Modern costing systems
advertisement

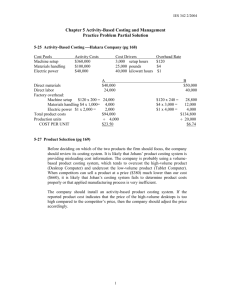
CURRENT COST ACCOUNTING METHODS CHALLENGE FOR ACCOUNTING PROFESSION Lívia Rác, dr Györgyi Petkovics Faculty of Economics, Subotica, Serbia 2008.10.02. Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion The place of cost accounting Accounting Financial acc. Managerial acc. bank Cost accounting Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion Development of cost accounting Traditional systems - Actual costing - Normal costing - Standard costing Modern systems - Target costing - Department c. - Activity-based c. - Variable c. - BSC Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion Importance of cost calculation How to assign indirect costs (tip for the waiter) to products? Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion Modern costing systems - Target costing - Department c. - Activity-based c. - Variable c. - BSC Modern costing systems Target costing – focuses on target cost per unit, which is the estimated unit cost of a product that, when sold at the target price, enables organization to earn the target profit per unit. - locked in = designed in costs - cost incurrence Department costing – instead of a single allocation base, uses separate indirect-cost rates for each department. It supposes that each department has different allocation base. Modern costing systems Activity-based costing – a technique for calculating object costs, in the way that overhead, selling, general and administrative costs assigned to an object reflect the overhead services actually consumed by that object. resources General ledger cost data activity activity cost pools cause-effect cost object (product, customer...) relation cost object (product, customer...) Modern costing systems Activity-based costing - every company has to determine its true economic costs with understanding the costs relation to its products/services - ABC is a simple concept that can be, and has to be adopted in a wide variety of ways Balanced Scorecard concept – translates a company’s strategy into a comprehensive set of performance measures. Financial Customer Internal bus. process Learning and growth Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion Traditional vs. modern costing Traditional costing Activity-based costing Only manufacturing costs are assigned to products. Manufacturing as well as nonmanufacturing costs can be assigned to products (some manufacturing costs may be excluded from product costs). Selling, general and administrative expenses are period expenses. Selling, general and administrative expenses can be assigned to products if there is a cost-effect relation between them. Traditional vs. modern costing Traditional costing Activity-based costing A single overhead rate is used for A number of overhead cost pools the entire factory: direct labor- or exist, with different allocation machine-hours. bases. Costs of unused capacity are assigned to products too. Costs of idle capacity are not assigned to products (only the costs of capacity they use). Overview • The place of cost accounting • Development of cost accounting • Importance of cost calculation • Modern costing systems • Traditional vs. modern costing • Conclusion Conclusion - New expressions: idle capacity, cost pools, activity-based concept, sunk cost, value- and non-value added costs, target pricing, relevant costs, etc. - most cost systems are based on financial accounting’s rules because of: - behavior problem - financial problem - technical problem - there is a need for maintaining two cost systems parallel Conclusion - managers need a road map - with modern costing methods company has to make a self-portrait - ABC is a concept to adopt, not the system to install - the accounting profession continuously has to improve costing methods, to provide a true picture about the company’s cost structure “Far better an approximate answer to the right question, than the exact answer to the wrong question.” (John Tukey, Princeton University.) liviar@eccf.su.ac.yu