TORT LAW
I’ll sue!!
Introduction
• Tort is the French word for a “wrong.”
• Tort law protects a variety of injuries and
provides remedies for them.
4-2
Introduction
(continued)
• Under tort law, an injured party can
bring a civil lawsuit to seek
compensation for a wrong done to the
party or the party’s property.
4-3
Introduction
(continued)
• Tort damages are monetary
damages that are sought from the
offending party.
• They are intended to compensate the
injured party for the injury suffered.
4-4
Copyright © 2004 by
Prentice-Hall. All rights
reserved.
Tort law imposes a duty on
persons and business agents
not to intentionally or
negligently injure others in
society.
4-5
Categories of Torts
Intentional Torts
Unintentional Torts
(Negligence)
Strict Liability Torts
4-6
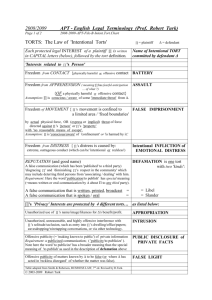
Torts
Intentional
Assault &
battery
Defamation
False
Imprisonment
Unintentional
Trespass
Negligent
Investigation
Nuisance
Negligence
Strict Liability
4-7
Intentional Torts
• A category of torts that requires that the
defendant possessed the intent to do the act that
caused the plaintiff’s injuries.
• There are two categories of intentional torts:
▫ Intentional torts against persons
▫ Intentional torts against property
4-8
Intentional Torts Against Persons
(continued)
• Assault
▫ The threat of immediate harm or offensive
contact; or
▫ Any action that arouses reasonable apprehension
of imminent harm.
▫ Actual physical contact is unnecessary.
4-9
Intentional Torts Against Persons
(continued)
• Battery
▫ Unauthorized and harmful or offensive physical
contact with another person.
▫ Actual physical contact is necessary.
4 - 10
Intentional Torts Against Persons
(continued)
• False Imprisonment
▫ The intentional confinement or restraint of
another person without authority or justification
and without that person’s consent.
4 - 11
Intentional Torts Against Persons
(continued)
• False Imprisonment (continued)
▫ Merchant Protection Statutes – allow
merchants to stop, detain, and investigate
suspected shoplifters without being held liable for
false imprisonment if:
There are reasonable grounds for the suspicion,
Suspects are detained for only a reasonable time, and
Investigations are conducted in a reasonable manner.
4 - 12
Intentional Torts Against Persons
(continued)
• Defamation of Character
▫ False statement(s) made by one person about
another. The plaintiff must prove that:
The defendant made an untrue statement
of fact about the plaintiff; and
The statement was intentionally or
accidentally published to a third party.
The words caused economic loss
4 - 13
Intentional Torts Against Persons
(continued)
• Defamation of Character (continued)
▫ Slander – oral defamation of character.
▫ Libel – a false statement that appears in a letter,
newspaper, magazine, book, photo, video, etc.
4 - 14
Defences to Defamation
• The statement was true
• Absolute and qualified privilege
• Fair comment
4 - 15
Absolute Privilege
• MPs and other public people can say things
openly and honestly without risk of being sued.
Qualified Privilege
• Expressing opinions as part of a public job.
Comments must be proven to be made without
malice.
4 - 16
Fair Comment
• Media critics who review various events provide
information to the public and therefore have the
right to comment honestly on events without
fear of legal action.
• *Must not be not be malicious
4 - 17
Intentional Torts Against Property
• There are two general categories of property:
▫ Real Property – consists of land and anything
permanently attached to that land.
▫ Personal Property – consist of things that are
movable.
Automobiles
Books
Clothes
Pets
4 - 18
Intentional Torts Against Property
(continued)
• Trespass to Land
▫ A tort that interferes with an owner’s right to
exclusive possession of land.
4 - 19
Intentional Torts Against Property
(continued)
• Trespass to Personal Property
▫ A tort that occurs whenever one person injures
another person’s personal property; or
▫ Interferes with that person’s enjoyment of his or her
personal property.
▫ Includes Landlord/Tenant agreements
4 - 20
Intentional Torts Against Property
(continued)
• Nuisance
▫ A tort that deprives a true owner of the use and
enjoyment of his or her personal property by:
Preventing enjoyment of someone’s property
Example?
4 - 21
Intentional Torts Against Property
(continued)
• Negligent Investigation
▫ Allows someone wrongly accused and convicted f a
crime to sue the police if they cause harm by
conducting an investigation negligently or sloppily
Example: Hill v. Hamilton-Wentworth
Regional Police Services Board, 2007
Pg. 415
4 - 22
Defenses for Trespass
4 - 23
4 - 24