTERNET BENEFITS TO ORGANIZATION • REDUCES COMMUNICATION COSTS • ENHANCES COMMUNICATION; COORDINATION • ACCELERATES KNOWLEDGE DISTRIBUTION • ELECTRONIC COMMERCE מחשבים ומערכות מידע 58 Intranet & Extranet Part 7 מחשבים ומערכות מידע 59 INTRANET • INTERNAL NETWORK • WWW TECHNOLOGY • FIREWALL: Security System to Prevent Invasion of Private Networks • OVERCOMES COMPUTER PLATFORM DIFFERENCES • OFTEN INSTALLED ON EXISTING NETWORK INFRASTRUCTURE * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 60 Intranets מחשבים ומערכות מידע 61 EXTRANET • PRIVATE INTRANET ACCESSIBLE TO SELECT OUTSIDERS • LINK ORGANIZATION TO – IMPORTANT CLIENTS – BUSINESS PARTNERS – TOP EXECUTIVES & BOARD MEMBERS * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 62 EXTRANET מחשבים ומערכות מידע 63 APPLICATIONS OF INTRANETS & EXTRANETS Regular Progress Reports, Minutes of Meetings, Assignments Group Collaboration Access to Manuals, Directories, Data Updates on Orders Check new Products, Catalogs, Place Orders Single Access Point Training, Policy * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 64 BENEFITS & LIMITATIONS OF INTRANETS & EXTRANETS BENEFITS: • Standard Documents Always Current, Available. Less Expensive than Paper • Can Create, Coordinate New Documents • Virtual Conferencing • Project, Order Tracking Simplified * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 65 BENEFITS & LIMITATIONS OF INTRANETS & EXTRANETS LIMITATIONS: • Can’t Replace Large TPS Programs (e.g.: Payroll; Accounting; Production / Operations; Marketing) • Too Slow for High-Speed Data Transfer • Not yet as Functional as Groupware • Require Tight Security Control and Careful Management Planning * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 66 Protocols and Standarts Part 8 מחשבים ומערכות מידע 67 PROTOCOL RULES & PROCEDURES TO GOVERN TRANSMISSION BETWEEN COMPONENTS IN A NETWORK * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 68 CONNECTIVITY Connectivity: MEASURE OF ABILITY OF COMPUTING DEVICES TO PASS & SHARE INFORMATION WITHOUT HUMAN INTERVENTION OPEN SYSTEMS: Software Able to Function on Different Computer Platforms. Nonproprietary Operating Systems, Applications, Protocols * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 69 CONNECTIVITY FOR NETWORKS • REFERENCE MODEL: Generic Framework for Thinking About a Problem • PROTOCOL: Statement of How Specific Task will be Performed • STANDARD: Approved Reference Models & Protocols; Determined by Standard-setting Groups * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 70 TCP / IP מחשבים ומערכות מידע 71 TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL / INTERNET PROTOCOL (TCP / IP) REFERENCE MODEL DEVELOPED BY DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE IN 1972 1. APPLICATION: Provides Screen Presentations 2. TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL (TCP): Breaks Data into Datagrams 3. INTERNET PROTOCOL (IP): Breaks, Sends Datagrams as Smaller IP Packets; Can Repeat Transmission to Increase Reliability * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 72 TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL / INTERNET PROTOCOL (TCP / IP) 4. NETWORK INTERFACE: Handles Addressing and Interface Between Computer & Network 5. PHYSICAL NET: Defines Electrical Transmission Characteristics for Sending Signal Along Networks to Destination * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 73 OPEN SYSTEM INTERCONNECT (OSI) INTERNATIONAL REFERENCE MODEL FOR LINKING DIFFERENT TYPES OF COMPUTERS & NETWORKS. LAYERS: 1. PHYSICAL: Transmission of Data over Medium 2. DATA LINK: Packaging, Transfer of Packets; Error Checking 3. NETWORK: Routing Packets Over WAN * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 74 OPEN SYSTEM INTERCONNECT (OSI) 4. TRANSPORT: Ensures Reliable Data Delivery 5. SESSION: Establishes Communication Links on Network 6. PRESENTATION: Code Conversion for Data