omis360-CH01 - Southeastern Louisiana University
advertisement

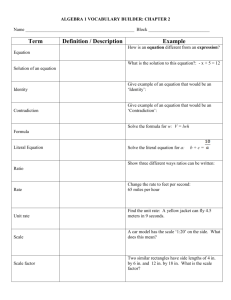
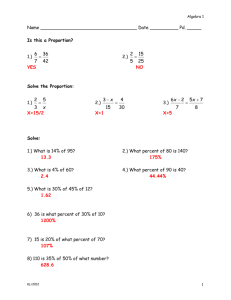
1 The Environment and the Tools Web Design, 5th Edition Chapter Objectives Describe the Internet and the World Wide Web Discuss ways to access the Internet and the web Categorize types of websites Identify web design tools Explain web design principles, roles, and required skills Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 2 The Internet and the World Wide Web A computer network consists of connected computers, mobile devices, printers, and data storage devices that share computing resources and data The Internet is a worldwide public network that connects millions of these private networks Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 3 The Internet and the World Wide Web Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 4 The Internet and the World Wide Web The World Wide Web (web) is a part of the Internet that consists of connected computers called web servers that store electronic documents called webpages A webpage is a specially formatted document that can contain images, text, interactive elements, and hyperlinks, which are links to other pages A website is a group of related webpages Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 5 Influence on Society Communication Education Entertainment and News E-commerce Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 6 Communication Bookmark / favorite Shortcut Internet Relay Chat (IRC) Web-based chat Instant messaging / IM chat Mobile IM (MIM) Collaborative workspaces / virtual meeting spaces Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools Blog Video sharing / Video blogging Social networking Social bookmarking Massively multiplayer online games (MMOGs) 3D virtual worlds Wiki 7 Communication Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 8 Education You can take an online course from an academic institution to earn a degree or certificate, or watch a video or read a blog post by an amateur expert – Several universities and academic institutions publish some or all educational materials online Formal and informal education Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 9 Entertainment and News Popular entertainment sites include music, videos, sports, games, and more News websites allow you to read news stories, and some even allow you to watch video clips – Some provide interactive elements Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 10 E-Commerce Electronic commerce or e-commerce encompasses a wide variety of online business activities, including consumer shopping and investing and the exchange of business data and transactions within a company or among multiple companies – Business-to-consumer (B2C) – Business-to-business (B2B) – Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 11 Cable Internet Access Allows users to connect to the Internet through their cable line Rapid transfer rates using a cable modem connected to a CATV line Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 12 Cable Internet Access Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 13 Fixed and Mobile Wireless Access Internet connectivity that uses satellite technology Radio signals provide high-speed connection – wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) Standards classified by generation – 3G – 4G Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 14 Telephone Line Access The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) used to be the main way all users connected to the Internet Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 15 Dial-Up Lines A dial-up line is a temporary connection that uses analog phone lines Least popular Internet access method Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 16 Digital Dedicated Lines A dedicated line is a constant connection between two communications devices Quality, consistency, and speed of the connection are better than a dial-up line Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 17 Digital Dedicated Lines Three popular types of digital dedicated lines – Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) – Digital subscriber lines (DSL) • Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) – T-carrier lines • T-1 line • Fractional T-1 line • T-3 line Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 18 ISDN Lines Integrated Services Digital Network ISDN allows a single telephone line to carry three or more signals (multiplexing) Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 19 DSL Digital subscriber line – Transmits at fast speeds on existing standard copper telephone wiring – Some installations can provide a dial tone Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) – Faster to receive data than to send data – Ideal for Internet access Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 20 T-carrier Lines Any of several types of digital lines that carry multiple signals over a single communications line Extremely fast data transfer rates T-1 line – Most popular T-carrier line – Fractional T-1 T-3 line – Equivalent to 28 T-1 lines Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 21 Internet Service Providers Internet Service Provider (ISP) – Has permanent Internet connection – Provides temporary connections – Regional ISP – National ISP • EarthLink Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 22 Web Browsers A web browser is a specific software program that requests, downloads, and displays webpages stored on a web server Some companies create mobile versions of their websites – Responsive web design (RWD) Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 