Finding the Exact Value of Trigonometric Functions
advertisement
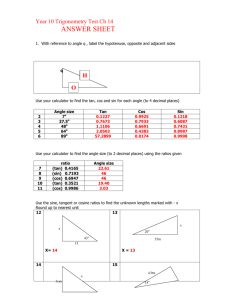
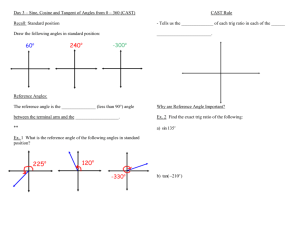
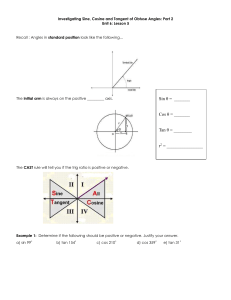
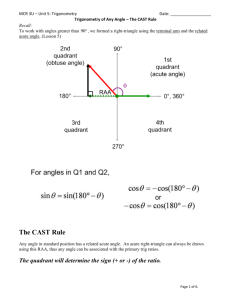
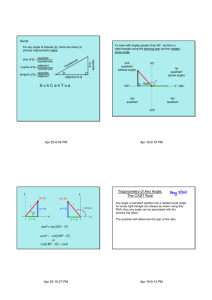
Finding the Exact Value of Trigonometric Functions Review: Special Right Triangles Find the missing side Lengths: π60° /3 1 1 2 π45° /4 1 π30° /6 3 2 π /°4 45 2 2 2 2 Important Points on Unit Circle 1 0,1 π90° /2 2π / 3 120° 3π / 4 135° π60° /3 π45° /4 π 30° /6 5π / 6 150° 1, 0 180° π -1 0 0° 11π /6 330° 7π / 6 210° 5π / 4 225° 4π /3 240° 7π315° /4 5π /3 300° 3π /2 270° -1 0, 1 1,0 1 Important Points on Unit Circle 1 3 , 2 2 2 2 , 2 2 π/2 2π / 3 3π / 4 3 1 , 2 2 1, 0 -1 3 1 , 2 2 1 0,1 5π / 6 π 1 3 , 2 2 π/3 π/4 1 1 2 2 , 2 2 1 45° 60° 30° 1/2 2 3 0 2 2 11π / 6 7π / 6 2 2 , 2 2 5π / 4 4π / 3 1 3 , 2 2 7π / 4 5π / 3 3π / 2 -1 0, 1 3 1 3π / 6 , 2 2 2 2 2 1/2 1 3 , 2 2 1,0 1 3 1 , 2 2 2 2 , 2 2 Important Points on Unit Circle 1 3 , 2 2 2 2 , 2 2 120° 3 1 , 2 2 1 0,1 90° 1 3 , 2 2 2 2 , 2 2 60° 135° 45° 150° 1, 0 180° -1 3 1 , 2 2 0° 330° 210° 2 2 , 2 2 3 1 , 2 2 30° 315° 225° 240° 1 3 , 2 2 270° 1,0 1 3 1 , 2 2 2 2 , 300° 2 2 1 3 , 2 2 -1 0, 1 Important Points on Unit Circle 1 3 , 2 2 2 2 , 2 2 π/2 2π / 3 3π / 4 3 1 , 2 2 1, 0 -1 3 1 , 2 2 1 0,1 1 3 , 2 2 π/3 π/4 2 2 , 2 2 3 1 , 2 2 π/6 5π / 6 π 0 11π / 6 7π / 6 2 2 , 2 2 5π / 4 4π / 3 1 3 , 2 2 7π / 4 5π / 3 3π / 2 -1 0, 1 1 3 , 2 2 1,0 1 3 1 , 2 2 2 2 , 2 2 Reference Angle On the left are 3 reference angles that we know exact trig values for. To find the reference angle for angles not in the 1st quadrant (the angles at right), ignore the integer in the numerator. 6 4 3 : 30 : 45 : 60 5 7 11 , , 6 6 6 3 5 7 , , 4 4 4 2 4 5 , , 3 3 3 Then multiply the number in the numerator by the degree to find the angle’s quadrant. Stewart’s Table: Finding Exact Values of Trig Functions R.A. Sin Cos 0 0 0 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 3 2 1 2 6 4 3 2 3 2 2 2 4 2 1 2 2 Each time the square root number goes up by 1 0 Reverse the order of the values from sine Tan 1. Find the value of the Reference Angle. 2. Find the angles quadrant to figure out the sign (+/-). Example 1 Find the exact value of the following: cos 34 Reference Angle: 4 Cosine of Reference Angle: cos 4 2 2 Quadrant of Reference Angle: 3 45 135 Second Quadrant Sign of Cosine in Second Quadrant: Therefore: cos 34 2 2 , , , , Negative Example 2 Solve: 2sin x 1 0 2sin x 1 1 sin x 2 Reference Angle that Makes sin x = 12 = 12 True: Solutions in the interval 0 x 2 : π/6 All solutions: 7 6 11 6 6 6 76 π/6 2 n where n is an integer 2 n 2 6 116 Slope on the Unit Circle 1 (cosӨ,sinӨ) Ө -1 cosӨ sinӨ What is the slope of the terminal side of an angle on the unit circle? Opposite 1 Adjacent sin opposite tan Slope = cos -1 adjacent A Definition of Tangent The tangent function is defined as: tan sin cos There are values for which the tangent function are undefined: Any Θ that makes cos(Θ)=0. 2, In general: 3 2 , 2 n 5 2 , 7 2 , 9 2 , 11 2 ,... For any integer n. Stewart’s Table: Finding Exact Values of Trig Functions R.A. Sin Cos 0 0 0 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 3 2 1 2 6 4 3 2 3 2 2 2 4 2 1 2 2 Each time the square root number goes up by 1 Tan 1. Find the value of 0 0 the 1 Reference 12 1 1 2 3 Angle. 3 2 2 3 3 3 2 2 1 2 2 3 2 3 2 12 2 1 0 Reverse the order of the values from sine 1 0 tan 2. Find the angles 3 quadrant to figure out +/-. sin cos Example 3 Find the exact value of the following: Thought process tan 53 Reference Angle: 3 Tangent of Reference Angle: tan 3 3 Quadrant of Angle: 5 60 300 Fourth Quadrant Sign of Tangent in Fourth Quadrant: , negative positive Negative , Therefore: tan 53 3 , , The only thing required for a correct answer (unless the question says explain)