Presentation 7. APPLICATION: Specialized User Functions (e.g.: Operating System; File Transfer; e-mail) * מחשבים ומערכות מידע 75 The End מחשבים ומערכות מידע חלק :VIסיום מבוא לחומרה The Turing Machine A device that could determine the truth of mathematical statements without human involvement by following a deterministic sequence of instructions. מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן HOW CHARACTERS ARE STORED * מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה יובל דן-גור HOW CHARACTERS ARE STORED BIT: Binary Digit. On/Off, 0/1, Magnetic/Not BYTE: Group of bits for one character – EBCDIC- Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (8 bits per byte) – ASCII- American Standard Code for Information Exchange (7 or 8 bits per byte) מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן PARITY BIT: extra bit added to each byte to Processing – the heart מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה יובל דן-גור TYPES OF MEMORY RAM : Random Access Memory – Dynamic: Changes thru processing – Static: Remains constant (power on) ROM : Read Only Memory (preprogrammed) – PROM: Program can be changed once – EPROM: Erasable thru ultraviolet light מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT CONTROL UNIT ROM ARITHMETIC/LOGIC UNIT CLOCK PRIMARY (MAIN) MEMORY מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן RAM History of microprocessors Intel: 1971 - 4004 1974 - 8080 1982 - 80286 1989 - 486 1993 - Pentium 1995 - Pentium Pro 1999 - Celeron 2000 transistors 250,000 transistors 5 million transistors 10 million - billions of transistors מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן INSTRUCTION & EXECUTION CYCLE E-CYCLE: 5. SEND DATA FROM MAIN MEMORY TO STORAGE REGISTER 6. COMMAND ALU 7. ALU PERFORMS OPERATION 8. SEND RESULT TO ACCUMULATOR * מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן Instruction (Fetch & Decode) and Execution Cycle מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן Moore’s “Law” Actually, more of an observation or prediction In the late 1960s, Gordon Moore (cofounder of Intel) predicted that the number of transistors that could be placed on a single chip would double every year Not quite right, more like every 18 months מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן )Moore’s Law (2 מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה יובל דן-גור Advances in # of transistors on a microprocessor 6000000 5000000 4000000 3000000 # of transistors 2000000 1000000 0 1960 1970 1980 1990 מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן 2000 Increasing MIPS each year 350 300 250 200 MIPS 150 100 50 0 2000 1995 1990 1985 1980 1975 מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה יובל דן-גור 1970 1965 Network Computers (NC) (Oracle and Sun), Or… Net PC : Intel’s industry spec. A massively pared-down computer that downloads both software and data from the network rather than storing locally. “Thin Client” Java’s role TCO!!! מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן SEQUENTIAL & PARALLEL PROCESSING SEQUENTIAL PARALLEL Program Program TASK 1 CPU CPU CPU CPU TASK 1 TASK 2 TASK 3 RESULT RESULT Program TASK 2 CPU RESULT מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן Purchasing secondary memory מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה יובל דן-גור DATA PROCESSING BATCH PROCESSING: transaction data stored until convenient to process as a group. Useful for less timesensitive actions. ON-LINE PROCESSING: transaction data entered directly into system, constantly updating files. Requires direct-access devices. * מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן CENTRALIZED / DISTRIBUTED CENTRALIZED: PROCESSING BY CENTRAL COMPUTER SITE – ONE STANDARD – GREATER CONTROL DISTRIBUTED: PROCESSING BY SEVERAL COMPUTER SITES LINKED BY NETWORKS – MORE FLEXIBILITY – FASTER RESPONSE מחשבים ומערכות מידע – יסמין ויערה גור-יובל דן The End