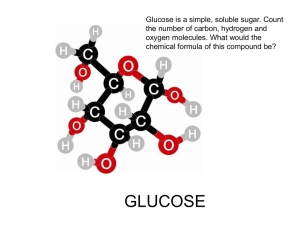
Unit 9 web

9. Carbohydrates
Chapter 16
CARBOHYDRATES
Contain C, H, O only
C
X
H
2Y
O
Y
= C
X
(H
2
O) i.e hydrates of carbon
Y most common names end in '-----ose'
Carbohydrates
General Structural Features
Usually 5/6 membered rings with C and one O
Many -OH groups
water soluble (simple ones )
easily broken down for energy
(already partly 'oxidized')
From Monosaccharides to Polysaccharides
The root saccharcomes from the
Latin saccharum , "sugar".
A monosaccharide is the smallest molecular unit of a carbohydrate .
Glucose, the prototypical monosaccharide, is the most abundant organic molecule on earth.
A disaccharide is a molecule formed from a combination of two monosaccharides, eg. sucrose
A polysaccharide is a molecular chain (maybe branched) of hundreds / thousands of monosaccharides, eg. cellulose
Common Carbohydrates
Carbohydrate
Formula
Monosaccharides, C
6
(H
2
O)
6
Glucose (blood sugar, grape sugar, dextrose) C
6
H
12
O
6
Fructose ( levulose )
Galactose
C
6
H
12
O
6
C
6
H
12
O
6
Disaccharides, C
12
(H
2
O)
11
Sucrose (table sugar,beet sugar, cane sugar) C
12
H
22
O
11
Maltose (malt sugar)
Cellobiose
C
12
H
22
O
11
C
12
H
22
O
11
Lactose (milk sugar ) C
12
H
22
O
11
Polysaccharides, C x
(H
2
O) y
Starch
Cellulose
Glucose – a 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxy hexanal
H O
H O
4
6
5
C
6
H
12
O
6
– a(aldo)hexose
6
H O
O
H
5
O
1 H O
4
3 2
3
O
2
1
OH
H O open chain
OH H O OH cyclic
(6 mem. ring = pyran)
Glucose – single then soluble
Polysaccharides – the Glycosidic Linkage
H O
+ H O
O O
H O OH H O
H O OH H O monosaccharides
OH
OH
+ H
2
O
O
O
O glycosidic linkage
*
O
O
O
O
O
O
O n * starch = 1,4 linkages = cellulose
STARCHES
Plant :
Amylose -straight chain (~200
-D glucose units)
Amylopectin - branched every ~25 units
(1000+
-D glucose units)
Dextrins -partial breakdown of amylopectin
(food additives , paste , fabric finishes )
Animal :
Glycogen
-branches every~12 units
-short-term energy in body (liver & muscle).
More Branching = Faster ‘Breakdown’
Amylopectin Glycogen
Amylose Helical Structure
• Left hand helix (partial)
Iodine test for Starch
• Helical structure of amylose holds the I 3ion; linear cellulose does not
Carbohydrates
The Most Common Energy Source
Chemical Breakdown / Reaction = Digestion
Complex
H
H
Dextrins
H
Simple
Mono-
(starch) (glucose)
O
acetate(2C) + CO
2
+ H
2
O + Energy
NB. can be reversed, ie. glucose
glycogen
Starch Breakdown / Digestion
Complex Dextrins Small Mono-
Energy Sources
Instant
Blood sugar(glucose): ~1g/L or 20Cal or ~30mins.
Short Term
Liver/Muscles(glycogen): ~325g or ~6 hrs.
the more muscle, the more glycogen any excess is converted into fat
Long Term
Fat(adipose tissue): ~ 20kg or ~35 days
Nutritional / Dietary Carbohydrates
Starch - the digestible carbohydrate(for humans)
Simple - mono-/disaccharides, eg. sugars
Complex -seeds/roots of plants, eg. grains(pasta), corn, potatoes, rice
Recommended - at least 55% of our Caloric intake
(10% sugar & 45% complex)
N A average - 20% sugar + 25% complex!
Cellulose - indigestible carbohydrate for humans
Soluble(pectins/gums) - fruits(apples), grain husks
(oat bran)
Insoluble(fiber/bulk/roughage) - potato skins, apple peels, celery, lettuce
Recommended - ~30g/day
NA average - ~15g/day
What is Dextrose?
