Chapter 6 - The New Republic CONDENSED
advertisement

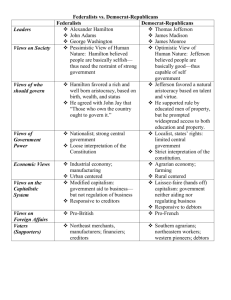
Chapter 6 The New Republic Sec. 1 – Govt. & Party Politics New York, 1789 – George Washington inaugurated into office Unanimous vote of electoral college (John Adams – VP) Great dignity and strong personality Role of new government still not determined Capital - NY to Philadelphia for 10 years New capital – District of Columbia DC; L’Enfant designed city to display power and authority Washington’s administration set precedents Cabinet: Jefferson (State), Hamilton (Treasury), Knox (War), Randolph (Attorney General) Hamilton’s Plan Jefferson – domestic affairs; great diplomat and leader; distrusted govt. Judiciary Act 1789 – Set up federal court system (13 federal courts, 3 circuit (appeals) courts and 6-member Supreme Court); John Jay (first Chief Justice) Hamilton – favored strong national gov. – believed it could accomplish great things Alexander Hamilton (Fed.) proposed plan to strengthen national power & develop a commercial and industrial economy Hamilton’s Plan cont. Pay off national & state debts Would restore credit and establish trustworthiness abroad Proposed excise taxes and high tariffs Placed tax on whiskey Hoped to pay off slowly so countries would take continued interest in U.S. (long term investment) Bank of U.S. established 1791 Hamilton’s Plan cont. Loose construction of the Constitution – broad interpretation; could do anything unless it said you CAN’T! Alarmed critics (Jefferson) – strict construction of Constitution – only those powers stated in Constitution; no “stretching” of powers Believed Federalists had betrayed the Revolution Opponents of Hamilton’s plan Resented federal power & new taxes, tariffs, Bank of U.S. Seemed like a return to the British monarchy – alarmed people Jefferson eventually resigned his post Whiskey Rebellion Many farmers refused to pay whiskey tax Followed the tradition of Stamp Act and Shay’s Rebellion – attacked collectors Washington & Hamilton determined to stop the rebellion; gathered troops and marched on W. Pennsylvania – rebellion dissolved ***Showed world that govt. would enforce the laws (unlike Shay’s Rebellion)*** Two Party System Whiskey Rebellion highlighted tensions Emerged into two parties: Federalists – Hamilton, Adams; northern merchants Democratic-Republicans – Jefferson, Madison; farmers But supporters from all parts of country Section 2 – Foreign Policy British had kept forts – Ohio River, Great Lakes – made U.S. mad Gave weapons to Indians to resist our expansion Battle of Fallen Timbers – General Anthony Wayne defeated Native Americans Treaty of Greenville - opened N.W. Territory French Revolution - 1789 Liberty, Equality, Fraternity Deteriorated into a “reign of terror” where thousands lost their lives, including King Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette Divided U.S. Federalists opposed it as extremist; anarchists who would destroy society French Revolution cont. Democratic Republicans supported it as an extension of the Am. Rev., Republican ideals; applauded its rejection of kings Americans torn between British who ruled the seas, or France who had helped us in the Revolution Chose neutrality – remained U.S. policy for a century Treaties with Britain and Spain Washington decides to improve relations with Britain Jay Treaty - Removed remaining British troops/forts in NW territory, expand trade w/GB Americans furious – a betrayal of France, sell-out to British Pinckney Treaty – with Spain; guaranteed shipping rights on Miss. River; established northern boundary of Florida Washington’s Farewell After 2 terms set precedent and stepped down Achievements: Indian defeat, western lands opened for settlement, Whiskey rebellion suppressed, kept nation out of war, improved economy and foreign trade, helped pay national debt Farewell Address – warned against “entangling alliances” and political parties Foreign Policy John Adams – 2nd Pres (Federalist) lacked prestige of GW; faced growing divisions in U.S. Drift towards war w/France – angry over Jay’s treaty w/Britain; began seizing Am. ships XYZ Affair – Adams sent officials to Paris, met by officials demanding bribe ($250K) and loan of $10 million; outraged Americans, “Millions for defense but not one cent for tribute.” Undeclared war, fired on, seized ships Adams keeps us out of major war w/France Alien and Sedition Acts Alien – Pres. could imprison or deport immigrants who criticized govt. – Most immigrants supported Dem-Rep.