Map Reading: Grids, Azimuths, and Direction
advertisement

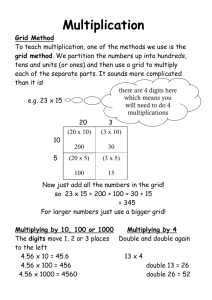
Map Reading II Reading a Grid & Determining Direction GRC JROTC COL. ALEXANDER Map Reading II Outline Purpose North (3 types) Types of Azimuths Measuring Azimuths Map Reading III Plotting Azimuths Practical Exercise Summary Conclusion Purpose To lay the groundwork for successful map reading and land navigation by exposing the cadet to determining grid and magnetic azimuths using a protractor and compass. Map Reading III North (x3 types) True North Map Reading III Magnetic North Grid North True North- line through North Pole. Magnetic Northdirection to northern magnetic pole (compass). Grid North-North as established by map maker. Types of Azimuth An azimuth is an angle measured clockwise from a base line direction (north). Grid- angle between grid north and a straight line plotted between two points on a map. Magnetic- angle determined by using a compass. Back- opposite direction of an azimuth. Map Reading III Measuring an Azimuth N Protractors E W Compasses Map Reading III S 360 degrees in a CIRCLE Measuring an Azimuth Protractors Map Reading III Measuring an Azimuth Compasses Magnetic Lensatic Compass (Military Type) Silva Polaris Compass (Civilian Orienteering) Map Reading III 3 Ways to Plot Azimuths 1. Plotting Azimuths between 2 points on a map. 2. Converting Magnetic Azimuths to Grid Azimuths. 3. Converting Grid Azimuths to Magnetic Azimuths. Map Reading III Reading a GRID 10-DIGIT GRID: EG 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1000M 100M 10M EG 1 1000M 100M 10M 8-DIGIT GRID: 2 3 4 5 6 1000M 100M Map Reading III 1M 10M 7 1M 8 1000M 100M 10M Reading a GRID 08 74 (4 digit) 084 742 (6 digit) COLUMBUS: 16S TENINO: Map Reading III 10T FL (or GL) 08 45 74 25 Square Identification 8-Digit Grid (w/in 10 M) EH (or EG) 15 85 82 20 Reading a GRID 76 75 1000 METERS 28 1 0 0 0 2. Then UP 28 M E T E R S 1. Read RIGHT 27 27 Map Reading III 75 76 Using a Protractor MAKE SURE THAT YOU USE THE CORRECT SCALE for the MAP you have 1:50,000 Map Reading III Using & Reading a Protractor 25 or 250 M 1 “GRID SQUARE” = 1000 M x 1000 M Each # (1, 2, 3, etc) = 100 METERS Each | in between = 50 METERS Map Reading III Slide protractor over to the RIGHT - 45 Line-Up Vertical Scale of protractor with 08 Grid 08 Reading a Protractor 09 75 Move UP 25 & place a dot or mark 75 UP RIGHT 74 74 08 45 74 25 Map Reading III 08 09 Use Protractor MUST BE PRECISE MUST slide protractor to the RIGHT to place mark CAUTION: You can’t put your pen/marker thru the plastic edge/overhang ! Map Reading III .09 2. Then UP STEP 1. Locate 2 points: • POS 1- EG1350 8009 and • POS 2- EG1610 8055 on the map. TENINO Map Sheet Point #1 .50 EG 1350 8009 POS 1 1. Read RIGHT 13 80 TENINO Map Sheet; Point #2 .55 EG 1610 8055 80 POS 1 POS 2 .10 1. Read RIGHT 2. Then UP STEP 1. Locate two points: • POS 1- EG13508009 and • POS 2- EG1610 8055 on the map. STEP 2. • Connect the points with a straight edge. • Draw a line extending beyond the points. POS 2 POS 1 STEP 3. Place index of protractor on line at a vertical (North/South) or horizontal (East/West) grid line. Keep the 0-180 degree line on the vertical grid line. POS 2 POS 1 STEP 4. Read the angle value on the grid scale. POS 2 POS 1 80 degrees 1420 mils BACK AZIMUTH RULE #1: IF THE AZIMUTH IS MORE THAN 180 DEGREES, THEN SUBTRACT 180 DEGREES. EXAMPLE: AZIMUTH 215 DEGREES -180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH 35 DEGREES RULE #2: IF THE AZIMUTH IS 180 DEGREES OR LESS, THEN ADD 180 DEGREES. EXAMPLE: AZIMUTH 80 DEGREES +180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH 260 DEGREES Map Reading III 3 Ways to Plot Azimuths 1. Plotting Azimuths between 2 points on a map. 2. Converting Magnetic Azimuths to Grid Azimuths. 3. Converting Grid Azimuths to Magnetic Azimuths. Map Reading III Plotting Azimuths Azimuths must be converted to the environment they will be used in. Grid to Magnetic (map-to-compass) Magnetic to Grid (compass-to-map). Use the Declination Diagram to find the conversion angle (GM Angle). For Grid to Magnetic Conversion Remember: Right-Add-Left-Subtract (RALS): GM to the Right Add GM. GM to the Left Subtract the GM. Map Reading III Plotting Azimuths; What is the GM Angle for Tenino? Map Reading III Declination Diagrams What is the GM Angle for Columbus? Practical Exercise Question #1: Given a Tenino Map (hint: find Declination Diagram). From your location you see a radio tower on magnetic azimuth of 275 degrees. What azimuth will you use to locate the radio tower on your map? Bonus: What would be the GRID azimuth from the tower to your position? Map Reading III Answer: # 1 MAGNETIC AZIMUTH: 275 DEGREES WESTERLY G-M ANGLE: + 21 DEGREES GRID AZIMUTH: BONUS: GRID AZIMUTH: 296 DEGREES 296 DEGREES OPPOSITE DIRECTION: - 180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH: 116 DEGREES Map Reading III Practical Exercise Question #2 Given a Tenino Map (hint: find Declination Diagram). After determining the map location for your rendezvous with the B Company platoon leader, you plotted the grid azimuth at 179 degrees. There are mine fields on both sides of your route so you want to make sure you travel in the right direction. What azimuth will you tell your compass man to follow? Bonus: You got half way to the rendezvous and were directed to dispatch a squad back to your original location. What azimuth should your squad leader follow? Map Reading III Answer: # 2 GRID AZIMUTH: 179 DEGREES EASTERLY G-M ANGLE: -21 DEGREES MAGNETIC AZIMUTH: BONUS: MAGNETIC AZIMUTH: 158 DEGREES 158 DEGREES OPPOSITE DIRECTION: +180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH: 338 DEGREES Map Reading III Practical Exercise Question #3 (TENINO Map) What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 06159015? What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 12859835? What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 10309650? What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG14508545? What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 02407981? What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 15329335? What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EH 18700030? Map Reading III Answer: PE # 3 What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 06159015? - DEPRESSION What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 12859835? - SADDLE What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 10309650? – RIDGE What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG14508545? – CLIFF What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 02407981? - DRAW What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EG 15329335? - SPUR What TERRAIN FEATURE is located at EH 18700030? - HILL Map Reading III Summary Map Reading III Purpose North Types of Azimuths Measuring Azimuths Plotting Azimuths Practical Exercise Conclusion Successful land navigations starts with map reading skills. Your ability to swap information between grid a magnetic environments is essential to helping you fight, survive, and win on the battlefield. Map Reading III Map Reading II Reading a Grid & Determining Direction GRC JROTC COL. ALEXANDER Map Reading II