23 Web Browsers Access webpages by entering its Uniform Resource Locator (URL) into the browser’s Address bar URL is comprised of the protocol, domain name and top-level domain designation – Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) – Domain name can be an IP address or a text version of this address Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 24 Web Browsers Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 25 Types of Websites Personal Organizational / Topical Commercial Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 26 Personal Limited developmental resources Uses: – Promote employment credentials – Share news and photos with friends and family – Share common interests or hobbies Do not post information that can be misused Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 27 Organizational / Topical Organizational websites contain information on particular organizations Topical websites focus on a specific subject Not all information is accurate Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 28 Commercial Used to promote and sell a product or service More sophisticated commercial websites generally produce greater revenue Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 29 Search Tools Web-based search tools – Search engines • Keywords Search engines might use a variety of methods to create its index – – – – Spiders or robots Meta tags Metasearch engines Search directories Search engine optimization (SEO) Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 30 Search Tools Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 31 Portals A portal is a website that offers a starting point for accessing information – – – – – General consumer portal Personal portal Vertical portal Corporate portal Hyperlocal portal Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 32 Web Design Tools Does the new technology meet currently accepted standards for web development and design? What specifically can the new technology do to further the purpose of my website? How will implementation of the new technology affect my website’s visual appeal, accessibility, and usability? What impact will adding this technology have on security and other website elements? What are the direct and indirect costs of implementing the new technology? How soon will I see a return on investing in this new technology? Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 33 Markup Languages Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Extensible Markup Language (XML) Extensible HTML (XHTML) Wireless Markup Language (WML) Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 34 Hypertext Markup Language Markup language used to create webpages Defines a webpage through HTML tags or HTML markup language World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) sets standards for HTML Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 35 Extensible Markup Language (XML), Extensible HTML (XHTML), and Wireless Markup Language (WML) XML uses markups to define the content of a webpage XHTML is a markup language that is a combination of the features of XML and HTML WML is a subset of XML – Used to design webpages for mobile browsers Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 36 Cascading Style Sheets Standardize the presentation of the content by applying styles to such elements – Font – Margins – Positioning – Background colors Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 37 Scripting Languages Programming languages used to write short programs that run on the server or the browser Browsers must support this technology Scripting languages – – – – Javascript Active Server Pages (ASP) PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP) MySQL Active content Malware Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 38 Text and HTML Editors A text editor is software used to create plain (ASCII) text files An HTML editor is a text editor enhanced with special features that are used to more easily insert HTML tags and their attributes – HTML-Kit – CoffeeCup – BBEdit – NoteTab Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 39 WYSIWYG Packages that automatically generate HTML code There are packages available for every level of expertise – – – – Microsoft Expression Web Adobe Dreamweaver Ephox EditLive! InnovaStudio WYSIWYG Editor Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 40 Web Templates and Content Management Systems A web template is a predesigned model that can be customized for fast website or webpage creation or updating A content management system (CMS) facilitates the management of web content development – Content repository An intranet is a private network within a large organization or commercial entity that uses Internet and web technologies to share information among only its members, employees, or business partners Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 41 Web Design Roles Web design can be done independently or with a partner or group Creative Role – Content writer / editor – SEO expert – Web designer – Web artist / graphic designer – Multimedia producer Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 42 Web Design Roles Technical Role – Web programmer – Database developer – Network / security administrator Oversight Role – Testers – Web administrator / webmaster Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 43 Chapter Summary Describe the Internet and the World Wide Web Discuss ways to access the Internet and the web Categorize types of websites Identify web design tools Explain web design principles, roles, and required skills Chapter 1: The Environment and the Tools 44 1 The Environment and the Tools Web Design, 5th Edition