Dextrose (Blood sugar) is the form of glucose that rotates the plane of polarized light in a clockwise direction.
What is “invert sugar?”
• Hydrolysis of (+)sucrose (table sugar) produces equal amounts of (+)glucose and (-) fructose (levulose).
• But, fructose optical rotation is larger (negatively) than glucose rotation is positively. Hence, the resulting solution is levorotatory (-).
• Thus, start with only (+) then get (-) after hydrolysis-so the net result of hydrolysis is inversion of the direction of the optical rotation
• Honey is mostly invert sugar –ie an equal mixture of glucose and fructose
Sucrose -> Glucose + Fructose (Invert)
OH O
H O sucrose(+66)
OH
H O H O
O sucrase
(invertase)
H O
D-glucose(+52)
(dextrose)
+
H O
O
D-fructose(-92)
(levulose)
OH
Maltose – the basic unit of Starch
H O
H O
OH O
H O
O
(down) - linkage
H O
OH O
OH
OH requires maltase
(humans > yes)
Cellobiose – the basic unit of Cellulose
(up) - linkage
OH
O
H O
H O H O
O
H O
OH
O
H O
OH requires cellobiase
(humans > no)
Why Dietary Fibre? It's Indigestible!
Beneficial statistical correlations for colon cancer, obesity, diabetes, heart disease.
Acts as a sponge for water and other substances
Functions as a physical 'cleaner'
Soluble - can help lower cholesterol levels reduces rate of glucose absorption
Insoluble - fills you up
eat less fat
'cleans' folds in intestinal walls no physical damage to intestinal walls adsorbs/removes many 'nasties'
Human Exploitation of Cellulose
Cellulose is a major component of grass, leaves, wood, cotton(produced by photosynthesis).
World Biomass Production = 10 11 tons annually
Present: Humans benefit indirectly by allowing ruminants(cows, sheep) to digest cellulose and convert it into protein which we eat.
Enzyme & Substrate : like a Lock & Key
Enzymes are huge protein molecules with intricate but well-defined shapes. They are the catalysts that bring about all the chemical reactions in our bodies.
For effective reactivity the molecule must fit into the convolutions of the shape of the enzyme.
Much like a key must fit the tumblers of a lock.
Lactose Intolerance
Lactase is the enzyme that specifically breaks the
-1,4- linkage of lactose to produce D-galactose and
D-glucose. Infants have a highly active form but
70% of adults have some lactase deficiency.
If lactose is not cleaved in small intestine it passes to the colon and 1) absorbs water or 2) is degraded by bacteria, resulting in cramps, diarrhea, etc.
About 10% of NA adults permanently lose their lactase compared to 3% of Danes and 97% of Thais.
Lactose (milk sugar) – a disaccharide
OH
OH
O
H O H O
D-galactose lactase + H
2
O
OH
O
O
H O H O
D-glucose
4-O-(
-D-galactopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranose
OH
• Buy it!
Solving the problem
Sweetness Index
Substance Relative Sweet Taste
Lactose 0.16
Maltose 0.33
Glucose 0.74
Sucrose 1.00
Fructose 1.73
(NB. Glucose + Fructose = Honey or Invert Sugar)
Aspartame 180
Saccharin 300
Sucrose : lots of –OH’s: high water solubility
-D-glucopyranosyl-
-D-fructofuranoside
Refined Sugar
NA sugar consumption: ~1kg (1750)
(annually/person) ~50 kg(1990)
Per day: 50, 000/365= 136 grams per person/day world-wide production = >80 million tons
(60% from cane; 40% from beets)
Dangers:
dumps too much glucose into blood too quickly
all other nutrients(vitamins, minerals) are removed
Everybody’s Comfort Food !
Wow !
