intentional tort
advertisement

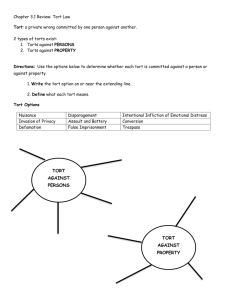
Section 4.1 Intentional Torts What You’ll Learn How to tell the difference between a crime and a tort (p. 80) How to explain the nature of tort law (p. 80) How various torts can be committed (p.81) How to define various intentional torts (pp. 81-86) Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Why It’s Important Learning the difference between a tort and a crime will help you understand how the justice system protects people from injury. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section Outline The Difference Between Criminal Law and Tort Law Intentional Torts Assault and Battery Trespass Nuisance False Imprisonment Defamation Invasion of Privacy Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Pre-Learning Question What is the difference between criminal law and tort law? Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts The Difference Between Criminal Law & Tort Law A crime is an act against not only a specific individual, but the general welfare, as well. A tort is a private wrong committed by one person against another. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts The Difference Between Criminal Law and Tort Law A tort will lead the wronged party to try and recover money as compensation for the loss or injury suffered. A tort does not, however, call upon the government to punish the wrongdoer. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts The Concept of Rights The law of torts is grounded in the concept of rights. Under tort law all people are entitled to certain rights. These include the right to: Be free from bodily harm. Enjoy a good reputation Conduct business without unwarranted interference. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts The Concept of Rights The law imposes a duty on all of us to respect the rights of others. Tort law governs this interplay between rights and duties. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Pre-Learning Question What is an intentional tort? Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Intentional Torts Torts can be committed either intentionally or unintentionally. An intentional tort occurs when a person knows and desires the consequences of his or her act. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Assault and Battery The tort of assault occurs when one person deliberately leads a person to believe they are about to be harmed. The tort of battery involves the unlawful, unprivileged touching of another person. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Assault and Battery The tort of assault is different from the crime of assault. The victim of a tort assault must know that the tortfeasor meant to commit harm. A tortfeasor is the person who committed the tort. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Trespass A trespass is the wrongful damage to or interference with the property of another. Nuisance The tort of nuisance is anything that interferes with the enjoyment of life or property. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Invasion of Privacy Invasion of privacy is interfering with a person’s right to be left alone, which includes the right to be free from unwanted publicity and interference with private matters. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts False Imprisonment Law enforcement officers must have probable cause or a warrant to arrest someone, or they can be sued for false imprisonment, or false arrest. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Defamation Defamation is the wrongful act of injuring another’s reputation by making false statements. Libel is a false statement in written form. Slander is a false statement made orally to a third party. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Raymond slapped his wife Charlotte while they were arguing about child support. Which tort did Raymond commit—assault or battery? Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Which definition best describes “tortfeasor”? a) A person charged with the crime of assault. b) A person charged with committing a tort. c) The attorney who represents a person accused of committing a tort. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts ANSWER Battery (b) A person charged with committing a tort. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section 4.1 Assessment Reviewing What You Learned 1. What is the difference between a crime and a tort? 2. What concept is at the heart of tort law? Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section 4.1 Assessment Reviewing What You Learned 3. How can a tort be committed? 4. What are the most common intentional torts? Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section 4.1 Assessment Reviewing What You Learned Answer 1) A crime is an offense against the public at large. A tort is a private wrong committed by one individual against another. 2) The law of torts is grounded in the concept of rights. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section 4.1 Assessment Reviewing What You Learned Answer 3) A tort can be committed intentionally or unintentionally. 4) Assault, battery, trespass, nuisance, false imprisonment, defamation, and invasion of privacy. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section 4.1 Assessment Critical Thinking Activity Tort Law If criminal law is responsible for dealing with individuals who commit wrongful acts, what purpose does tort law serve? Why do you need to understand the different intentional torts? Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts Section 4.1 Intentional Torts Section 4.1 Assessment Critical Thinking Activity Answer Tort Law Tort law compensates victims, and in order to properly represent his or her client as a tortfeasor or a victim, an attorney must have a proper understanding of the different intentional torts. Understanding Business and Personal Law The Law of Torts