(why?) Sedition – Made it a crime for citizens who published or said anything false, scandalous about the govt. Silenced much Republican opposition with this VA and KY Resolutions Response to A & S acts – Rep. believed they violated Constitutional right to free speech VA & KY Resolutions declared the Sedition Act unconstitutional Nullification is a defiance of federal power Growing tensions in U.S. – State power vs. Federal power is a sign of things to come... Election of 1800 Jefferson wins election against Adams Aaron Burr, running mate got same number of votes Went to the House to decide Hamilton (congressman) preferred Jefferson so swayed vote to him Later Burr killed Hamilton in a duel for slandering him Section 3 - Jefferson Election of 1800 a “revolution” in government principles according to Jefferson Known now as Jeffersonian Republicans or Republicans (NOT the modern Republican party) Reduced military, streamlined government bureaucracy, increased trade, sale of western lands More common style than the aristocratic Federalists, but Jefferson was wealthy, educated and refined The Marshall Court John Marshall new Chief Justice Helped build prestige and power of Court Established judicial review in Marbury v. Madison – courts can determine constitutionality of laws Established federal authority over state authority – Gibbons v. Ogden, McCulloch v. Maryland Loose constructionist - increased power of court tremendously; not stated anywhere in Constitution Louisiana Purchase - 1803 Napoleon sold all French claims to U.S. for $15 million – Louisiana Purchase Jefferson concerned over the purchase and spending public funds Contradicted his principles about govt. power but signed anyway; doubled size of the U.S. Lewis & Clark expedition; 2 years, reached Pacific; helped by Sacajawea Foreign Troubles British began kidnapping American sailors to serve in British military – impressment (at war with France); interfering with trade also Embargo of 1807 as punishment – outlawed trade w/ foreign countries New Englanders hated embargo; bankrupted merchants, hurt farmers who couldn’t export Embargo backfired Hurt his 2nd term, retired to Monticello unpopular Section 4 – War of 1812 More battles w/Native Americans; Americans believed GB supplying weapons Tecumseh defeated at Tippecanoe War Hawks – Clay and Calhoun called for war against GB (impressments of American sailors) to restore national honor Federalists don’t want war with GB (why?) War of 1812 cont War breaks out 1812 Early defeats for Americans Disastrous invasion of Canada Navy did surprisingly well though Battle of Lake Erie – victory for U.S. Andrew Jackson crushed Creek Indians of Alabama, killed Tecumseh, invaded Florida and defeated Seminole Indians War of 1812 cont. Major attacks by British (including New Orleans) Burned White House (Madison flees – Dolly saves picture of George) & Capitol Ft. McHenry (Baltimore) – Francis Scott Key wrote Star Spangled Banner Americans win on Lake Champlain Cont. Treaty of Ghent – ended war 1815 Not all supported war (Federalists) – capital burned, treasury depleted, trade stopped due to blockade (“Mr. Madison’s war”) Andrew Jackson’s important battle of New Orleans – two weeks after treaty! Created illusion that this had led to British defeat Hartford Convention 1814 – Federalists had looked weak & defeatist in opposing war; wanted to consider leaving nation (secession) Post War - results Surge of national pride (nationalism) Nation grows – settlement spreads west End of Federalist party (for favoring GB) Settlers going into Florida too, conflicts with Seminoles; fugitive slaves heading to Florida Spain cedes Florida to U.S. – Adams – Onis Treaty of 1819; US now larger/stronger War showed the nation would endure