An Informative Label ?! …..Not Likely
Refined Sugar in some Processed Foods
Food % Sugar
Jello ~83
Coffeemate ~65
Shake’N Bake ~50
Salad Dressing ~30
Ketchup ~29
Ice cream ~21
Peaches(in syrup) ~18
Peanut butter ~9
Coca Cola ~9
Sugar in human blood
• Blood sugar is glucose (dextrose)
• It is the only fuel for the brain and the
Central nervous system (CNS) and supplies the E for basal metabolism
• For continuous supply, a concentration of
0.06 to 0.11 weight % is maintained
Control of Blood Sugar (normal ~100mg/dL)
Too Low
(<75mg/dL) = hypoglycemia(fainting)
Too High
(>150mg/dL) = hyperglycemia/diabetes
Urine test for diabetes
• Above 0.16 weight % in blood , glucose seeps through the kidneys into the urine
Diabetes Mellitus
Type I (insulin dependent): ~10% of all diabetics
(juvenile onset)
Type II (non-insulin dependent; insulin receptors in cells have become inactivated by excess use of sugar): ~90% of all diabetics (formerly called adult onset but now found in 10-12 year olds!)
NB. Diabetes is:
1) second only to trauma for leg amputation
2) leading cause of blindness in adults over 20
3) leading cause of kidney failure
4) almost triples risk of heart attack or stroke
Type 1 Diabetes
• Body produces virtually no insulin
• Thus insulin needed for treatment
• Absence of insulin causes uncontrolled lipolysis of fat and severe wasting of body tissues, eventually resulting in death
Living with Type 2 Diabetes
• Body makes too little insulin or its effect is resisted
• In some cases insulin is needed
• sometimes controlled with a reduced sugar diet
• Loss of weight will cause an increase in the number of insulin receptors, hence improved condition
Canadians Discover Insulin (1921)
• Frederick Banting and his assistant Charles Best isolated insulin from the pancreas of dogs (canine insulin) and administered it to Type 1 patients
• Nobel Prize awarded to Banting and McLeod for this work
Structural Differences
• Porcine & canine insulin are identical and have 50/51 amino acids in common with human insulin
• Bovine insulin and human insulin have
48/51 amino acids in common
• Thus porcine insulin most often used
Source of Human Insulin
• Patients who are allergic to these can now get cloned Insulin marketed as the Drug
Humulin
Synthesis of Human Insulin
• Saran Narang (NRC Ottawa) 1930-2007
• Synthesised the proinsulin gene
• Enabled mass production of Humulin
• Via recombinant DNA
• Insulin is a protein
• 51 amino acids
• DNA>RNA>protein
Other molecules with sugar type structures
Fake Fats
•
Simplesse from egg white or milk proteins
Emulsified starch in Hellman’s light mayonaisse
Emulsified protein - gelatin + water
Olestra* ($200 million, by Proctor&Gamble) may cause cramps/diarrhea(
dehydration) reduces absorption of vit. A, D, E, K (fatsoluble vitamins) into body
* not digested; available in USA since 1996; must carry warning label; not legal in Canada
H O
Olestra = Sucrose Octa Palmitate
OH O
OH
H O H O
O
H O
OH
H O
O
Not OH but OR (R = O=C-C
16
(sat. = palmitate)
NB. At least 6OHs esterified to be non-metabolized
Olestra – Indigestible !
Olestra a Triglyceride
Chitin (an exoskeleton polymer)
OH O
(D)-glucosamine
H O
NH
2 H O
OH
*
O
H O
OH O
O
NH
CH
3
O
H O
OH O
O
NH
CH
3
O n
*
Glucosamine
• A simple amino sugar C
6
H
13
NO
5
.
• Produced commercially by hydrolysis of crustacean exoskeletons
• Used in treatment of osteoarthritis
• Sold as a salt-either HCl or sulfate
• Typical dose up to 1.5gr/day
Glucosamine (3-aminoglucose)
Blood Typing by Glycoprotein Antigens
Type A: acetylgalactosamine-galactose-acetylglucosamine-PRO fucose
Type B: lactose-galactose-acetylglucosamine-PRO fucose
Type O: galactose-acetylglucosamine-PRO fucose
Chocolate - Covered Cherries
Cherries are first coated with sugar paste(sucrose) + sucrase(enzyme). After hardening they are dipped in chocolate and stored. After 1-
2 weeks the sucrose is hydrolyzed/split by the sucrase into glucose + fructose which dissolves easily in the cherry juice.
Chemistry is Everywhere !
3 Cherry Blossom Questions
• One ingredient is called “invertase” .What is another name for this?
• Another ingredient is soy lecithin. What function does it serve?
• Another ingredient is “modified vegetable oil” How has it been modified?
Problem set #3
• Chapt 13 #1
• Chapt 15#1,8,9,10,11,25,29
• Chapt 16#1,9,11,12,18