Lesson 4.2
advertisement

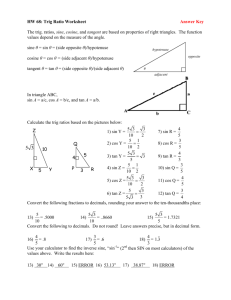
Lesson 4.2 A circle with center at (0, 0) and radius 1 is called a unit circle. The equation of this circle would be x y 1 2 2 (0,1) (-1,0) (1,0) (0,-1) Let's pick a point on the circle. We'll choose a point where the x is 1/2. If the x is 1/2, what is the y value? x y 1 2 1 2 y 1 2 3 2 y 4 (-1,0) 3 y 2 2 2 x = 1/2 (0,1) 1 3 2, 2 (1,0) 1 3 , 2 2 (0,-1) Now, draw a right triangle from the origin to the point when x = ½. Use this triangle to find the values of sin, cos, and tan. (0,1) 1 (-1,0) 1 3 , 2 2 3 2 sin (1,0) 1 2 tan (0,-1) cos 3 2 3 1 2 1 21 1 2 3 2 3 1 2 For any point on the unit circle: Sine is the y value Cosine is the x value. 𝑦 Tangent is 𝑥 Find the sin, cos, and tan of the angle 2 2 , 2 2 (-1,0) (0,1) 1 3 , 2 2 sin (1,0) tan (0,-1) 1 3 , 2 2 cos 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 How many degrees are in each division? 0,1 2 2 2 , 2 sin 225 2 2 2 , 2 90° 135° 45° 2 2 1,0 180° 45° 0° 1,0 225° 2 2 2 , 2 270° 0,1 315° 2 2 , 2 2 How about radians? 0,1 2 2 2 , 2 1,0 7 sin 4 2 2 135° 180° 5 4225° 2 2 , 2 2 2 2 2 , 2 90° 3 4 2 45° 4 3 2 270° 0° 1,0 7 4 315° 2 0,1 2 , 2 2 How many degrees are in each division? 1 3 , 2 2 cos 330 23 3 1 , 2 2 1,0 0,1 120° 1 3 , 2 2 90° 60° 150° 30° 180° 3 1 , 2 2 0° 1,0 30° 210° 3 1 2 , 2 sin 240 3 2 330° 240° 1 3 , 2 2 270° 300° 0,1 3 1 , 2 2 1 3 , 2 2 How about radians? 1 3 , 2 2 120° 3 1 , 2 2 1,0 0,1 1 3 , 2 2 90° 60° 150° 30° 6 180° 30° 3 1 , 2 2 0° 1,0 210° 3 1 2 , 2 330° 240° 1 3 , 2 2 270° 300° 0,1 3 1 , 2 2 1 3 , 2 2 1 3 , 2 2 Let’s think about the function f() = sin Domain: Range: All real numbers. -1 sin 1 (0, 1) (1, 0) (-1, 0) (0, -1) Let’s think about the function f() = cos Domain: Range: All real numbers -1 cos 1 (0, 1) (-1, 0) (1, 0) (0, -1) Let’s think about the function f() = tan Domain: x ≠ n( /2), where n is an odd integer Range: All real numbers Trig functions: Look at the unit circle and determine sin 420°. Sine is periodic with a period of 360° or 2. 1 3 , 2 2 So sin 420° = sin 60°. Reciprocal functions have the same period. PERIODIC PROPERTIES sin( + 2) = sin cosec( + 2) = cosec cos( + 2) = cos sec( + 2) = sec tan( + ) = tan cot( + ) = cot 9 tan 1 4 This would have the same value as tan Subtract the period until you reach an angle measure you know. 4 Positive vs. Negative & Even vs. Odd Even if: f(-x) = f(x) Odd if: f(-x) = -f(x) What is cos 1 2 3 ? What is cos ? 3 1 2 1 3 , 2 2 Remember negative angle means to go clockwise cos cos What is sin 3 Cosine is an even function. ? 3 2 What is sin ? 3 3 2 1 3 , 2 2 sin sin What is tan 3 Sine is an odd function. ? 3 What is tan ? 3 3 1 3 , 2 2 EVEN-ODD PROPERTIES sin(- ) = - sin (odd) cosec(- ) = - cosec (odd) cos(- ) = cos (even) sec(- ) = sec (even) tan(- ) = - tan (odd) cot(- ) = - cot (odd) Problem Set 4.2