Development of a Quantitative Comet Assay for
advertisement

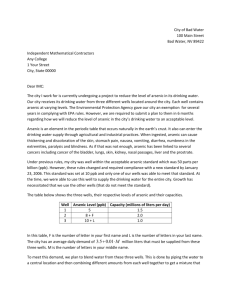
Development of a Quantitative Comet Assay for DNA Damage Yeong-Nam Jeong and Dr. Elizabeth Murray Marshall University, Integrated Science and Technology Department Arsenic Experiment 1 (2 Hours) Figure 4 Abstract Our ecosystem is very closely connected. Environmental pollution can lead to immediate consequences like organism death or lack of reproduction. It can also lead to long-range consequences through mutations and DNA damage. Fish can be affected very directly by environmental contamination in water. We are developing a quantitative assay to assess DNA damage in vitro due to heavy metal contamination using a tissue culture line of Poeciliopsis lucida, the desert pupfish, which is used for other toxicology assays. 60 Diameter 50 Low levels of arsenic As2O5 and were assayed (5uM and 10uM of As2O3 and 25uM and 50uM of As2O5) for one and two hours and compared with 1X PBS controls. Initially, comets were easily seen at these arsenic concentrations, but there was also a high level of background comets. Therefore, more extensive control assays were performed to characterize the sources of background DNA damage (exposure to trypsin EDTA and 1X PBS for varying amounts of time). The comet assays were also repeated in triplicate with the improved protocol. The length of comets was measured using a digital imaging. 40 30 20 10 0 Control As2O3 25 ppm As2O5 50 ppm Treatments This research demonstrates that arsenic can damage cells. Fewer cells survived after 1 or 2 hours of arsenic exposure, and they were more damaged than control cells. As2O3 was worse than As2O5 even though As2O5 is more water soluble. Longer exposure and higher concentrations greatly increased both the number of comets and the length of the tails. In control assay, 1X PBS buffer and trypsin also affected cell damage. It was critical to work quickly when trypsinizing and counting cells to reduce background comet development. Arsenic Experiment 2 (2 Hours) Figure 5 70 60 Introduction Diameter 50 Figure 2. Arsenic in Appalachian coal. http://www.epa.gov/ttbnrmrl/ArsenicPres/252.pdf 40 30 20 Arsenic occurs in the environment naturally and because of human actions like mining or pesticide use. Arsenic (As) is a chemical element commonly found in rocks and minerals. Usually As is not found in its pure metal form. There are two main categories of arsenic compounds, organic and inorganic. Organic arsenic compounds are combined with Hydrogen and Carbon, while inorganic arsenic compounds contain Oxygen, Chlorine, and Sulfur. Organic arsenic is less harmful than inorganic arsenic [1]. Arsenic is found in coal in Appalachia, especially in Kentucky and Alabama. This coal contributes to high levels of arsenic in streams, which is increased when it is mined. When this coal is burned, the fly ash can have high levels of Arsenic, which in Northern West Virginia has lead to higher levels of arsenic in water. 10 0 Control As2O3 10 uM As2O5 25 uM As2O5 50 uM Treatments Objectives •Perform comet assay with P. lucida cells with two levels of two arsenic compounds As2O3 and As2O5 with 1 and 2 hours exposure to arsenic. Figure 6 Arsenic Experiment 3 (1 Hour) •Reduce background comet level of the assay. •Count and measure cells from photomicrographs to develop a quantitative assay. 40 35 The Comet Assay is a fast, sensitive method to determine if a chemical breaks DNA at the level of an individual cell [4]. The alkaline Comet assay was introduced by Singh et al. in 1988 [5] and is a standard method for determining DNA damage. It is used for genotoxicity testing, biomonitoring and molecular epidemiology, and basic research in DNA damage and repair. The assay is simple, sensitive, versatile, speedy, and economical. Comet assay provides an estimate of how much damage is present in cells and whether it is double or single-stranded breakage. Cells are treated with a toxin, and then embedded in low melting temperature (LMP) agarose on a glass slide. The cells in agarose are treated with chemicals to lyse the membranes, release the DNA and denature it to single stranded form. Then the slides are placed in an electrophoresis chamber and run at low voltage in alkaline pH buffer for a short time. Then the DNA is stained and the cells are examined using a microscope. If DNA is intact, the stain reveals a round shape, because the DNA retains the round nucleus shape from before the cells lysed. If the DNA is damaged, the broken DNA trails behind the round nucleus shape like the tail of a comet. If DNA is more broken, it has a longer tail and a smaller round shape. If the DNA is broken up too much, you can no longer see any cells. PHLC-1 cells are derived from a liver tumor from Poeciliopsis lucida, a small desert fish commonly called the topminnow,. Because this cell line retains hepatocyte properties, it is used for in vitro toxicology assays and is well characterized by environmental toxicologists. They are used to screen heavy metals and other environmental toxins using a combined stress protein and cytotoxicity assay [6,7]. The Single Cell Gel/Comet Assay has also been developed as an assay for DNA damage and genetic toxicology [4,5]. We have used PLHC-1 cell line