Quiz 4
advertisement

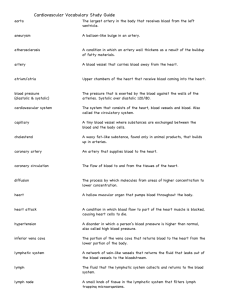
1) The mammilothalamic tract projects to: A. Anterior nucleus of thalamus B. VPL C. VPM D. Medial geniculate E. Pulvinar 2) The mediodorsal nucleus (DM) of the thalamus projects to: A. Basal ganglia B. Cerebellum C. Prefrontal cortex D. Area 17 E. Area 312 3) Which of the following thalamic nuclei play a role in planning and executing movement? A. MD B. VPL C. VPM D. VA/VL E. Reticular nuclei 4) What structure is responsible for delineating the 3 major thalamic divisions? A. Internal capsule B. Internal medullary lamina C. External medullary lamina D. Caudate E. Putamen 5) Specifically, which nucleus relays basal ganglia output to the premotor and supplementary motor cortical areas of the frontal lobe? A. VA B. VPL C. Medial geniculate D. Pulvinar E. VL 6) 7) 8) 9) 18 10) What is the most common location of congenital berry aneurysms? A. Anterior communicating artery B. Middle cerebral artery C. Basilar artery D. Posterior communicating artery E. Vertebral artery 11) Which of the following is the term used to describe a swollen optic disk due to pathology? A. Papilledema B. Internuclear opthalmoplegia C. Nystagmus D. Scatoma E. Strabismus 12) Which cranial nerve is responsible for crying? A. V B. VI C. VII D. VIII E. IX 13) The superior oblique muscle typically: A. moves the eye down and out B. is innervated by VI C. moves the eye up and out D. is innervated by III E. moves the eye medially 14) Which test is being demonstrated here? A. Rinne B. Babinski C. Weber D. Urine E. Arsland 15) Which neurotransmitter may play a role in migraine? A. Serotonin B. Ach C. Dopamine D. Vasopressin E. Glutamate 16) A tiny little “lake like” lesion is termed a: A. TIA B. Embolism C. Thrombosis D. Lacunar lesion E. Berry aneurysm 17) This neuropathy/myopathy is characterized by a transient paralysis: A. Guillain-Barre B. Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy C. ALS D. Brown Sequard lesion E. Spinal cord transection 18) Which of the following is a cause of Meniere’s disease? A. Severed 3rd nerve B. Polio C. Damaged membranous labyrinth D. Damaged ninth nerve E. Stroke 19) Alcoholism and diabetes can often lead to: A. Stroke B. Pregnancy C. Neuropathy D. Uncal herniation E. Tonsilar herniation 20) End of Quiz #4 1) The mammilothalamic tract projects to: A. Anterior nucleus of thalamus B. VPL C. VPM D. Medial geniculate E. Pulvinar 2) The mediodorsal nucleus (DM) of the thalamus projects to: A. Basal ganglia B. Cerebellum C. Prefrontal cortex D. Area 17 E. Area 312 3) Which of the following thalamic nuclei play a role in planning and executing movement? A. MD B. VPL C. VPM D. VA/VL E. Reticular nuclei 4) What structure is responsible for delineating the 3 major thalamic divisions? A. Internal capsule B. Internal medullary lamina C. External medullary lamina D. Caudate E. Putamen 5) Specifically, which nucleus relays basal ganglia output to the premotor and supplementary motor cortical areas of the frontal lobe? A. VA B. VPL C. Medial geniculate D. Pulvinar E. VL 6) 7) 8) 9) 18 10) What is the most common location of congenital berry aneurysms? A. Anterior communicating artery B. Middle cerebral artery C. Basilar artery D. Posterior communicating artery E. Vertebral artery 11) Which of the following is the term used to describe a swollen optic disk due to pathology? A. Papilledema B. Internuclear opthalmoplegia C. Nystagmus D. Scatoma E. Strabismus 12) Which cranial nerve is responsible for crying? A. V B. VI C. VII D. VIII E. IX 13) The superior oblique muscle typically: A. moves the eye down and out B. is innervated by VI C. moves the eye up and out D. is innervated by III E. moves the eye medially 14) Which test is being demonstrated here? A. Rinne B. Babinski C. Weber D.Urine E. Arsland 15) Which neurotransmitter may play a role in migraine? A. Serotonin B. Ach C. Dopamine D. Vasopressin E. Glutamate 16) A tiny little “lake like” lesion is termed a: A. TIA B. Embolism C. Thrombosis D. Lacunar lesion E. Berry aneurysm 17) This neuropathy/myopathy is characterized by a transient paralysis: A. Guillain-Barre B. Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy C. ALS D. Brown Sequard lesion E. Spinal cord transection 18) Which of the following is a cause of Meniere’s disease? A. Severed 3rd nerve B. Polio C. Damaged membranous labyrinth D. Damaged nineth nerve E. stroke 19) Alcoholism and diabetes can often lead to: A. Stroke B. Pregnancy C. Neuropathy D. Uncal herniation E. Tonsilar herniation 20)