to develop the Comet Assay for DNA damage using exposure to two types of inorganic arsenic, As2O3 and As2O5 . Diameter Methods Cell culture P. lucida cell lines were obtained from ATCC and cultured in humidified CO2 incubator at 30° C. Cells were grown in Minimal Essential Medium Eagle with 1mM Sodium pyruvate, 2 mM L-glutamine and 1500 mg sodium bicarbonate/L supplemented with 5% Fetal Calf serum and 1% Pen Strep. Cells were split every 2-3 days. Experiments were performed on confluent cells. Arsenic Treatment As2O3 and As2O5 were dissolved in 1X PBS and serially diluted. To treat cells with arsenic, media was removed and cells were washed with 1X PBS. 10 ml of arsenic solution was added and cells were replaced in the incubator. After 1 or 2 hours, arsenic was removed from cells and cells were washed with 1X PBS. Cells were collected using Trypsin-EDTA treatment for 1 minute or until cells were released from flask. Cells were centrifuged and trypsin was removed. Cells were washed in 1X PBS, stained with Trypan blue and counted and diluted to 1 x 105 /ml. Comet Assay 50 ul of cells were mixed with 500 ul LMP agarose and 75 ul was spread on Trevigen comet slides. Subsequent treatment followed Trevigen Comet Assay protocol. Electrophoresis was for 10 minutes in 1X TBE at 22 volts (4 mAmps). Slides were dried overnight and stained for 5 -10 minutes in 100 ul Syber green stain. Slides were imaged using Olympus BX51microscope and photomicrographs were take at using Olympus Microsuite™ Basic software. We measured a minimum of 50 cells per slide per treatment group using the horizontal measurement tool. These measurements were exported to Excel spreadsheet. 25 20 15 10 5 0 Control As2O3 5 uM As2O3 10 uM As2O5 10 uM As2O5 25 uM Treatments Figure 7 Control Assay Experiments 60 50 Diameter The U.S. EPA has established the maximum contaminant level (MCL) for arsenic in drinking water of 50 ppb (50 ug/L) which will change to 10 ppb (10 ug/L) in January 2006 [2]. Arsenic has been linked to several forms of cancer (bladder, lungs, skin, kidney, nasal passages, liver, and prostate). Arsenic exposure is associated with cardiovascular, pulmonary, immunological, and neurological, and endocrine problems. Inorganic arsenic has both acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) toxicity [2]. How arsenic causes cancer is not well understood. Jia et al. report that the two most common forms of inorganic arsenic forms found in drinking water, As2O3 and As2O5, cause DNA damage to rat astroglia cells (primary nerve cells) as detected by the Comet Assay [3]. 30 40 Series1 30 Series2 Series3 20 10 0 Immediate 1 hour PBS 1 hour PBS 15 min. Trypsin 2 hour PBS 2 hour PBS 15 min. Trypsin Treatments Conclusion Results Both forms of Arsenic cause DNA damage in the Comet Assay. Longer exposure and higher concentration caused more comets (Figures 3-6). We saw some comets in control assays (Figure 2). We repeated control assays three times with different treatments (longer exposure to PBS and trypsin) (Figure 7). We concluded 2 hour exposure with PBS and quick removal of trypsin was the best for controls. We saw that pentavalent arsenic caused more comets than trivalent arsenic, but we used higher concentrations. We originally used lower trivalent arsenic concentrations because it was reported to cause more comets in rat cells [3]. Commercial PBS gave lower background comets than homemade PBS in Figure 7 (series 2 vs. series 1 and 3). It was important to stain the comets only 5 minutes, or they had too much background staining. P. lucida cells were easy to use but they had variability in size, leading to higher standard errors. Both forms of Arsenic cause DNA damage in the Comet Assay. Longer exposure and higher concentration cause more damage. We plan to repeat the assays for pentavalent and trivalent arsenic with a different range of concentrations and freshly made solutions. We hope to collect data on arsenic concentrations in streams in Cabell and Wayne counties and collect fish and molluscs to determine if they are affected by arsenic exposure. References 1. http://www.uky.edu/WaterResources/SYMP01-ITAC.HTML 2. http://www.epa.gov/watersecurity/guide/chemicalsensorforarsenic.html 3. Jin Y, Sun G, Li X, Li G, Lu C, Qu L. Study on the toxic effects induced by different arsenicals in primary cultured rat astroglia. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004;196:396-403. 4. Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF. Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2000; 35:20621. 5. Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Mar;175(1):18491. 6. Ryan JA , Hightower LE . Evaluation of heavy-metal ion toxicity in fish cells using a combined stress protein and cytotoxicity assay. Environ. Tox. Chem 1994; 13: 1231-1240. 7. Krone PH, Blechinger SR, Evans TG, Ryan JA, Noonan EJ, Hightower LE. Use of fish liver PLHC-1 cells and zebrafish embryos in cytotoxicity assays. Methods. 2005; 35:176-87. Acknowledgements Figure 1. Arsenic in Well water in the US. Ryker, S.J., Nov. 2001, Mapping arsenic in groundwater: Geotimes v.46 no.11, p.34-36. Thanks to Dr. Simon Collier and his lab for use of the Olympus microscope. Figure 3. Control Assay on left ( 2 hr PBS) compared with 25 ppm As2O3 on right.